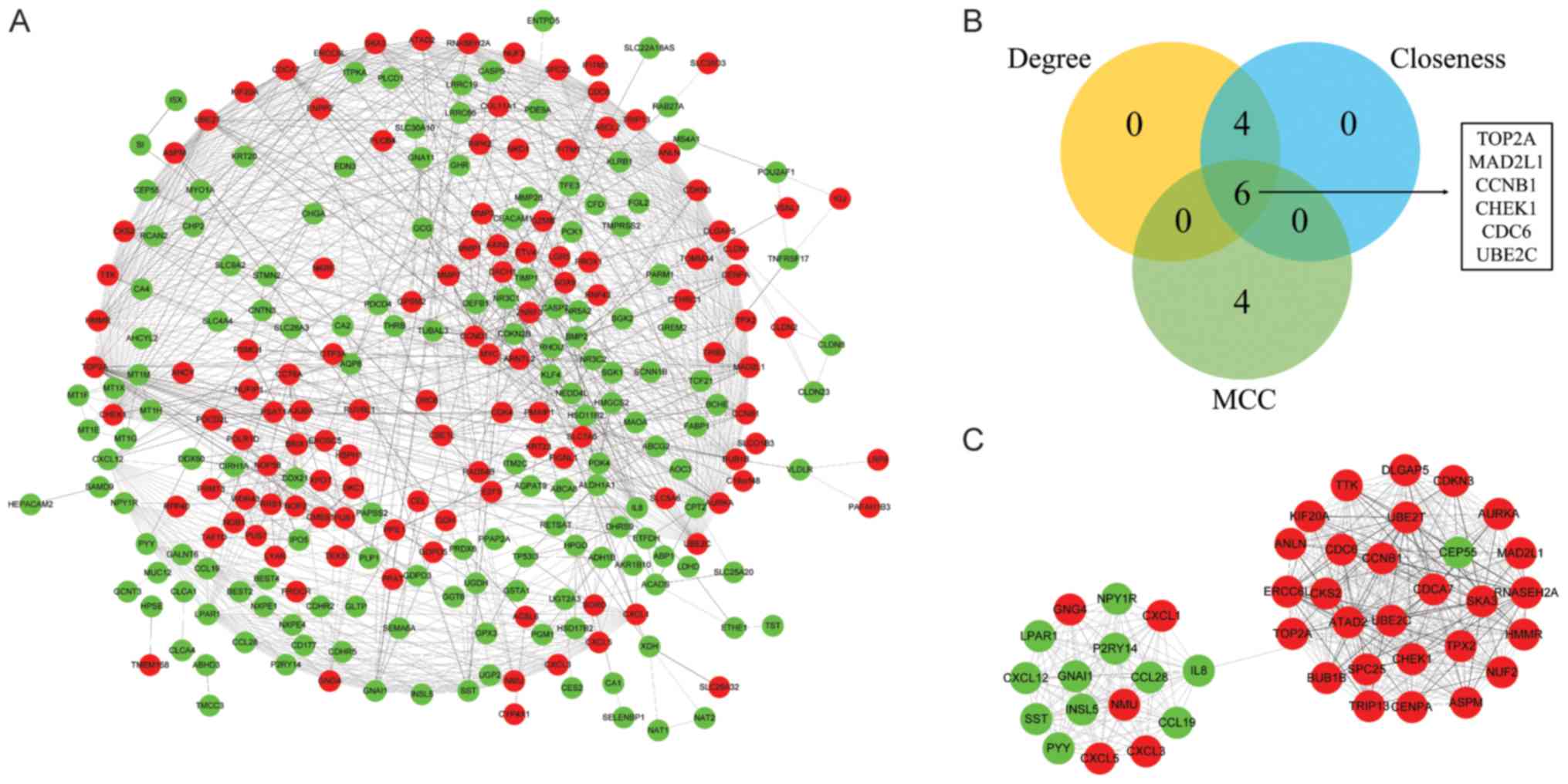
|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
O'Connell JB, Maggard MA and Ko CY: Colon
cancer survival rates with the new American joint committee on
cancer sixth edition staging. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1420–1425.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aslinia F, Uradomo L, Steele A, Greenwald
BD and Raufman JP: Quality assessment of colonoscopic cecal
intubation: An analysis of 6 years of continuous practice at a
university hospital. Am J Gastroenterol. 101:721–731. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Uraoka T, Ramberan H, Matsuda T, Fujii T
and Yahagi N: Cold polypectomy techniques for diminutive polyps in
the colorectum. Dig Endosc. 26 (Suppl 2):S98–S103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Martín-López JE, Beltrán-Calvo C,
Rodríguez-López R and Molina-López T: Comparison of the accuracy of
CT colonography and colonoscopy in the diagnosis of colorectal
cancer. Colorectal Dis. 16:O82–O89. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liang B, Li C and Zhao J: Identification
of key pathways and genes in colorectal cancer using bioinformatics
analysis. Med Oncol. 33:1112016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Guo Y, Bao Y, Ma M and Yang W:
Identification of key candidate genes and pathways in colorectal
cancer by integrated bioinformatical analysis. Int J Mol Sci.
