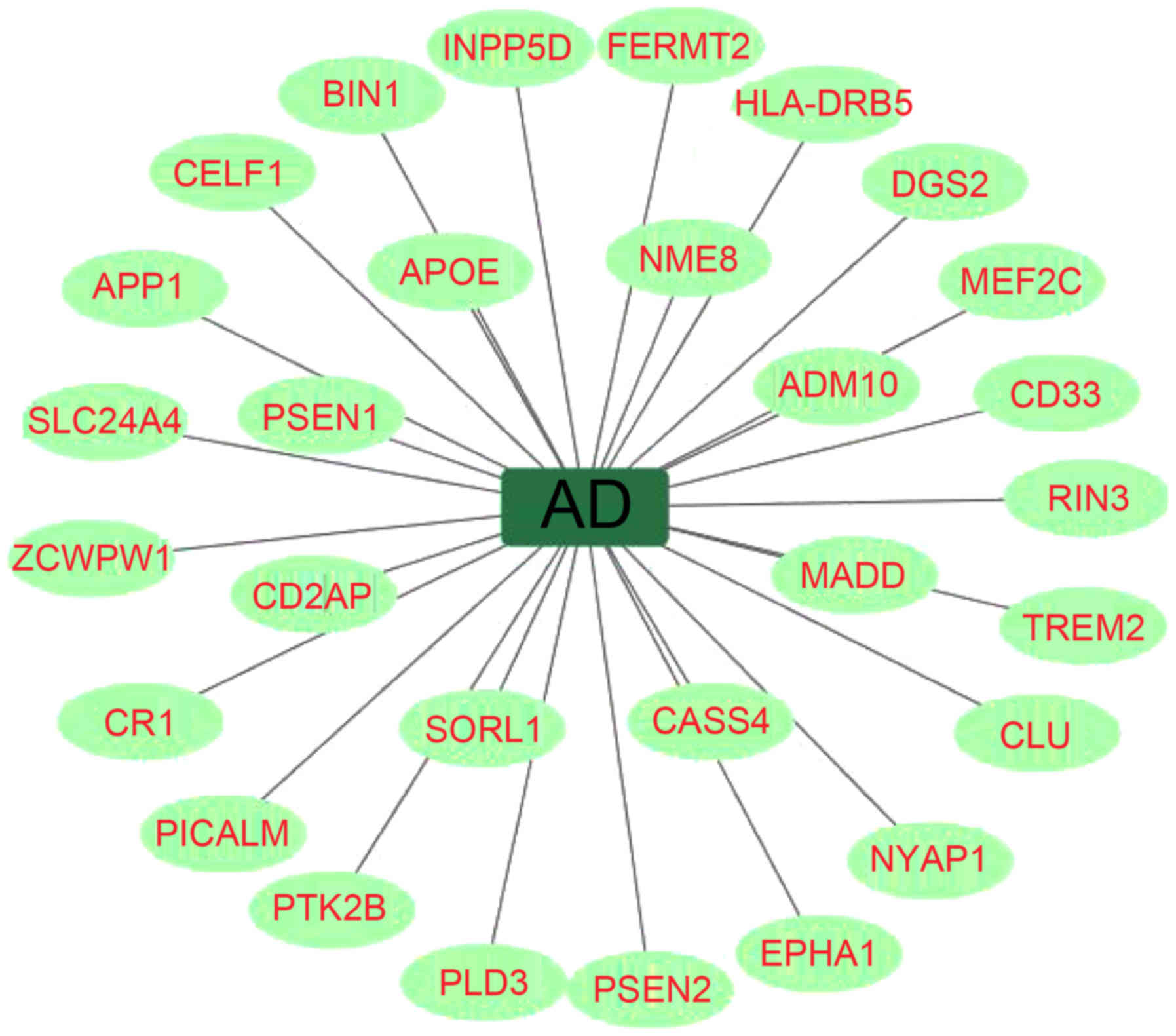
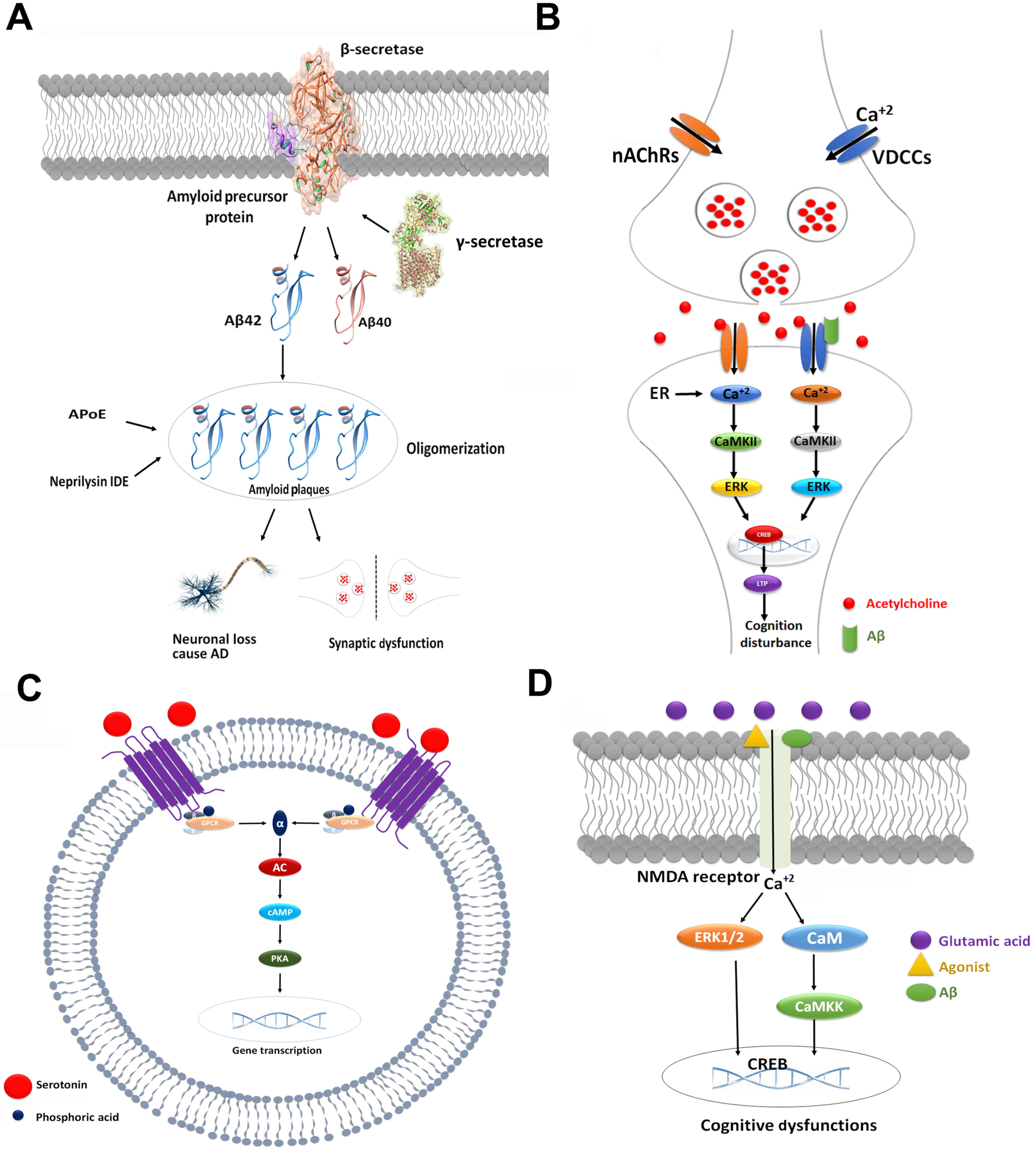
|
1
|
Hedden T and Gabrieli JD: Insights into
the ageing mind: A view from cognitive neuroscience. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 5:87–96. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ganguli M: Depression, cognitive
impairment and dementia: Why should clinicians care about the web
of causation? Indian J Psychiatry. 51 Suppl 1:S29–S34.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tarawneh R and Holtzman DM: The clinical
problem of symptomatic Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive
impairment. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0061482012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burns A and Iliffe S: Alzheimer's disease.
