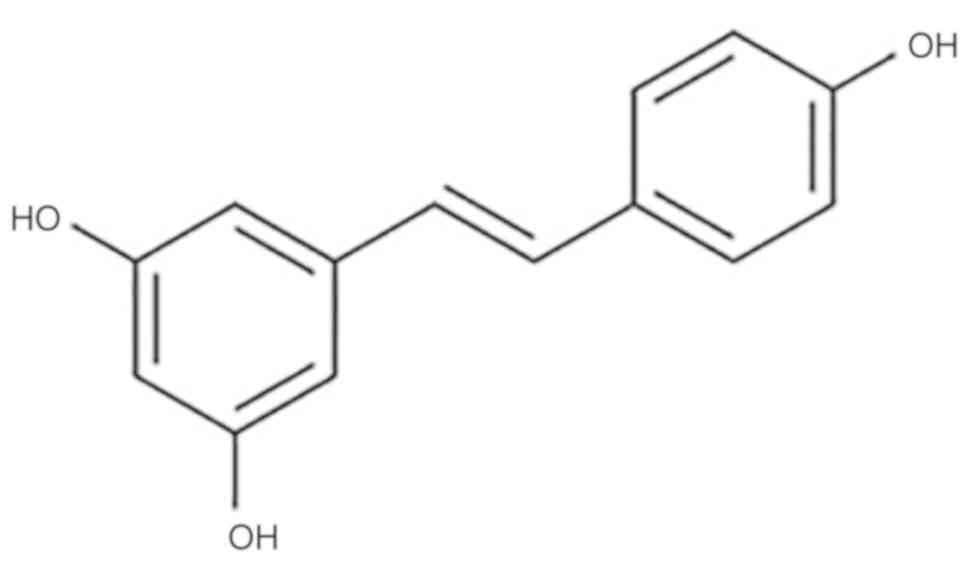
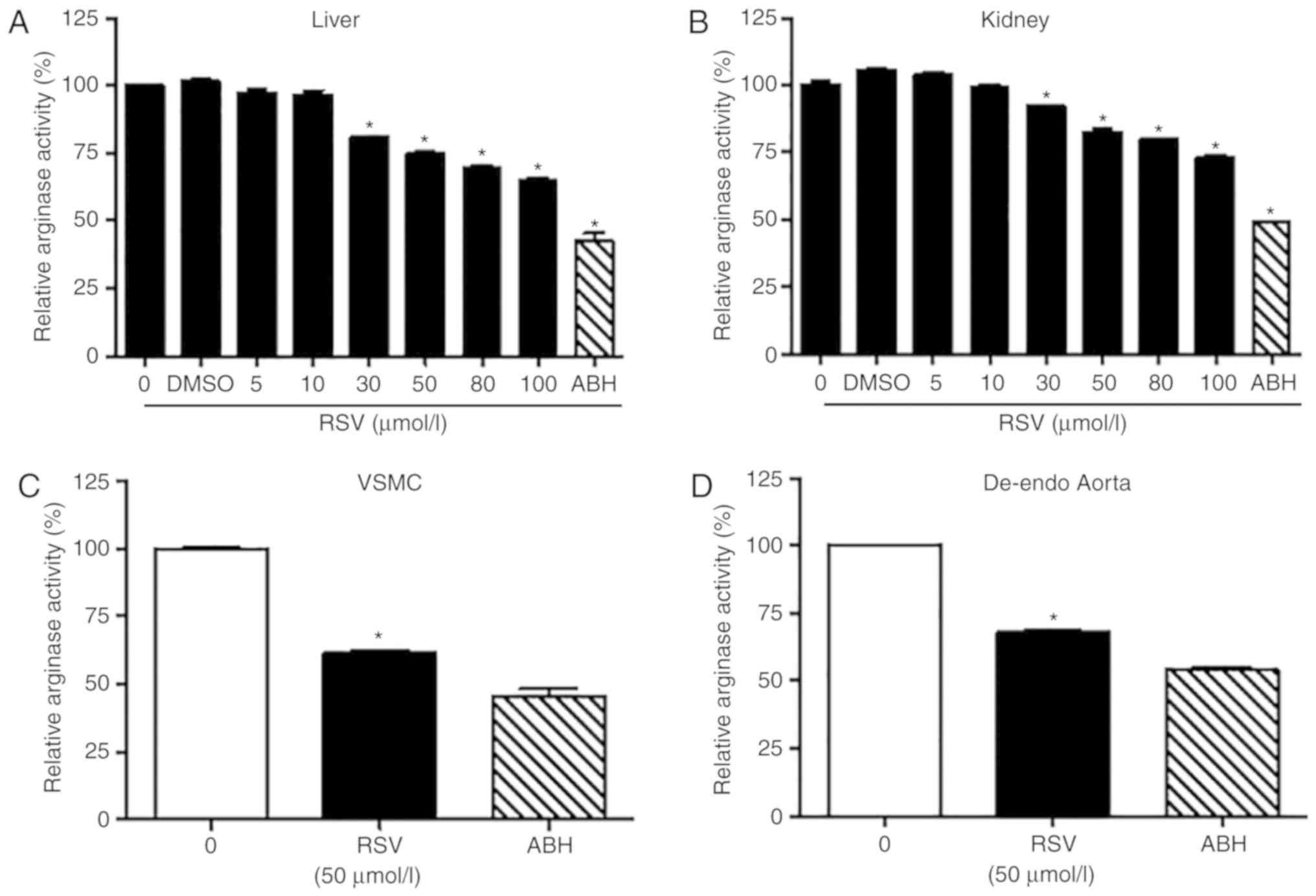
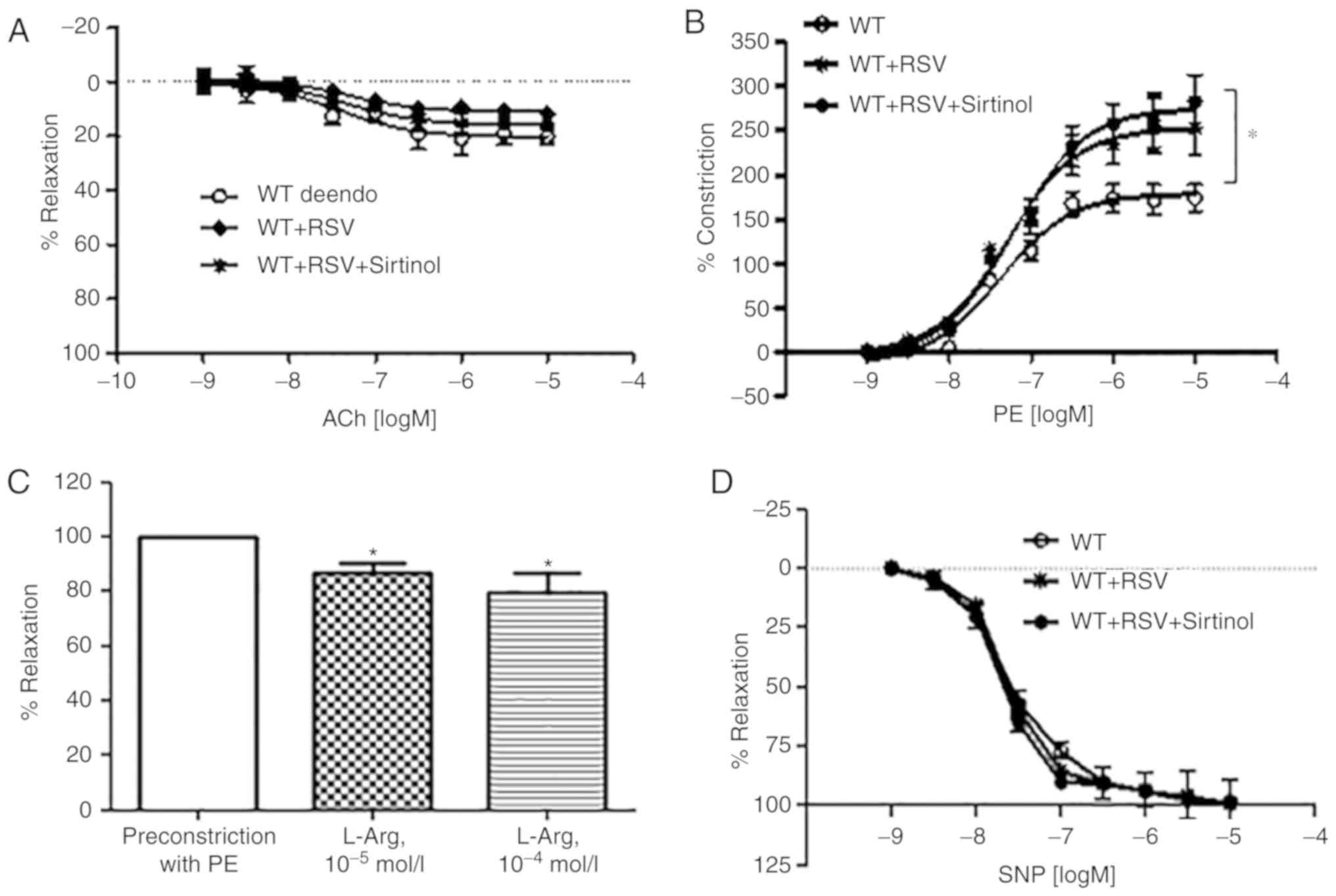
|
1
|
Morris SM Jr: Arginine metabolism:
Boundaries of our knowledge. J Nutr. 137 (6 Suppl 2):1602S–1609S.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pernow J and Jung C: Arginase as a
potential target in the treatment of cardiovascular disease:
Reversal of arginine steal? Cardiovasc Res. 98:334–343. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Peyton KJ, Ensenat D, Azam MA, Keswani AN,
Kannan S, Liu XM, Wang H, Tulis DA and Durante W: Arginase promotes
neointima formation in rat injured carotid arteries. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 29:488–494. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiong Y, Yu Y, Montani JP, Yang Z and Ming
XF: Arginase-II induces vascular smooth muscle cell senescence and
apoptosis through p66Shc and p53 independently of its l-arginine
ureahydrolase activity: Implications for atherosclerotic plaque
vulnerability. J Am Heart Assoc. 2:e0000962013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yoon J and Ryoo S: Arginase inhibition
reduces interleukin-1β-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation by increasing nitric oxide synthase-dependent nitric
oxide production. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 435:428–433. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Koo BH, Yi BG, Jeong MS, Kwon SH, Hoe KL,
Kwon YG, Won MH, Kim YM and Ryoo S: Arginase II inhibition prevents
interleukin-8 production through regulation of p38 MAPK
phosphorylation activated by loss of mitochondrial membrane
