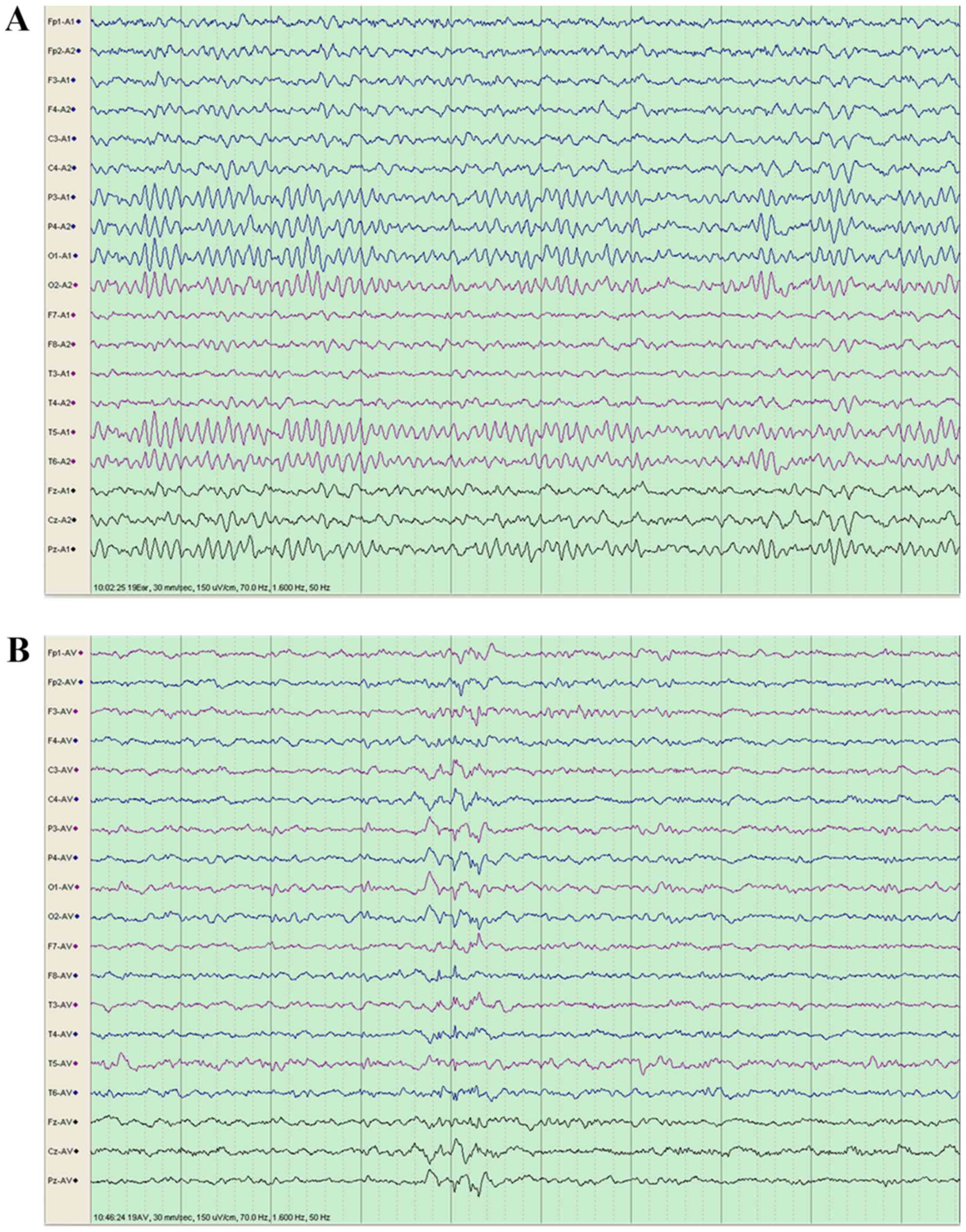
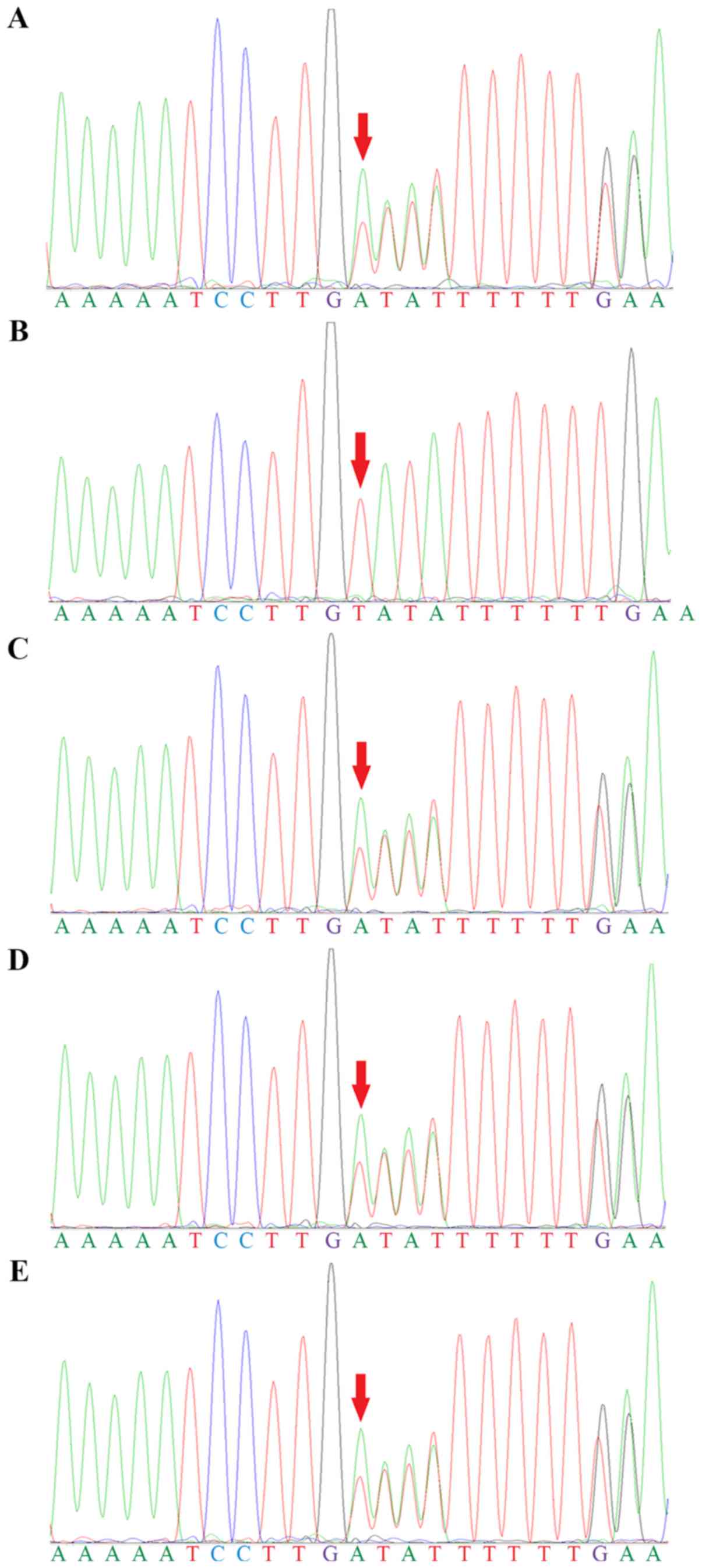
|
1
|
Sperringer JE, Addington A and Hutson SM:
Branched-chain amino acids and brain metabolism. Neurochem Res.
42:1697–1709. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Menkes JH, Hurst PL and Craig JM: A new
syndrome: progressive familial infantile cerebral dysfunction
associated with an unusual urinary substance. Pediatrics.
14:462–467. 1954.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wasim M, Awan FR, Khan HN, Tawab A, Iqbal
M and Ayesha H: Aminoacidopathies: Prevalence, etiology, screening,
and treatment options. Biochem Genet. 56:7–21. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tabbouche O, Saker A and Mountain H:
Identification of three novel mutations by studying the molecular
genetics of maple syrup urine disease (MSUD) in the lebanese
population. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 1:273–279. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rodan LH, Aldubayan SH, Berry GT and Levy
HL: Acute illness protocol for maple syrup urine disease. Pediatr
Emerg Care. 34:64–67. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Puckett RL, Lorey F, Rinaldo P, Lipson MH,
Matern D, Sowa ME, Levine S, Chang R, Wang RY and Abdenur JE: Maple
syrup urine disease: Further evidence that newborn screening may
fail to identify variant forms. Mol Genet Metab. 100:136–142. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Su L, Lu Z, Li F, Shao Y, Sheng H, Cai Y
and Liu L: Two homozygous mutations in the exon 5 of BCKDHB gene
that may cause the classic form of maple syrup urine disease. Metab
Brain Dis. 32:765–772. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li X, Ding Y, Liu Y, Ma Y, Song J, Wang Q,
Li M, Qin Y and Yang Y: Eleven novel mutations of the BCKDHA,
BCKDHB and DBT genes associated with maple syrup urine disease in
the Chinese population: Report on eight cases. Eur J Med Genet.
58:617–623. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sowell J, Pollard L and Wood T:
Quantification of branched-chain amino acids in blood spots and
plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the
diagnosis of maple syrup urine disease. J Sep Sci. 34:631–639.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wechsler D: Wechsler Intelligence Scale
for Children. 5th. NCS Pearson; San Antonio, TX: 2014
|
|
11
|
Li H: Aligning sequence reads, clone
sequences and assembly contigs with BWA-MEM. arXiv preprint arXiv.
