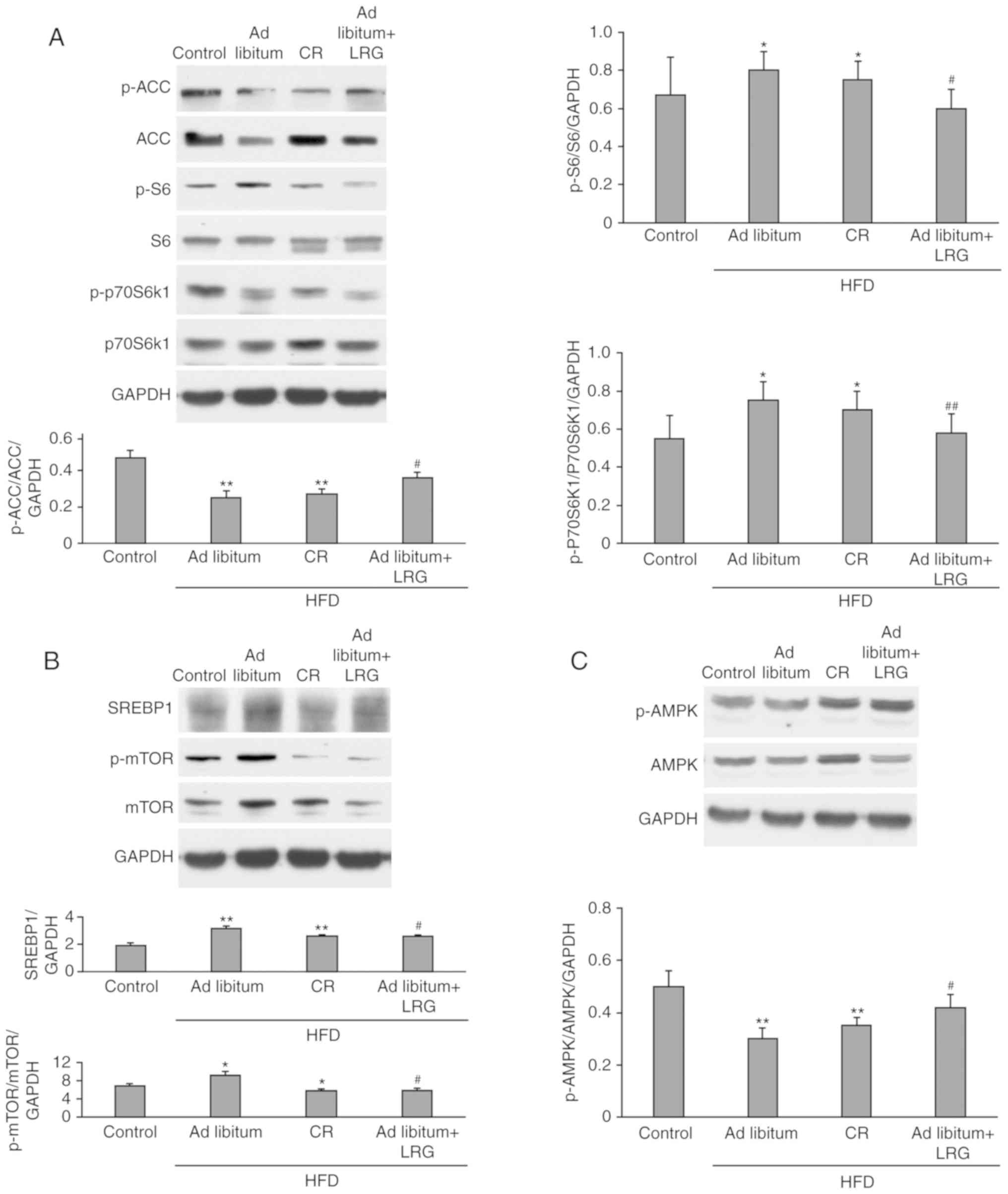
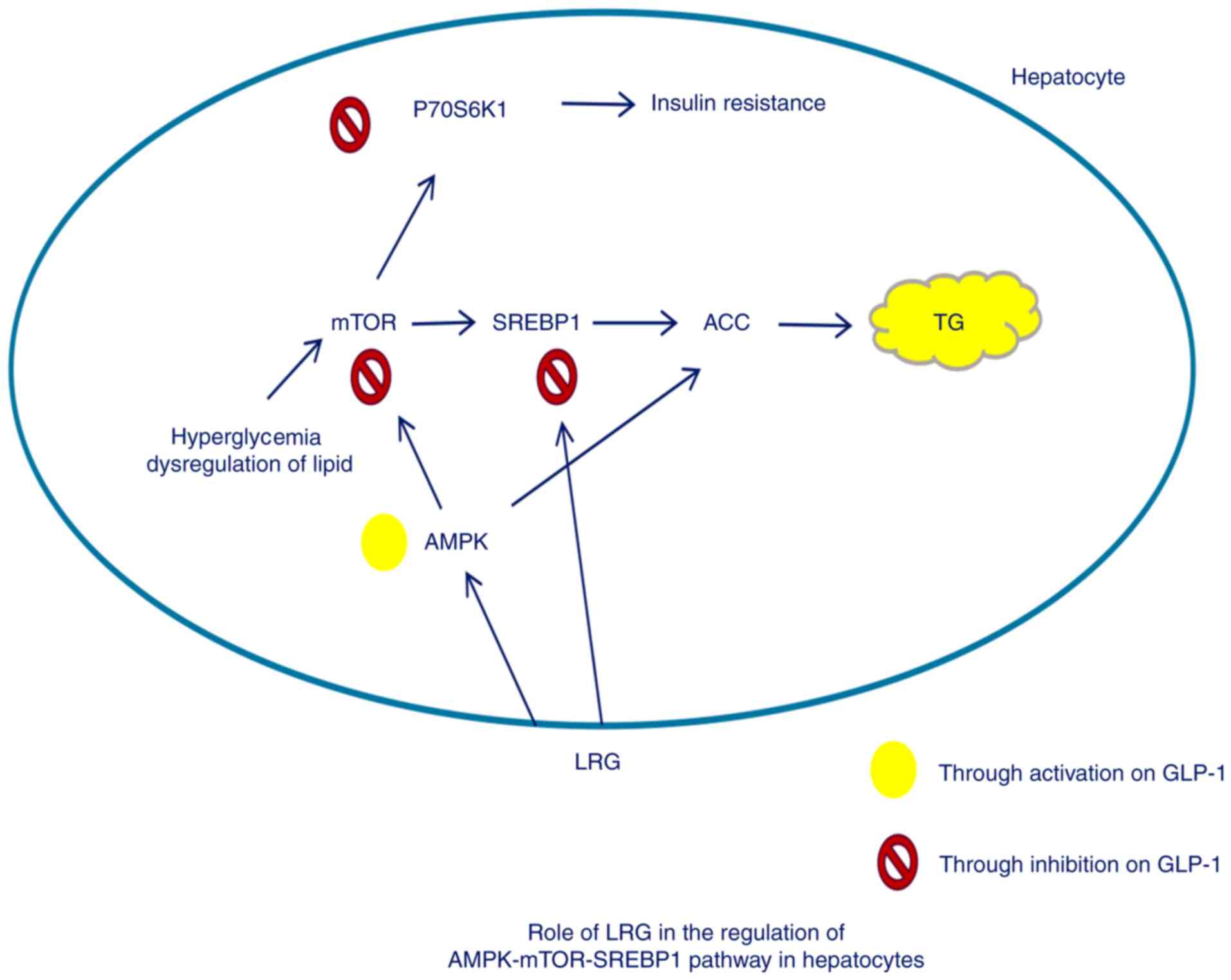
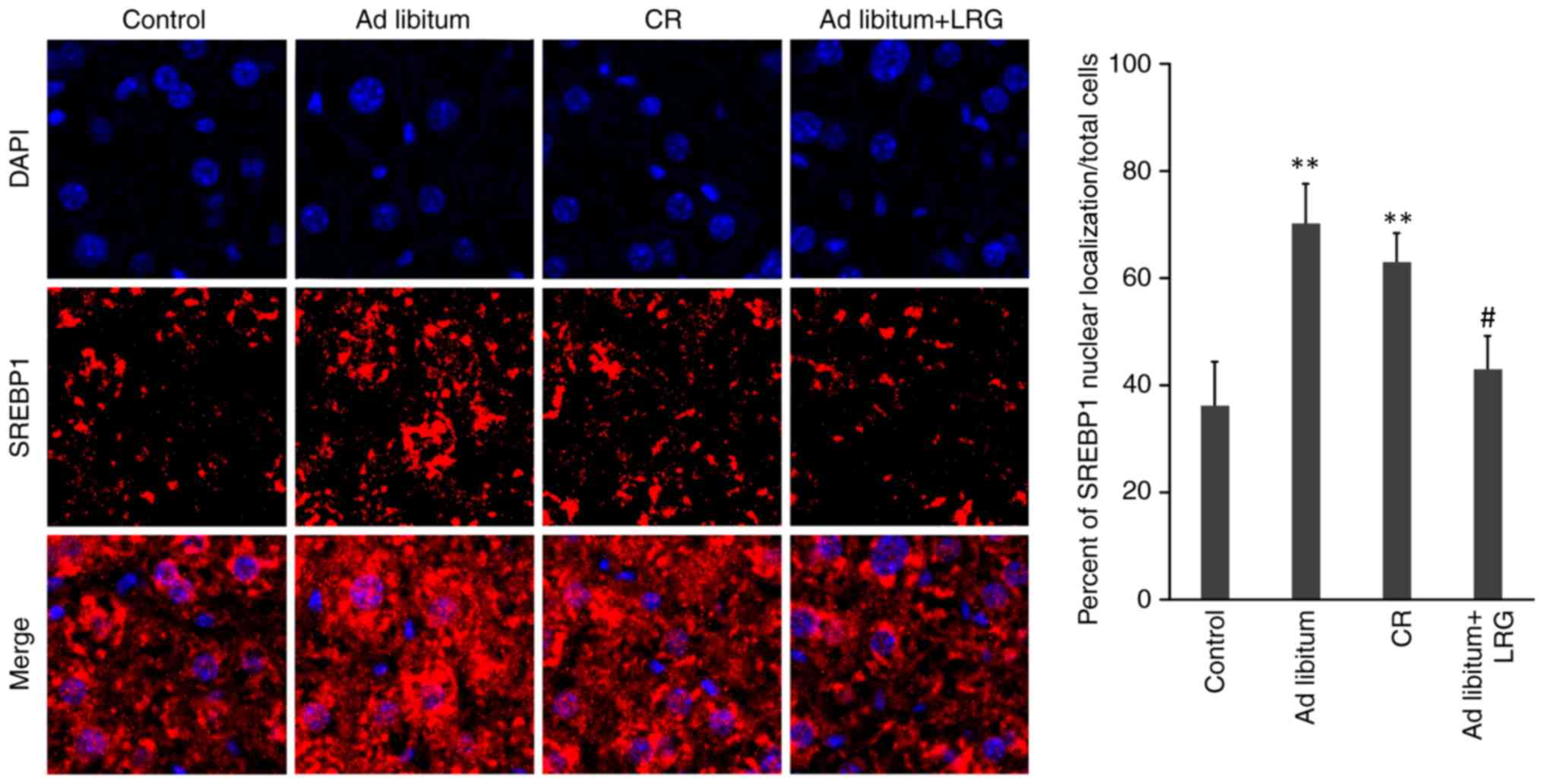
|
1
|
Vernon G, Baranova A and Younossi ZM:
Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 34:274–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thorn SR, Baquero KC, Newsom SA, El Kasmi
KC, Bergman BC, Shulman GI, Grove KL and Friedman JE: Early life
exposure to maternal insulin resistance has persistent effects on
hepatic NAFLD in juvenile nonhuman primates. Diabetes.
