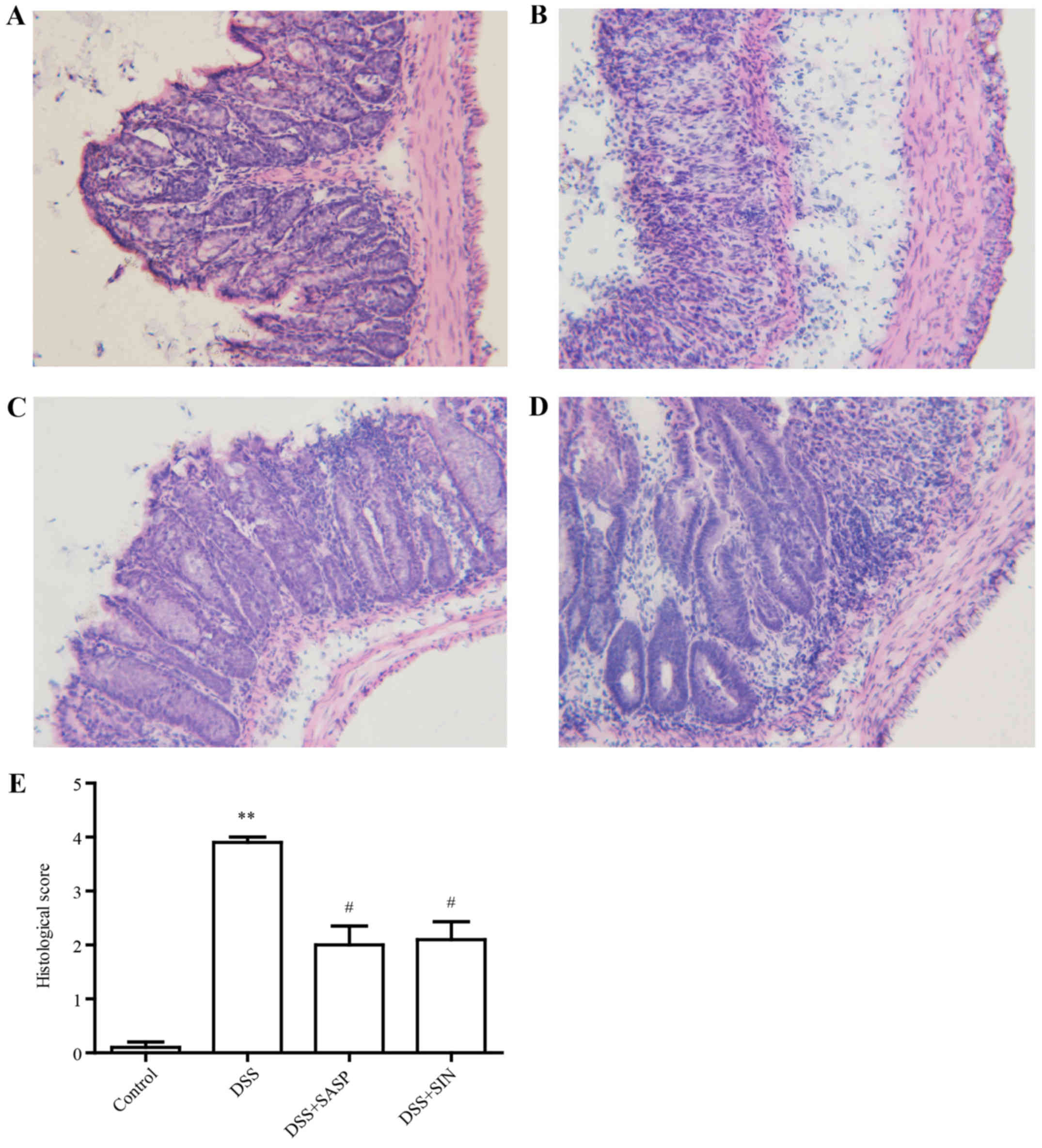
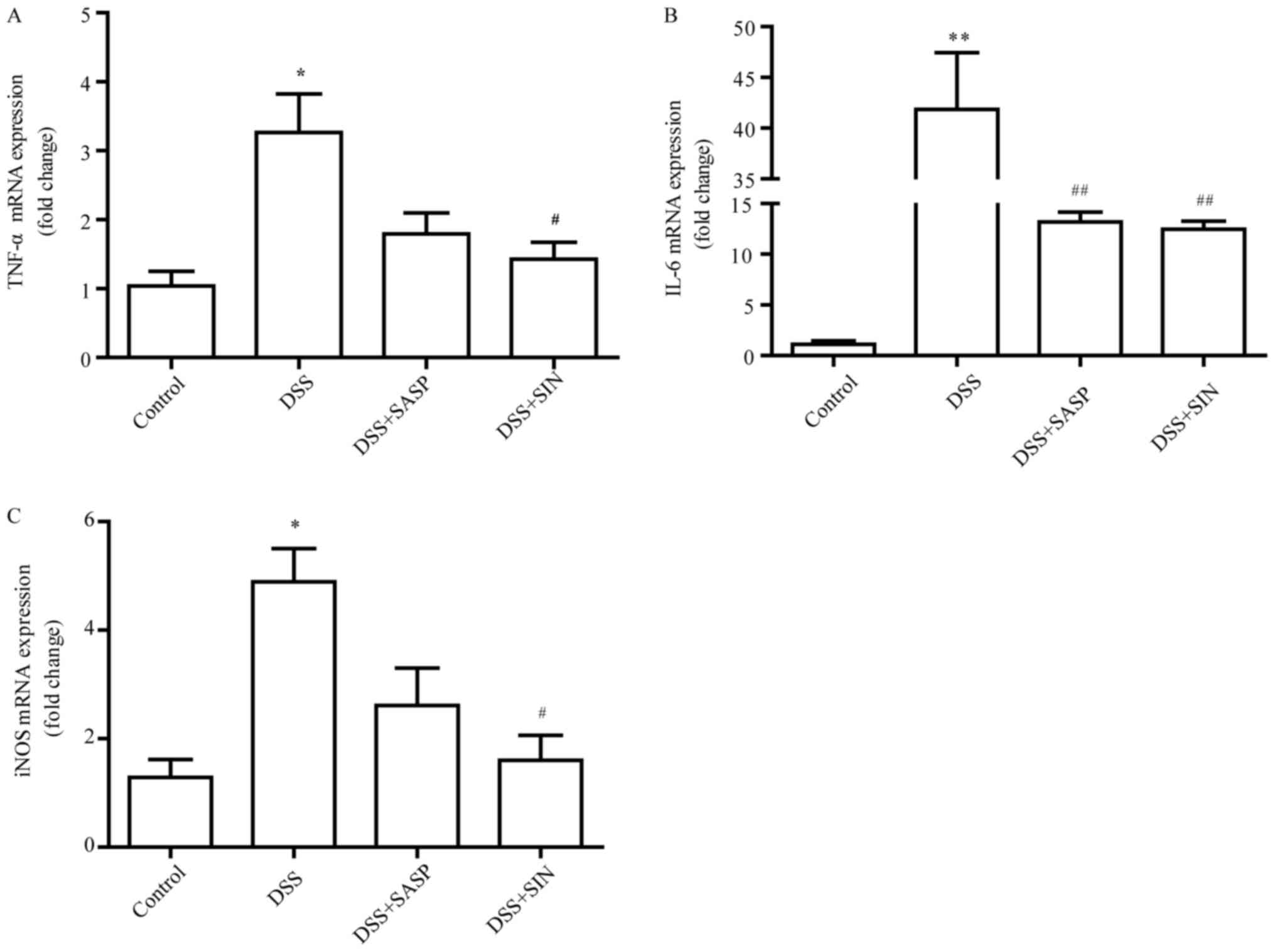
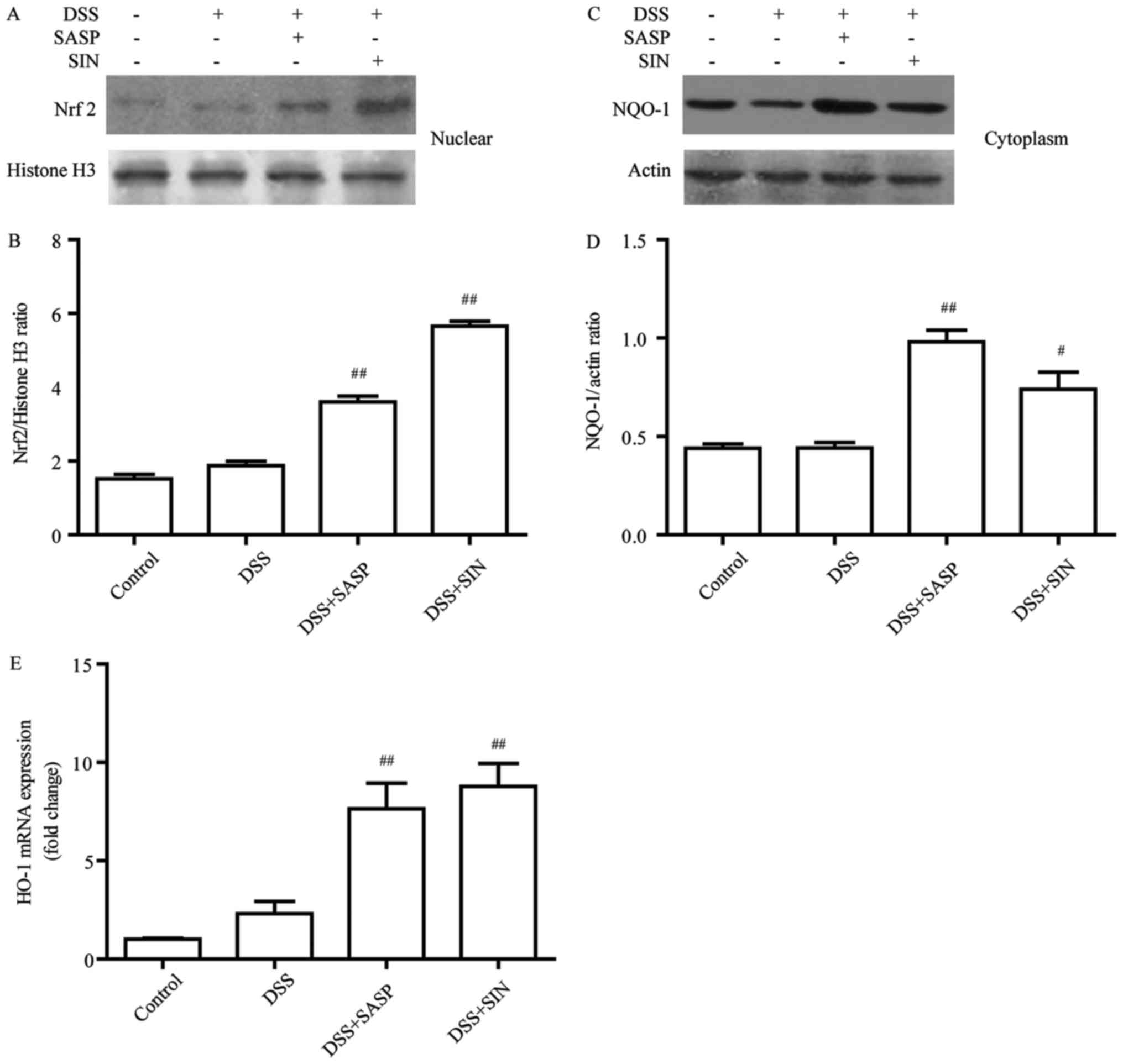
|
1
|
Abraham C and Cho JH: Inflammatory bowel
disease. N Engl J Med. 361:2066–2078. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Munkholm P: Review article: The incidence
and prevalence of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2 Suppl 18:1–5. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kaistha A and Levine J: Inflammatory bowel
disease: The classic gastrointestinal autoimmune disease. Curr
Probl Pediatr Adolesc Health Care. 44:328–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Danese S, Malesci A and Vetrano S:
Colitis-associated cancer: The dark side of inflammatory bowel
disease. Gut. 60:1609–1610. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pandurangan AK, Mohebali N, Norhaizan ME
and Looi CY: Gallic acid attenuates dextran sulfate sodium-induced
experimental colitis in BALB/c mice. Drug Des Devel Ther.
