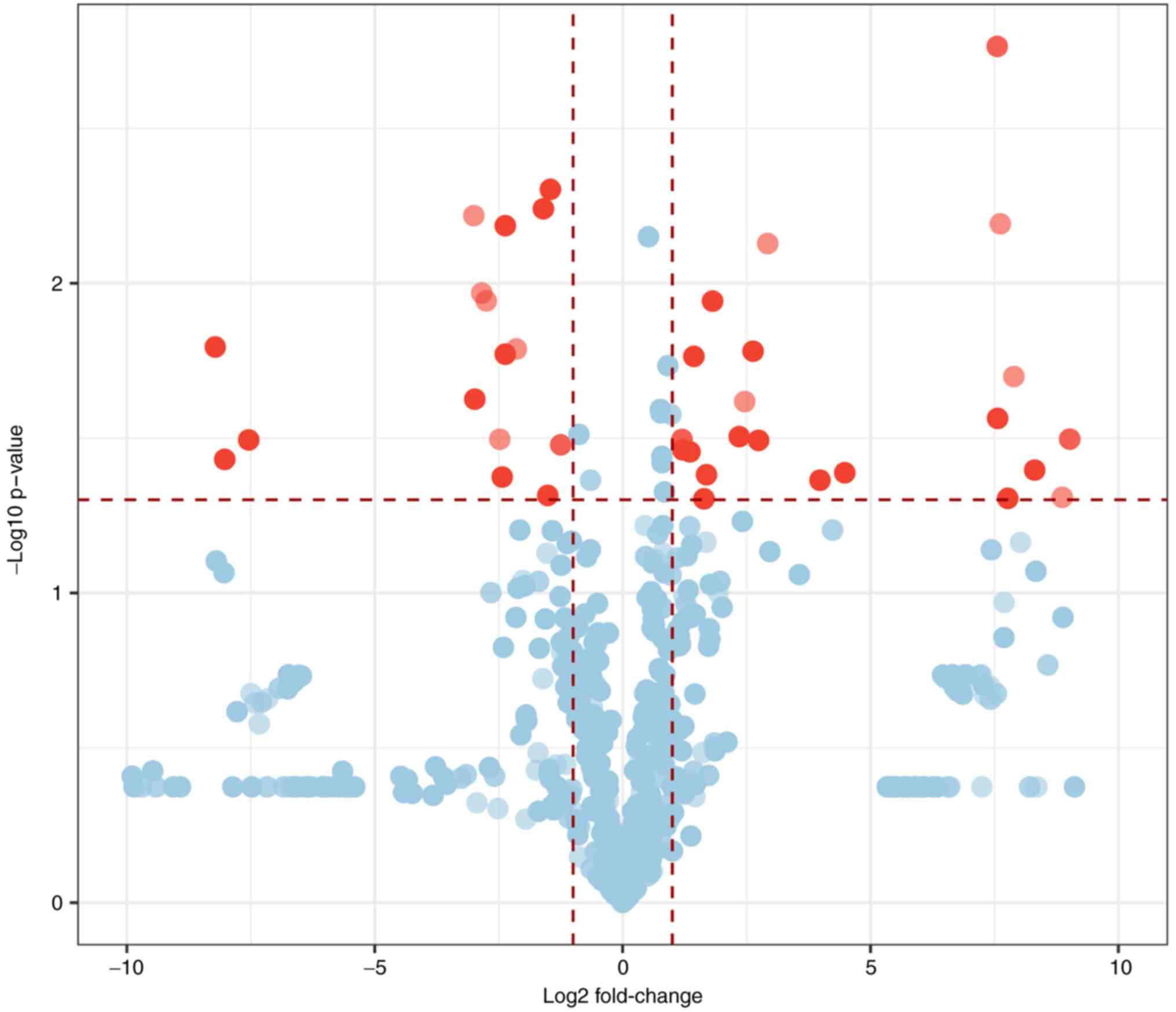
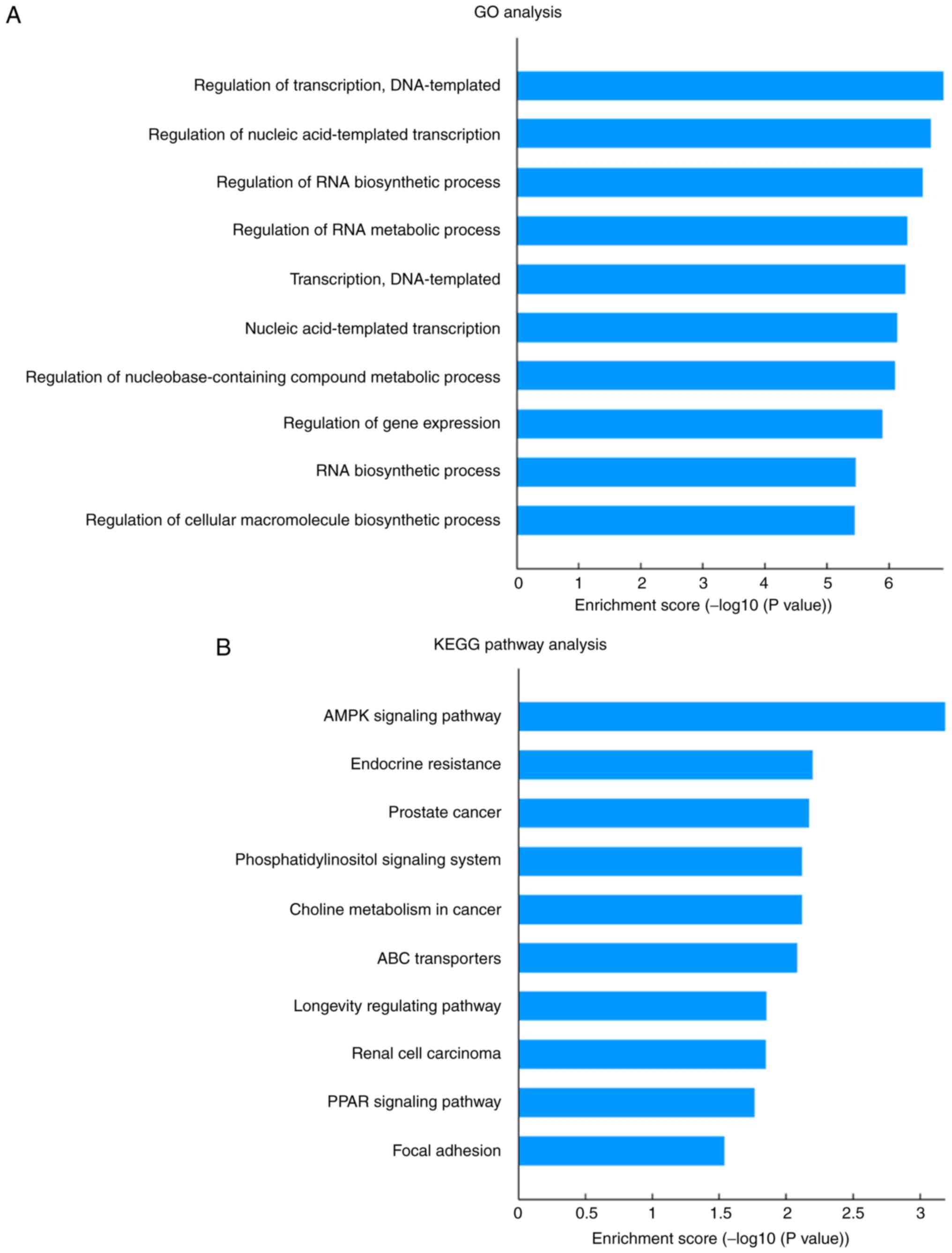
|
1
|
Takeuchi K and Shimizu K: Hypoplasia of
the bilateral internal carotid arteries. Brain Nerve. 9:37–43.