BMJ. 338:b1582009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mendez MF: Early-onset alzheimer's
disease: Nonamnestic subtypes and type 2 AD. Arch Med Res.
43:677–685. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Amaducci LA, Fratiglioni L, Rocca WA,
Fieschi C, Livrea P, Pedone D, Bracco L, Lippi A, Gandolfo C, Bino
G, et al: Risk factors for clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's
disease: A case-control study of an Italian population. Neurology.
36:922–931. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mayeux R: Understanding Alzheimer's
disease: Expect more genes and other things. Ann Neurol.
39:689–690. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Blennow K, de Leon MJ and Zetterberg H:
Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 368:387–403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Waring SC and Osenberg RN: Genome-wide
association studies in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 65:329–334.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Selkoe DJ: Translating cell biology into
therapeutic advances in Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 399 6738
Suppl:S23–S31. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Mahley RW, Weisgraber KH and Huang Y:
Apolipoprotein E4: A causative factor and therapeutic target in
neuropathology, including Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 103:5644–5651. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Strittmatter WJ, Saunders AM, Schmechel D,
Pericak-Vance M, Enghild J, Salvesen GS and Roses AD:
Apolipoprotein E: High-avidity binding to beta-amyloid and
increased frequency of type 4 allele in late-onset familial
Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 90:1977–1981. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bertram L and Tanzi ER: Genome-wide
association studies in Alzheimer's disease. Hum Mol Genet.
18:R137–R145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Killin LO, Starr JM, Shiue IJ and Russ TC:
Environmental risk factors for dementia: A systematic review. BMC
Geriatr. 16:1752016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dosunmu R, Wu J, Basha MR and Zawia NH:
Environmental and dietary risk factors in Alzheimer's disease.
Expert Rev Neurother. 7:887–900. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wenk GL: Neuropathologic changes in
Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Psychiatry. 64 Suppl 9:S7–S10.
2003.
|
|
17
|
Tiraboschi P, Sabbagh MN, Hansen LA,
Salmon DP, Merdes A, Gamst A, Masliah E, Alford M, Thal LJ and
Corey-Bloom J: Alzheimer disease without neocortical
neurofibrillary tangles: ‘A second look’. Neurology. 62:1141–1147.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Priller C, Bauer T, Mitteregger G, Krebs
B, Kretzschmar HA and Herms J: Synapse formation and function is
modulated by the amyloid precursor protein. J Neurosci.
26:7212–7221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Turner PR, O'Connor K, Tate WP and Abraham
WC: Roles of amyloid precursor protein and its fragments in
regulating neural activity, plasticity and memory. Prog Neurobiol.
70:1–32. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hooper NM: Roles of proteolysis and lipid
rafts in the processing of the amyloid precursor protein and prion
protein. Biochem Soc Trans. 33:335–338. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ohnishi S and Takano K: Amyloid fibrils
from the viewpoint of protein folding. Cell Mol Life Sci.
61:511–524. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jope RS and Johnson GV: The glamour and
gloom of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Trends Biochem Sci. 29:95–102.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hooper C, Killick R and Lovestone S: The
GSK3 hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 104:1433–1439.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jope RS, Yuskaitis CJ and Beurel E:
Glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3): Inflammation, diseases and
therapeutics. Neurochem Res. 32:577–595. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Paterson D and Nordberg A: Neuronal
nicotinic receptors in the human brain. Prog Neurobiol. 61:75–111.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Clader JW and Wang Y: Muscarinic receptor
agonists and antagonists in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Curr Pharm Des. 11:3353–3361. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jiang S, Li Y, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Bu G, Xu H
and Zhang YW: M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer's
disease. Neurosci Bull. 30:295–307. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsang SW, Lai MK, Kirvell S, Francis PT,
Esiri MM, Hope T, Chen CP and Wong PT: Impaired coupling of
muscarinic M1 receptors to G-proteins in the neocortex is
associated with severity of dementia in Alzheimer's disease.
Neurobiol Aging. 27:1216–1223. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jones CK, Brady AE, Davis AA, Xiang Z,
Bubser M, Tantawy MN, Kane AS, Bridges TM, Kennedy JP, Bradley SR,
et al: Novel selective allosteric activator of the M1 muscarinic
acetylcholine receptor regulates amyloid processing and produces
antipsychotic-like activity in rats. J Neurosci. 28:10422–10433.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Poulin B, Butcher A, McWilliams P,
Bourgognon JM, Pawlak R, Kong KC, Bottrill A, Mistry S, Wess J,
Rosethorne EM, et al: The M3-muscarinic receptor regulates learning
and memory in a receptor phosphorylation/arrestin-dependent manner.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:9440–9445. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wevers A and Schröder H: Nicotinic
acetylcholine receptors in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis.
1:207–219. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rinne JO, Myllykylä T, Lönnberg P and
Marjamäki P: A Postmortem study of brain nicotinic receptors in
Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res. 547:167–170. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Young JW, Meves JM, Tarantino IS, Caldwell
S and Geyer MA: Delayed procedural learning in α7-nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor knockout mice. Genes Brain Behav.
10:720–733. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dziewczapolski G, Glogowski CM, Masliah E
and Heinemann SF: Deletion of the alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine
receptor gene improves cognitive deficits and synaptic pathology in
a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurosci. 29:8805–8815.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen L, Wang H, Zhang Z, Li Z, He D,
Sokabe M and Chen L: DMXB (GTS-21) ameliorates the cognitive
deficits in beta amyloid (25–35(−)) injected mice through
preventing the dysfunction of alpha7 nicotinic receptor. J Neurosci
Res. 88:1784–1794. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Faghih R, Gfesser GA and Gopalakrishnan M:
Advances in the discovery of novel positive allosteric modulators
of the alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor. Recent Pat CNS Drug
Discov. 2:99–106. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Roncarati R, Scali C, Comery TA, Grauer
SM, Aschmi S, Bothmann H, Jow B, Kowal D, Gianfriddo M, Kelley C,
et al: Procognitive and neuroprotective activity of a novel alpha7
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonist for treatment of
neurodegenerative and cognitive disorders. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
329:459–468. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gubbins EJ, Gopalakrishnan M and Li J:
Alpha7 nAChR-mediated activation of MAP kinase pathways in PC12
cells. Brain Res. 1328:1–11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Miwa JM, Stevens TR, King SL, Caldarone
BJ, Ibanez-Tallon I, Xiao C, Fitzsimonds RM, Pavlides C, Lester HA,
Picciotto MR and Heintz N: The prototoxin lynx1 acts on nicotinic
acetylcholine receptors to balance neuronal activity and survival
in vivo. Neuron. 51:587–600. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Turner TJ: Nicotine enhancement of
dopamine release by a calcium-dependent increase in the size of the
readily releasable pool of synaptic vesicles. J Neurosci.