9:3923–3934. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Stachel I, Geismann C, Aden K, Deisinger
F, Rosenstiel P, Schreiber S, Sebens S, Arlt A and Schafer H:
Modulation of nuclear factor E2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) activation
by the stress response gene immediate early response-3 (IER3) in
colonic epithelial cells: A novel mechanism of cellular adaption to
inflammatory stress. J Biol Chem. 289:1917–1929. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Uruno A and Motohashi H: The Keap1-Nrf2
system as an in vivo sensor for electrophiles. Nitric Oxide.
25:153–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim J, Cha YN and Surh YJ: A protective
role of nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (Nrf2) in
inflammatory disorders. Mutat Res. 690:12–23. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cheng Y, Zhang J, Hou W, Wang D, Li F,
Zhang Y and Yuan F: Immunoregulatory effects of sinomenine on the
T-bet/GATA-3 ratio and Th1/Th2 cytokine balance in the treatment of
mesangial proliferative nephritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 9:894–899.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang Q and Li XK: Immunosuppressive and
anti-inflammatory activities of sinomenine. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:373–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tong B, Yu J, Wang T, Dou Y, Wu X, Kong L,
Dai Y and Xia Y: Sinomenine suppresses collagen-induced arthritis
by reciprocal modulation of regulatory T cells and Th17 cells in
gut-associated lymphoid tissues. Mol Immunol. 65:94–103. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mu H, Yao RB, Zhao LJ, Shen SY, Zhao ZM
and Cai H: Sinomenine decreases MyD88 expression and improves
inflammation-induced joint damage progression and symptoms in rat
adjuvant-induced arthritis. Inflammation. 36:1136–1144. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xiong L and Yang L: Effects of alkaloid
sinomenine on levels of IFN-γ, IL-1β, TNF-α and IL-6 in a rat renal
allograft model. Immunotherapy. 4:785–791. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li Y, Duan Z, Tian Y, Liu Z and Wang Q: A
novel perspective and approach to intestinal octreotide absorption:
Sinomenine-mediated reversible tight junction opening and its
molecular mechanism. Int J Mol Sci. 14:12873–12892. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cheng H, Xia B, Guo Q, Zhang L, Wang F,
Jiang L, Wang Z, Zhang Y and Li C: Sinomenine attenuates
2,4,6-trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colitis in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 7:604–611. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu Q, Zhu S, Zhou R, Yi F, Bing Y, Huang
S, Wang Z, Wang C and Xia B: Effects of sinomenine on the
expression of microRNA-155 in 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic
acid-induced colitis in mice. PloS One. 8:e737572013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Leonardi I, Nicholls F, Atrott K, Cee A,
Tewes B, Greinwald R, Rogler G and Frey-Wagner I: Oral
administration of dextran sodium sulphate induces a
caecum-localized colitis in rabbits. Int J Exp Pathol. 96:151–162.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: The
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. J Pharmacol
Pharmacother. 1:94–99. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Bang B and Lichtenberger LM: Methods of
inducing inflammatory bowel disease in mice. Curr Protoc Pharmacol.
72:5.58.1–5.58.42. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Koboziev I, Karlsson F, Zhang S and
Grisham MB: Pharmacological intervention studies using mouse models
of the inflammatory bowel diseases: Translating preclinical data
into new drug therapies. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 17:1229–1245. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vong LB, Tomita T, Yoshitomi T, Matsui H
and Nagasaki Y: An orally administered redox nanoparticle that
accumulates in the colonic mucosa and reduces colitis in mice.
Gastroenterology. 143:1027–1036.e1023. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sann H, Erichsen Jv, Hessmann M, Pahl A
and Hoffmeyer A: Efficacy of drugs used in the treatment of IBD and
combinations thereof in acute DSS-induced colitis in mice. Life
Sci. 92:708–718. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feldman AT and Wolfe D: Tissue processing
and hematoxylin and eosin staining. Methods Mol Biol. 1180:31–43.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pandurangan AK and Esa NM: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3-a promising target in
colitis-associated cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:551–560.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lowenberg M and D'Haens G: Novel targets
for inflammatory bowel disease therapeutics. Curr Gastroenterol
Rep. 15:3112013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhu H and Li YR: Oxidative stress and
redox signaling mechanisms of inflammatory bowel disease: Updated
experimental and clinical evidence. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
237:474–480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang A, Keita AV, Phan V, McKay CM,
Schoultz I, Lee J, Murphy MP, Fernando M, Ronaghan N, Balce D, et
al: Targeting mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species to
reduce epithelial barrier dysfunction and colitis. Am J Pathol.
