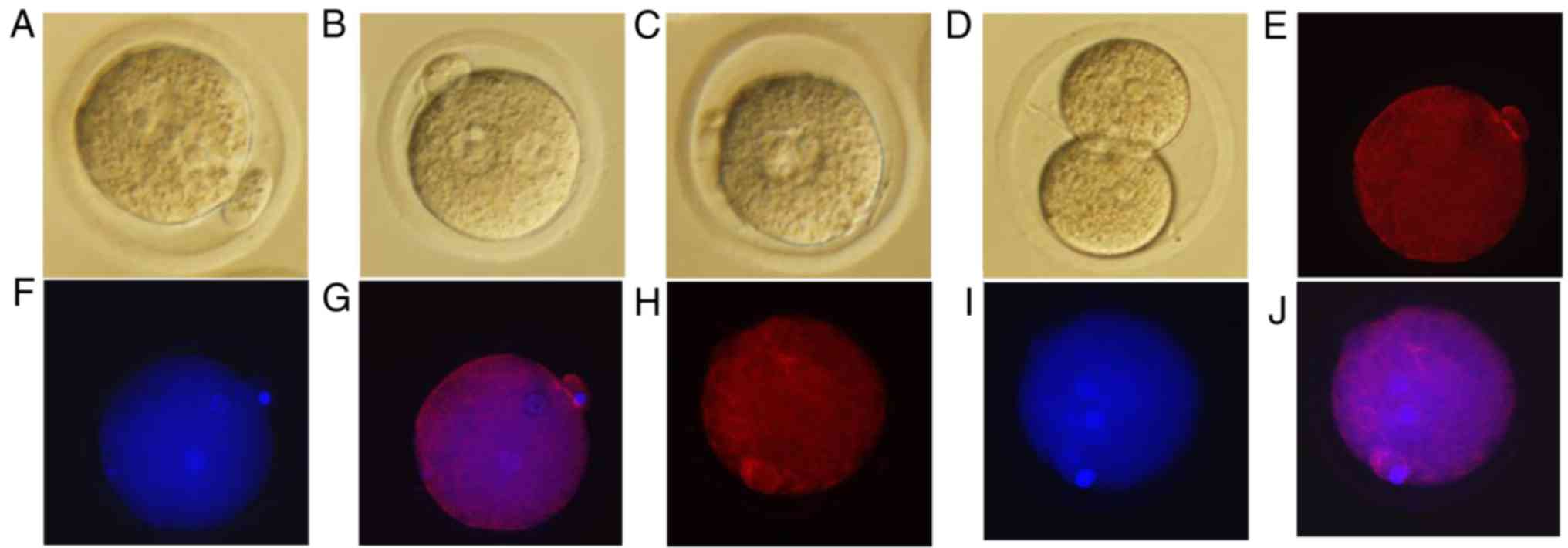
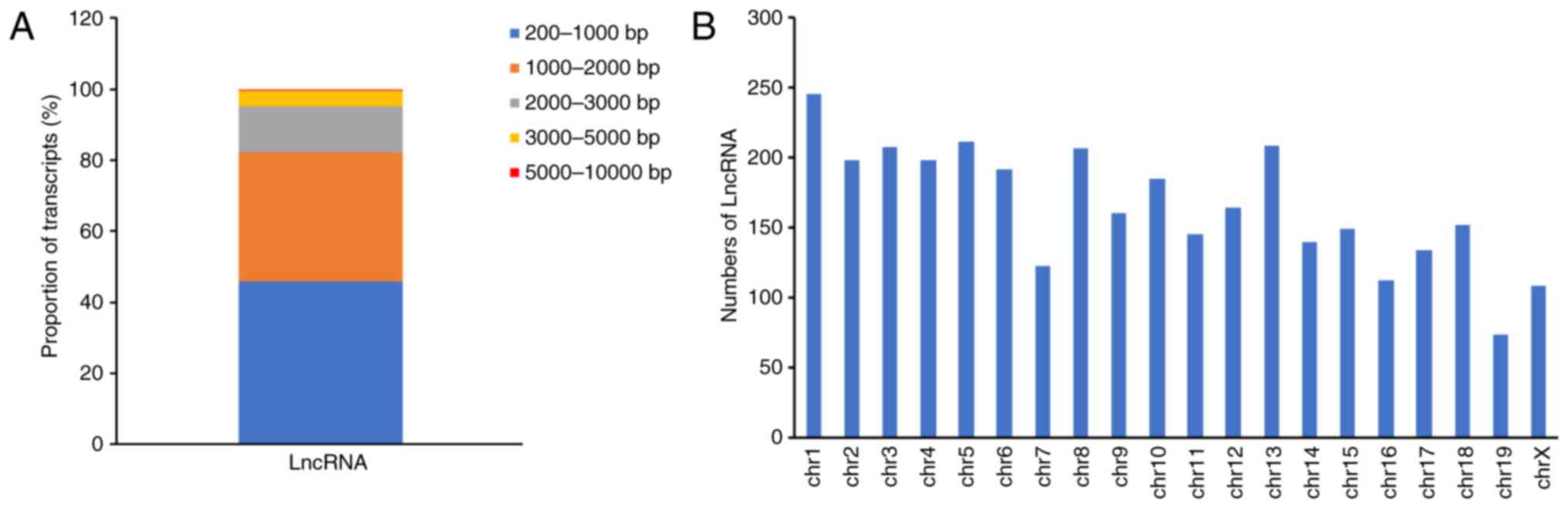
|
1
|
Aoki F, Worrad DM and Schultz RM:
Regulation of transcriptional activity during the first and second
cell cycles in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Dev Biol.
