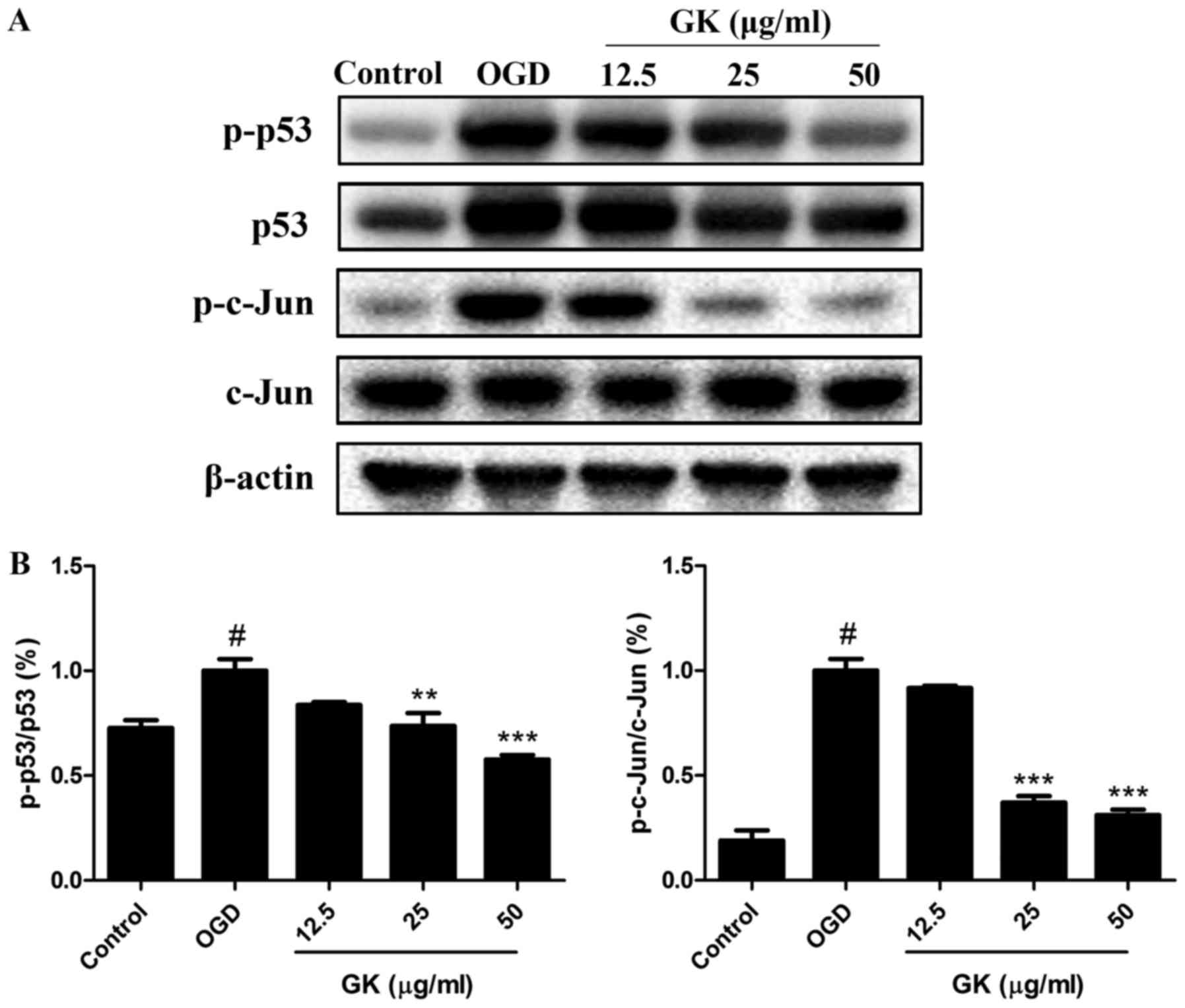
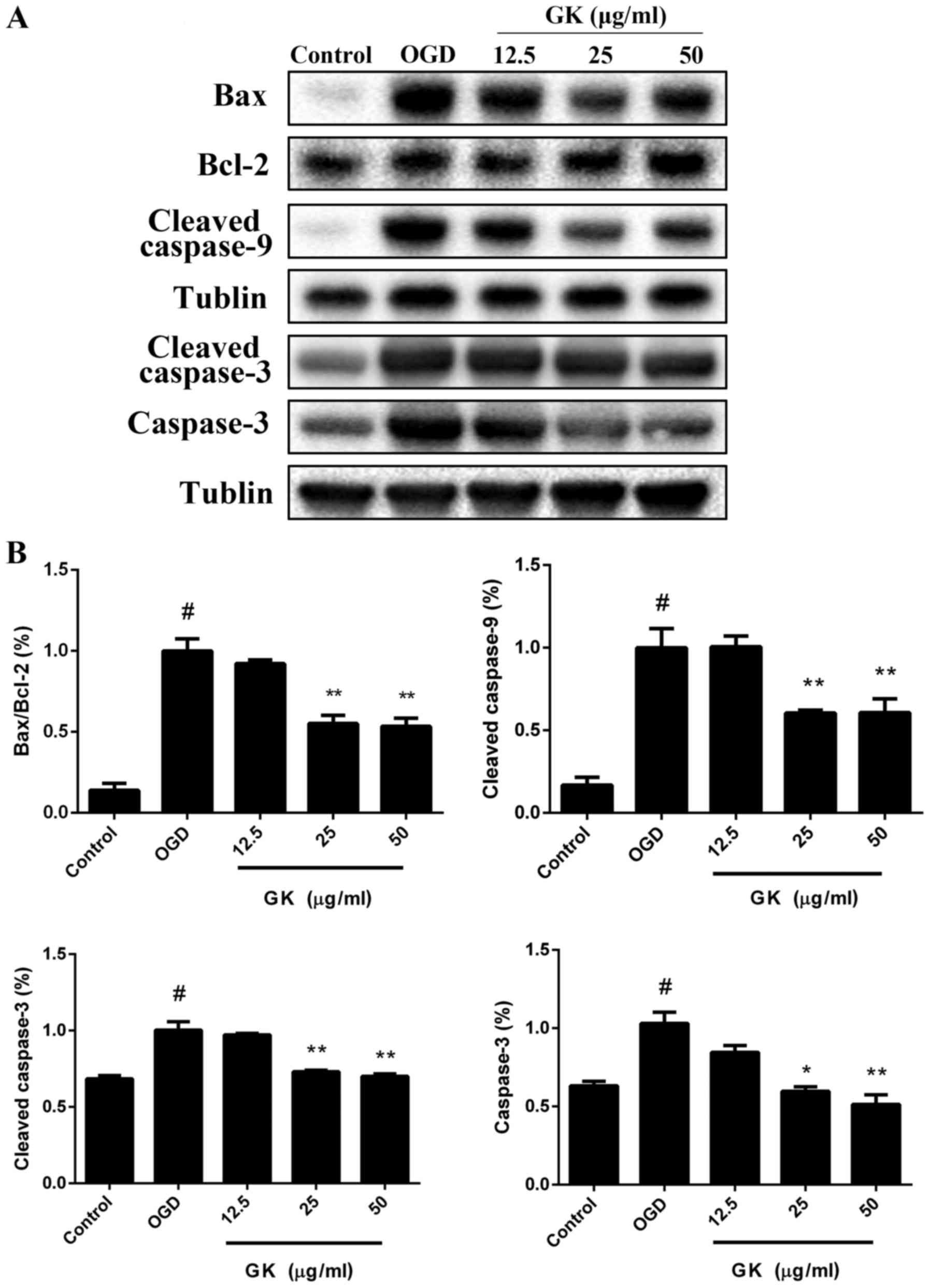
|
1
|
Shu ZM, Shu XD, Li HQ, Sun Y, Shan H, Sun
XY, Du RH, Lu M, Xiao M, Ding JH and Hu G: Ginkgolide B protects
against ischemic stroke via modulating microglia polarization in
mice. CNS Neurosci Ther. 22:729–739. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Writing Group Members, . Mozaffarian D,
Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de
Ferranti S, Després JP, et al: Heart disease and stroke
statistics-2016 update: A report from the American heart
association. Circulation. 133:e38–e360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fann DY, Lee SY, Manzanero S, Chunduri P,
Sobey CG and Arumugam TV: Pathogenesis of acute stroke and the role
of inflammasomes. Ageing Res Rev. 12:941–966. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sun J and Nan G: The mitogen-activated
protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway as a discovery target in
stroke. J Mol Neurosci. 59:90–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fann DY, Lim YA, Cheng YL, Lok KZ,
Chunduri P, Baik SH, Drummond GR, Dheen ST, Sobey CG, Jo DG, et al:
Evidence that NF-κB and MAPK signaling promotes NLRP inflammasome
activation in neurons following ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol.
