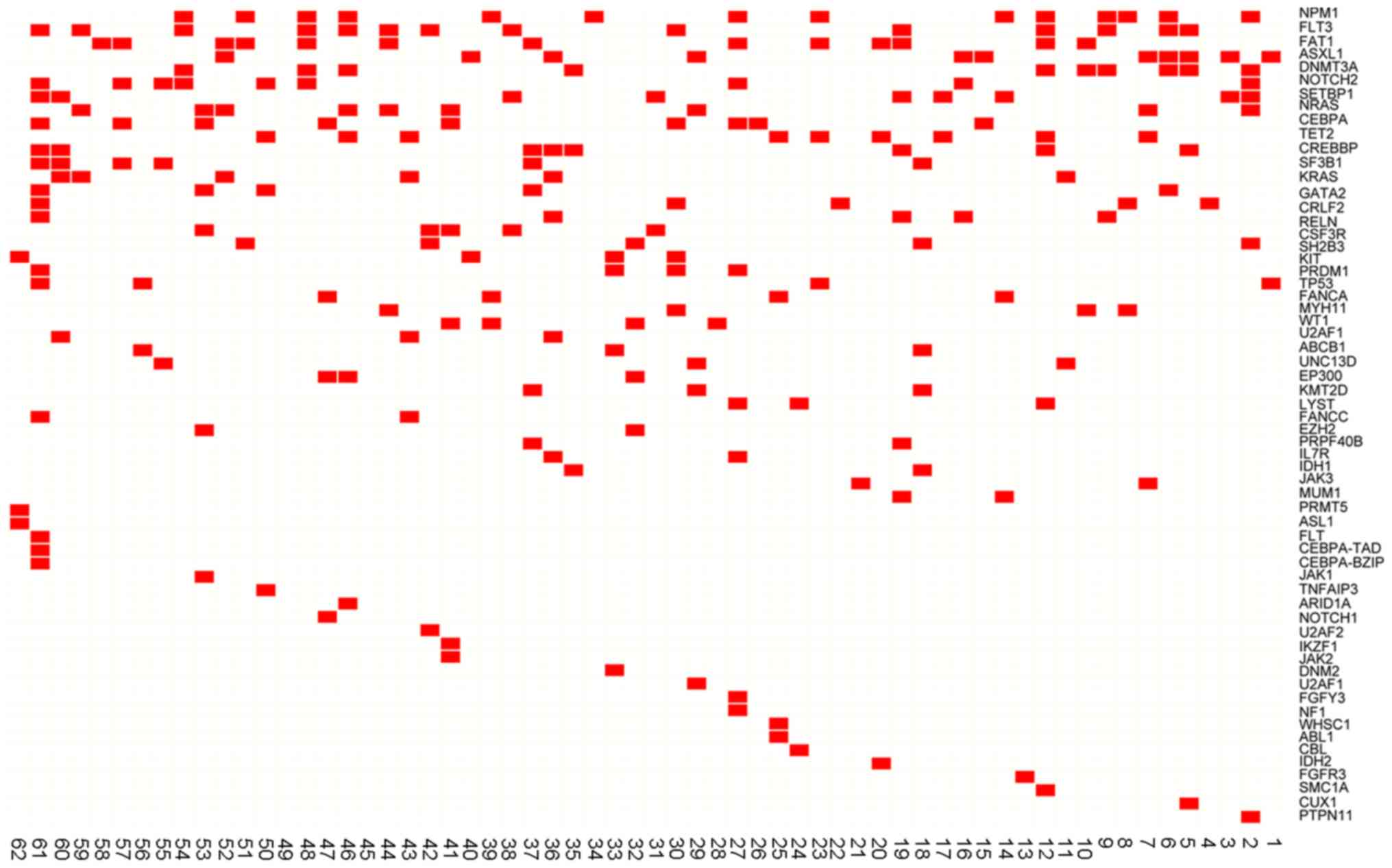
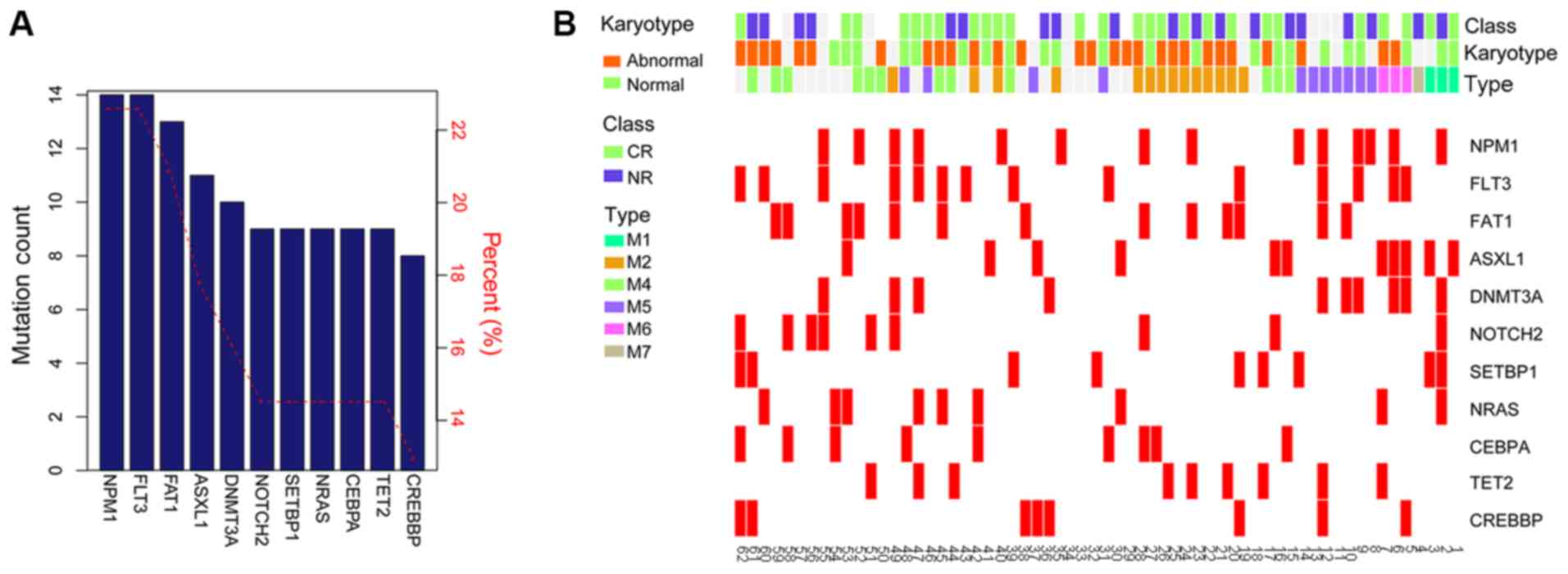
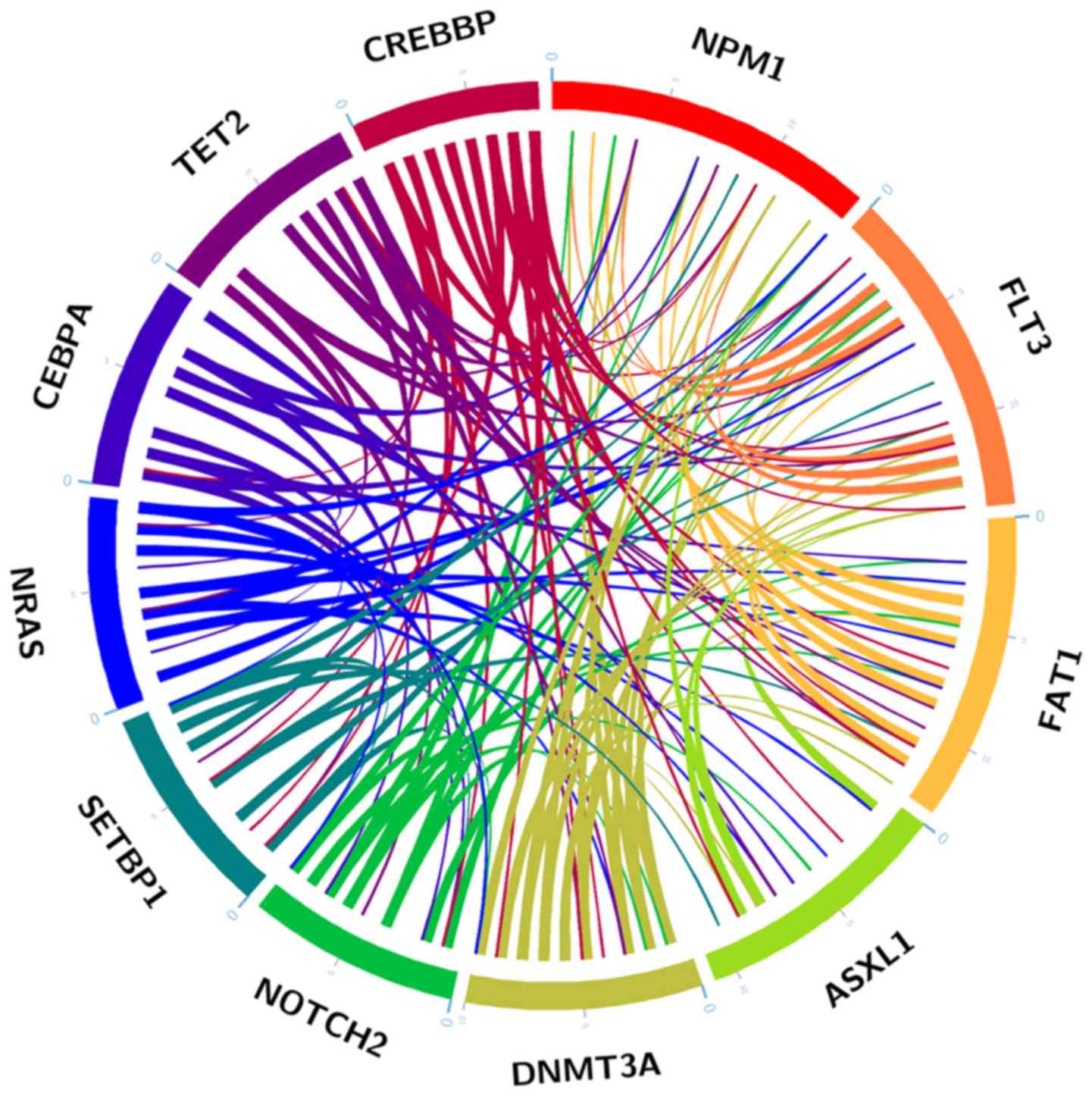
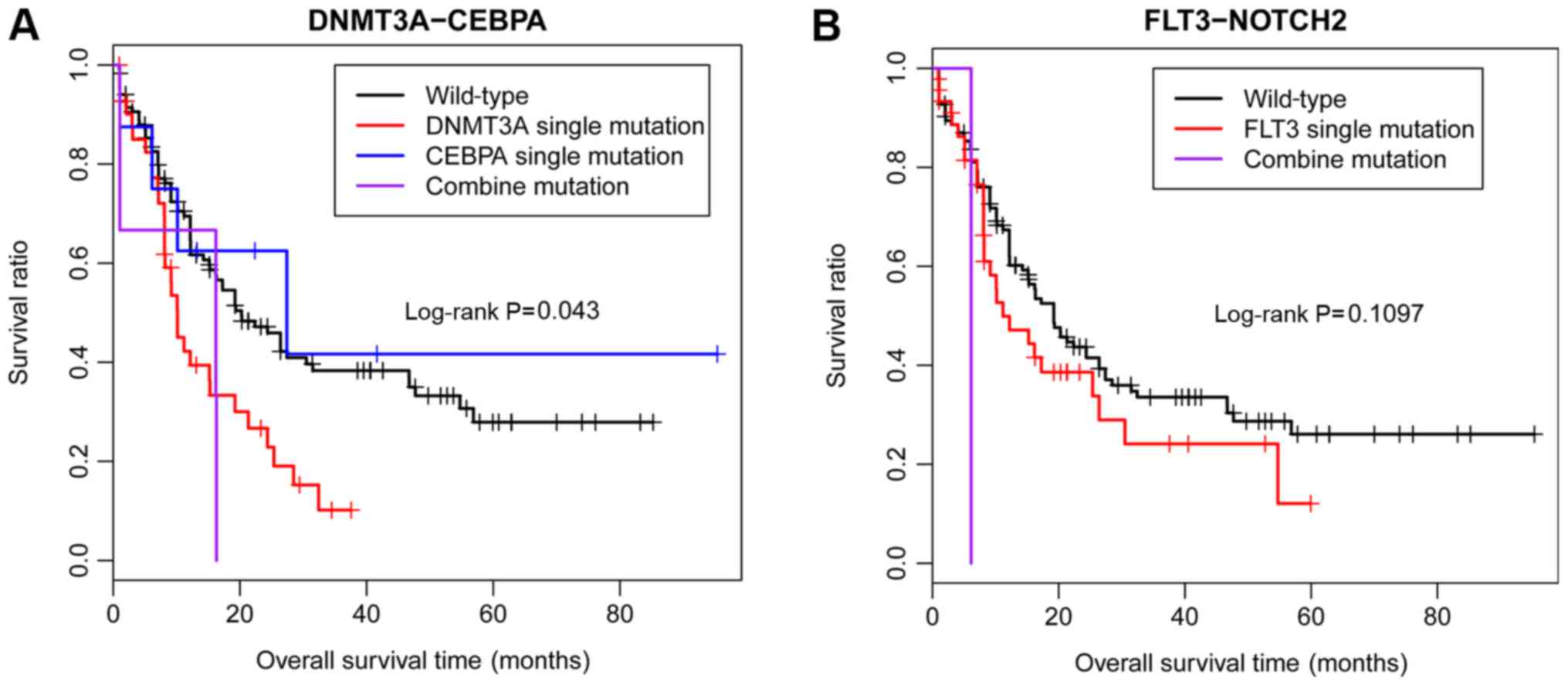
|
1
|
Khwaja A, Bjorkholm M, Gale RE, Levine RL,
Jordan CT, Ehninger G, Bloomfield CD, Estey E, Burnett A,
Cornelissen JJ, et al: Acute myeloid leukaemia. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 2:160102016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pan Y, Liu D, Wei Y, Su D, Lu C, Hu Y and
Zhou F: Azelaic acid exerts antileukemic activity in acute myeloid
leukemia. Front Pharmacol. 8:3592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liang H, Zheng QL, Fang P, Zhang J, Zhang