63:2702–2713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chackelevicius CM, Gambaro SE, Tiribelli C
and Rosso N: Th17 involvement in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
progression to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. World J
Gastroenterol. 22:9096–9103. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clarke JD, Dzierlenga AL, Nelson NR, Li H,
Werts S, Goedken MJ and Cherrington NJ: Mechanism of altered
metformin distribution in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Diabetes.
64:3305–3313. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Little TJ, Doran S, Meyer JH, Smout AJ,
O'Donovan DG, Wu KL, Jones KL, Wishart J, Rayner CK, Horowitz M and
Feinle-Bisset C: The release of GLP-1 and ghrelin, but not GIP and
CCK, by glucose is dependent upon the length of small intestine
exposed. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 291:E647–E655. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kitade H, Chen G, Ni Y and Ota T:
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance: New
insights and potential new treatments. Nutrients. 9(pii): E3872017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Byrne CD and Targher G: NAFLD: A
multisystem disease. J Hepatol. 62 (Suppl):S47–S64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yamazaki S, Satoh H and Watanabe T:
Liraglutide enhances insulin sensitivity by activating
AMP-activated protein kinase in male Wistar rats. Endocrinology.
155:3288–3301. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bakan I and Laplante M: Connecting mTORC1
signaling to SREBP-1 activation. Curr Opin Lipidol. 23:226–234.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li S, Ogawa W, Emi A, Hayashi K, Senga Y,
Nomura K, Hara K, Yu D and Kasuga M: Role of S6K1 in regulation of
SREBP1c expression in the liver. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
412:197–202. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim LC, Cook RS and Chen J: mTORC1 and
mTORC2 in cancer and the tumor microenvironment. Oncogene.
36:2191–2201. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Song YM, Lee YH, Kim JW, Ham DS, Kang ES,
Cha BS, Lee HC and Lee BW: Metformin alleviates hepatosteatosis by
restoring SIRT1-mediated autophagy induction via an AMP-activated
protein kinase-independent pathway. Autophagy. 11:46–59. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
He Q, Sha S, Sun L, Zhang J and Dong M:
GLP-1 analogue improves hepatic lipid accumulation by inducing
autophagy via AMPK/mTOR pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
476:196–203. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Soliman GA: The integral role of mTOR in
lipid metabolism. Cell Cycle. 10:861–862. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Quan HY, Kim DY, Kim SJ, Jo HK, Kim GW and
Chung SH: Betulinic acid alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver by
inhibiting SREBP1 activity via the AMPK-mTOR-SREBP signaling
pathway. Biochem Pharmacol. 85:1330–1340. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang S, Li X, Guo H, Yuan Z, Wang T, Zhang
L and Jiang Z: Emodin alleviates hepatic steatosis by inhibiting
SREBP1 activity via the CaMKK-AMPK-mTOR-p70S6K signaling pathway:
Emodin alleviates NAFLD by CaMKK-AMPK-mTOR-SREBP1. Hepatol Res.
47:2016.
|
|
17
|
Jones B, Bloom SR, Buenaventura T, Tomas A
and Rutter GA: Control of insulin secretion by GLP-1. Peptides.
100:75–84. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ayala JE, Bracy DP, James FD, Julien BM,
Wasserman DH and Drucker DJ: The glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
regulates endogenous glucose production and muscle glucose uptake
independent of its incretin action. Endocrinology. 150:1155–1164.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee J, Hong SW, Rhee EJ and Lee WY: GLP-1
receptor agonist and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes
Metab J. 36:262–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Butler PC: Glucagon-like peptide 1 drugs
as second-line therapy for type 2 diabetes. JAMA Intern Med.
