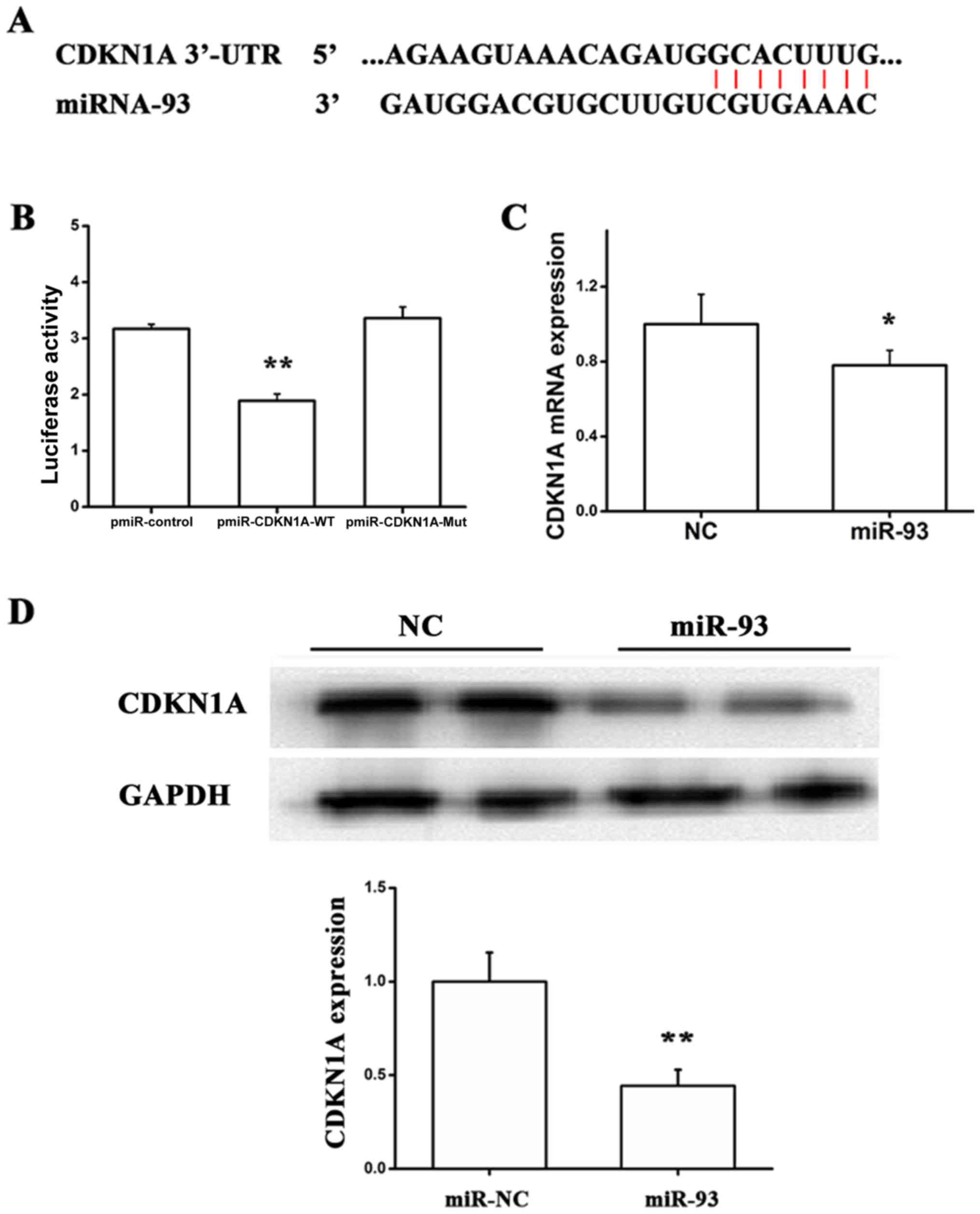
|
1
|
Lentz SR, Sobey CG, Piegors DJ, Bhopatkar
MY, Faraci FM, Malinow MR and Heistad DD: Vascular dysfunction in
monkeys with diet-induced hyperhomocyst(e)inemia. J Clin Invest.
98:24–29. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tawakol A, Omland T, Gerhard M, Wu JT and
Creager MA: Hyperhomocyst(e)inemia is associated with impaired
endothelium-dependent vasodilation in humans. Circulation.