24:11328–11336. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shen JX and Yakel JL: Nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor-mediated calcium signaling in the nervous
system. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:673–680. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bitner RS, Bunnelle WH, Anderson DJ,
Briggs CA, Buccafusco J, Curzon P, Decker MW, Frost JM, Gronlien
JH, Gubbins E, et al: Broad-spectrum efficacy across cognitive
domains by alpha7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor agonism
correlates with activation of ERK1/2 and CREB phosphorylation
pathways. J Neurosci. 27:10578–10587. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chang KT and Berg DK: Voltage-gated
channels block nicotinic regulation of CREB phosphorylation and
gene expression in neurons. Neuron. 32:855–865. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hu M, Liu QS, Chang KT and Berg DK:
Nicotinic regulation of CREB activation in hippocampal neurons by
glutamatergic and nonglutamatergic pathways. Mol Cell Neurosci.
21:616–625. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ji D, Lape R and Dani JA: Timing and
location of nicotinic activity enhances or depresses hippocampal
synaptic plasticity. Neuron. 31:131–141. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Auld DS, Kornecook TJ, Bastianetto S and
Quirion R: Alzheimer's disease and the basal forebrain cholinergic
system: Relations to beta-amyloid peptides, cognition, and
treatment strategies. Prog Neurobiol. 68:209–245. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lilja AM, Porras O, Storelli E, Nordberg A
and Marutle A: Functional interactions of fibrillar and oligomeric
amyloid-β with alpha7 nicotinic receptors in Alzheimer's disease. J
Alzheimers Dis. 23:335–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Claeysen S, Bockaert J and Giannoni P:
Serotonin: A new hope in alzheimer's disease? ACS Chem Neurosci.
6:940–943. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Geldenhuys WJ and Van der Schyf CJ: Role
of serotonin in Alzheimer's disease: A new therapeutic target? CNS
Drugs. 25:765–781. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Xu Y, Yan J, Zhou P, Li J, Gao H, Xia Y
and Wang Q: Neurotransmitter receptors and cognitive dysfunction in
Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease. Prog Neurobiol.
97:1–13. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li Y, Huang XF, Deng C, Meyer B, Wu A, Yu
Y, Ying W, Yang GY, Yenari MA and Wang Q: Alterations in 5-HT2A
receptor binding in various brain regions among
6-hydroxydopamine-induced Parkinsonian rats. Synapse. 3:224–230.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Polter AM and Li X: 5-HT1A
receptor-regulated signal transduction pathways in brain. Cell
Signal. 22:1406–1412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sumiyoshi T, Park S, Jayathilake K, Roy A,
Ertugrul A and Meltzer HY: Effect of buspirone, a serotonin1A
partial agonist, on cognitive function in schizophrenia: A
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Schizophr Res.
95:158–168. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lai MK, Tsang SW, Francis PT, Keene J,
Hope T, Esiri MM, Spence I and Chen CP: Postmortem serotoninergic
correlates of cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease.
Neuroreport. 13:1175–1178. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Garcia-Alloza M, Hirst WD, Chen CP,
Lasheras B, Francis PT and Ramírez MJ: Differential involvement of
5-HT(1B/1D) and 5-HT6 receptors in cognitive and non-cognitive
symptoms in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology.
29:410–416. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Blin J, Baron JC, Dubois B, Crouzel C,
Fiorelli M, Attar-Lévy D, Pillon B, Fournier D, Vidailhet M and
Agid Y: Loss of brain 5-HT2 receptors in Alzheimer's disease. In
vivo assessment with positron emission tomography and
[18F]setoperone. Brain. 116:497–510. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hasselbalch SG, Madsen K, Svarer C,
Pinborg LH, Holm S, Paulson OB, Waldemar G and Knudsen GM: Reduced
5-HT2A receptor binding in patients with mild cognitive impairment.
Neurobiol Aging. 29:1830–1838. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Lai MK, Tsang SW, Alder JT, Keene J, Hope
T, Esiri MM, Francis PT and Chen CP: Loss of serotonin 5HT2A
receptors in the postmortem temporal cortex correlates with rate of
cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease. Psychopharmacology
(Berl). 179:673–677. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Ramírez MJ: 5-HT6 receptors and
Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 5:152013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Ruat M, Traiffort E, Arrang JM,
Tardivel-Lacombe J, Diaz J, Leurs R and Schwartz JC: A novel rat
serotonin (5-HT6) receptor: Molecular cloning, localization and
stimulation of cAMP accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
193:268–276. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mitchell ES and Neumaier JF: 5-HT6
receptors: A novel target for cognitive enhancement. Pharmacol
Ther. 108:320–333. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Perez-García G and Meneses A: Oral
administration of the 5-HT6 receptor antagonists SB-357134 and
SB-399885 improves memory formation in an autoshaping learning
task. Phar Biochem Behav. 81:673–682. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Da Silva Costa V, Duchatelle P, Boulouard
M and Dauphin F: Selective 5-HT6 receptor blockade improves spatial
recognition memory and reverses age-related deficits in spatial
recognition memory in the mouse. Neuropsychopharmacology.
34:488–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
West PJ, Marcy VR, Marino MJ and
Schaffhauser H: Activation of the 5-HT(6) receptor attenuates
longterm potentiation and facilitates GABAergic neurotransmission
in rat hippocampus. Neuroscience. 164:692–701. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang G and Stackman RW Jr: The role of
serotonin 5-HT2A receptors in memory and cognition. Front
Pharmacol. 6:2252015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yun HM and Rhim H: The serotonin-6
receptor as a novel therapeutic target. Exp Neurobiol. 20:159–168.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Nichols DE and Nichols CD: Serotonin
receptors. Chem Rev. 108:1614–1641. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Hirst WD, Stean TO, Rogers DC, Sunter D,
Pugh P, Moss SF, Bromidge SM, Riley G, Smith DR, Bartlett S, et al:
SB-399885 is a potent, selective 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with
cognitive enhancing properties in aged rat water maze and novel
object recognition models. Eur J Pharmacol. 553:109–119. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Schechter LE, Lin Q, Smith DL, Zhang G,
Shan Q, Platt B, Brandt MR, Dawson LA, Cole D, Bernotas R, et al:
Neuropharmacological profile of novel and selective 5-HT6 receptor
agonists: WAY-181187 and WAY-208466. Neuropsychopharmacology.