T, Liu W, Guo M, Robinson CL, Chen SB, Chen XP, et al: Targeting
the PI3K/AKT pathway via GLI1 inhibition enhanced the drug
sensitivity of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Sci Rep. 7:403612017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sanders MA and Valk PJ: The evolving
molecular genetic landscape in acute myeloid leukaemia. Curr Opin
Hematol. 20:79–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kohlmann A, Grossmann V, Nadarajah N and
Haferlach T: Next-generation sequencing-feasibility and
practicality in haematology. Br J Haematol. 160:736–753. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Corces-Zimmerman MR, Hong WJ, Weissman IL,
Medeiros BC and Majeti R: Preleukemic mutations in human acute
myeloid leukemia affect epigenetic regulators and persist in
remission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:2548–2553. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shih AH, Meydan C, Shank K,
Garrett-Bakelman FE, Ward PS, Intlekofer AM, Nazir A, Stein EM,
Knapp K, Glass J, et al: Combination targeted therapy to disrupt
aberrant oncogenic signaling and reverse epigenetic dysfunction in
IDH2- and TET2-mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Discov.
7:494–505. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yen K, Travins J, Wang F, David MD, Artin
E, Straley K, Padyana A, Gross S, DeLaBarre B, Tobin E, et al:
AG-221, a first-in-class therapy targeting acute myeloid leukemia
harboring oncogenic IDH2 mutations. Cancer Discov. 7:478–493. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Feng J, Li Y, Jia Y, Fang Q, Gong X, Dong
X, Ru K, Li Q, Zhao X, Liu K, et al: Spectrum of somatic mutations
detected by targeted next-generation sequencing and their
prognostic significance in adult patients with acute lymphoblastic
leukemia. J Hematol Oncol. 10:612017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Feng J, Gong XY, Jia YJ, Liu KQ, Li Y,
Dong XB, Fang QY, Ru K, Li QH, Wang HJ, et al: Spectrum of somatic
mutations and their prognostic significance in adult patients with
B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi.