1957.
|
|
2
|
Kim JS: Moyamoya disease: Epidemiology,
clinical features, and diagnosis. J Stroke. 18:2–11. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Acker G, Fekonja L and Vajkoczy P:
Surgical management of moyamoya disease. Stroke. 49:476–482. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kuriyama S, Kusaka Y, Fujimura M, Wakai K,
Tamakoshi A, Hashimoto S, Tsuji I, Inaba Y and Yoshimoto T:
Prevalence and clinicoepidemiological features of moyamoya disease
in Japan: Findings from a nationwide epidemiological survey.
Stroke. 39:42–47. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dai D, Lu Q, Huang Q, Yang P, Hong B, Xu
Y, Zhao W, Liu J and Li Q: Serum miRNA signature in Moyamoya
disease. PLoS One. 9:e1023822014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gao F, Yu L, Zhang D, Zhang Y, Wang R and
Zhao J: Long noncoding RNAs and their regulatory network: Potential
therapeutic targets for adult moyamoya disease. World Neurosurg.
93:111–119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cole C, Sobala A, Lu C, Thatcher SR,
Bowman A, Brown JW, Green PJ, Barton GJ and Hutvagner G: Filtering
of deep sequencing data reveals the existence of abundant
Dicer-dependent small RNAs derived from tRNAs. RNA. 15:2147–2160.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kawaji H, Nakamura M, Takahashi Y,
Sandelin A, Katayama S, Fukuda S, Daub CO, Kai C, Kawai J, Yasuda
J, et al: Hidden layers of human small RNAs. BMC Genomics.
9:1572008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lee YS, Shibata Y, Malhotra A and Dutta A:
A novel class of small RNAs: TRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs).
Genes Dev. 23:2639–2649. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Martens-Uzunova ES, Olvedy M and Jenster
G: Beyond microRNA-novel RNAs derived from small non-coding RNA and
their implication in cancer. Cancer Lett. 340:201–211. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kumar P, Kuscu C and Dutta A: Biogenesis
and function of transfer RNA-related fragments (tRFs). Trends
Biochem Sci. 41:679–689. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anderson P and Ivanov P: TRNA fragments in
human health and disease. FEBS Lett. 588:4297–4304. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen Q, Yan M, Cao Z, Li X, Zhang Y, Shi
J, Feng GH, Peng H, Zhang X, Zhang Y, et al: Sperm tsRNAs
contribute to intergenerational inheritance of an acquired
metabolic disorder. Science. 351:397–400. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Blanco S, Dietmann S, Flores JV, Hussain
S, Kutter C, Humphreys P, Lukk M, Lombard P, Treps L, Popis M, et
al: Aberrant methylation of tRNAs links cellular stress to
neuro-developmental disorders. EMBO J. 33:2020–2039. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Research Committee on the Pathology and
Treatment of Spontaneous Occlusion of the Circle of Willis; Health
Labour Sciences Research Grant for Research on Measures for
Infractable Diseases, : Guidelines for diagnosis and treatment of
moyamoya disease (spontaneous occlusion of the circle of Willis).
Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 52:245–266. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Heid CA, Stevens J, Livak KJ and Williams
PM: Real time quantitative PCR. Genome Res. 6:986–994. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shigematsu M and Kirino Y: tRNA-derived
short non-coding RNA as interacting partners of argonaute proteins.
Gene Regul Syst Bio. 9:27–33. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Karaiskos S and Grigoriev A: Dynamics of
