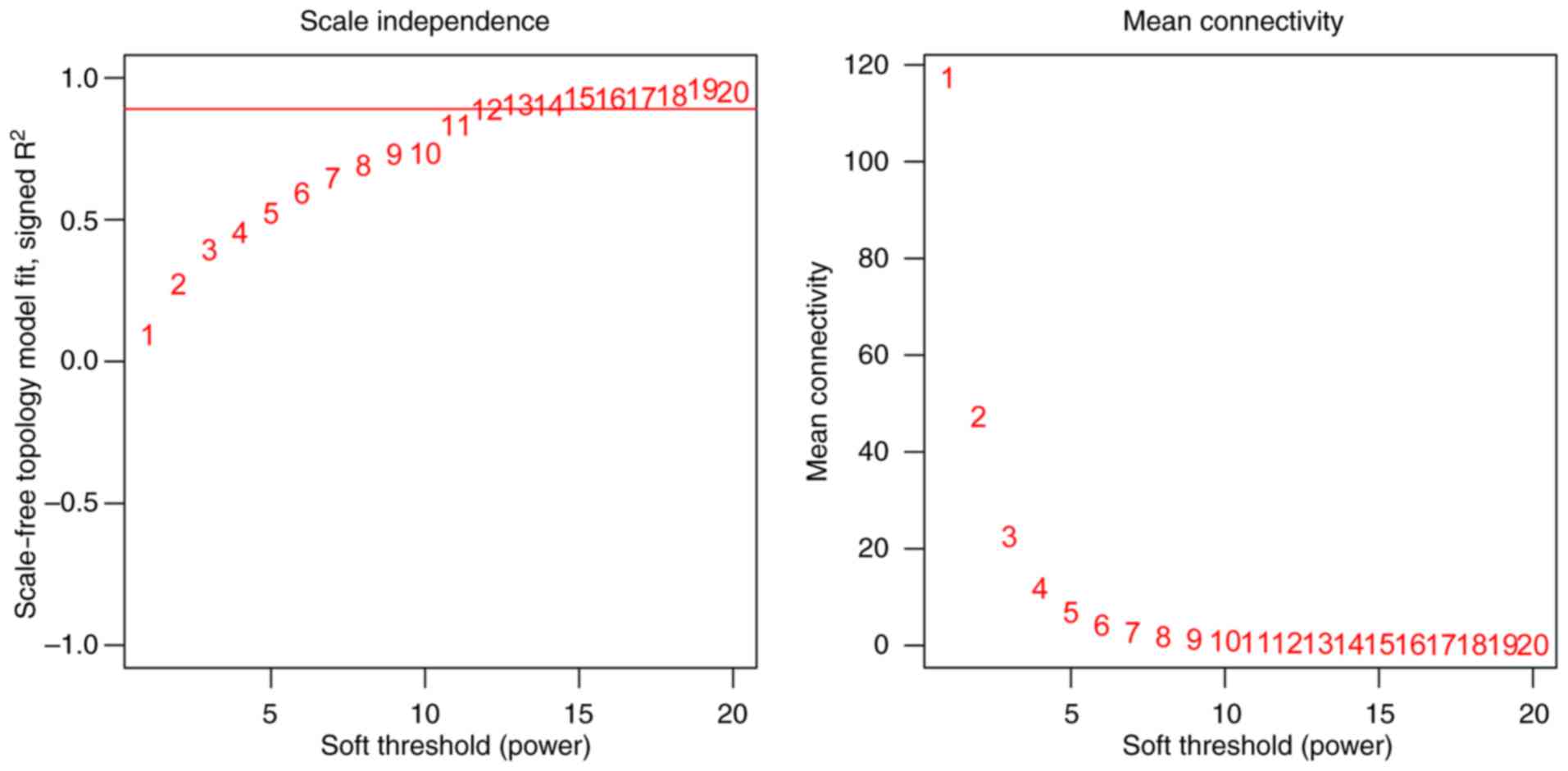
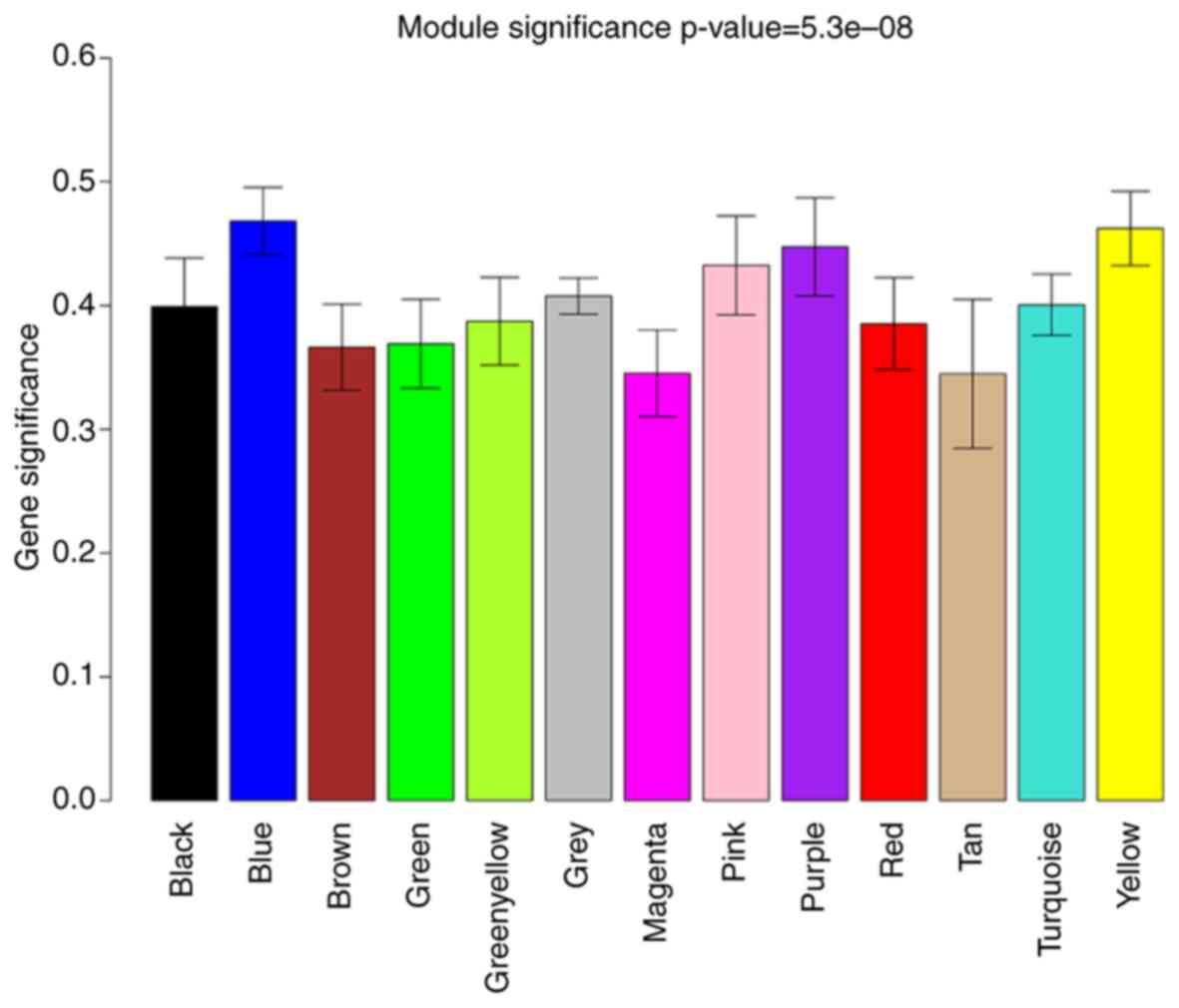
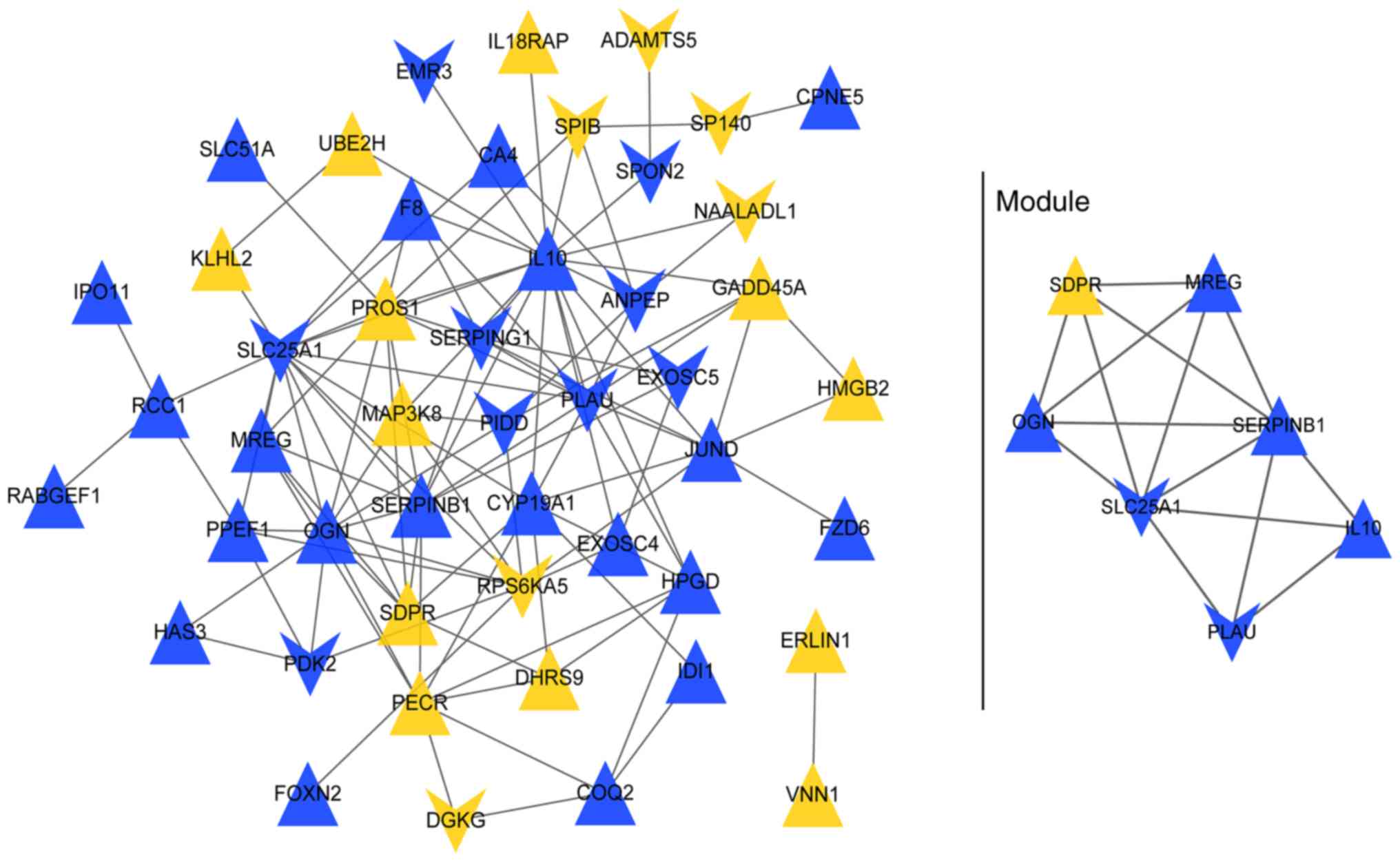
|
1
|
Rhodes A, Evans LE, Alhazzani W, Levy MM,
Antonelli M, Ferrer R, Kumar A, Sevransky JE, Sprung CL, Nunnally
ME, et al: Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for
management of sepsis and septic shock: 2016. Crit Care Med.
45:486–552. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsai D, Stewart P, Goud R, Gourley S,
Hewagama S, Krishnaswamy S, Wallis SC, Lipman J and Roberts JA:
Total and unbound ceftriaxone pharmacokinetics in critically ill
Australian Indigenous patients with severe sepsis. Int J Antimicrob
Agents. 48:748–752. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NK,
Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, Angus DC and Reinhart K;
International Forum of Acute Care Trialists, : Assessment of global
incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis.current
estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 193:259–272.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng W, Wang S, Shen C, Zhao D, Li D and
Shang Y: Epidemiology of hospitalized burns patients in china: A
Systematic Review. Burn Open. 2:8–16. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mitra P, Guha D, Nag SS, Mondal BC and
