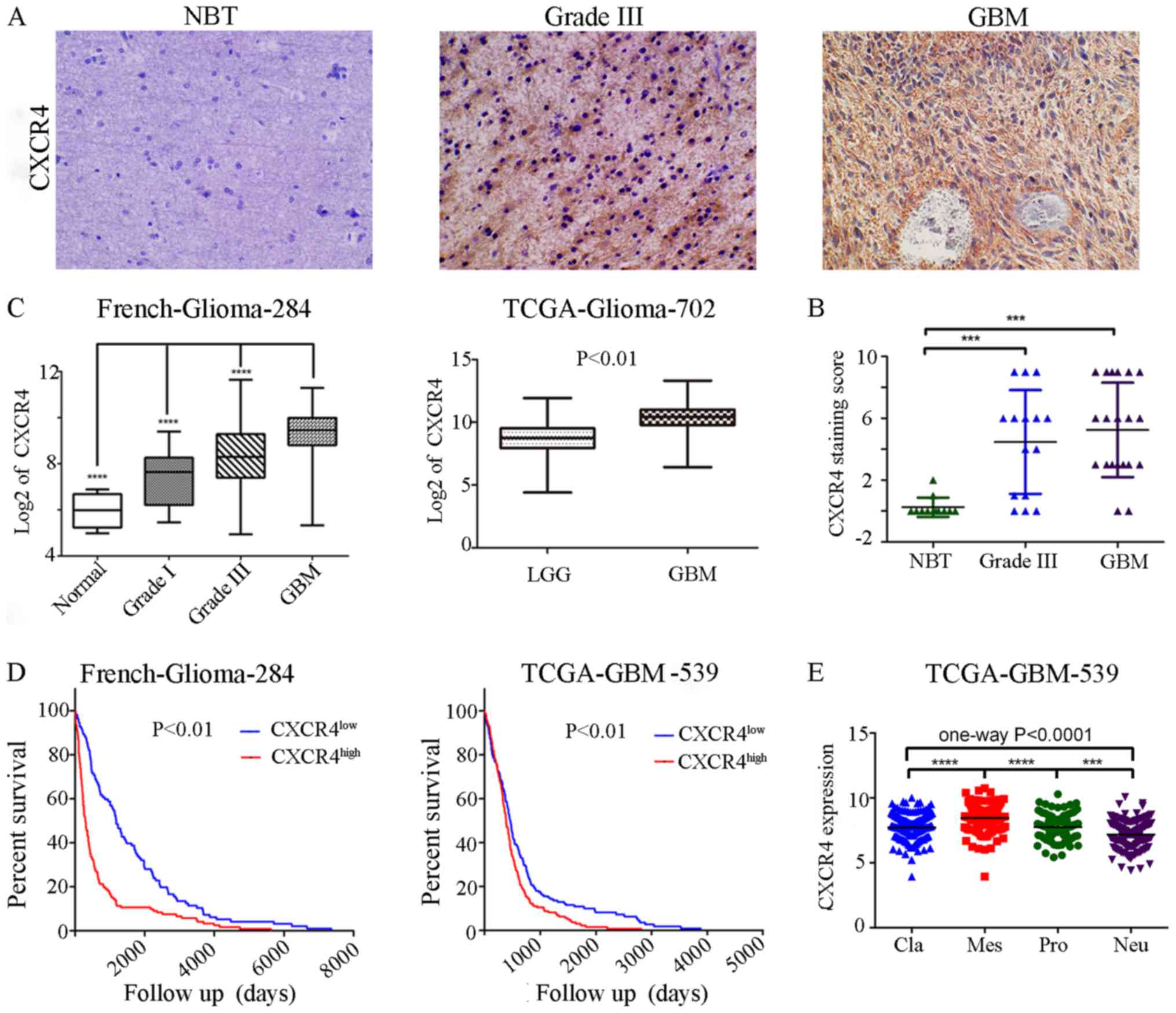
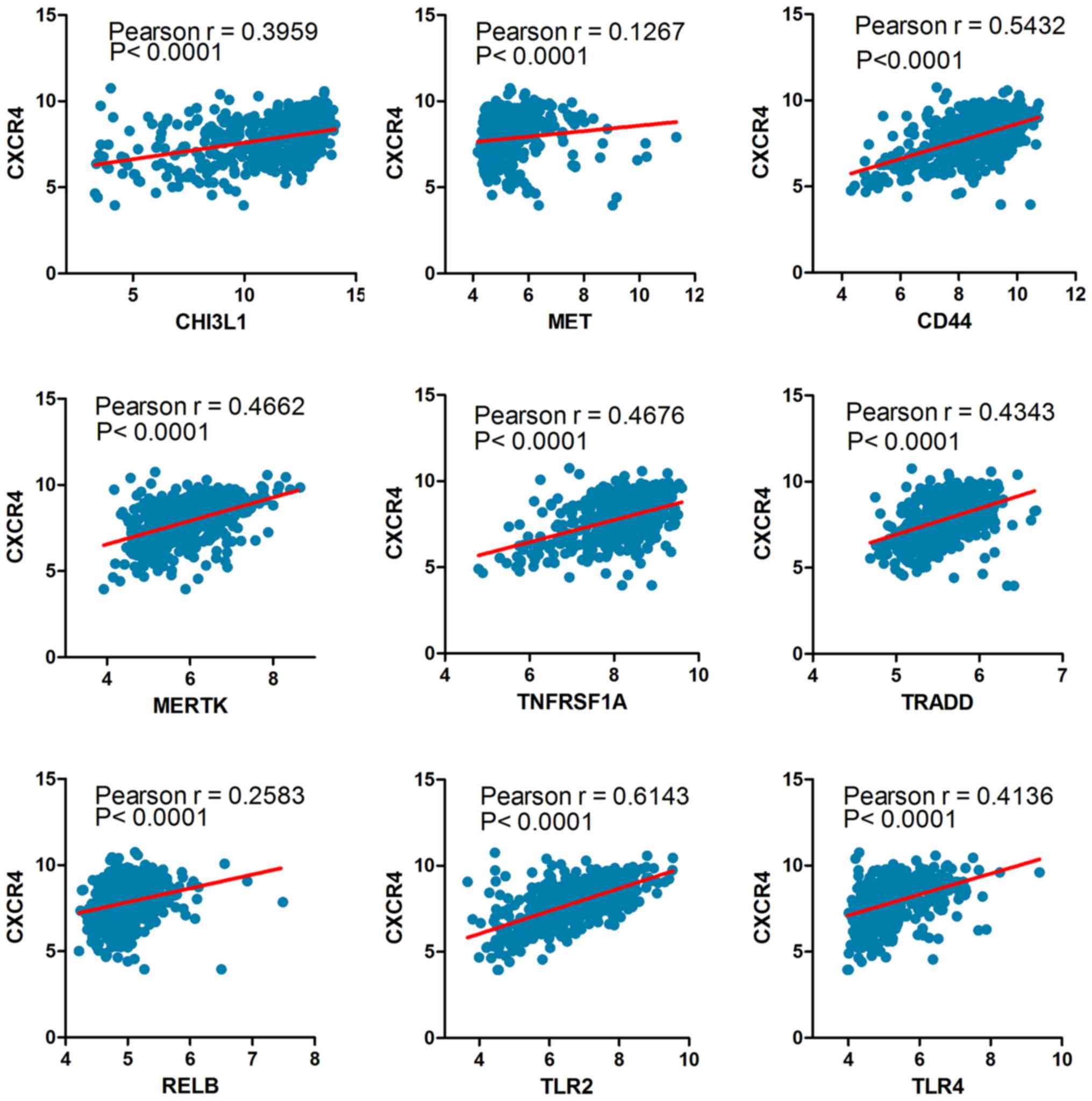
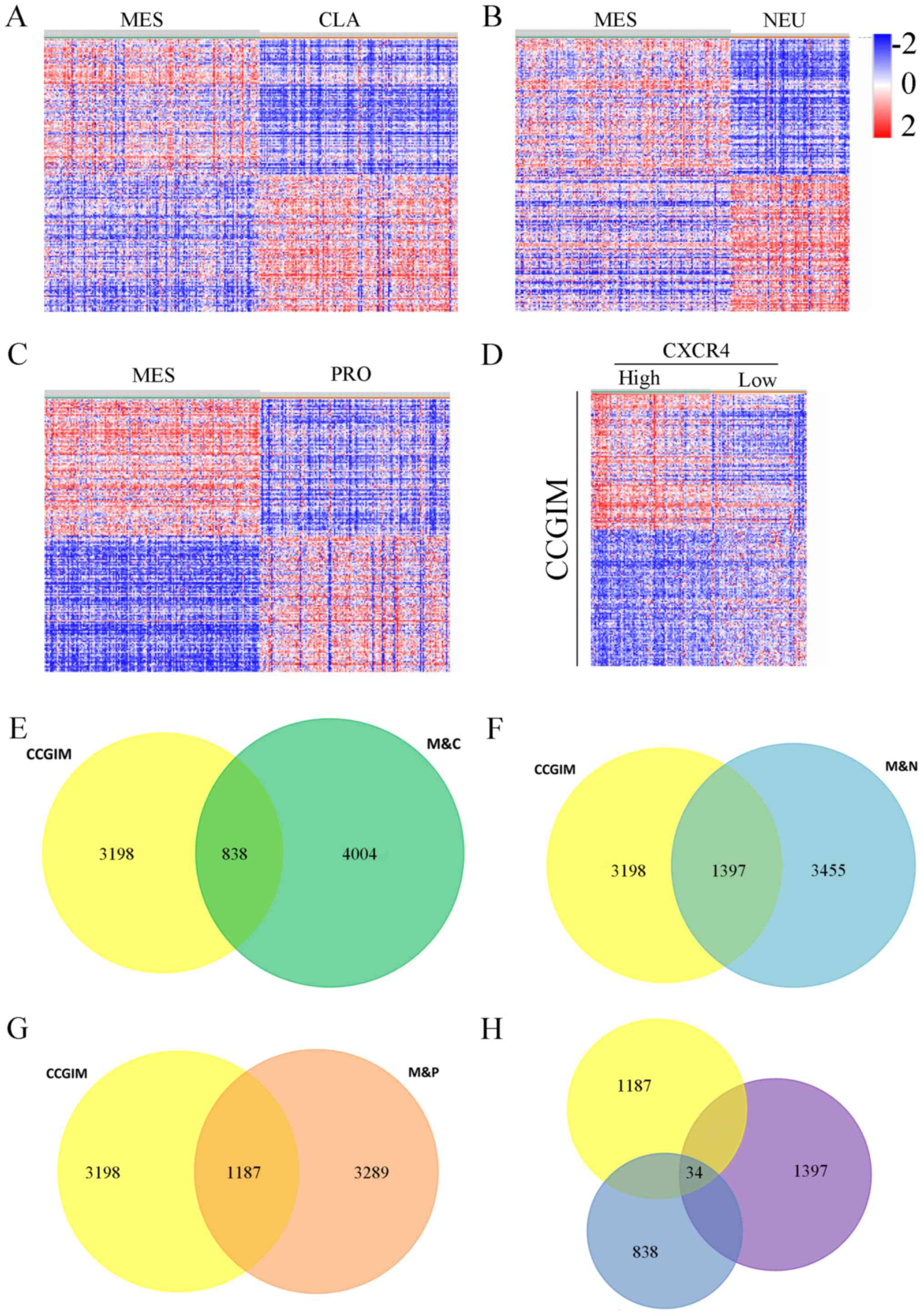
|
1
|
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Xu J, Kromer C,
Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C and Barnholtz-Sloan JS: CBTRUS statistical
report: Primary brain and other central nervous system tumors
diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro Oncol. 18
Suppl_5:v1–v75. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W, Henriksson R,
Saran F, Nishikawa R, Carpentier AF, Hoang-Xuan K, Kavan P, Cernea
D, et al: Bevacizumab plus radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly
diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 370:709–722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Louis DN, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD, Cavenee
WK, Burger PC, Jouvet A, Scheithauer BW and Kleihues P: The 2007
WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta
Neuropathol. 114:97–109. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coons SW, Johnson PC, Scheithauer BW,
Yates AJ and Pearl DK: Improving diagnostic accuracy and