95:1119–1121. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Faxon DP, Fuster V, Libby P, Beckman JA,
Hiatt WR, Thompson RW, Topper JN, Annex BH, Rundback JH, Fabunmi
RP, et al: Atherosclerotic vascular disease conference: Writing
group III: Pathophysiology. Circulation. 109:2617–2625. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Criqui MH, Fronek A, Barrett-Connor E,
Klauber MR, Gabriel S and Goodman D: The prevalence of peripheral
arterial disease in a defined population. Circulation. 71:510–515.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Selvin E and Erlinger TP: Prevalence of
and risk factors for peripheral arterial disease in the United
States: Results from the National health and nutrition examination
survey, 1999–2000. Circulation. 110:738–743. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Norgren L, Hiatt WR, Dormandy JA, Nehler
MR, Harris KA, Fowkes FG; TASC II Working Group, ; Bell K,
Caporusso J, Durand-Zaleski I, et al: Inter-society consensus for
the management of peripheral arterial disease (TASC II). Eur J Vasc
Endovasc Surg. 33 (Suppl 1):S1–S75. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Morisaki K, Yamaoka T and Iwasa K: Risk
factors for wound complications and 30-day mortality after major
lower limb amputations in patients with peripheral arterial
disease. Vascular. 26:12–17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Weragoda J, Seneviratne R, Weerasinghe MC
and Wijeyaratne SM: Risk factors of peripheral arterial disease: A
case control study in Sri Lanka. BMC Res Notes. 9:5082016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Forés R, Alzamora MT, Pera G, Valverde M,
Angla M, Baena-Díez JM and Mundet-Tuduri X: Evolution and degree of
control of cardiovascular risk factors after 5 years of follow-up
and their relationship with the incidence of peripheral arterial
disease: ARTPER cohort. Med Clin (Barc). 148:107–113. 2017.(In
English, Spanish). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Trionfini P and Benigni A: MicroRNAs as
master regulators of glomerular function in health and disease. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 28:1686–1696. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kato M and Natarajan R: MicroRNAs in
diabetic nephropathy: Functions, biomarkers, and therapeutic
targets. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1353:72–88. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Stather PW, Sylvius N, Wild JB, Choke E,
Sayers RD and Bown MJ: Differential microRNA expression profiles in
peripheral arterial disease. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 6:490–497.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fichtlscherer S, De Rosa S, Fox H,
Schwietz T, Fischer A, Liebetrau C, Weber M, Hamm CW, Röxe T,
Müller-Ardogan M, et al: Circulating microRNAs in patients with
coronary artery disease. Circ Res. 107:677–684. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Savita U and Karunagaran D:
MicroRNA-106b-25 cluster targets β-TRCP2, increases the expression
of Snail and enhances cell migration and invasion in H1299 (non
small cell lung cancer) cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
434:841–847. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Fang L, Deng Z, Shatseva T, Yang J, Peng
C, Du WW, Yee AJ, Ang LC, He C, Shan SW and Yang BB: MicroRNA
miR-93 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting
integrin-β8. Oncogene. 30:806–821. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fang L, Du WW, Yang W, Rutnam ZJ, Peng C,
Li H, O'Malley YQ, Askeland RW, Sugg S, Liu M, et al: MiR-93
enhances angiogenesis and metastasis by targeting LATS2. Cell
Cycle. 11:4352–4365. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu S, Patel SH, Ginestier C, Ibarra I,
Martin-Trevino R, Bai S, McDermott SP, Shang L, Ke J, Ou SJ, et al:
MicroRNA93 regulates proliferation and differentiation of normal
and malignant breast stem cells. PLoS Genet. 8:e10027512012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li F, Liang X, Chen Y, Li S and Liu J:
Role of microRNA-93 in regulation of angiogenesis. Tumour Biol.
35:10609–10613. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Xu YF, Mao YP, Li YQ, Ren XY, He QM, Tang
XR, Sun Y, Liu N and Ma J: MicroRNA-93 promotes cell growth and
invasion in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by targeting disabled
homolog-2. Cancer Lett. 363:146–155. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu G, Friggeri A, Yang Y, Park YJ,
Tsuruta Y and Abraham E: miR-147, a microRNA that is induced upon
Toll-like receptor stimulation, regulates murine macrophage
inflammatory responses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:15819–15824.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang F, Huang XR, Chung AC, Hou CC, Lai KN
and Lan HY: Essential role for Smad3 in angiotensin II-induced
tubular epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Pathol. 221:390–401.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koka V, Huang XR, Chung AC, Wang W, Truong
LD and Lan HY: Angiotensin II up-regulates angiotensin I-converting
enzyme (ACE), but down-regulates ACE2 via the AT1-ERK/p38 MAP
kinase pathway. Am J Pathol. 172:1174–1183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sun Q, Chen RR, Shen Y, Mooney DJ,
Rajagopalan S and Grossman PM: Sustained vascular endothelial
growth factor delivery enhances angiogenesis and perfusion in
ischemic hind limb. Pharm Res. 22:1110–1116. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ge Y, Sun Y and Chen J: IGF-II is
regulated by microRNA-125b in skeletal myogenesis. J Cell Biol.