Dasgupta S: Role of plasma fibrinogen in diagnosis and prediction
of short term outcome in neonatal sepsis. Indian J Hematol Blood
Transfus. 33:195–199. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kang S, Tanaka T, Masuda K and Kishimoto
T: Implications of IL-6 Targeting Therapy for Sepsis. Immunotherapy
(Los Angel). 3:1382017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kurt AN, Aygun AD, Godekmerdan A, Kurt A,
Dogan Y and Yilmaz E: Serum IL-1beta, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-alpha
levels in early diagnosis and management of neonatal sepsis.
Mediators Inflamm. 2007:313972007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Thimmulappa RK, Lee H, Rangasamy T, Reddy
SP, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW and Biswal S: Nrf2 is a critical
regulator of the innate immune response and survival during
experimental sepsis. J Clin Invest. 116:984–995. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schuetz P, Birkhahn R, Sherwin R, Jones
AE, Singer A, Kline JA, Runyon MS, Self WH, Courtney DM, Nowak RM,
et al: Serial procalcitonin predicts mortality in severe sepsis
patients: Results from the multicenter procalcitonin monitoring
sepsis (MOSES) Study. Crit Care Med. 45:781–789. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Riedel S: Procalcitonin and the role of
biomarkers in the diagnosis and management of sepsis. Diagn
Microbiol Infect Dis. 73:221–227. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wacker C, Prkno A, Brunkhorst FM and
Schlattmann P: Procalcitonin as a diagnostic marker for sepsis: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Infect Dis. 13:426–435.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu X, Yang J, Yu L and Long D: Plasma
miRNA-223 correlates with risk, inflammatory markers as well as
prognosis in sepsis patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 97:e113522018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bao YYX and Chen Z: The early diagnostic
value of microRNA-223 for patients with complication of sepsis
after ureteroscopic lithotrity. Chin J Integr Tradit West Med
Intensive Crit Care. 24:465–468. 2017.(In Chinese).
|
|
14
|
Tili E, Michaille JJ, Cimino A, Costinean
S, Dumitru CD, Adair B, Fabbri M, Alder H, Liu CG, Calin GA and
Croce CM: Modulation of miR-155 and miR-125b levels following
lipopolysaccharide/TNF-alpha stimulation and their possible roles
in regulating the response to endotoxin shock. J Immunol.