interobserver concordance in the classification and grading of
primary gliomas. Cancer. 79:1381–1393. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sun Y, Zhang W, Chen D, Lv Y, Zheng J,
Lilljebjörn H, Ran L, Bao Z, Soneson C, Sjögren HO, et al: A glioma
classification scheme based on coexpression modules of EGFR and
PDGFRA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:3538–3543. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brennan CW, Verhaak RG, McKenna A, Campos
B, Noushmehr H, Salama SR, Zheng S, Chakravarty D, Sanborn JZ,
Berman SH, et al: The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma.
Cell. 155:462–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Verhaak RG, Hoadley KA, Purdom E, Wang V,
Qi Y, Wilkerson MD, Miller CR, Ding L, Golub T, Mesirov JP, et al:
Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes
of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1,
EGFR, and NF1. Cancer Cell. 17:98–110. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brennan CW, Verhaak RG, McKenna A, Campos
B, Noushmehr H, Salama SR, Zheng S, Chakravarty D, Sanborn JZ,
Berman SH, et al: The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma.
Cell. 155:462–477. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Eckel-Passow JE, Lachance DH, Molinaro AM,
Walsh KM, Decker PA, Sicotte H, Pekmezci M, Rice T, Kosel ML,
Smirnov IV, et al: glioma groups based on 1p/19q, IDH and TERT
promoter mutations in tumors. N Engl J Med. 372:2499–2508. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Louis DN, Perry A, Reifenberger G, von
Deimling A, Figarella-Branger D, Cavenee WK, Ohgaki H, Wiestler OD,
Kleihues P and Ellison DW: The 2016 World Health Organization
classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary.
Acta Neuropathol. 131:803–820. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tabouret E, Nguyen AT, Dehais C,
Carpentier C, Ducray F, Idbaih A, Mokhtari K, Jouvet A, Uro-Coste
E, Colin C, et al: Prognostic impact of the 2016 WHO classification
of diffuse gliomas in the French POLA cohort. Acta Neuropathol.
132:625–634. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dunn GP, Rinne ML, Wykosky J, Genovese G,
Quayle SN, Dunn IF, Agarwalla PK, Chheda MG, Campos B, Wang A, et
al: Emerging insights into the molecular and cellular basis of
glioblastoma. Genes Dev. 26:756–784. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Phillips HS, Kharbanda S, Chen R, Forrest
WF, Soriano RH, Wu TD, Misra A, Nigro JM, Colman H, Soroceanu L, et
al: Molecular subclasses of high-grade glioma predict prognosis,
delineate a pattern of disease progression, and resemble stages in
neurogenesis. Cancer Cell. 9:157–173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cheng W, Zhang C, Ren X, Jiang Y, Han S,
Liu Y, Cai J, Li M, Wang K, Liu Y, et al: Bioinformatic analyses
reveal a distinct Notch activation induced by STAT3 phosphorylation
in the mesenchymal subtype of glioblastoma. J Neurosurg.
126:249–259. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cooper LA, Gutman DA, Chisolm C, Appin C,
Kong J, Rong Y, Kurc T, Van Meir EG, Saltz JH, Moreno CS and Brat
DJ: The tumor microenvironment strongly impacts master
transcriptional regulators and gene expression class of
glioblastoma. Am J Pathol. 180:2108–2119. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Krock BL, Skuli N and Simon MC:
Hypoxia-induced angiogenesis: Good and evil. Genes Cancer.