potential in nLDL-stimulated hAoSMCs. Exp Mol Med. 50:e4382018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koo BH, Hwang HM, Yi BG, Lim HK, Jeon BH,
Hoe KL, Kwon YG, Won MH, Kim YM, Berkowitz DE and Ryoo S: Arginase
II contributes to the Ca2+/CaMKII/eNOS axis by regulating Ca2+
concentration between the cytosol and mitochondria in a
p32-dependent manner. J Am Heart Assoc. 7:e0095792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jackson WF: Ion channels and vascular
tone. Hypertension. 35:173–178. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hilgers RH and Webb RC: Molecular aspects
of arterial smooth muscle contraction: Focus on Rho. Exp Biol Med
(Maywood). 230:829–835. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Woodrum DA and Brophy CM: The paradox of
smooth muscle physiology. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 177:135–143. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wynne BM, Chiao CW and Webb RC: Vascular
smooth muscle cell signaling mechanisms for contraction to
angiotensin II and endothelin-1. J Am Soc Hypertens. 3:84–95. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Schmitt CA and Dirsch VM: Modulation of
endothelial nitric oxide by plant-derived products. Nitric Oxide.
21:77–91. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Opie LH and Lecour S: The red wine
hypothesis: From concepts to protective signalling molecules. Eur
Heart J. 28:1683–1693. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Leifert WR and Abeywardena MY:
Cardioprotective actions of grape polyphenols. Nutr Res.
28:729–737. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Villalba JM and Alcain FJ: Sirtuin