18(pii): E7222017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hong Y, Downey T, Eu KW, Koh PK and Cheah
PY: A ‘metastasis-prone’ signature for early-stage mismatch-repair
proficient sporadic colorectal cancer patients and its implications
for possible therapeutics. Clin Exp Metastasis. 27:83–90. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okazaki S, Ishikawa T, Iida S, Ishiguro M,
Kobayashi H, Higuchi T, Enomoto M, Mogushi K, Mizushima H, Tanaka
H, et al: Clinical significance of UNC5B expression in colorectal
cancer. Int J Oncol. 40:209–216. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P,
Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH,
Sherman PM, Holko M, et al: NCBI GEO: Archive for functional
genomics data sets-update. Nucleic Acids Res 41 (Database Issue).
D991–D995. 2013.
|
|
11
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization, and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
EdgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Oliveros JC: VENNY. An interactive tool
for comparing lists with Venn Diagrams. 2007.
|
|
15
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
The Gene Ontology Consortium: The gene
ontology resource: 20 years and still GOing strong. Nucleic Acids
Res. 47(D1): D330–D338. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Furumichi M, Morishima
K and Tanabe M: New approach for understanding genome variations in
KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1): D590–D595. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M, Sato Y
and Morishima K: KEGG: New perspectives on genomes, pathways,
diseases and drugs. Nucleic Acids Res. 45(D1): D353–D361. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Yan GR and He QY: DOSE: An
R/Bioconductor package for disease ontology semantic and enrichment
analysis. Bioinformatics. 31:608–609. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bindea G, Mlecnik B, Hackl H, Charoentong
P, Tosolini M, Kirilovsky A, Fridman WH, Pagès F, Trajanoski Z and
Galon J: ClueGO: A cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally
grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks.
Bioinformatics. 25:1091–1093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: CytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4):S112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takada I and Makishima M: Control of
inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancer by synthetic
vitamin D receptor ligands. Curr Med Chem. 24:868–875. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vermeulen K, Van Bockstaele DR and
Berneman ZN: The cell cycle: A review of regulation, deregulation
and therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 36:131–149. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Aarts M, Linardopoulos S and Turner NC:
Tumour selective targeting of cell cycle kinases for cancer
treatment. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 13:529–535. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Rieder G, Hofmann JA, Hatz RA, Stolte M
and Enders GA: Up-regulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase in
helicobacter pylori-associated gastritis may represent an increased
risk factor to develop gastric carcinoma of the intestinal type.
Int J Med Microbiol. 293:403–412. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hashibe M, Galeone C, Buys SS, Gren L,
Boffetta P, Zhang ZF and La Vecchia C: Coffee, tea, caffeine
intake, and the risk of cancer in the PLCO cohort. Br J Cancer.
113:809–816. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guertin KA, Loftfield E, Boca SM, Sampson
JN, Moore SC, Xiao Q, Huang WY, Xiong X, Freedman ND, Cross AJ and
Sinha R: Serum biomarkers of habitual coffee consumption may
provide insight into the mechanism underlying the association
between coffee consumption and colorectal cancer. Am J Clin Nutr.
101:1000–1011. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Merighi S, Benini A, Mirandola P, Gessi S,
Varani K, Simioni C, Leung E, Maclennan S, Baraldi PG and Borea PA:
Caffeine inhibits adenosine-induced accumulation of
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha, vascular endothelial growth
factor, and interleukin-8 expression in hypoxic human colon cancer
cells. Mol Pharmacol. 72:395–406. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Long Y, Sanchez-Espiridion B, Lin M, White
L, Mishra L, Raju GS, Kopetz S, Eng C, Hildebrandt MAT, Chang DW,
et al: Global and targeted serum metabolic profiling of colorectal
cancer progression. Cancer. 123:4066–4074. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen L, Lu D, Sun K, Xu Y, Hu P, Li X and
Xu F: Identification of biomarkers associated with diagnosis and
prognosis of colorectal cancer patients based on integrated
bioinformatics analysis. Gene. 692:119–125. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Coss A, Tosetto M, Fox EJ, Sapetto-Rebow
B, Gorman S, Kennedy BN, Lloyd AT, Hyland JM, O'Donoghue DP,
Sheahan K, et al: Increased topoisomerase IIalpha expression in
colorectal cancer is associated with advanced disease and
chemotherapeutic resistance via inhibition of apoptosis. Cancer
Lett. 276:228–238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bofin AM, Ytterhus B and Hagmar BM: TOP2A
and HER-2 gene amplification in fine needle aspirates from breast
carcinomas. Cytopathology. 14:314–319. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kanta SY, Yamane T, Dobashi Y, Mitsui F,
Kono K and Ooi A: Topoisomerase IIalpha gene amplification in
gastric carcinomas: Correlation with the HER2 gene. An
immunohistochemical, immunoblotting, and multicolor fluorescence in
situ hybridization study. Hum Pathol. 37:1333–1343. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kruger S, Lange I, Kausch I and Feller AC:
Protein expression and gene copy number analysis of topoisomerase
2alpha, HER2 and P53 in minimally invasive urothelial carcinoma of
the urinary bladder-a multitissue array study with prognostic
implications. Anticancer Res. 25:263–271. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Depowski PL, Rosenthal SI, Brien TP,
Stylos S, Johnson RL and Ross JS: Topoisomerase IIalpha expression
in breast cancer: Correlation with outcome variables. Mod Pathol.