2:1117–1133. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gagliardi F, Narayanan A, Reni M, Franzin
A, Mazza E, Boari N, Bailo M, Zordan P and Mortini P: The role of
CXCR4 in highly malignant human gliomas biology: Current knowledge
and future directions. Glia. 62:1015–1023. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Passaro D, Irigoyen M, Catherinet C,
Gachet S, Da Costa De Jesus C, Lasgi C, Quang Tran C and Ghysdael
J: CXCR4 Is required for leukemia-initiating cell activity in t
cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Cancer Cell. 27:769–779. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Luker KE, Lewin SA, Mihalko LA, Schmidt
BT, Winkler JS, Coggins NL, Thomas DG and Luker GD: Scavenging of
CXCL12 by CXCR7 promotes tumor growth and metastasis of
CXCR4-positive breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 31:4750–4758. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Seo CH, Kim JR, Kim MS and Cho KH: Hub
genes with positive feedbacks function as master switches in
developmental gene regulatory networks. Bioinformatics.
25:1898–1904. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tabouret E, Tchoghandjian A, Denicolai E,
Delfino C, Metellus P, Graillon T, Boucard C, Nanni I, Padovani L,
Ouafik L, et al: Recurrence of glioblastoma after
radio-chemotherapy is associated with an angiogenic switch to the
CXCL12-CXCR4 pathway. Oncotarget. 6:11664–11675. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huse JT and Holland EC: Targeting brain
cancer: Advances in the molecular pathology of malignant glioma and
medulloblastoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 10:319–331. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen J, McKay RM and Parada LF: Malignant
glioma: Lessons from genomics, mouse models, and stem cells. Cell.
149:36–47. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li M, Chang CJ, Lathia JD, Wang L, Pacenta
HL, Cotleur A and Ransohoff RM: Chemokine receptor CXCR4 signaling
modulates the growth factor-induced cell cycle of self-renewing and
multipotent neural progenitor cells. Glia. 59:108–118. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ho SY, Ling TY, Lin HY, Liou JT, Liu FC,
Chen IC, Lee SW, Hsu Y, Lai DM and Liou HH: SDF-1/CXCR4 signaling
maintains stemness signature in mouse neural stem/progenitor cells.
Stem Cells Int. 2017:24937522017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wagner EF and Nebreda AR: Signal
integration by JNK and p38 MAPK pathways in cancer development. Nat
Rev Cancer. 9:537–549. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dhillon AS, Hagan S, Rath O and Kolch W:
MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene. 26:3279–3290.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rhodes LV, Short SP, Neel NF, Salvo VA,
Zhu Y, Elliott S, Wei Y, Yu D, Sun M, Muir SE, et al: Cytokine
receptor CXCR4 mediates estrogen-independent tumorigenesis,
metastasis, and resistance to endocrine therapy in human breast
cancer. Cancer Res. 71:603–613. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Burger M, Glodek A, Hartmann T,
Schmitt-Gräff A, Silberstein LE, Fujii N, Kipps TJ and Burger JA:
Functional expression of CXCR4 (CD184) on small-cell lung cancer
cells mediates migration, integrin activation, and adhesion to
stromal cells. Oncogene. 22:8093–8101. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liao YX, Fu ZZ, Zhou CH, Shan LC, Wang ZY,
Yin F, Zheng LP, Hua YQ and Cai ZD: AMD3100 reduces CXCR4-mediated
survival and metastasis of osteosarcoma by inhibiting JNK and Akt,
but not p38 or Erk1/2, pathways in in vitro and mouse experiments.
Oncol Rep. 34:33–42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sun Y, Cheng Z, Ma L and Pei G:
Beta-arrestin2 is critically involved in CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis,
and this is mediated by its enhancement of p38 MAPK activation. J
Biol Chem. 277:49212–49219. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|