activators and inhibitors. Biofactors. 38:349–359. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Haider UG, Sorescu D, Griendling KK,
Vollmar AM and Dirsch VM: Resveratrol suppresses angiotensin
II-induced Akt/protein kinase B and p70 S6 kinase phosphorylation
and subsequent hypertrophy in rat aortic smooth muscle cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 62:772–777. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ushio-Fukai M, Griendling KK, Becker PL,
Hilenski L, Halleran S and Alexander RW: Epidermal growth factor
receptor transactivation by angiotensin II requires reactive oxygen
species in vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 21:489–495. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thompson AM, Martin KA and Rzucidlo EM:
Resveratrol induces vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation
through stimulation of SirT1 and AMPK. PLoS One. 9:e854952014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Lindstedt KA and Kovanen PT: Mast
cell granule remnants carry LDL into smooth muscle cells of the
synthetic phenotype and induce their conversion into foam cells.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 15:801–810. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ryoo S, Gupta G, Benjo A, Lim HK, Camara
A, Sikka G, Lim HK, Sohi J, Santhanam L, Soucy K, et al:
Endothelial arginase II: A novel target for the treatment of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 102:923–932. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Böger RH, Bode-Böger SM, Mügge A, Kienke
S, Brandes R, Dwenger A and Frölich JC: Supplementation of
hypercholesterolaemic rabbits with L-arginine reduces the vascular
release of superoxide anions and restores NO production.