33:1323–1335. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Laureys G, Clinckers R, Gerlo S, Spooren
A, Wilczak N, Kooijman R, Smolders I, Michotte Y and De Keyser J:
Astrocytic beta(2)-adrenergic receptors: From physiology to
pathology. Prog Neurobiol. 91:189–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Shimohama S, Taniguchi T, Fujiwara M and
Kameyama M: Biochemical characterization of alphaadrenergic
receptors in human brain and changes in Alzheimer-type dementia. J
Neurochem. 47:1295–1301. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Kalaria RN and Harik SI: Increased alpha
2- and beta 2-adrenergic receptors in cerebral microvessels in
Alzheimer disease. Neurosci Lett. 106:233–238. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Russo-Neustadt A and Cotman CW: Adrenergic
receptors in Alzheimer's disease brain: Selective increases in the
cerebella of aggressive patients. J Neurosci. 17:5573–5580. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Contreras F, Fouillioux C, Bolívar A,
Simonovis N, Hernández-Hernández R, Armas-Hernandez MJ and Velasco
M: Dopamine, hypertension and obesity. J Hum Hypertens. 16 Suppl
1:S13–S17. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Nilsson A, Eriksson M, Muly EC, Akesson E,
Samuelsson EB, Bogdanovic N, Benedikz E and Sundström E: Analysis
of NR3A receptor subunits in human native NMDA receptors. Brain
Res. 1186:102–112. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Janssen WG, Vissavajjhala P, Andrews G,
Moran T, Hof PR and Morrison JH: Cellular and synaptic distribution
of NR2A and NR2B in macaque monkey and rat hippocampus as
visualized with subunit-specific monoclonal antibodies. Exp Neurol.
191 Suppl 1:S28–S44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Proctor DT, Coulson EJ and Dodd PR:
Post-synaptic scaffolding protein interactions with glutamate
receptors in synaptic dysfunction and Alzheimer's disease. Prog
Neurobiol. 93:509–521. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Sun H, Zhang J, Zhang L, Liu H, Zhu H and
Yang Y: Environmental enrichment influences BDNF and NR1 levels in
the hippocampus and restores cognitive impairment in chronic
cerebral hypoperfused rats. Curr Neurovasc Res. 7:268–280. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Amadoro G, Ciotti MT, Costanzi M, Cestari
V, Calissano P and Canu N: NMDA receptor mediates tau-induced
neurotoxicity by calpain and ERK/MAPK activation. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 103:2892–2897. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Fortin DA, Davare MA, Srivastava T, Brady
JD, Nygaard S, Derkach VA and Soderling TR: Long-term
potentiation-dependent spine enlargement requires synaptic
Ca2+-permeable AMPA receptors recruited by CaM-kinase I. J
Neurosci. 30:11565–11575. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Guetg N, Aziz Abdel S, Holbro N, Turecek
R, Rose T, Seddik R, Gassmann M, Moes S, Jenoe P, Oertner TG, et
al: NMDA receptor-dependent GABAB receptor internalization via
CaMKII phosphorylation of serine 867 in GABAB1. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:13924–13929. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Silva T, Reis J, Teixeira J and Borges F:
Alzheimer's disease, enzyme targets and drug discovery struggles:
From natural products to drug prototypes. Ageing Res Rev.
15:116–145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Colović MB, Krstić DZ, Lazarević-Pašti TD,
Bondžić AM and Vasić VM: Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors:
Pharmacology and Toxicology. Curr Neuropharmacol. 11:315–335. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
de Almeida JP and Saldanha C: Nonneuronal
cholinergic system in human erythrocytes: Biological role and
clinical relevance. J Membr Biol. 234:227–234. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Massoulié J, Pezzementi L, Bon S, Krejci E
and Vallette FM: Molecular and cellular biology of cholinesterases.
Prog Neurobiol. 41:31–91. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Schliebs R and Arendt T: The significance
of the cholinergic system in the brain during aging and in
Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 113:1625–1644. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Schliebs R and Arendt T: The cholinergic
system in aging and neuronal degeneration. Behav Brain Res.
221:555–563. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Greig NH, Lahiri DK and Sambamurti K:
Butyrylcholinesterase: An important new target in Alzheimer's
disease therapy. Int Psychogeriatr. 14 Suppl 1:S77–S91. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Lane RM, Kivipelto M and Greig NH:
Acetylcholinesterase and its inhibition in Alzheimer disease. Clin
Neuropharmacol. 27:141–149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Lane RM, Potkin SG and Enz A: Targeting
acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase in dementia. Int J
Neuropsychopharmacol. 9:101–124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Grossberg GT: Cholinesterase Inhibitors
for the treatment of alzheimer's disease: Getting on and staying
on. Curr Ther Res Clin Exp. 64:216–235. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Francis PT, Palmer AM, Snape M and Wilcock
GK: The cholinergic hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: A review of
progress. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 66:137–147. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Prakash A, Kalra J, Mani V, Ramasamy K and
Majeed AB: Pharmacological approaches for Alzheimer's disease:
Neurotransmitter as drug targets. Expert Rev Neurother. 15:53–71.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Akasofu S, Kimura M, Kosasa T, Sawada K
and Ogura H: Study of neuroprotection of donepezil, a therapy for
Alzheimer's disease. Chem Biol Interact. 175:222–226. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Takada Y, Yonezawa A, Kume T, Katsuki H,
Kaneko S, Sugimoto H and Akaike A: Nicotinic acetycholine
receptor-mediated neuroprotection by donepezil against glutamate
neurotoxicity in rat cortical neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
306:772–777. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Farlow M, Veloso F, Moline M, Yardley J,
Brand-Schieber E, Bibbiani F, Zou H, Hsu T and Satlin A: Safety and
tolerability of donepezil 23 mg in moderate to severe Alzheimer's
disease. BMC Neurol. 11:572011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Barar FSK: Essentials of
Pharmacotherapeutics, Antiparkinsonian drugs. 4th edition. S. Chand
and Company Ltd.; New Delhi: pp. 1692007
|
|
98
|
Bai DL, Tang XC and He XC: Huperzine A, a
potential therapeutic agent for treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Curr Med Chem. 7:355–374. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Yan J, Sun L, Wu G, Yi P, Yang F, Zhou L,
Zhang X, Li Z, Yang X, Luo H and Qiu M: Rational design and
synthesis of highly potent antiacetylcholinesterase activity
huperzine A derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem. 17:6937–6941. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Li J, Wu HM, Zhou RL, Liu GJ and Dong BR:
Huperzine A for Alzheimer's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
16:CD0055922008.
|
|
101
|
Camps PE, El Achab R, Morral J,
Muñoz-Torrero D, Badia A, Baños JE, Vivas NM, Barril X, Orozco M
and Luque FJ: New tacrine-huperzine A hybrids (huprines): Highly
potent tight-binding acetylcholinesterase inhibitors of interest
for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. J Med Chem. 43:4657–4666.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Mehta M, Adem A and Sabbagh M: New
Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors for Alzheimer's Disease. Int J
Alzheimers Dis. 2012:7289832012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Feng S, Wang Z, He X, Zheng S, Xia Y,
Jiang H, Tang X and Bai D: Bis-huperzine B: Highly potent and
selective acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. J Med Chem. 48:655–657.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Jung HA, Min BS, Yokozawa T, Lee JH, Kim
YS and Choi JS: Anti-Alzheimer and antioxidant activities of
Coptidis Rhizoma alkaloids. Biol Pharm Bull. 32:1433–1438. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Kulkarni SK and Dhir A: Berberine: A plant
alkaloid with therapeutic potential for central nervous system
disorders. Phytother Res. 24:317–324. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Turner AJ, Fisk L and Nalivaeva NN:
Targeting amyloid-degrading enzymes as therapeutic strategies in
neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1035:1–20. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Ghosh AK, Gemma S and Tang J:
Beta-Secretase as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease.
