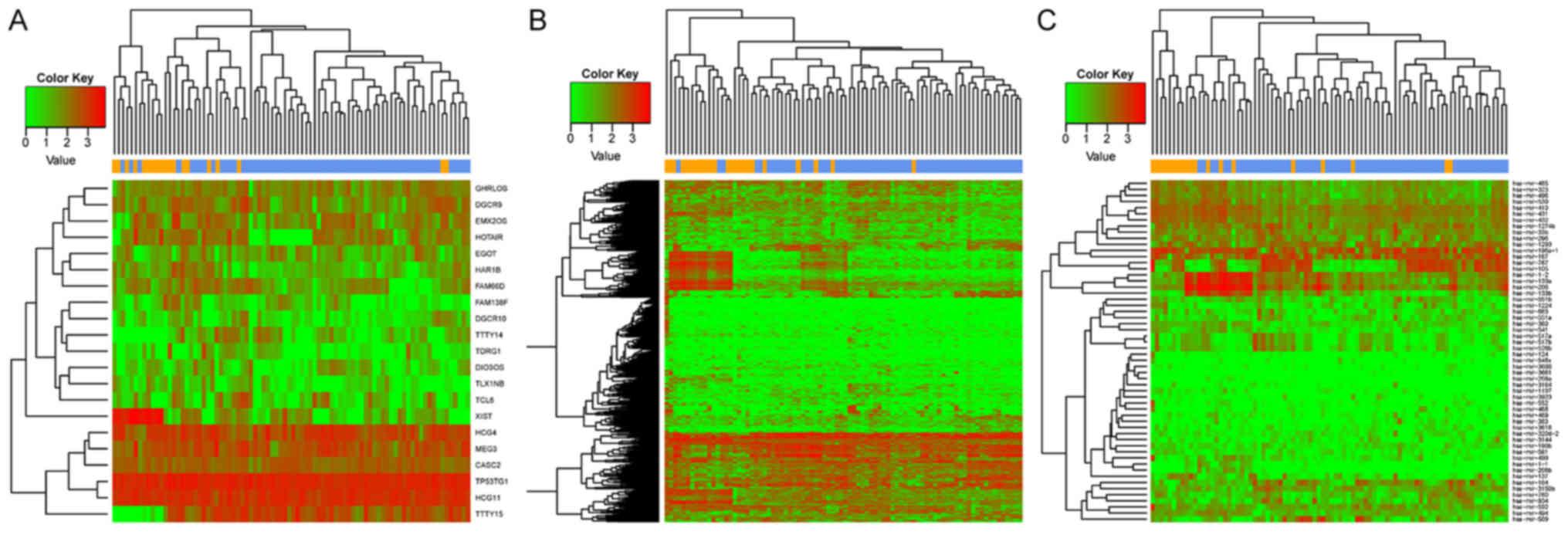
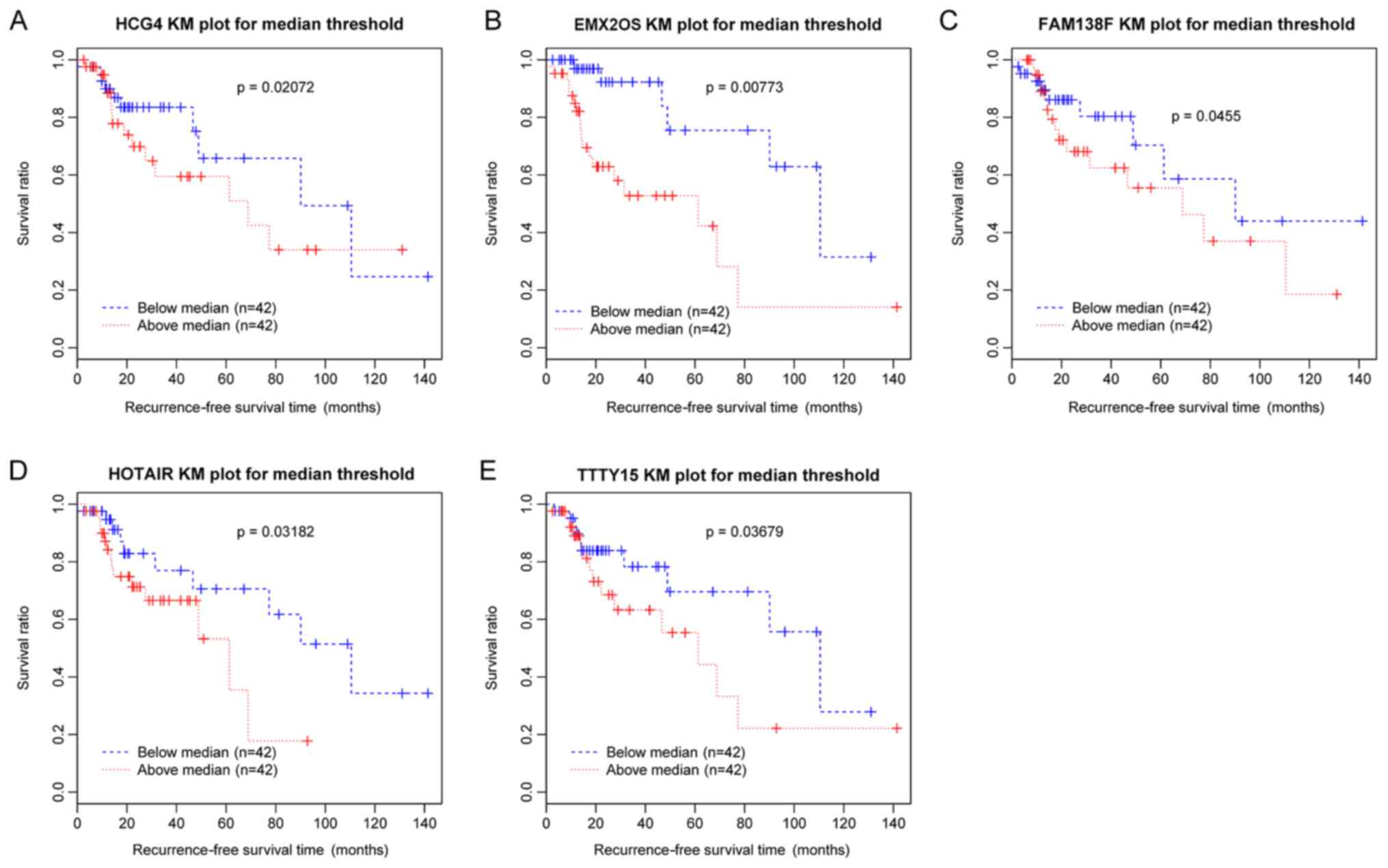
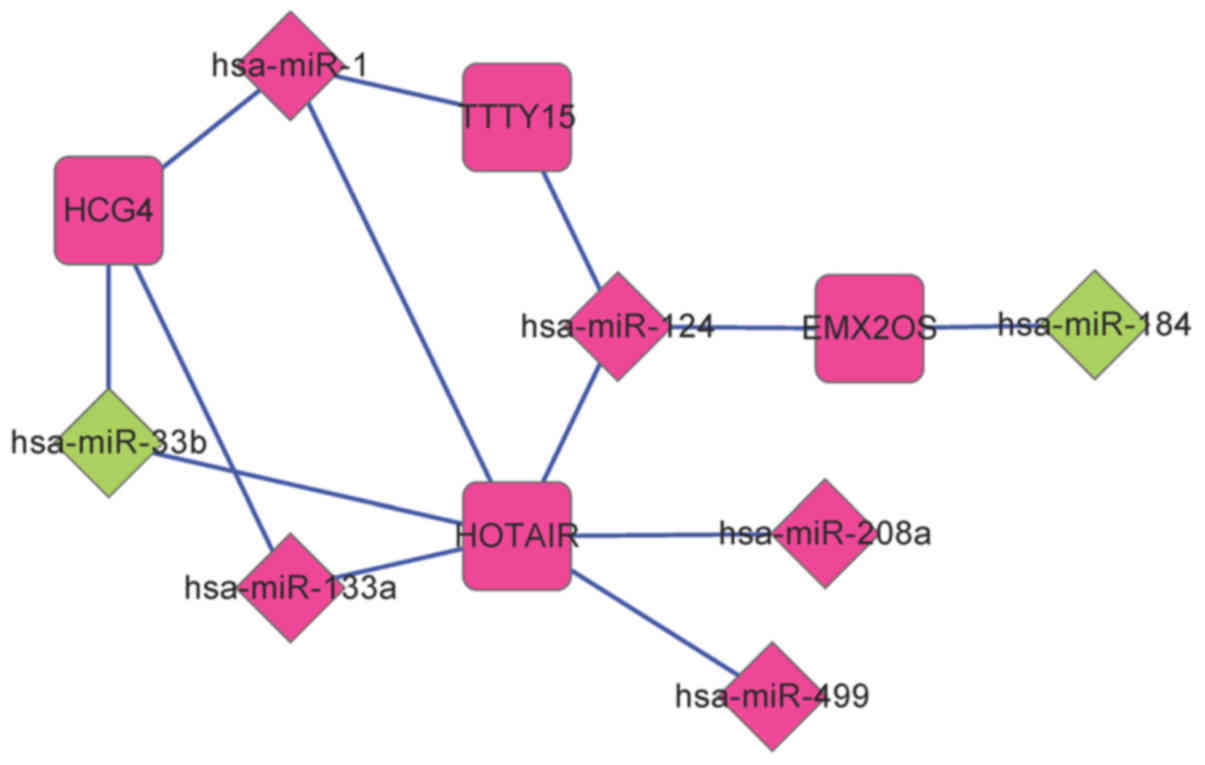
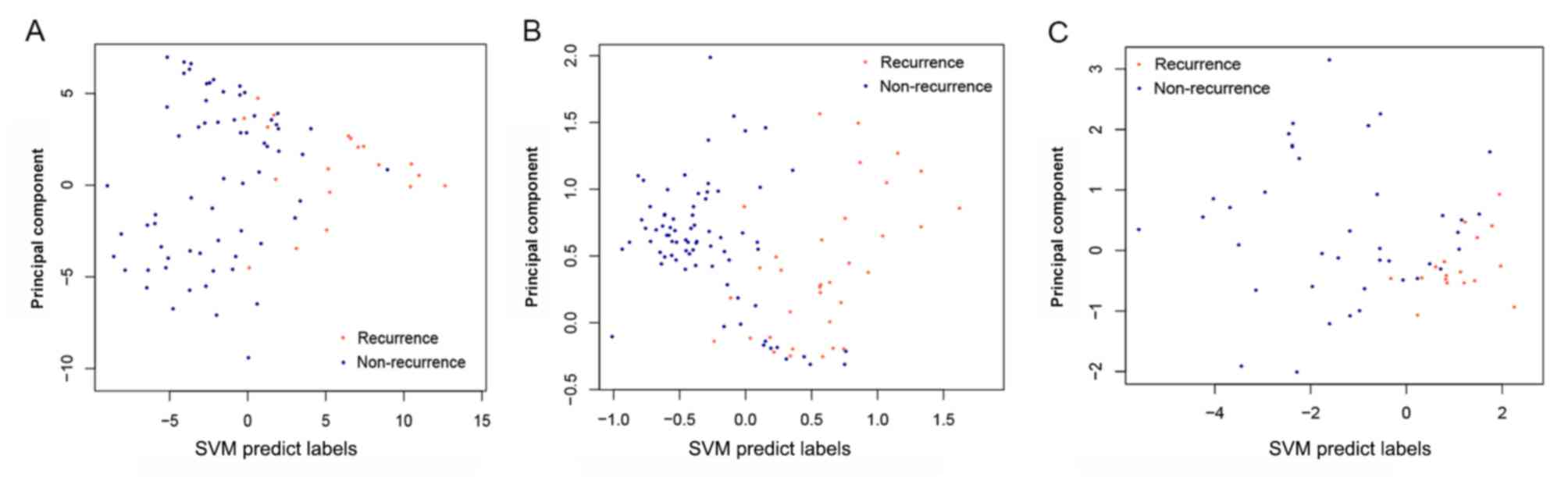
|
1
|
Piccirillo JF: Importance of comorbidity
in head and neck cancer. Laryngoscope. 125:22422015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hoffman HT, Porter K, Karnell LH, Cooper
JS, Weber RS, Langer CJ, Ang KK, Gay G, Stewart A and Robinson RA:
Laryngeal cancer in the United States: Changes in demographics,
patterns of care, and survival. Laryngoscope. 116 (Suppl 111):1–13.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tamaki A, Miles BA, Lango M, Kowalski L
and Zender CA: AHNS Series: Do you know your guidelines? Review of
current knowledge on laryngeal cancer. Head Neck. 40:170–181. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wei KR, Zheng RS, Liang ZH, Sun KX, Zhang
SW, Li ZM, Zeng HM, Zou XN, Chen WQ and He J: Incidence and
mortality of laryngeal cancer in China, 2014. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za
Zhi. 40:736–743. 2018.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Haas I, Hauser U and Ganzer U: The dilemma
of follow-up in head and neck cancer patients. Eur Arch
Otorhinolaryngol. 258:177–183. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Johansen LV, Grau C and Overgaard J:
Glottic carcinoma--patterns of failure and salvage treatment after
curative radiotherapy in 861 consecutive patients. Radiother Oncol.