1303.3997v2. 2013.
|
|
12
|
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A,
Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly
M and DePristo MA: The genome analysis toolkit: A MapReduce
framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome
Res. 20:1297–1303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
D'Angelo R, Donato L, Venza I, Scimone C,
Aragona P and Sidoti A: Possible protective role of the ABCA4 gene
c.1268A>G missense variant in Stargardt disease and syndromic
retinitis pigmentosa in a Sicilian family: Preliminary data. Int J
Mol Med. 39:1011–1020. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hoffmann GF and Kölker S: Defects in amino
acid catabolism and the urea cycle. Handb Clin Neurol.
113:1755–1773. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Richards S, Aziz N, Bale S, Bick D, Das S,
Gastier-Foster J, Grody WW, Hegde M, Lyon E, Spector E, et al:
Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence
variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American college
of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular
pathology. Genet Med. 17:405–424. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lindqvist Y, Schneider G, Ermler U and
Sundström M: Three-dimensional structure of transketolase, a
thiamine diphosphate dependent enzyme, at 2.5 A resolution. EMBO J.
11:2373–2379. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
AEvarsson A, Chuang JL, Wynn RM, Turley S,
Chuang DT and Hol WG: Crystal structure of human branched-chain
alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase and the molecular basis of multienzyme
complex deficiency in maple syrup urine disease. Structure.
8:277–291. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bashyam MD, Chaudhary AK, Sinha M,
Nagarajaram HA, Devi AR, Bashyam L, Reddy EC and Dalal A: Molecular
genetic analysis of MSUD from India reveals mutations causing
altered protein truncation affecting the C-termini of E1α and E1β.
J Cell Biochem. 113:3122–3132. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Edelmann L, Wasserstein MP, Kornreich R,
Sansaricq C, Snyderman SE and Diaz GA: Maple syrup urine disease:
Identification and carrier-frequency determination of a novel
founder mutation in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Am J Hum
Genet. 69:863–868. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo Y, Liming L and Jiang L: Two novel
compound heterozygous mutations in the BCKDHB gene that cause the
intermittent form of maple syrup urine disease. Metab Brain Dis.
30:1395–1400. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zinnanti WJ, Lazovic J, Griffin K, Skvorak
KJ, Paul HS, Homanics GE, Bewley MC, Cheng KC, Lanoue KF and
Flanagan JM: Dual mechanism of brain injury and novel treatment
strategy in maple syrup urine disease. Brain. 132:903–918. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sitta A, Ribas GS, Mescka CP, Barschak AG,
Wajner M and Vargas CR: Neurological damage in MSUD: The role of
oxidative stress. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 34:157–165. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang YP, Qi ML, Li TT and Zhao YJ: Two
novel mutations in the BCKDHB gene (R170H, Q346R) cause the classic
form of maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). Gene. 498:112–115. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Simon E, Schwarz M and Wendel U: Social
outcome in adults with maple syrup urine disease (MSUD). J Inherit
Metab Dis. 30:2642007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Blackburn PR, Gass JM, Vairo FPE, Farnham
KM, Atwal HK, Macklin S, Klee EW and Atwal PS: Maple syrup urine
disease: Mechanisms and management. Appl Clin Genet. 10:57–66.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kilicarslan R, Alkan A, Demirkol D, Toprak
H and Sharifov R: Maple syrup urine disease: Diffusion-weighted MRI
findings during acute metabolic encephalopathic crisis. Jpn J
Radiol. 30:522–525. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schönberger S, Schweiger B, Schwahn B,
Schwarz M and Wendel U: Dysmyelination in the brain of adolescents
and young adults with maple syrup urine disease. Mol Genet Metab.
82:69–75. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brown G: Defects of thiamine transport and
metabolism. J Inherit Metab Dis. 37:577–585. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mescka CP, Guerreiro G, Donida B,
Marchetti D, Wayhs CA, Ribas GS, Coitinho AS, Wajner M, Dutra-Filho
CS and Vargas CR: Investigation of inflammatory profile in MSUD
patients: Benefit of L-carnitine supplementation. Metab Brain Dis.
30:1167–1174. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ribas GS, Vargas CR and Wajner M:
L-carnitine supplementation as a potential antioxidant therapy for
inherited neurometabolic disorders. Gene. 533:469–476. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li X, Yang Y, Gao Q, Gao M, Lv Y, Dong R,
Liu Y, Zhang K and Gai Z: Clinical characteristics and mutation
analysis of five Chinese patients with maple syrup urine disease.
Metab Brain Dis. 33:741–751. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Díaz VM, Camarena C, de la Vega Á,
Martínez-Pardo M, Díaz C, López M, Hernández F, Andrés A and Jara
P: Liver transplantation for classical maple syrup urine disease:
Long-term follow-up. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 59:636–639.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bouchereau J, Leduc-Leballeur J, Pichard
S, Imbard A, Benoist JF, Abi Warde MT, Arnoux JB, Barbier V,
Brassier A, Broué P, et al: Neurocognitive profiles in MSUD
school-age patients. J Inherit Metab Dis. 40:377–383. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|