179:5082–5089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Menges T, König IR, Hossain H, Little S,
Tchatalbachev S, Thierer F, Hackstein H, Franjkovic I, Colaris T,
Martens F, et al: Sepsis syndrome and death in trauma patients are
associated with variation in the gene encoding tumor necrosis
factor. Crit Care Med. 36:1456–1462, e1-e6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(D1): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bandettini WP, Kellman P, Mancini C,
Booker OJ, Vasu S, Leung SW, Wilson JR, Shanbhag SM, Chen MY and
Arai AE: MultiContrast Delayed Enhancement (MCODE) improves
detection of subendocardial myocardial infarction by late
gadolinium enhancement cardiovascular magnetic resonance: A
clinical validation study. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 14:832012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Mielke LA, Elkins KL, Wei L, Starr R,
Tsichlis PN, O'Shea JJ and Watford WT: Tumor progression locus 2
(Map3k8) is critical for host defense against Listeria
monocytogenes and IL-1 beta production. J Immunol. 183:7984–7993.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leon LR, White AA and Kluger MJ: Role of
IL-6 and TNF in thermoregulation and survival during sepsis in
mice. Am J Physiol. 275:R269–R277. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Stuber F, Udalova IA, Book M, Drutskaya
LN, Kuprash DV, Turetskaya RL, Schade FU and Nedospasov SA: −308
tumor necrosis factor (TNF) polymorphism is not associated with
survival in severe sepsis and is unrelated to lipopolysaccharide
inducibility of the human TNF promoter. J Inflamm. 46:42–50.
1995-1996.
|
|
24
|
Riedemann NC, Guo RF and Ward PA: Novel
strategies for the treatment of sepsis. Nat Med. 9:517–524. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oberholzer C, Oberholzer A, Bahjat FR,
Minter RM, Tannahill CL, Abouhamze A, LaFace D, Hutchins B,
Clare-Salzler MJ and Moldawer LL: Targeted adenovirus-induced
expression of IL-10 decreases thymic apoptosis and improves
survival in murine sepsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:11503–11508.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Filgueiras LR Jr, Martins JO, Serezani CH,
Capelozzi VL, Montes MBA and Jancar S: Sepsis-induced acute lung
injury (ALI) is milder in diabetic rats and correlates with
impaired NFkB activation. PLoS One. 7:e449872012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li Q and Verma IM: NF-kappaB regulation in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:725–734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Karin M: Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer
development and progression. Nature. 441:431–436. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang C, Yu L, Tu Q, Zhao Y, Zhang H and
Zhao S: Assignment of a member of the ribosomal protein S6 kinase
family, RPS6KA5, to human chromosome 14q31-->q32.1 by radiation
hybrid mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 87:261–262. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Funding AT, Johansen C, Kragballe K,
Otkjaer K, Jensen UB, Madsen MW, Fjording MS, Finnemann J,
Skak-Nielsen T, Paludan SR and Iversen L: Mitogen- and
stress-activated protein kinase 1 is activated in lesional
psoriatic epidermis and regulates the expression of
pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Invest Dermatol. 126:1784–1791. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu X, Zhan Z, Xu L, Ma F, Li D, Guo Z, Li
N and Cao X: MicroRNA-148/152 impair innate response and antigen
presentation of TLR-triggered dendritic cells by targeting CaMKIIα.
J Immunol. 185:7244–7251. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Aslam R, Speck ER, Kim M, Crow AR, Bang
KW, Nestel FP, Ni H, Lazarus AH, Freedman J and Semple JW: Platelet
Toll-like receptor expression modulates lipopolysaccharide-induced
thrombocytopenia and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in
vivo. Blood. 107:637–641. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Eidson LN, Inoue K, Young LJ, Tansey MG
and Murphy AZ: Toll-like receptor 4 mediates morphine-induced
neuroinflammation and tolerance via soluble tumor necrosis factor
signaling. Neuropsychopharmacology. 42:661–670. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Holst B, Szakmany T, Raby AC, Hamlyn V,
Durno K, Hall JE and Labéta MO: Soluble Toll-like receptor 2 is a
biomarker for sepsis in critically ill patients with multi-organ
failure within 12 h of ICU admission. Intensive Care Med Exp.
5:22017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|