192:69–81. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Couffinhal T, Silver M, Zheng LP, Kearney
M, Witzenbichler B and Isner JM: Mouse model of angiogenesis. Am J
Pathol. 152:1667–1679. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bao H, Lv F and Liu T: A pro-angiogenic
degradable Mg-poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) implant combined with
rhbFGF in a rat limb ischemia model. Acta Biomaterial. 64:279–289.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
McDermott MM, Greenland P, Liu K, Guralnik
JM, Celic L, Criqui MH, Chan C, Martin GJ, Schneider J, Pearce WH,
et al: The ankle brachial index is associated with leg function and
physical activity: The walking and leg circulation study. Ann
Intern Med. 136:873–883. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mcdermott MG, Liu K, Jack M, Guralnik MD,
Mehta S, Criqui MH, Martin GJ and Greenland P: The ankle brachial
index independently predicts walking velocity and walking endurance
in peripheral arterial disease. J Am Geriatr Soc. 46:1355–1362.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
McDermott MM, Liu K, Greenland P, Guralnik
JM, Criqui MH, Chan C, Pearce WH, Schneider JR, Ferrucci L, Celic
L, et al: Functional decline in peripheral arterial disease:
Associations with the ankle brachial index and leg symptoms. JAMA.
292:453–461. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lewis BP, Burge CB and Bartel DP:
Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that
thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 120:15–20.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
John B, Enright AJ, Aravin A, Tuschl T,
Sander C and Marks DS: Correction: Human MicroRNA targets. PLoS
Biol. 2:e3632004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hazarika S, Farber CR, Dokun AO,
Pitsillides AN, Wang T, Lye RJ and Annex BH: MicroRNA-93 controls
perfusion recovery following hind-limb ischemia by modulating
expression of multiple genes in the cell cycle pathway.
Circulation. 127:1818–1828. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M, le Sage
C, Nagel R, Nair S, Egan DA, Li A, Huang G, Klein-Szanto AJ, et al:
The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and
metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:202–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Slovut DP and Sullivan TM: Critical limb
ischemia: Medical and surgical management. Vasc Med. 13:281–291.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Z, Yang D, Xie P, Ren G, Sun G, Zeng X
and Sun X: MiR-106b and MiR-15b modulate apoptosis and angiogenesis
in myocardial infarction. Cell Physiol Biochem. 29:851–862. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kuehbacher A, Urbich C, Zeiher AM and
Dimmeler S: Role of Dicer and Drosha for endothelial microRNA
expression and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 101:59–68. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chamorro-Jorganes A, Araldi E, Penalva LO,
Sandhu D, Fernández-Hernando C and Suárez Y: MicroRNA-16 and
microRNA-424 regulate cell-autonomous angiogenic functions in
endothelial cells via targeting vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor-2 and fibroblast growth factor receptor-1. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:2595–2606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dokun AO, Keum S, Hazarika S, Li Y,
Lamonte GM, Wheeler F, Marchuk DA and Annex BH: A quantitative
trait locus (LSq-1) on mouse chromosome 7 is linked to the absence
of tissue loss after surgical hindlimb ischemia. Circulation.
117:1207–1215. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chalothorn D, Clayton JA, Zhang H, Pomp D
and Faber JE: Collateral density, remodeling and VEGF-A expression
differ widely between mouse strains. Physiol Genomics. 30:179–191.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Long J, Wang Y, Wang W, Chang BH and
Danesh FR: Identification of microRNA-93 as a novel regulator of
vascular endothelial growth factor in hyperglycemic conditions. J
Biol Chem. 285:23457–23465. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Negishi M, Wongpalee S P, Sarkar S, Park
J, Lee KY, Shibata Y, Reon BJ, Abounader R, Suzuki Y, Sugano S and
Dutta A: A new lncRNA, APTR, associates with and represses the
CDKN1A/p21 promoter by recruiting polycomb proteins. PLoS One.
9:e952162014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nuntharatanapong N, Chen K, Sinhaseni P
and Keaney JF Jr: EGF receptor-dependent JNK activation is involved
in arsenite-induced p21Cip1/Waf1 upregulation and endothelial
apoptosis. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 289:H99–H107. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yamagata K, Suzuki S and Tagami M:
Docosahexaenoic acid prevented tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced
endothelial dysfunction and senescence. Prostaglandins Leukot
Essent Fatty Acids. 104:11–18. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yin DX, Zhao HM, Sun DJ, Yao J and Ding
DY: Identification of candidate target genes for human peripheral
arterial disease using weighted gene co-expression network
analysis. Mol Med Rep. 12:8107–8112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Spinetti G, Cordella D, Fortunato O,
Sangalli E, Losa S, Gotti A, Carnelli F, Rosa F, Riboldi S, Sessa
F, et al: Global remodeling of the vascular stem cell niche in bone
marrow of diabetic patients: Implication of the microRNA-155/FOXO3a
signaling pathway. Circ Res. 11:510–522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|