13:542–547. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dingemans AM, Witlox MA, Stallaert RA, van
der Valk P, Postmus PE and Giaccone G: Expression of DNA
topoisomerase IIalpha and topoisomerase IIbeta genes predicts
survival and response to chemotherapy in patients with small cell
lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 5:2048–2058. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mu XC, Tran TA, Ross JS and Carlson JA:
Topoisomerase II-alpha expression in melanocytic nevi and malignant
melanoma. J Cutan Pathol. 27:242–248. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhou Q, Abraham AD, Li L, Babalmorad A,
Bagby S, Arcaroli JJ, Hansen RJ, Valeriote FA, Gustafson DL,
Schaack J, et al: Topoisomerase IIα mediates TCF-dependent
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colon cancer. Oncogene.
35:4990–4999. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fernandez-Cid A, Riera A, Tognetti S,
Herrera MC, Samel S, Evrin C, Winkler C, Gardenal E, Uhle S, Speck
C, et al: An ORC/Cdc6/MCM2-7 complex is formed in a multistep
reaction to serve as a platform for MCM double-hexamer assembly.
Mol Cell. 50:577–588. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Randell JC, Bowers JL, Rodriguez HK and
Bell SP: Sequential ATP hydrolysis by Cdc6 and ORC directs loading
of the Mcm2-7 helicase. Mol Cell. 21:29–39. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim GS, Kang J, Bang SW and Hwang DS: Cdc6
localizes to S- and G2-phase centrosomes in a cell cycle-dependent
manner. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 456:763–767. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Barkley LR, Hong HK, Kingsbury SR, James
M, Stoeber K and Williams GH: Cdc6 is a rate-limiting factor for
proliferative capacity during HL60 cell differentiation. Exp Cell
Res. 313:3789–3799. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Huang M, Miao ZH, Zhu H, Cai YJ, Lu W and
Ding J: Chk1 and Chk2 are differentially involved in homologous
recombination repair and cell cycle arrest in response to DNA
double-strand breaks induced by camptothecins. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:1440–1449. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
van't Veer LJ, Dai H, van de Vijver MJ, He
YD, Hart AA, Mao M, Peterse HL, van der Kooy K, Marton MJ,
Witteveen AT, et al: Gene expression profiling predicts clinical
outcome of breast cancer. Nature. 415:530–536. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Hernando E, Nahle Z, Juan G,
Diaz-Rodriguez E, Alaminos M, Hemann M, Michel L, Mittal V, Gerald
W, Benezra R, et al: Rb inactivation promotes genomic instability
by uncoupling cell cycle progression from mitotic control. Nature.
430:797–802. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chen X, Yan CC, Zhang X and You ZH: Long
non-coding RNAs and complex diseases: From experimental results to
computational models. Brief Bioinform. 18:558–576. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chen X, Xie D, Zhao Q and You ZH:
MicroRNAs and complex diseases: From experimental results to
computational models. Brief Bioinform. 20:515–539. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chen X, Wang L, Qu J, Guan NN and Li JQ:
Predicting miRNA-disease association based on inductive matrix
completion. Bioinformatics. 34:4256–4265. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Chen X, Xie D, Wang L, Zhao Q, You ZH and
Liu H: BNPMDA: Bipartite network projection for MiRNA-disease
association prediction. Bioinformatics. 34:3178–3186. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Chen X, Yin J, Qu J and Huang L: MDHGI:
Matrix decomposition and heterogeneous graph inference for
miRNA-disease association prediction. PLoS Computat Biol.
14:e10064182018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chen X and Huang L: LRSSLMDA: Laplacian
regularized sparse subspace learning for MiRNA-disease association
prediction. PLoS Comput Biol. 13:e10059122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|