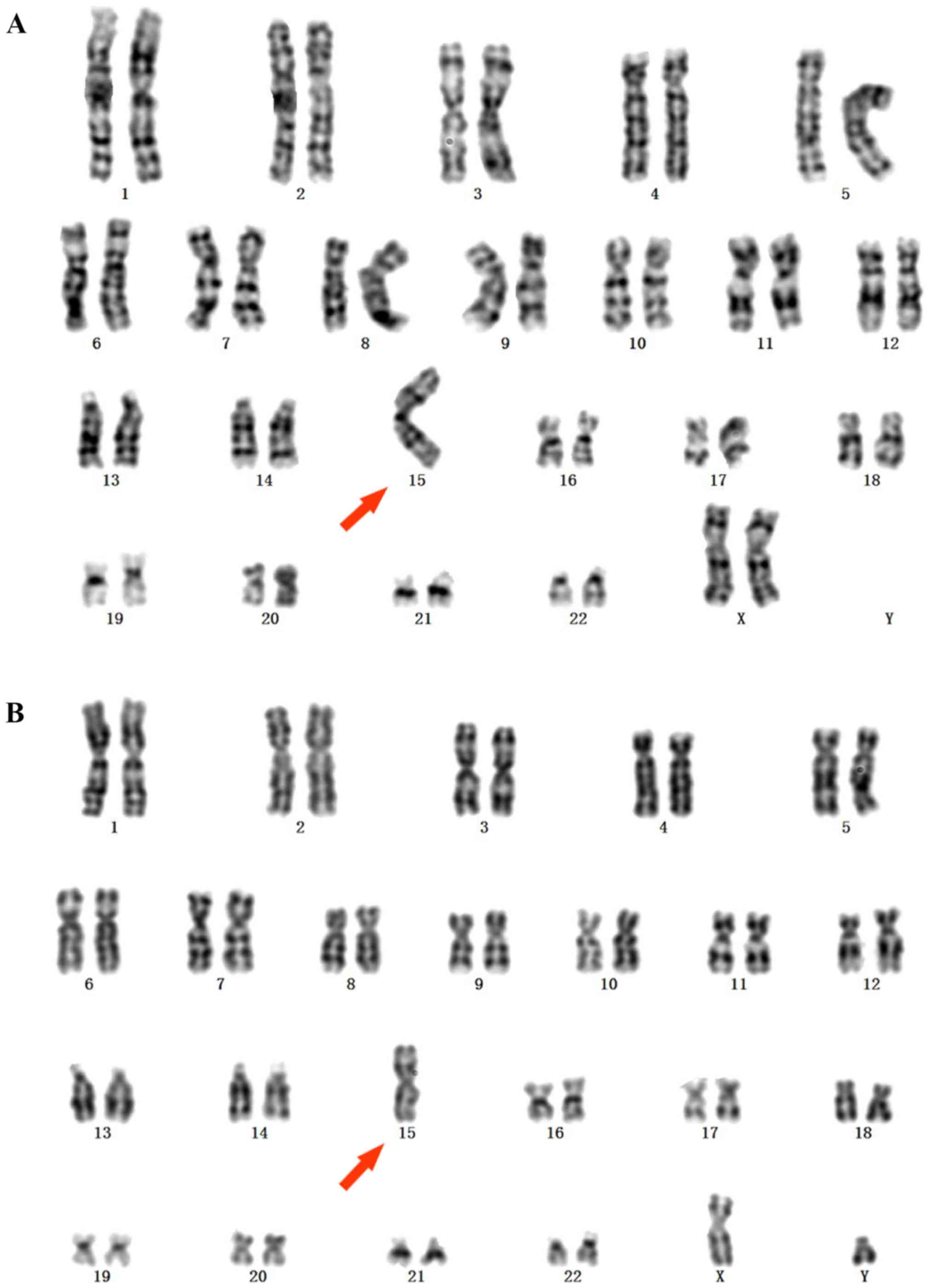
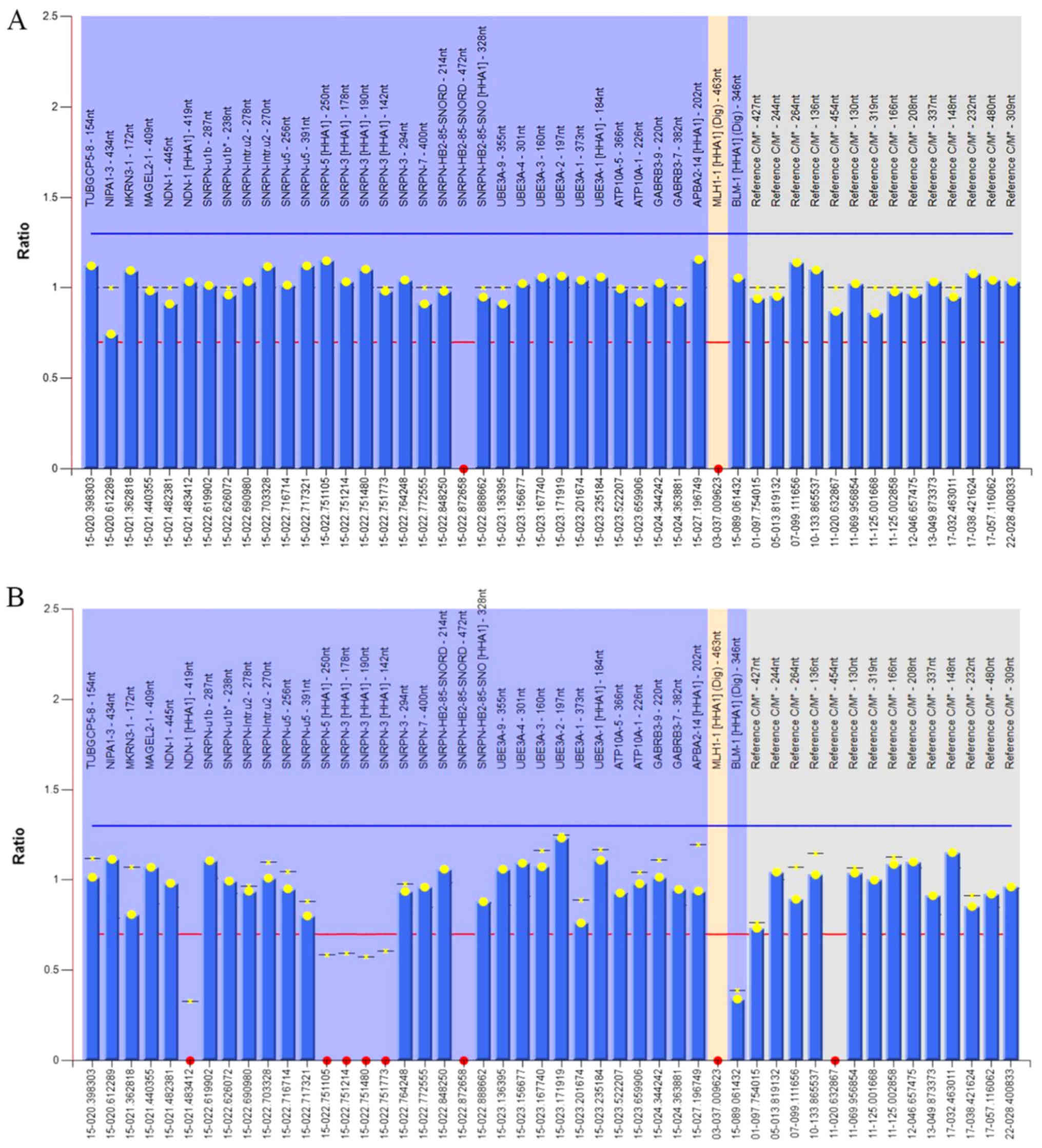
|
1
|
Kishino T, Lalande M and Wagstaff J:
UBE3A/E6-AP mutations cause Angelman syndrome. Nat Genet. 15:70–73.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rougeulle C, Glatt H and Lalande M: The
Angelman syndrome candidate gene, UBE3A/E6-AP, is imprinted in
brain. Nat Genet. 17:14–15. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sato M: Early origin and evolution of the
angelman syndrome ubiquitin ligase gene Ube3a. Front Cell Neurosci.