39:98–104. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, Brunning
RD, Borowitz MJ, Porwit A, Harris NL, Le Beau MM,
Hellström-Lindberg E, Tefferi A and Bloomfield CD: The 2008
revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of
myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: Rationale and important
changes. Blood. 114:937–951. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Löffler H: Morphology, immunology,
cytochemistry, and cytogenetics and the classification of subtypes
in AML. Haematol Blood Transfus. 33:239–242. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sherry ST, Ward MH, Kholodov M, Baker J,
Phan L, Smigielski EM and Sirotkin K: dbSNP: The NCBI database of
genetic variation. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:308–311. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
1000 Genomes Project Consortium, ;
Abecasis GR, Auton A, Brooks LD, DePristo MA, Durbin RM, Handsaker
RE, Kang HM, Marth GT and McVean GA: An integrated map of genetic
variation from 1,092 human genomes. Nature. 491:56–65. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Adzhubei I, Jordan DM and Sunyaev SR:
Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using
PolyPhen-2. Curr Protoc Hum Genet Chapter. 7:Unit7.202013.
|
|
16
|
Forbes SA, Bindal N, Bamford S, Cole C,
Kok CY, Beare D, Jia M, Shepherd R, Leung K, Menzies A, et al:
COSMIC: Mining complete cancer genomes in the catalogue of somatic
mutations in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:D945–D950. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ito K and Murphy D: Application of ggplot2
to pharmacometric graphics. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol.
2:e792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Plackett RL: Karl pearson and the
Chi-squared test. Int Stat Rev. 51:59–72. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Goel MK, Khanna P and Kishore J:
Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate. Int J
Ayurveda Res. 1:274–278. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang YY, Zhou XB, Wang QZ and Zhu XY:
Quality of reporting of multivariable logistic regression models in
Chinese clinical medical journals. Medicine (Baltimore).
96:e69722017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium: The gene
ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47:D330–D338. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima
K and Tanabe M: New approach for understanding genome variations in
KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D590–D595. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Huang Da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bennett JM, Catovsky D, Daniel MT,
Flandrin G, Galton DA, Gralnick HR and Sultan C: Proposed revised
criteria for the classification of acute myeloid leukemia: A report
of the French-American-British Cooperative Group. Ann Intern Med.
103:620–625. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mukherjee A, Nan X, Ensor J, Randhawa JK,
Pingali SRK, Zieske AW, Olsen RJ, Chung B and Iyer SP: An integer
weighted genomic mutation score (GMS) using next generation
sequencing is predictive of prognosis in intermediate risk AML
patients. Blood. 130:39402017.
|
|
29
|
Klco JM, Miller CA, Griffith M, Petti A,
Spencer DH, Ketkar-Kulkarni S, Wartman LD, Christopher M, Lamprecht
TL, Helton NM, et al: Association between mutation clearance after
induction therapy and outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia. JAMA.
314:811–822. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wander SA, Levis MJ and Fathi AT: The
evolving role of FLT3 inhibitors in acute myeloid leukemia:
Quizartinib and beyond. Ther Adv Hematol. 5:65–77. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pasquet M, Bellanné-Chantelot C, Tavitian
S, Prade N, Beaupain B, Larochelle O, Petit A, Rohrlich P, Ferrand
C, Van Den Neste E, et al: High frequency of GATA2 mutations in
patients with mild chronic neutropenia evolving to MonoMac
syndrome, myelodysplasia, and acute myeloid leukemia. Blood.
121:822–829. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Im AP, Sehgal AR, Carroll MP, Smith BD,
Tefferi A, Johnson DE and Boyiadzis M: DNMT3A and IDH mutations in
acute myeloid leukemia and other myeloid malignancies: Associations
with prognosis and potential treatment strategies. Leukemia.
28:1774–1783. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Etchin J, Sanda T, Mansour MR, Kentsis A,
Montero J, Le BT, Christie AL, McCauley D, Rodig SJ, Kauffman M, et
al: KPT-330 inhibitor of CRM1 (XPO1)-mediated nuclear export has
selective anti-leukaemic activity in preclinical models of T-cell
acute lymphoblastic leukaemia and acute myeloid leukaemia. Br J
Haematol. 161:117–127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Höckendorf U, Yabal M and Jost PJ:
RIPK3-dependent cell death and inflammasome activation in FLT3-ITD
expressing LICs. Oncotarget. 7:57483–57484. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kurtz SE, Wilmot B, McWeeney S, Vellanki
A, Local A, Benbatoul K, Folger P, Sheng S, Zhang H, Howell SB, et
al: CG'806, a first-in-class FLT3/BTK inhibitor, exhibits potent
activity against AML patient samples with mutant or wild type FLT3,
as well as other hematologic malignancy subtypes. Clin Cancer Res.