Neurotherapeutics. 5:399–408. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Sathya M, Premkumar P, Karthick C, Moorthi
P, Jayachandran KS and Anusuyadevi M: BACE1 in Alzheimer's disease.
Clin Chim Acta. 414:171–178. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Asai M, Hattori C, Iwata N, Saido TC,
Sasagawa N, Szabó B, Hashimoto Y, Maruyama K, Tanuma S, Kiso Y and
Ishiura S: The novel beta-secretase inhibitor KMI-429 reduces
amyloid beta peptide production in amyloid precursor protein
transgenic and wild-type mice. J Neurochem. 96:533–540. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Luo X and Yan R: Inhibition of BACE1 for
therapeutic use in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
3:618–628. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Hussain I, Hawkins J, Harrison D, Hille C,
Wayne G, Cutler L, Buck T, Walter D, Demont E, Howes C, et al: Oral
administration of a potent and selective non peptidic BACE-1
inhibitor decreases beta-cleavage of amyloid precursor protein and
amyloid-beta production in vivo. J Neurochem. 100:802–809. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Iserloh U, Pan J, Stamford AW, Kennedy ME,
Zhang Q, Zhang L, Parker EM, McHugh NA, Favreau L, Strickland C and
Voigt J: Discovery of an orally efficaceous
4-phenoxypyrrolidine-based BACE-1 inhibitor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
18:418–422. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Chang WP, Huang X, Downs D, Cirrito JR,
Koelsch G, Holtzman DM, Ghosh AK and Tang J: Beta-secretase
inhibitor GRL-8234 rescues age-related cognitive decline in APP
transgenic mice. FASEB J. 25:775–784. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Mangialasche F, Solomon A, Winblad B,
Mecocci P and Kivipelto M: Alzheimer's disease: Clinical trials and
drug development. Lancet Neurol. 9:702–716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Dovey HF, John V, Anderson JP, Chen LZ, de
Saint Andrieu P, Fang LY, Freedman SB, Folmer B, Goldbach E,
Holsztynska EJ, et al: Functional gamma-secretase inhibitors reduce
beta-amyloid peptide levels in brain. J Neurochem. 76:173–181.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Wolfe MS: Inhibition and modulation of
gamma-secretase for Alzheimer's disease. Neurotherapeutics.
5:391–398. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Lanz TA, Himes CS, Pallante G, Adams L,
Yamazaki S, Amore B and Merchant KM: The gamma-secretase inhibitor
N-[N-(3,5-difluorophenacetyl)-L-alanyl]-S-phenylglycine t-butyl
ester reduces A beta levels in vivo in plasma and cerebrospinal
fluid in young (plaque-free) and aged (plaque-bearing) Tg2576 mice.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 305:864–871. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Imbimbo BP: Alzheimer's disease:
γ-secretase inhibitors. Drug Discov Today. 5:169–175. 2008.
|
|
119
|
De Strooper B, Vassar R and Golde T: The
secretases: Enzymes with therapeutic potential in Alzheimer
disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 6:99–107. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Panza F, Frisardi V, Imbimbo BP, Capurso
C, Logroscino G, Sancarlo D, Seripa D, Vendemiale G, Pilotto A and
Solfrizzi V: REVIEW: γ -Secretase inhibitors for the treatment of
alzheimer's disease: The current state. CNS Neurosci Ther.
16:272–284. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Martone RL, Zho H, Atchison K, Comery T,
Xu JZ, Huang X, Gong X, Jin M, Kreft A, Harrison B, et al:
Begacestat (GSI-953): A novel, selective thiophene sulphonamide
inhibitor of amyloid precursor protein gamma-secretase for the
treatment of Alzheimer's disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
331:598–608. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Hopkins CR: ACS chemical neuroscience
molecule spotlight on begacestat (GSI-953). ACS Chem Neurosci.
3:3–4. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Han SH and Mook-Jung I: Diverse molecular
targets for terapeutic strategies in alzheimer's disease. J Korean
Med Sci. 29:893–902. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Desire L, Marcade M, Peillon H, Drouin D,
Sol O and Pando M: Clinical trials of EHT 0202, a neuroprotective
and procognitive alpha-secretase stimulator for Alzheimer's
disease. Alzheimers Dement. 5:P255–P256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Snow AD, Cummings J, Lake T, Hu Q,
Esposito L, Cam J, Hudson M, Smith E and Runnels S: Exebryl-1: A
novel small molecule currently in human clinical trials as a
disease-modifying drug for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.
Alzheimer's Dement. 5:P4182009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Hu S, Begum AN, Jones MR, Oh MS, Beech WK,
Beech BH, Yang F, Chen P, Ubeda OJ, Kim PC, et al: GSK3 inhibitors
show benefits in an Alzheimer's disease (AD) model of
neurodegeneration but adverse effects in control animals. Neurobiol
Dis. 33:193–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E and
Hyman BT: Neuropathological alterations in alzheimer disease. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 1:a0061892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Harper JD and Lansbury PT Jr: Models of
amyloid seeding in Alzheimer's disease and scrapie: Mechanistic
truths and physiological consequences of the time-dependent
solubility of amyloid proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 66:385–407. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Inouye H and Kirschner DA: A beta
fibrillogenesis: Kinetic parameters for fibril formation from congo
red binding. J Struct Biol. 130:123–129. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Jarrett JT, Berger EP and Lansbury PT: The
carboxy terminus of the beta amyloid protein is critical for the
seeding of amyloid formation: Implications for the pathogenesis of
Alzheimer's disease. Biochemistry. 32:4693–4697. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kim JR, Lee Muresan KY and Murphy RM: Urea
modulation of beta-amyloid fibril growth: Experimental studies and
kinetic models. Protein Sci. 13:2888–2898. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Lomakin A, Chung DS, Benedek GB, Kirschner
DA and Teplow DB: On the nucleation and growth of amyloid
beta-protein fibrils: Detection of nuclei and quantitation of rate
constants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:1125–1129. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Lomakin A, Teplow DB, Kirschner DA and
Benedek GB: Kinetic theory of fibrillogenesis of amyloid
beta-protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:7942–7947. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
McLaurin J, Franklin T, Zhang X, Deng J
and Fraser PE: Interactions of Alzheimer amyloid-beta peptides with
glycosaminoglycans effects on fibril nucleation and growth. Eur J
Biochem. 266:1101–1110. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Murphy RM and Pallitto MM: Probing the
kinetics of beta-amyloid self-association. J Struct Biol.
130:109–122. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Naiki H and Nakakuki K: First-order
kinetic model of Alzheimer's beta-amyloid fibril extension in
vitro. Lab Invest. 74:374–383. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Tomski SJ and Murphy RM: Kinetics of
aggregation of synthetic beta-amyloid peptide. Arch Biochem
Biophys. 294:630–638. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Walsh DM, Lomakin A, Benedek GB, Condron
MM and Teplow DB: Amyloid beta-protein fibrillogenesis: Detection
of a protofibrillar intermediate. J Biol Chem. 272:22364–22372.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Harper JD, Wong SS, Lieber CM and Lansbury
PT Jr: Assembly of A beta amyloid protofibrils: An in vitro model
for a possible early event in Alzheimer's disease. Biochemistry.