11:622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Greer PL, Hanayama R, Bloodgood BL,
Mardinly AR, Lipton DM, Flavell SW, Kim TK, Griffith EC, Waldon Z,
Maehr R, et al: The angelman syndrome protein Ube3A regulates
synapse development by ubiquitinating arc. Cell. 140:704–716. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Clayton-Smith J and Laan L: Angelman
syndrome: A review of the clinical and genetic aspects. J Med
Genet. 40:87–95. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fridman C and Koiffmann CP: Origin of
uniparental disomy 15 in patients with Prader-Willi or Angelman
syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 94:249–253. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Knoll JH, Glatt KA, Nicholls RD, Malcolm S
and Lalande M: Chromosome 15 uniparental disomy is not frequent in
Angelman syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 48:16–21. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Siegel DH and Slavotinek A: Uniparental
disomy. Pediatr Dermatol. 22:482–487. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shaffer LG: Risk estimates for uniparental
disomy following prenatal detection of a nonhomologous Robertsonian
translocation. Prenat Diagn. 26:303–307. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Poyatos D, Guitart M, Gabau E, Brun C,
Mila M, Vaquerizo J and Coll MD: Severe phenotype in Angelman
syndrome resulting from paternal isochromosome 15. J Med Genet.
39:E42002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bis DM, Schule R, Reichbauer J, Synofzik
M, Rattay TW, Soehn A, de Jonghe P, Schöls L and Züchner S:
Uniparental disomy determined by whole-exome sequencing in a
spectrum of rare motoneuron diseases and ataxias. Mol Genet Genomic
Med. 5:280–286. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Carmichael H, Shen Y, Nguyen TT,
Hirschhorn JN and Dauber A: Whole exome sequencing in a patient
with uniparental disomy of chromosome 2 and a complex phenotype.
Clin Genet. 84:213–222. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kurth I, Baumgartner M, Schabhuttl M,
Tomni C, Windhager R, Strom TM, Wieland T, Gremel K and
Auer-Grumbach M: Whole exome sequencing in congenital pain
insensitivity identifies a novel causative intronic NTRK1-mutation
due to uniparental disomy. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet.
171:875–878. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gormez Z, Bakir-Gungor B and Sagiroglu MS:
HomSI: A homozygous stretch identifier from next-generation
sequencing data. Bioinformatics. 30:445–447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li H and Durbin R: Fast and accurate short
read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics.
25:1754–1760. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A, Fennell T,
Ruan J, Homer N, Marth G, Abecasis G and Durbin R; 1000 Genome
Project Data Processing Subgroup, : The sequence Alignment/Map
format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 25:2078–2079. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Talevich E, Shain AH, Botton T and Bastian
BC: CNVkit: Genome-Wide copy number detection and visualization
from targeted DNA sequencing. PLoS Comput Biol. 12:e10048732016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
McLaren W, Gil L, Hunt SE, Riat HS,
Ritchie GR, Thormann A, Flicek P and Cunningham F: The ensembl
variant effect predictor. Genome Biol. 17:1222016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ng PC and Henikoff S: SIFT: Predicting
amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Res.