63:257–267. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dai MY, Wang Y, Chen C, Li F, Xiao BK,
Chen SM and Tao ZZ: Phenethyl isothiocyanate induces apoptosis and
inhibits cell proliferation and invasion in Hep-2 laryngeal cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 35:2657–2664. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Miao S, Mao X, Zhao S, Song K, Xiang C, Lv
Y, Jiang H, Wang L, Li B, Yang X, et al: miR-217 inhibits laryngeal
cancer metastasis by repressing AEG-1 and PD-L1 expression.
Oncotarget. 8:62143–62153. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Saito K, Inagaki K, Kamimoto T, Ito Y,
Sugita T, Nakajo S, Hirasawa A, Iwamaru A, Ishikura T, Hanaoka H,
et al: MicroRNA-196a is a putative diagnostic biomarker and
therapeutic target for laryngeal cancer. PLoS One. 8:e714802013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang JQ, Liu HX, Liang Z, Sun YM and Wu M:
Over-expression of p53, p21 and Cdc2 in histologically negative
surgical margins is correlated with local recurrence of laryngeal
squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:4295–4302.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang JQ, Liang Z, Wu M, Sun YM and Liu HX:
Expression of p27 and PTEN and clinical characteristics in early
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and their correlation with
recurrence. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:5715–5720. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Memczak S, Jens M, Elefsinioti A, Torti F,
Krueger J, Rybak A, Maier L, Mackowiak SD, Gregersen LH, Munschauer
M, et al: Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with
regulatory potency. Nature. 495:333–338. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hansen TB, Jensen TI, Clausen BH, Bramsen
JB, Finsen B, Damgaard CK and Kjems J: Natural RNA circles function
as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature. 495:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin C, Zhang Y and Li J: Upregulation of
MiR-196a promotes cell proliferation by downregulating p27kip1 in
laryngeal cancer. Biol Res. 49:402016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun X, Liu B, Zhao XD, Wang LY and Ji WY:
MicroRNA-221 accelerates the proliferation of laryngeal cancer cell
line Hep-2 by suppressing Apaf-1. Oncol Rep. 33:1221–1226. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li M, Chen SM, Chen C, Zhang ZX, Dai MY,
Zhang LB, Wang SB, Dai Q and Tao ZZ: microRNA-299-3p inhibits
laryngeal cancer cell growth by targeting human telomerase reverse
transcriptase mRNA. Mol Med Rep. 11:4645–4649. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang T, Li S, Liu J, Yin D, Yang X and
Tang Q: lncRNA-NKILA/NF-κB feedback loop modulates laryngeal cancer
cell proliferation, invasion, and radioresistance. Cancer Med.
7:2048–2063. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bai Z, Shi E, Wang Q, Dong Z and Xu P: A
potential panel of two-long non-coding RNA signature to predict
recurrence of patients with laryngeal cancer. Oncotarget.
8:69641–69650. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fountzilas E, Kotoula V, Angouridakis N,
Karasmanis I, Wirtz RM, Eleftheraki AG, Veltrup E, Markou K,
Nikolaou A, Pectasides D, et al: Identification and validation of a
multigene predictor of recurrence in primary laryngeal cancer. PLoS
One. 8:e704292013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carvalho B, Bengtsson H, Speed TP and
Irizarry RA: Exploration, normalization, and genotype calls of
high-density oligonucleotide SNP array data. Biostatistics.
8:485–499. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fountzilas E, Markou K, Vlachtsis K,
Nikolaou A, Arapantoni-Dadioti P, Ntoula E, Tassopoulos G, Bobos M,
Konstantinopoulos P, Fountzilas G, et al: Identification and
validation of gene expression models that predict clinical outcome
in patients with early-stage laryngeal cancer. Ann Oncol.