38:8972–8980. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Pallitto MM and Murphy RM: A mathematical
model of the kinetics of beta-amyloid fibril growth from the
denaturated state. Biophys J. 81:1805–1822. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Barrow CJ, Yasuda A, Kenny PT and Zagorski
MG: Solution conformations and aggregational properties of
synthetic amyloid beta peptides of Alzheimer's disease. analysis of
circular dichroism spectra. J Mol Biol. 225:1075–1093. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Cruz L, Urbanc B, Buldyrev SV, Christie R,
Gómez-Isla T, Havlin S, McNamara M, Stanley HE and Hyman BT:
Aggregation and disaggregation of senile plaques in Alzheimer
disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:7612–7616. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Urbanc B, Cruz L, Buldyrev SV, Havlin S,
Hyman BT and Stanley HE: Dynamic feedback in an
aggregation-disaggregation model. Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas
Fluids Relat Interdiscip Topics. 60:2120–2126. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
De Caluwé J and Dupont G: The progression
towards Alzheimer's disease described as a bistable switch arising
from the positive loop between amyloids and Ca(2+). J Theor Biol.
331:12–18. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Ortega F, Stott J, Visser S and Bendtsen
C: Interplay between α-, β-, and γ-secretases determines biphasic
amyloid-β protein level in the presence of γ-secretases inhibitor.
J Biol Chem. 288:785–792. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Schmidt V, Baum K, Lao A, Rateitschak K,
Schmitz Y, Teichmann A, Wiesner B, Petersen CM, Nykjaer A, Wolf J,
et al: Quantative modelling of amyloidogenic processing and its
influence by SORLA in Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J. 31:187–200.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Guardia-Laguarta C, Pera M and Lleó A:
Gamma-Secretase as a therapeutic target in Alzheimer's disease.
Curr Drug Targets. 11:506–517. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Anastasio TJ: Data driven modelling of
Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis. J Theor Biol. 290:60–72. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Anastasio TJ: Exploring the contribution
of estrogen to amyloid-beta regulation: A novel multifactorial
computational modelling approach. Front Pharmacol. 4:162013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Anastasio TJ: Computational identification
of potential multitarget treatments for ameliorating the adverse
effects of amyloid-β on synaptic plasticity. Front Pharmacol.
5:852014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Craft DL, Wein LM and Selkoe DJ: A
mathematical model of the impact of novel treatments on the A beta
burden in the Alzheimer's brain, CSF and plasma. Bull Math Biol.
64:1011–1031. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Proctor CJ and Gray DA: GSK3 and p53-is
there a link in Alzheimer's disease? Mol Neurodegener. 5:72010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Diem AK, Tan M, Bressloff NW, Hawkes C,
Morris AW, Weller RO and Carare RO: A simulation model of
periarterial clearance of amyloid-β from the brain. Front Aging
Neurosci. 8:182016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Proctor CJ, Boche D, Gray DA and Nicoll
JA: Investigating interventions in alzheimer's disease with
computer simulation models. PLoS ONE. 8:e736312013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Kyrtsos CR and Baras JS: Studying the role
of ApoE in Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis using a systems biology
model. J Bioinform Comput Biol. 11:13420032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Chen C: beta-Amyloid increases dendritic
Ca2+ influx by inhibiting the A-type K+ current in hippocampal CA1
pyramidal neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 338:1913–1919. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Good TA and Murphy RM: Effect of
beta-amyloid block of the fast-inactivating K+ channel on
intracellular Ca2+ and excitability in a modeled neuron. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 93:15130–15135. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Hoffman DA, Magee JC, Colbert CM and
Johnston D: K+ channel regulation of signal propagation in
dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Nature. 387:869–875.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Culmone V and Migliore M: Progressive
effect of beta amyloid peptides accumulation on CA1 pyramidal
neurons: A model study suggesting possible treatments. Front Comp
Neurosci. 6:522012.
|
|
160
|
Wilson RS, Boyle PA, Yu L, Barnes LL,
Schneider JA and Bennett DA: Life-span cognitive activity,
neuropathologic burden, and cognitive aging. Neurology. 81:314–321.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Abramov E, Dolev I, Fogel H, Ciccotosto
GD, Ruff E and Slutsky I: Amyloid-beta as a positive endogenous
regulator of release probability at hippocampal synapses. Nat
Neurosci. 12:1567–1576. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Parodi J, Sepulveda FJ, Roa J, Opazo C,
Inestrosa NC and Aguayo LG: Beta-amyloid causes depletion of
synaptic vesicles leading to neurotransmission failure. J Biol
Chem. 285:2506–2514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Romani A, Marchetti C, Bianchi D,
Leinekugel X, Poirazi P, Migliore M and Marie H: Computational
modeling of the effects of amyloid-beta on release probability at
hippocampal synapses. Front Comp Neurosci. 7:12013.
|
|
164
|
Hasselmo ME and Wyble BP: Free recall and
recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: Simulating
effects of scopolamine on human memory function. Behav Brain Res.
89:1–34. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Menschik ED and Finkel LH: Neuromodulatory
control hippocampal function: Towards a model of Alzheimer's
disease. Artif Intell Med. 13:99–121. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Buzsáki G: Two-stage model of memory trace
formation: A role for noisy brain states. Neuroscience. 31:551–570.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Buzsáki G and Chrobak JJ: Temporal
structure in spatially organized neuronal ensembles: A role for
interneuronal networks. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 5:504–510. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Lisman JE and Idiart MA: Storage of 7 +/-
2 short-term memories in oscillatory subcycles. Science.
267:1512–1515. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Lisman J: The theta/gamma discrete phase
code occurring during the hippocampal phase precession may be a
more general brain coding scheme. Hippocampus. 15:913–922. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Roberts PD, Spiros A and Geerts H:
Simulations of symptomatic treatments for Alzheimer's disease:
Computational analysis of pathology and mechanisms of drug action.
Alzheimers Res Ther. 4:502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Bianchi D, De Michele P, Marchetti C,
Tirozzi B, Cuomo S, Marie H and Migliore M: Effects of increasing
CREB-dependent transcription on the storage and recall processes in
a hippocampal CA1 microcircuit. Hippocampus. 24:165–177. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Cutsuridis V, Cobb S and Graham BP:
Encoding and retrieval in the hippocampal CA1 microcircuit model.
Hippocampus. 20:423–446. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Horn D, Ruppin E, Usher M and Hermann M:
Neural network modeling of memory deterioration in Alzheimer's
disease. Neural Comput. 5:736–749. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Ruppin E and Reggia JA: A neural model of
memory impairment in diffuse cerebral atrophy. Br J Psychiatry.
166:19–28. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Hasselmo ME: Runaway synaptic modification
in models of cortex: Implications for Alzheimer's disease. Neural
Netw. 7:13–40. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Hasselmo ME: A computational model of the
progression of Alzheimer's disease. MD Comput. 14:181–191.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Siegle GJ and Hasselmo ME: Using
connectionist models to guide assessment of psychological disorder.