23:442017.
|
|
36
|
Nishida A, Yuasa M, Kageyama K, Ishiwata
K, Takagi S, Yamamoto H, Asano-Mori Y, Yamamoto G, Uchida N, Izutsu
K, et al: High disease-free and overall survival rate following
allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for FLT3-mutated
acute myeloid leukemia even in non-remission status. Blood.
128:22832016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lewis KL, Caton ML, Bogunovic M, Greter M,
Grajkowska LT, Ng D, Klinakis A, Charo IF, Jung S, Gommerman JL, et
al: Notch2 receptor signaling controls functional differentiation
of dendritic cells in the spleen and intestine. Immunity.
35:780–791. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Varnum-Finney B, Halasz LM, Sun M, Gridley
T, Radtke F and Bernstein ID: Notch2 governs the rate of generation
of mouse long- and short-term repopulating stem cells. J Clin
Invest. 121:1207–1216. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Fernandez-Mercado M, Pellagatti A, Di
Genua C, Larrayoz MJ, Winkelmann N, Aranaz P, Burns A, Schuh A,
Calasanz MJ, Cross NC and Boultwood J: Mutations in SETBP1 are
recurrent in myelodysplastic syndromes and often coexist with
cytogenetic markers associated with disease progression. Br J
Haematol. 163:235–239. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Makishima H, Yoshida K, Nguyen N,
Przychodzen B, Sanada M, Okuno Y, Ng KP, Gudmundsson KO,
Vishwakarma BA, Jerez A, et al: Somatic SETBP1 mutations in myeloid
malignancies. Nat Genet. 45:942–946. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Cristóbal I, Blanco FJ, Garcia-Orti L,
Marcotegui N, Vicente C, Rifon J, Novo FJ, Bandres E, Calasanz MJ,
Bernabeu C and Odero MD: SETBP1 overexpression is a novel
leukemogenic mechanism that predicts adverse outcome in elderly
patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 115:615–625. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Inoue D, Kitaura J, Matsui H, Hou HA, Chou
WC, Nagamachi A, Kawabata KC, Togami K, Nagase R, Horikawa S, et
al: SETBP1 mutations drive leukemic transformation in ASXL1-mutated
MDS. Leukemia. 29:847–857. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ley TJ, Ding L, Walter MJ, McLellan MD,
Lamprecht T, Larson DE, Kandoth C, Payton JE, Baty J, Welch J, et
al: DNMT3A mutations in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med.
363:2424–2433. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Abdel-Wahab O, Pardanani A, Rampal R,
Lasho TL, Levine RL and Tefferi A: DNMT3A mutational analysis in
primary myelofibrosis, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and advanced
phases of myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia. 25:1219–1220.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kao HW, Liang DC, Kuo MC, Wu JH, Dunn P,
Wang PN, Lin TL, Shih YS, Liang ST, Lin TH, et al: High frequency
of additional gene mutations in acute myeloid leukemia with MLL
partial tandem duplication: DNMT3A mutation is associated with poor
prognosis. Oncotarget. 6:33217–33225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Quintás-Cardama A, Hu C, Qutub A, Qiu YH,
Zhang X, Post SM, Zhang N, Coombes K and Kornblau SM: p53 pathway
dysfunction is highly prevalent in acute myeloid leukemia
independent of TP53 mutational status. Leukemia. 31:1296–1305.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ufkin ML, Peterson S, Yang X, Driscoll H,
Duarte C and Sathyanarayana P: miR-125a regulates cell cycle,
proliferation, and apoptosis by targeting the ErbB pathway in acute
myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res. 38:402–410. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Curran E, Corrales L and Kline J:
Targeting the innate immune system as immunotherapy for acute
myeloid leukemia. Front Oncol. 5:832015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Takam Kamga P, Bassi G, Cassaro A, Midolo
M, Di Trapani M, Gatti A, Carusone R, Resci F, Perbellini O,
Gottardi M, et al: Notch signalling drives bone marrow stromal
cell-mediated chemoresistance in acute myeloid leukemia.
Oncotarget. 7:21713–21727. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Witkowski MT, Cimmino L, Hu Y, Trimarchi
T, Tagoh H, McKenzie MD, Best SA, Tuohey L, Willson TA, Nutt SL, et
al: Activated Notch counteracts Ikaros tumor suppression in mouse
and human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia.
29:1301–1311. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|