23:2146–2153. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Uoh KI, Kahng B and Kim D: Universal
behavior of load distribution in scale-free networks. Phys Rev
Lett. 87:2787012001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Eisen MB, Spellman PT, Brown PO and
Botstein D: Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression
patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:14863–14868. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baur B and Bozdag S: A Feature Selection
Algorithm to Compute Gene Centric Methylation from Probe Level
Methylation Data. PLoS One. 11:e01489772016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang X, Lu X, Shi Q, Xu XQ, Leung HC,
Harris LN, Iglehart JD, Miron A, Liu JS and Wong WH: Recursive SVM
feature selection and sample classification for mass-spectrometry
and microarray data. BMC Bioinformatics. 7:1972006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rivals I, Personnaz L, Taing L and Potier
MC: Enrichment or depletion of a GO category within a class of
genes: Which test? Bioinformatics. 23:401–407. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ge X, Lyu P, Cao Z, Li J, Guo G, Xia W and
Gu Y: Overexpression of miR-206 suppresses glycolysis,
proliferation and migration in breast cancer cells via PFKFB3
targeting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 463:1115–1121. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wei C, Wang S, Ye ZQ and Chen ZQ: miR-206
inhibits renal cell cancer growth by targeting GAK. J Huazhong Univ
Sci Technolog Med Sci. 36:852–858. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ren XL, He GY, Li XM, Men H, Yi LZ, Lu GF,
Xin SN, Wu PX, Li YL, Liao WT, et al: MicroRNA-206 functions as a
tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting FMNL2. J Cancer
Res Clin Oncol. 142:581–592. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang T, Liu M, Wang C, Lin C, Sun Y and
Jin D: Down-regulation of MiR-206 promotes proliferation and
invasion of laryngeal cancer by regulating VEGF expression.
Anticancer Res. 31:3859–3863. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yang Q, Zhang C, Huang B, Li H, Zhang R,
Huang Y and Wang J: Downregulation of microRNA-206 is a potent
prognostic marker for patients with gastric cancer. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:953–957. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zheng J, Xiao X, Wu C, Huang J, Zhang Y,
Xie M, Zhang M and Zhou L: The role of long non-coding RNA HOTAIR
in the progression and development of laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma interacting with EZH2. Acta Otolaryngol. 137:90–98. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang J, Zhou Y, Lu J, Sun Y, Xiao H, Liu M
and Tian L: Combined detection of serum exosomal miR-21 and HOTAIR
as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Med Oncol. 31:1482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li D, Feng J, Wu T, Wang Y, Sun Y, Ren J
and Liu M: Long intergenic noncoding RNA HOTAIR is overexpressed
and regulates PTEN methylation in laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 182:64–70. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Di W, Li Q, Shen W, Guo H and Zhao S: The
long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes thyroid cancer cell growth,
invasion and migration through the miR-1-CCND2 axis. Am J Cancer
Res. 7:1298–1309. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yu D, Zhang C and Gui J: RNA-binding
protein HuR promotes bladder cancer progression by competitively
binding to the long noncoding HOTAIR with miR-1. OncoTargets Ther.
10:2609–2619. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Glazer CA, Smith IM, Bhan S, Sun W, Chang
SS, Pattani KM, Westra W, Khan Z and Califano JA: The role of
MAGEA2 in head and neck cancer. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
137:286–293. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rayner KJ, Suárez Y, Dávalos A, Parathath
S, Fitzgerald ML, Tamehiro N, Fisher EA, Moore KJ and
Fernández-Hernando C: MiR-33 contributes to the regulation of
cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 328:1570–1573. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lin Y, Liu AY, Fan C, Zheng H, Li Y, Zhang
C, Wu S, Yu D, Huang Z, Liu F, et al: MicroRNA-33b Inhibits Breast
Cancer Metastasis by Targeting HMGA2, SALL4 and Twist1. Sci Rep.