Psychol Assess. 14:263–278. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Bhattacharya BS, Coyle D and Maguire LP: A
thalamo-cortico-thalamic neural mass model to study alpha rhythms
in Alzheimer's Disease. Neural Netw. 24:631–645. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Gluck MA, Myers CE, Nicolle MM and Johnson
S: Computational models of the hippocampal region: Implications for
prediction of risk for Alzheimer's disease in non-demented elderly.
Curr Alzheimer Res. 3:247–257. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Moustafa AA, Keri S, Herzallah MM, Myers
CE and Gluck MA: A neural model of hippocampal-striatal
interactions in associative learning and transfer generalization in
various neurological and psychiatric patients. Brain Cogn.
74:132–144. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
McAuley MT, Kenny RA, Kirkwood TB,
Wilkinson DJ, Jones JJ and Miller VM: A mathematical model of
aging-related and cortisol induced hippocampal dysfunction. BMC
Neurosci. 10:262009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Jack CR Jr and Holtzman DM: Biomarker
modeling of Alzheimer's disease. Neuron. 80:1347–1358. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Mayeux R: Biomarkers: Potential uses and
limitations. NeuroRx. 1:182–188. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Blennow K, Hampel H and Zetterberg H:
Biomarkers in amyloid-β immunotherapy trials in Alzheimer's
disease. Neuropsychopharmacology. 39:189–201. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Blennow K, Zetterberg H and Fagan AM:
Fluid biomarkers in alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect
Med. 2:a0062212012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois
B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, Gamst A, Holtzman DM, Jagust WJ, Petersen
RC, et al: The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to
Alzheimer's disease: Recommendations from the national institute on
aging-alzheimer's association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines
for alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7:270–279. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Dubois B, Feldman HH, Jacova C, Cummings
JL, Dekosky ST, Barberger-Gateau P, Delacourte A, Frisoni G, Fox
NC, Galasko D, et al: Revising the definition of Alzheimer's
disease: A new lexicon. Lancet Neurol. 9:1118–1127. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Jack CR Jr, Albert MS, Knopman DS, McKhann
GM, Sperling RA, Carrillo MC, Thies B and Phelps CH: Introduction
to the recommendations from the national institute on
aging-alzheimer's association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines
for alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7:257–262. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman
BT, Jack CR Jr, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux
R, et al: The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease:
Recommendations from the national institute on aging-alzheimer's
association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for alzheimer's
disease. Alzheimers Dement. 7:263–269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Castro-Chavira SA, Fernandez T, Nicolini
H, Diaz-Cintra S and Prado-Alcala RA: Genetic markers in biological
fluids for aging-related major neurocognitive disorder. Curr
Alzheimer Res. 12:200–209. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Sonnen JA, Montine KS, Quinn JF, Kaye JA,
Breitner JCS and Montine TJ: Biomarkers for cognitive impairment
and dementia in elderly people. Lancet Neurol. 7:704–714. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Dekkers MP, Nikoletopoulou V and Barde YA:
Cell biology in neuroscience: Death of developing neurons: New
insights and implications for connectivity. J Cell Biol.
203:385–393. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Terry RD: Basis of structural Alzheimer
disease and some pathogenic conceptsAlzheimer's disease: From
molecular biology to therapy. Becker P and Giacobini F: Birkhäuser
Publishing Ltd.; Cambridge, MA: pp. 19–23. 1996
|
|
194
|
Burggren A and Brown J: Imaging markers of
structural and functional brain changes that precede cognitive
symptoms in risk for Alzheimer's disease. Brain Imaging Behav.
8:251–261. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Zlokovic BV: Neurovascular pathways to
neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease and other disorders. Nat
Rev Neurosci. 12:723–738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Desikan RS, Cabral HJ, Hess CP, Dillon WP,
Glastonbury CM, Weiner MW, Schmansky NJ, Greve DN, Salat DH,
Buckner RL, et al: Automated MRI measures identify individuals with
mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease. Brain.
132:2048–2057. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Dickerson BC and Wolk DA: Alzheimer's
Disease Neuroimaging Initiative: MRI cortical thickness biomarker
predicts AD-like CSF and cognitive decline in normal adults.
Neurology. 78:84–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Hua X, Leow AD, Lee S, Klunder AD, Toga
AW, Lepore N, Chou YY, Brun C, Chiang MC, Barysheva M, et al: 3D
characterization of brain atrophy in Alzheimer's disease and mild
cognitive impairment using tensor-based morphometry. Neuroimage.
41:19–34. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Morra JH, Tu Z, Apostolova LG, Green AE,
Avedissian C, Madsen SK, Parikshak N, Hua X, Toga AW, Jack CR Jr,
et al: Validation of a fully automated 3D hippocampal segmentation
method using subjects with Alzheimer's disease mild cognitive
impairment, and elderly controls. Neuroimage. 43:59–68. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Morra JH, Tu Z, Apostolova LG, Green AE,
Avedissian C, Madsen SK, Parikshak N, Toga AW, Jack CR Jr, Schuff
N, et al: Automated mapping of hippocampal atrophy in 1-year repeat
MRI data from 490 subjects with Alzheimer's disease, mild cognitive
impairment and elderly controls. Neuroimage. 45 1 Suppl:S3–S15.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
Mirra SS and Markesbery WR: The
Neuropathology of Alzheimer's DiseaseAlzheimer's Disease: Cause
(s), Diagnosis, Treatment and Care. Khachaturian ZS and Radebaugh
TS: CRC press; New York, NY: pp. 111–123. 1996
|
|
202
|
Price DL: Aging of the brain and dementia
of the Alzheimer typePrinciples of Neural Sciences. Kandel ER and
Jessel TM: McGraw-Hill; New York, NY: pp. 1149–1168. 2000
|
|
203
|
Teipel SJ, Bayer W, Alexander GE, Bokde
AL, Zebuhr Y, Teichberg D, Müller-Spahn F, Schapiro MB, Möller HJ,
Rapoport SI and Hampel H: Regional pattern of hippocampus and
corpus callosum atrophy in Alzheimer's disease in relation to
dementia severity: Evidence for early neocortical degeneration.
Neurobiol Aging. 24:85–94. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Xanthakos S, Krishnan KR, Kim DM and
Charles HC: Magnetic resonance imaging of Alzheimer's disease. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 20:597–626. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Moon WJ, Park JY, Yun WS, Jeon JY, Moon
YS, Kim H, Kwak KC, Lee JM and Han SH: A comparison of substantia
nigra T1 hyperintensity in parkinson's disease dementia,
alzheimer's disease and age-matched controls: Volumetric analysis
of neuromelanin imaging. Korean J Radiol. 17:633–640. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E and
Hyman BT: Neuropathological alterations in alzheimer disease. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 1:a0061892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Avila J, Lim F, Moreno F, Belmonte C and
Cuello AC: Tau function and dysfunction in neurons: Its role in
neurodegenerative disorders. Mol Neurobiol. 25:213–231. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Cole SL and Vassar R: The Alzheimer's
disease beta-secretase enzyme, BACE1. Mol Neurodegener. 2:222007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Zetterberg H, Andreasson U, Hansson O, Wu
G, Sankaranarayanan S, Andersson ME, Buchhave P, Londos E, Umek RM,
Minthon L, et al: Elevated cerebrospinal fluid BACE1 activity in
incipient Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 65:1102–1107. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Selkoe DJ: Cell biology of protein
misfolding: The examples of Alzheimer's and Parkinson's diseases.