181:296–307. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Latham KE, Garrels JI, Chang C and Solter
D: Quantitative analysis of protein synthesis in mouse embryos. I.
Extensive reprogramming at the one- and two-cell stages.
Development. 112:921–932. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gundersen GG and Worman HJ: Nuclear
positioning. Cell. 152:1376–1389. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clift D and Schuh M: Restarting life:
Fertilization and the transition from meiosis to mitosis. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 14:549–562. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schatten G, Simerly C and Schatten H:
Microtubule configurations during fertilization, mitosis, and early
development in the mouse and the requirement for egg
microtubule-mediated motility during mammalian fertilization. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 82:4152–4156. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wu C, Guo X, Wang F, Li X, Tian XC, Li L,
Wu Z and Zhang S: Simulated microgravity compromises mouse oocyte
maturation by disrupting meiotic spindle organization and inducing
cytoplasmic blebbing. PLoS One. 6:e222142011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kutter C, Watt S, Stefflova K, Wilson MD,
Goncalves A, Ponting CP, Odom DT and Marques AC: Rapid turnover of
long noncoding RNAs and the evolution of gene expression. PLoS
Genet. 8:e10028412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamazaki N, Uesaka M, Nakashima K, Agata K
and Imamura T: Gene activation-associated long noncoding RNAs
function in mouse preimplantation development. Development.
142:910–920. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang K, Huang K, Luo Y and Li S:
Identification and functional analysis of long non-coding RNAs in
mouse cleavage stage embryonic development based on single cell
transcriptome data. BMC Genomics. 15:8452014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan L, Yang M, Guo H, Yang L, Wu J, Li R,
Liu P, Lian Y, Zheng X, Yan J, et al: Single-cell RNA-Seq profiling
of human preimplantation embryos and embryonic stem cells. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 20:1131–1139. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang KC and Chang HY: Molecular mechanisms
of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell. 43:904–914. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Mercer TR and Mattick JS: Structure and
function of long noncoding RNAs in epigenetic regulation. Nat
Struct Mol Biol. 20:300–307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ulitsky I and Bartel DP: lincRNAs:
Genomics, evolution, and mechanisms. Cell. 154:26–46. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pauli A, Rinn JL and Schier AF: Non-coding
RNAs as regulators of embryogenesis. Nat Rev Genet. 12:136–149.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hamatani T, Carter MG, Sharov AA and Ko
MS: Dynamics of global gene expression changes during mouse
preimplantation development. Dev Cell. 6:117–131. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang QT, Piotrowska K, Ciemerych MA,
Milenkovic L, Scott MP, Davis RW and Zernicka-Goetz M: A
genome-wide study of gene activity reveals developmental signaling
pathways in the preimplantation mouse embryo. Dev Cell. 6:133–144.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie D, Chen CC, Ptaszek LM, Xiao S, Cao X,
Fang F, Ng HH, Lewin HA, Cowan C and Zhong S: Rewirable gene
regulatory networks in the preimplantation embryonic development of
three mammalian species. Genome Res. 20:804–815. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tang F, Barbacioru C, Nordman E, Bao S,
Lee C, Wang X, Tuch BB, Heard E, Lao K and Surani MA: Deterministic
and stochastic allele specific gene expression in single mouse
blastomeres. PLoS One. 6:e212082011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li XY, Cui XS and Kim NH: Transcription
profile during maternal to zygotic transition in the mouse embryo.
Reprod Fertil Dev. 18:635–645. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang F, Barbacioru C, Wang Y, Nordman E,
Lee C, Xu N, Wang X, Bodeau J, Tuch BB, Siddiqui A, et al: mRNA-Seq
whole-transcriptome analysis of a single cell. Nat Methods.