Atherosclerosis. 117:273–284. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nguyen MC and Ryoo S: Intravenous
administration of piceatannol, an arginase inhibitor, improves
endothelial dysfunction in aged mice. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol.
21:83–90. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Koo BH, Yi BG, Wang WK, Ko IY, Hoe KL,
Kwon YG, Won MH, Kim YM, Lim HK and Ryoo S: Arginase inhibition
suppresses native low-density lipoprotein-stimulated vascular
smooth muscle cell proliferation by NADPH oxidase inactivation.
Yonsei Med J. 59:366–375. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
You H, Gao T, Cooper TK, Morris SM Jr and
Awad AS: Diabetic nephropathy is resistant to oral L-arginine or
L-citrulline supplementation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
307:F1292–F1301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brooks WW, Conrad CH, Robinson KG, Colucci
WS and Bing OH: L-arginine fails to prevent ventricular remodeling
and heart failure in the spontaneously hypertensive rat. Am J
Hypertens. 22:228–234. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wilson AM, Harada R, Nair N,
Balasubramanian N and Cooke JP: L-arginine supplementation in
peripheral arterial disease: No benefit and possible harm.
Circulation. 116:188–195. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wood JG, Rogina B, Lavu S, Howitz K,
Helfand SL, Tatar M and Sinclair D: Sirtuin activators mimic
caloric restriction and delay ageing in metazoans. Nature.
430:686–689. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Howitz KT, Bitterman KJ, Cohen HY, Lamming
DW, Lavu S, Wood JG, Zipkin RE, Chung P, Kisielewski A, Zhang LL,
et al: Small molecule activators of sirtuins extend Saccharomyces
cerevisiae lifespan. Nature. 425:191–196. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baur JA, Pearson KJ, Price NL, Jamieson
HA, Lerin C, Kalra A, Prabhu VV, Allard JS, Lopez-Lluch G, Lewis K,
et al: Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a
high-calorie diet. Nature. 444:337–342. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pearson KJ, Baur JA, Lewis KN, Peshkin L,
Price NL, Labinskyy N, Swindell WR, Kamara D, Minor RK, Perez E, et
al: Resveratrol delays age-related deterioration and mimics
transcriptional aspects of dietary restriction without extending
life span. Cell Metab. 8:157–168. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xiong Y, Yepuri G, Forbiteh M, Yu Y,
Montani JP, Yang Z and Ming XF: ARG2 impairs endothelial autophagy
through regulation of MTOR and PRKAA/AMPK signaling in advanced
atherosclerosis. Autophagy. 10:2223–2238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Sareen D, Darjatmoko SR, Albert DM and
Polans AS: Mitochondria, calcium, and calpain are key mediators of
resveratrol-induced apoptosis in breast cancer. Mol Pharmacol.
72:1466–1475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Garcia-Sanchez L, Santofimia-Castaño P,
Miro-Moran A, Tapia JA, Salido GM and Gonzalez A: Resveratrol
mobilizes Ca2+ from intracellular stores and induces c-Jun
N-terminal kinase activation in tumoral AR42J cells. Mol Cell
Biochem. 362:15–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chang HJ, Chou CT, Chang HT, Liang WZ,
Hung TY, Li YD, Fang YC, Kuo CC, Kuo DH, Shieh P and Jan CR:
Mechanisms of resveratrol-induced changes in cytosolic free calcium
ion concentrations and cell viability in OC2 human oral cancer
cells. Hum Exp Toxicol. 34:289–299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Selvaraj S, Sun Y, Sukumaran P and Singh
BB: Resveratrol activates autophagic cell death in prostate cancer
cells via downregulation of STIM1 and the mTOR pathway. Mol
Carcinog. 55:818–831. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bordage S, Pham TN, Zedet A, Gugglielmetti
AS, Nappey M, Demougeot C and Girard-Thernier C: Investigation of
mammal arginase inhibitory properties of natural ubiquitous
polyphenols by using an optimized colorimetric microplate assay.
Planta Med. 83:647–653. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Woo A, Min B and Ryoo S:
Piceatannol-3′-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside as an active component of
rhubarb activates endothelial nitric oxide synthase through
inhibition of arginase activity. Exp Mol Med. 42:524–532. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Timmers S, Konings E, Bilet L, Houtkooper
RH, van de Weijer T, Goosens GH, Hoeks J, van der Krieken S, Ryu D,
Kersten S, et al: Calorie restriction-like effects of 30 days of
resveratrol supplementation on energy metabolism and metabolic
profile in obese humans. Cell Metab. 14:612–622. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|