31:3812–3814. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adzhubei IA, Schmidt S, Peshkin L,
Ramensky VE, Gerasimova A, Bork P, Kondrashov AS and Sunyaev SR: A
method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat
Methods. 7:248–249. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stenson PD, Mort M, Ball EV, Shaw K,
Phillips A and Cooper DN: The human gene mutation database:
Building a comprehensive mutation repository for clinical and
molecular genetics, diagnostic testing and personalized genomic
medicine. Hum Genet. 133:1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Danecek P, Auton A, Abecasis G, Albers CA,
Banks E, DePristo MA, Handsaker RE, Lunter G, Marth GT, Sherry ST,
et al: The variant call format and VCFtools. Bioinformatics.
27:2156–2158. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Glenn CC, Driscoll DJ, Yang TP and
Nicholls RD: Genomic imprinting: Potential function and mechanisms
revealed by the Prader-Willi and Angelman syndromes. Mol Hum
Reprod. 3:321–332. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tonk V, Schultz RA, Christian SL, Kubota
T, Ledbetter DH and Wilson GN: Robertsonian (15q;15q) translocation
in a child with Angelman syndrome: Evidence of uniparental disomy.
Am J Med Genet. 66:426–428. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Freeman SB, May KM, Pettay D, Fernhoff PM
and Hassold TJ: Paternal uniparental disomy in a child with a
balanced 15;15 translocation and Angelman syndrome. Am J Med Genet.
45:625–630. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fridman C, Varela MC, Nicholls RD and
Koiffmann CP: Unusual clinical features in an Angelman syndrome
patient with uniparental disomy due to a translocation 15q15q. Clin
Genet. 54:303–308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ramsden S, Gaunt L, Seres-Santamaria A and
Clayton-Smith J: A case of Angelman syndrome arising as a result of
a de novo Robertsonian translocation. Acta Genet Med Gemellol
(Roma). 45:255–261. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Horvath E, Horvath Z, Isaszegi D, Gergev
G, Nagy N, Szabó J, Sztriha L, Széll M and Endreffy E: Early
detection of Angelman syndrome resulting from de novo paternal
isodisomic 15q UPD and review of comparable cases. Mol Cytogenet.
6:352013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Robinson WP, Christian SL, Kuchinka BD,
Peñaherrera MS, Das S, Schuffenhauer S, Malcolm S, Schinzel AA,
Hassold TJ and Ledbetter DH: Somatic segregation errors
predominantly contribute to the gain or loss of a paternal
chromosome leading to uniparental disomy for chromosome 15. Clin
Genet. 57:349–358. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Smith A, Robson L and Buchholz B: Normal
growth in Angelman syndrome due to paternal UPD. Clin Genet.
53:223–225. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Varela MC, Kok F, Otto PA and Koiffmann
CP: Phenotypic variability in Angelman syndrome: Comparison among
different deletion classes and between deletion and UPD subjects.
Eur J Hum Genet. 12:987–992. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Williams CA, Beaudet AL, Clayton-Smith J,
Knoll JH, Kyllerman M, Laan LA, Magenis RE, Moncla A, Schinzel AA,
Summers JA and Wagstaff J: Angelman syndrome 2005: Updated
consensus for diagnostic criteria. Am J Med Genet A. 140:413–418.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu X, Petrovski S, Xie P, Ruzzo EK, Lu
YF, McSweeney KM, Ben-Zeev B, Nissenkorn A, Anikster Y, Oz-Levi D,
et al: Whole-exome sequencing in undiagnosed genetic diseases:
Interpreting 119 trios. Genet Med. 17:774–781. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Stranneheim H and Wedell A: Exome and
genome sequencing: A revolution for the discovery and diagnosis of
monogenic disorders. J Intern Med. 279:3–15. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Pfundt R, Del Rosario M, Vissers LELM,
Kwint MP, Janssen IM, de Leeuw N, Yntema HG, Nelen MR, Lugtenberg
D, Kamsteeg EJ, et al: Detection of clinically relevant copy-number
variants by exome sequencing in a large cohort of genetic
disorders. Genet Med. 19:667–675. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|