Nat Cell Biol. 6:1054–1061. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Cairns NJ, Ikonomovic MD, Benzinger T,
Storandt M, Fagan AM, Shah AR, Reinwald LT, Carter D, Felton A,
Holtzman DM, et al: Absence of Pittsburgh compound B detection of
cerebral amyloid beta in a patient with clinical, cognitive, and
cerebrospinal fluid markers of Alzheimer disease: A case report.
Arch Neurol. 66:1557–1562. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Selkoe DJ: Alzheimer's disease: A central
role for amyloid. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 53:438–447. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
de Courten-Myers GM: Cerebral amyloid
angiopathy and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Ageing. 25:603–604.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
214
|
Haglund M, Sjöbeck M and Englund E: Severe
cerebral amyloid angiopathy characterizes an underestimated variant
of vascular dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 18:132–137. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Tian J, Shi J, Bailey K and Mann DM:
Negative association between amyloid plaques and cerebral amyloid
angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett. 352:137–140.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Hassan M, Sehgel SA and Sajid R:
Regulatory cascade of neuronal loss and glucose metabolism. CNS
Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 13:1232–1245. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Budinger TF: Neuroimaging Applications for
the Study of Alzheimer's DiseaseAlzheimer's Disease: Cause (s),
Diagnosis, Treatment and Care. Khachaturian ZS and Radebaugh TS:
CRC press; New York, NY: pp. 146–169. 1996
|
|
218
|
Hoyer S: Oxidative metabolism deficiencies
in brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neurol Scand.
94:18–24. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
219
|
Planel E, Miyasaka T, Launey T, Chui DH,
Tanemura K, Sato S, Murayama O, Ishiguro K, Tatebayashi Y and
Takashima A: Alterations in glucose metabolism induce hypothermia
leading to tau hyperphosphorylation through differential inhibition
of kinase and phosphatase activities: Implications for alzheimer's
disease. J Neurosci. 24:2401–2411. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Evans PH: Free radicals in brain
metabolism and pathology. Br Med Bull. 49:577–587. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Eckert A, Keil U, Kressmann S, Schindowski
K, Leutner S, Leutz S and Müller WE: Effects of EGb 761 Ginkgo
biloba extract on mitochondrial function and oxidative stress.
Pharmacopsychiatry. 1 Suppl 1:S15–S23. 2003.
|
|
222
|
Baloyannis SJ, Costa V and Michmizos D:
Mitochondrial alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Alzheimers
Dis Other Demen. 19:89–93. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Choi JK, Carreras I, Aytan N,
Jenkins-Sahlin E, Dedeoglu A and Jenkins BG: The effects of aging,
housing and ibuprofen treatment on brain neurochemistry in a triple
transgene Alzheimer's disease mouse model using magnetic resonance
spectroscopy and imaging. Brain Res. 1590:85–96. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Braak H and Braak E: Frequency of stages
of Alzheimer-related lesions in different age categories. Neurobiol
Aging. 18:351–357. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Haroutunian V, Purohit DP, Perl DP, Marin
D, Khan K, Lantz M, Davis KL and Mohs RC: Neurofibrillary tangles
in nondemented elderly subjects and mild Alzheimer disease. Arch
Neurol. 56:713–718. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Price JL and Morris JC: Tangles and
plaques in nondemented aging and ‘preclinical’ Alzheimer's disease.
Ann Neurol. 45:358–368. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
227
|
Jack CR Jr, Dickson DW, Parisi JE, Xu YC,
Cha RH, O'Brien PC, Edland SD, Smith GE, Boeve BF, Tangalos EG, et
al: Antemortem MRI findings correlate with hippocampal
neuropathology in typical aging and dementia. Neurology.
58:750–757. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Senjem ML, Gunter JL, Shiung MM, Petersen
RC and Jack CR Jr: Comparison of different methodological
implementations of voxel-based morphometry in neurodegenerative
disease. Neuroimage. 26:600–608. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Tarawneh R, D'Angelo G, Macy E, Xiong C,
Carter D, Cairns NJ, Fagan AM, Head D, Mintun MA, Ladenson JH, et
al: Visinin like protein-1: Diagnostic and prognostic biomarker in
Alzheimer disease. Ann Neurol. 70:274–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
230
|
Struyfs H, Van Hecke W, Veraart J, Sijbers
J, Slaets S, De Belder M, Wuyts L, Peters B, Sleegers K, Robberecht
C, et al: Diffusion kurtosis imaging: A possible MRI biomarker for
AD diagnosis? J Alzheimers Dis. 48:937–948. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
James OG, Doraiswamy PM and Borges-Neto S:
PET Imaging of tau pathology in alzheimer's disease and
tauopathies. Front Neurol. 6:382015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Baird AL, Westwood S and Lovestone S:
Blood-based proteomic biomarkers of alzheimer's disease pathology.
Front Neurol. 6:2362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Anderso NL and Anderson NG: The human
plasma proteome: History, character, and diagnostic prospects. Mol
Cell Proteomics. 1:845–867. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Montagne A, Barnes SR, Sweeney MD,
Halliday MR, Sagare AP, Zhao Z, Toga AW, Jacobs RE, Liu CY, Amezcua
L, et al: Blood-brain barrier breakdown in the aging human
hippocampus. Neuron. 85:296–302. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Lewczuk P, Esselmann H, Bibl M, Paul S,
Svitek J, Miertschischk J, Meyrer R, Smirnov A, Maler JM, Klein C,
et al: Electrophoretic separation of amyloid beta peptides in
plasma. Electrophoresis. 25:3336–3343. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
Fox NC, Black RS, Gilman S, Rossor MN,
Griffith SG, Jenkins L and Koller M: AN1792(QS-21)-201 Study:
Effects of Abeta immunization (AN1792) on MRI measures of cerebral
volume in Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 64:1563–1572. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Frisoni GB and Delacourte A: Neuroimaging
outcomes in clinical trials in Alzheimer's disease. J Nutr Health
Aging. 13:209–212. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
238
|
Rinne JO, Brooks DJ, Rossor MN, Fox NC,
Bullock R, Klunk WE, Mathis CA, Blennow K, Barakos J, Okello AA, et
al: 11C-PiB PET assessment of change in fibrillar amyloid-beta load
in patients with Alzheimer's disease treated with bapineuzumab: A
phase 2, double-blind, placebo-controlled, ascending-dose study.
Lancet Neurol. 9:363–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
239
|
Sperling RA, Jack CR Jr and Aisen PS:
Testing the right target and right drug at the right stage. Sci
Transl Med. 3:111cm332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Geerts H, Dacks PA, Devanarayan V, Haas M,
Khachaturian ZS, Gordon MF, Maudsley S, Romero K and Stephenson D:
Brain Health Modeling Initiative (BHMI): Big data to smart data in
Alzheimer's disease: The brain health modeling initiative to foster
actionable knowledge. Alzheimers Dement. 12:1014–1021. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|