5:99952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun Q, Zhang W, Guo Y, Li Z, Chen X, Wang
Y, Du Y, Zang W and Zhao G: Curcumin inhibits cell growth and
induces cell apoptosis through upregulation of miR-33b in gastric
cancer. Tumour Biol. 37:13177–13184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Karatas OF: Antiproliferative potential of
miR-33a in laryngeal cancer Hep-2 cells via targeting PIM1. Head
Neck. 40:2455–2461. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Burfoot RK, Jensen CJ, Field J, Stankovich
J, Varney MD, Johnson LJ, Butzkueven H, Booth D, Bahlo M, Tait BD,
et al: SNP mapping and candidate gene sequencing in the class I
region of the HLA complex: Searching for multiple sclerosis
susceptibility genes in Tasmanians. Tissue Antigens. 71:42–50.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang M, Meng B and Liu Y, Yu J, Chen Q and
Liu Y: MiR-124 Inhibits Growth and Enhances Radiation-Induced
Apoptosis in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer by Inhibiting STAT3. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 44:2017–2028. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen Z, Liu S, Tian L, Wu M, Ai F, Tang W,
Zhao L, Ding J, Zhang L and Tang A: miR-124 and miR-506 inhibit
colorectal cancer progression by targeting DNMT3B and DNMT1.
Oncotarget. 6:38139–38150. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Roman-Gomez J, Agirre X, Jiménez-Velasco
A, Arqueros V, Vilas-Zornoza A, Rodriguez-Otero P, Martin-Subero I,
Garate L, Cordeu L, San José-Eneriz E, et al: Epigenetic regulation
of microRNAs in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol.
27:1316–1322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Peng XH, Huang HR, Lu J, Liu X, Zhao FP,
Zhang B, Lin SX, Wang L, Chen HH, Xu X, et al: MiR-124 suppresses
tumor growth and metastasis by targeting Foxq1 in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 13:1862014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Patnaik SK, Kannisto E, Knudsen S and
Yendamuri S: Evaluation of microRNA expression profiles that may
predict recurrence of localized stage I non-small cell lung cancer
after surgical resection. Cancer Res. 70:36–45. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhao Y, Ling Z, Hao Y, Pang X, Han X,
Califano JA, Shan L and Gu X: MiR-124 acts as a tumor suppressor by
inhibiting the expression of sphingosine kinase 1 and its
downstream signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 8:25005–25020. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang M, Piao L, Datta J, Lang JC, Xie X,
Teknos TN, Mapp AK and Pan Q: miR-124 Regulates the
Epithelial-Restricted with Serine Box/Epidermal Growth Factor
Receptor Signaling Axis in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
Mol Cancer Ther. 14:2313–2320. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Spigoni G, Gedressi C and Mallamaci A:
Regulation of Emx2 expression by antisense transcripts in murine
cortico-cerebral precursors. PLoS One. 5:e86582010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang CA, Bauer S, Ho YC, Sotzny F, Chang
JG and Scheibenbogen C: The expression signature of very long
non-coding RNA in myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue
syndrome. J Transl Med. 16:2312018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang L, Sun Y, Sun Y, Meng L and Xu X:
First case of AML with rare chromosome translocations: A case
report of twins. BMC Cancer. 18:4582018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhu Y, Ren S, Jing T, Cai X, Liu Y, Wang
F, Zhang W, Shi X, Chen R, Shen J, et al: Clinical utility of a
novel urine-based gene fusion TTTY15-USP9Y in predicting prostate
biopsy outcome. Urol Oncol. 33:384.e9–384.e20. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Kao SY, Tsai MM, Wu CH, Chen JJ, Tseng SH,
Lin SC and Chang KW: Co-targeting of multiple microRNAs on
factor-Inhibiting hypoxia-Inducible factor gene for the
pathogenesis of head and neck carcinomas. Head Neck. 38:522–528.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Hu S, Ewertz M, Tufano RP, Brait M,
Carvalho AL, Liu D, Tufaro AP, Basaria S, Cooper DS, Sidransky D,
et al: Detection of serum deoxyribonucleic acid methylation
markers: A novel diagnostic tool for thyroid cancer. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 91:98–104. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Afifi S, Gholamhosseini H and Sinha R: SVM
classifier on chip for melanoma detection. In: Proceedings of the
39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in
Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC). IEEE; Seogwipo: pp. 270–274.
2017, PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Tuo Y, An N and Zhang M: Feature genes in
metastatic breast cancer identified by MetaDE and SVM classifier
methods. Mol Med Rep. 17:4281–4290. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhao J, Cheng W, He X, Liu Y, Li J, Sun J,
Li J, Wang F and Gao Y: Construction of a specific SVM classifier
and identification of molecular markers for lung adenocarcinoma
based on lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network. OncoTargets Ther. 11:3129–3140.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|