55:1082–1096. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nakka VP, Gusain A, Mehta SL and Raghubir
R: Molecular mechanisms of apoptosis in cerebral ischemia: Multiple
neuroprotective opportunities. Mol Neurobiol. 37:7–38. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu X, Yan Y, Bao L, Chen B, Zhao Y and Qi
R: Ginkgolide B inhibits platelet release by blocking Syk and p38
MAPK phosphorylation in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Thromb Res.
134:1066–1073. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang S, Wang Z, Fan Q, Guo J, Galli G, Du
G, Wang X and Xiao W: Ginkgolide K protects the heart against
endoplasmic reticulum stress injury by activating the
inositol-requiring enzyme 1α/X box-binding protein-1 pathway. Br J
Pharmacol. 173:2402–2418. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma S, Liu X, Xun Q and Zhang X:
Neuroprotective effect of Ginkgolide K against H2O2-induced PC12
cell cytotoxicity by ameliorating mitochondrial dysfunction and
oxidative stress. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:217–225. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao Y, Signore AP, Yin W, Cao G, Yin XM,
Sun F, Luo Y, Graham SH and Chen J: Neuroprotection against focal
ischemic brain injury by inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and
attenuation of the mitochondrial apoptosis-signaling pathway. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 25:694–712. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng A, Chan SL, Milhavet O, Wang S and
Mattson MP: p38 MAP kinase mediates nitric oxide-induced apoptosis
of neural progenitor cells. J Biol Chem. 276:43320–43327. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cao G, Minami M, Pei W, Yan C, Chen D,
O'Horo C, Graham SH and Chen J: Intracellular Bax translocation
after transient cerebral ischemia: Implications for a role of the
mitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathway in ischemic neuronal
death. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 21:321–333. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bourgain RH, Andries R and Braquet P:
Effect of ginkgolide PAF-acether antagonists on arterial
thrombosis. Adv Prostaglandin Thromboxane Leukot Res. 17B:815–817.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang ZZ, Li J, Li SX, Feng W and Wang H:
Effect of ginkgolide B on striatal extracellular amino acids in
middle cerebral artery occluded rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
136:117–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cain K, Brown DG, Langlais C and Cohen GM:
Caspase activation involves the formation of the aposome, a large
(approximately 700 kDa) caspase-activating complex. J Biol Chem.
274:22686–22692. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim HE, Du F, Fang M and Wang X: Formation
of apoptosome is initiated by cytochrome c-induced dATP hydrolysis
and subsequent nucleotide exchange on Apaf-1. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 102:17545–17550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mouw G, Zechel JL, Zhou Y, Lust WD, Selman
WR and Ratcheson RA: Caspase-9 inhibition after focal cerebral
ischemia improves outcome following reversible focal ischemia.
Metab Brain Dis. 17:143–151. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yuan J and Yankner BA: Apoptosis in the
nervous system. Nature. 407:802–809. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sulejczak D, Czarkowska-Bauch J, Macias M
and Skup M: Bcl-2 and Bax proteins are increased in neocortical but
not in thalamic apoptosis following devascularizing lesion of the
cerebral cortex in the rat: An immunohistochemical study. Brain
Res. 1006:133–149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poppe M, Reimertz C, Düssmann H, Krohn AJ,
Luetjens CM, Böckelmann D, Nieminen AL, Kögel D and Prehn JH:
Dissipation of potassium and proton gradients inhibits
mitochondrial hyperpolarization and cytochrome c release during
neural apoptosis. J Neurosci. 21:4551–4563. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hara A, Iwai T, Niwa M, Uematsu T, Yoshimi
N, Tanaka T and Mori H: Immunohistochemical detection of Bax and
Bcl-2 proteins in gerbil hippocampus following transient forebrain
ischemia. Brain Res. 711:249–253. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gong X, Liu A, Ming X, Deng P and Jiang Y:
UV-induced interaction between p38 MAPK and p53 serves as a
molecular switch in determining cell fate. FEBS Lett.
584:4711–4716. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bogoyevitch MA, Ngoei KR, Zhao TT, Yeap YY
and Ng DC: c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling: Recent advances
and challenges. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1804:463–475. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Smeal T, Binetruy B, Mercola D,
Grover-Bardwick A, Heidecker G, Rapp UR and Karin M:
Oncoprotein-mediated signalling cascade stimulates c-Jun activity
by phosphorylation of serines 63 and 73. Mol Cell Biol.
12:3507–3513. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
McGahan L, Hakim AM and Robertson GS:
Hippocampal Myc and p53 expression following transient global
ischemia. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 56:133–145. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|