184:2516–2527. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mouzaoui S, Djerdjouri B, Makhezer N,
Kroviarski Y, El-Benna J and Dang PM: Tumor necrosis
factor-α-induced colitis increases NADPH oxidase 1 expression,
oxidative stress, and neutrophil recruitment in the colon:
Preventive effect of apocynin. Mediators Inflamm. 2014:3124842014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Fernandes CG, da Rosa MS, Seminotti B,
Pierozan P, Martell RW, Lagranha VL, Busanello EN, Leipnitz G and
Wajner M: In vivo experimental evidence that the major metabolites
accumulating in 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency
induce oxidative stress in striatum of developing rats: A potential
pathophysiological mechanism of striatal damage in this disorder.
Mol Genet Metab. 109:144–153. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goes AC, Pinto FM, Fernandes GC, Barbosa
JS, Correia ES, Ribeiro RA, Guimaraes SB, Lima Junior RC, Brito GA
and Rodrigues LV: Electroacupuncture ameliorates experimental
colitis induced by TNBS through activation of interleukin-10 and
inhibition of iNOS in mice. Acta Cir Bras. 29:787–793. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mouzaoui S, Rahim I and Djerdjouri B:
Aminoguanidine and curcumin attenuated tumor necrosis factor
(TNF)-α-induced oxidative stress, colitis and hepatotoxicity in
mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 12:302–311. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Park SY, Neupane GP, Lee SO, Lee JS, Kim
MY, Kim SY, Park BC, Park YJ and Kim JA: Protective effects of
pogostemon cablin bentham water extract on inflammatory cytokine
expression in TNBS-induced colitis in rats. Arch Pharm Res.
37:253–262. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Leppkes M, Roulis M, Neurath MF, Kollias G
and Becker C: Pleiotropic functions of TNF-α in the regulation of
the intestinal epithelial response to inflammation. Int Immunology.
26:509–515. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chalaris A, Garbers C, Rabe B, Rose-John S
and Scheller J: The soluble Interleukin 6 receptor: Generation and
role in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cell Biol. 90:484–494. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Moriasi C, Subramaniam D, Awasthi S,
Ramalingam S and Anant S: Prevention of colitis-associated cancer:
Natural compounds that target the IL-6 soluble receptor. Anticancer
Agents Med Chem. 12:1221–1238. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bryan HK, Olayanju A, Goldring CE and Park
BK: The Nrf2 cell defence pathway: Keap1-dependent and -independent
mechanisms of regulation. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:705–717. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Araujo JA, Zhang M and Yin F: Heme
oxygenase-1, oxidation, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Front
Pharmacol. 3:1192012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Durante W: Protective role of heme
oxygenase-1 against inflammation in atherosclerosis. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 16:2372–2388. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gao Z, Han Y, Hu Y, Wu X, Wang Y, Zhang X,
Fu J, Zou X, Zhang J, Chen X, et al: Targeting HO-1 by
epigallocatechin-3-gallate reduces contrast-induced renal injury
via anti-oxidative stress and anti-inflammation pathways. PloS One.
11:e01490322016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cheng HT, Yen CJ, Chang CC, Huang KT, Chen
KH, Zhang RY, Lee PY, Miaw SC, Huang JW, Chiang CK, et al: Ferritin
heavy chain mediates the protective effect of heme oxygenase-1
against oxidative stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1850:2506–2517.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wagner AE, Will O, Sturm C, Lipinski S,
Rosenstiel P and Rimbach G: DSS-induced acute colitis in C57BL/6
mice is mitigated by sulforaphane pre-treatment. J Nutr Biochem.
24:2085–2091. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|