176:1–3. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang XC, Gusdon AM, Liu H and Qu S:
Effects of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists on
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and inflammation. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:14821–14830. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dong Y, Lv Q, Li S, Wu Y, Li L, Li J,
Zhang F, Sun X and Tong N: Efficacy and safety of glucagon-like
peptide-1 receptor agonists in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Res Hepatol
Gastroenterol. 41:284–295. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hansen BC, Gografe S, Pritt S, Jen KC,
McWhirter CA, Barman SM, Comuzzie A, Greene M, McNulty JA, Michele
DE, et al: Ensuring due process in the IACUC and animal welfare
setting: Considerations in developing noncompliance policies and
procedures for institutional animal care and use committees and
institutional officials. FASEB J. 31:4216–4225. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cheluvappa R, Scowen P and Eri R: Ethics
of animal research in human disease remediation, its institutional
teaching; and alternatives to animal experimentation. Pharmacol Res
Perspect. 5:2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu J, Wang G, Jia Y and Xu Y: GLP-1
receptor agonists: Effects on the progression of non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 31:329–335. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Peterson TR, Sengupta SS, Harris TE,
Carmack AE, Kang SA, Balderas E, Guertin DA, Madden KL, Carpenter
AE, Finck BN and Sabatini DM: mTOR complex 1 regulates lipin 1
localization to control the SREBP pathway. Cell. 146:408–420. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lempiäinen H, Uotila A, Urban J, Dohnal I,
Ammerer G, Loewith R and Shore D: Sfp1 interaction with TORC1 and
Mrs6 reveals feedback regulation on TOR signaling. Mol Cell.
33:704–716. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gowans GJ, Hawley SA, Ross FA and Hardie
DG: AMP is a true physiological regulator of AMP-activated protein
kinase by both allosteric activation and enhancing net
phosphorylation. Cell Metab. 18:556–566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bojic LA, Telford DE, Fullerton MD, Ford
RJ, Sutherland BG, Edwards JY, Sawyez CG, Gros R, Kemp BE,
Steinberg GR and Huff MW: PPARδ activation attenuates hepatic
steatosis in Ldlr-/- mice by enhanced fat oxidation, reduced
lipogenesis, and improved insulin sensitivity. J Lipid Res.
55:1254–1266. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: An emerging
role of mTOR in lipid biosynthesis. Curr Biol. 19:R1046–R1052.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Melnik BC: Linking diet to acne
metabolomics, inflammation, and comedogenesis: An update. Clin
Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 8:371–388. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Carling D and Viollet B: Beyond energy
homeostasis: The expanding role of AMP-activated protein kinase in
regulating metabolism. Cell Metab. 21:799–804. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jeong KJ, Kim GW and Chung SH:
AMP-activated protein kinase: An emerging target for ginseng. J
Ginseng Res. 38:83–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Horton JD, Goldstein JL and Brown MS:
SREBPs: Activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty
acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest. 109:1125–1131. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Düvel K, Yecies JL, Menon S, Raman P,
Lipovsky AI, Souza AL, Triantafellow E, Ma Q, Gorski R, Cleaver S,
et al: Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream
of mTOR complex 1. Mol Cell. 39:171–183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kelleher AR, Kimball SR, Dennis MD,
Schilder RJ and Jefferson LS: The mTORC1 signaling repressors
REDD1/2 are rapidly induced and activation of p70S6K1 by leucine is
defective in skeletal muscle of an immobilized rat hindlimb. Am J
Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 304:E229–E236. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ricoult SJ, Yecies JL, Ben-Sahra I and
Manning BD: Oncogenic PI3K and K-Ras stimulate de novo lipid
synthesis through mTORC1 and SREBP. Oncogene. 35:1250–1260. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: Regulation of
mTORC1 and its impact on gene expression at a glance. J Cell Sci.
126:1713–1719. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Katsurada K and Yada T: Neural effects of
gut- and brain-derived glucagon-like peptide-1 and its receptor
agonist. J Diabetes Investig. 7 (Suppl 1):S64–S69. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cariou B: Pleiotropic effects of insulin
and GLP-1 receptor agonists: Potential benefits of the association.
Diabetes Metab 41 (6 Suppl 1). 6S28–6S35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Seufert J and Gallwitz B: The
extra-pancreatic effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists: A focus on the
cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and central nervous systems.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 16:673–688. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|