6:377–382. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fan X, Zhang X, Wu X, Guo H, Hu Y, Tang F
and Huang Y: Single-cell RNA-seq transcriptome analysis of linear
and circular RNAs in mouse preimplantation embryos. Genome Biol.
16:1482015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Serra L, Chang DZ, Macchietto M, Williams
K, Murad R, Lu D, Dillman AR and Mortazavi A: Adapting the
smart-seq2 protocol for robust single worm RNA-seq. Bio Protoc.
8:e27292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Trapnell C, Roberts A, Goff L, Pertea G,
Kim D, Kelley DR, Pimentel H, Salzberg SL, Rinn JL and Pachter L:
Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat Protoc. 7:562–578. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kong L, Zhang Y, Ye ZQ, Liu XQ, Zhao SQ,
Wei L and Gao G: CPC: Assess the protein-coding potential of
transcripts using sequence features and support vector machine.
Nucleic Acids Res. 35:W345–W349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Scmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu GQ, Wang X, Zhou HY, Chai KQ, Xue Q,
Zheng AH, Zhu XM, Xiao JY, Ying XH, Wang FW, et al: Evidence for
transcriptional interference in a dual-luciferase reporter system.
Sci Rep. 5:176752015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Tafer H and Hofacker IL: RNAplex: A fast
tool for RNA-RNA interaction search. Bioinformatics. 24:2657–2663.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cote I, Vigneault C, Laflamme I, Laquerre
J, Fournier E, Gilbert I, Scantland S, Gagne D, Blondin P and
Robert C: Comprehensive cross production system assessment of the
impact of in vitro microenvironment on the expression of messengers
and long non-coding RNAs in the bovine blastocyst. Reproduction.
142:99–112. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Plourde D, Vigneault C, Lemay A, Breton L,
Gagne D, Laflamme I, Blondin P and Robert C: Contribution of oocyte
source and culture conditions to phenotypic and transcriptomic
variation in commercially produced bovine blastocysts.
Theriogenology. 78:116–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shalek AK, Satija R, Adiconis X, Gertner
RS, Gaublomme JT, Raychowdhury R, Schwartz S, Yosef N, Malboeuf C,
Lu D, et al: Single-cell transcriptomics reveals bimodality in
expression and splicing in immune cells. Nature. 498:236–240. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wills QF, Livak KJ, Tipping AJ, Enver T,
Goldson AJ, Sexton DW and Holmes C: Single-cell gene expression
analysis reveals genetic associations masked in whole-tissue
experiments. Nat Biotechnol. 31:748–752. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wuhr M, Dumont S, Groen AC, Needleman DJ
and Mitchison TJ: How does a millimeter-sized cell find its center?
Cell Cycle. 8:1115–1121. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chew TG, Lorthongpanich C, Ang WX, Knowles
BB and Solter D: Symmetric cell division of the mouse zygote
requires an actin network. Cytoskeleton (Hoboken). 69:1040–1046.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Reinsch S and Gonczy P: Mechanisms of
nuclear positioning. J Cell Sci. 111:2283–2295. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gadadhar S, Bodakuntla S, Natarajan K and
Janke C: The tubulin code at a glance. J Cell Sci. 130:1347–1353.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Sarkar H, Arya S, Rai U and Majumdar SS: A
study of differential expression of testicular genes in various
reproductive phases of hemidactylus flaviviridis (Wall Lizard) to
derive their association with onset of spermatogenesis and its
relevance to mammals. PLoS One. 11:e1511502016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Thomas DG and Robinson DN: The fifth
sense: Mechanosensory regulation of alpha-actinin-4 and its
relevance for cancer metastasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 71:68–74.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhao X, Khurana S, Charkraborty S, Tian Y,
Sedor JR, Bruggman LA and Kao HY: α Actinin 4 (ACTN4) regulates
glucocorticoid receptor-mediated transactivation and
transrepression in podocytes. J Biol Chem. 292:1637–1647. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hsu KS and Kao HY: Alpha-actinin 4 and
tumorigenesis of breast cancer. Vitam Horm. 93:323–351. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shao H, Wang JH, Pollak MR and Wells A:
α-actinin-4 is essential for maintaining the spreading, motility
and contractility of fibroblasts. PLoS One. 5:e139212010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hamill KJ, Hopkinson SB, Skalli O and
Jones JC: Actinin-4 in keratinocytes regulates motility via an
effect on lamellipodia stability and matrix adhesions. FASEB J.
27:546–556. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|