tRNA fragments and their targets in aging mammalian brain. F1000Res
5. ISCB Comm J. 27582016.
|
|
20
|
Haussecker D, Huang Y, Lau A, Parameswaran
P, Fire AZ and Kay MA: Human tRNA-derived small RNAs in the global
regulation of RNA silencing. RNA. 16:673–695. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kumar P, Anaya J, Mudunuri SB and Dutta A:
Meta-analysis of tRNA derived RNA fragments reveals that they are
evolutionarily conserved and associate with AGO proteins to
recognize specific RNA targets. BMC Biol. 12:782014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Maute RL, Schneider C, Sumazin P, Holmes
A, Califano A, Basso K and Dalla-Favera R: tRNA-derived microRNA
modulates proliferation and the DNA damage response and is
down-regulated in B cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:1404–1409. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Miyoshi K, Miyoshi T and Siomi H: Many
ways to generate microRNA-like small RNAs: Non-canonical pathways
for microRNA production. Mol Genet Genomics. 284:95–103. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Suzuki J and Takaku A: Cerebrovascular
‘moyamoya’ disease. Disease showing abnormal net-like vessels in
base of brain. Arch Neurol. 20:288–299. 1969. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
van Swieten JC, Koudstaal PJ, Visser MC,
Schouten HJ and van Gijn J: Interobserver agreement for the
assessment of handicap in stroke patients. Stroke. 19:604–607.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Scott RM and Smith ER: Moyamoya disease
and moyamoya syndrome. N Engl J Med. 360:1226–1237. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mineharu Y, Liu W, Inoue K, Matsuura N,
Inoue S, Takenaka K, Ikeda H, Houkin K, Takagi Y, Kikuta K, et al:
Autosomal dominant moyamoya disease maps to chromosome 17q25.3.
Neurology. 70:2357–2363. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li Q, Hu B, Hu GW, Chen CY, Niu X, Liu J,
Zhou SM, Zhang CQ, Wang Y and Deng ZF: tRNA-derived small
non-coding RNAs in response to ischemia inhibit angiogenesis. Sci
Rep. 6:208502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ivanov P: Emerging roles of tRNA-derived
fragments in viral infections: The case of respiratory syncytial
virus. Mol Ther. 23:1557–1558. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Borek E, Baliga BS, Gehrke CW, Kuo CW,
Belman S, Troll W and Waalkes TP: High turnover rate of transfer
RNA in tumor tissue. Cancer Res. 37:3362–3366. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Speer J, Gehrke CW, Kuo KC, Waalkes TP and
Borek E: tRNA breakdown products as markers for cancer. Cancer.
44:2120–2123. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Karaiskos S, Naqvi AS, Swanson KE and
Grigoriev A: Age-driven modulation of tRNA-derived fragments in
Drosophila and their potential targets. Biol Direct. 10:512015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sobala A and Hutvagner G: Transfer
RNA-derived fragments: Origins, processing, and functions. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2:853–862. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park IH, Kang JH, Lee KS, Nam S, Ro J and
Kim JH: Identification and clinical implications of circulating
microRNAs for estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Tumour
Biol. 35:12173–12180. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yeung ML, Bennasser Y, Watashi K, Le SY,
Houzet L and Jeang KT: Pyrosequencing of small non-coding RNAs in
HIV-1 infected cells: Evidence for the processing of a
viral-cellular double-stranded RNA hybrid. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:6575–6586. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gebetsberger J and Polacek N: Slicing
tRNAs to boost functional ncRNA diversity. RNA Biol. 10:1798–1806.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nagata D, Mogi M and Walsh K:
AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling in endothelial cells
is essential for angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stress. J Biol
Chem. 278:31000–31006. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Fisslthaler B and Fleming I: Activation
and signaling by the AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial
cells. Circ Res. 105:114–127. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ouchi N, Shibata R and Walsh K:
AMP-activated protein kinase signaling stimulates VEGF expression
and angiogenesis in skeletal muscle. Circ Res. 96:838–846. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chmelova J, Kolar Z, Prochazka V, Curik R,
Dvorackova J, Sirucek P, Kraft O and Hrbac T: Moyamoya disease is
associated with endothelial activity detected by anti-nestin
antibody. Biomed Pap Med Fac Univ Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub.
154:159–162. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Karar J and Maity A: PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
in angiogenesis. Front Mol Neurosci. 4:512011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Morello F, Perino A and Hirsch E:
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signalling in the vascular system.
Cardiovasc Res. 82:261–271. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|