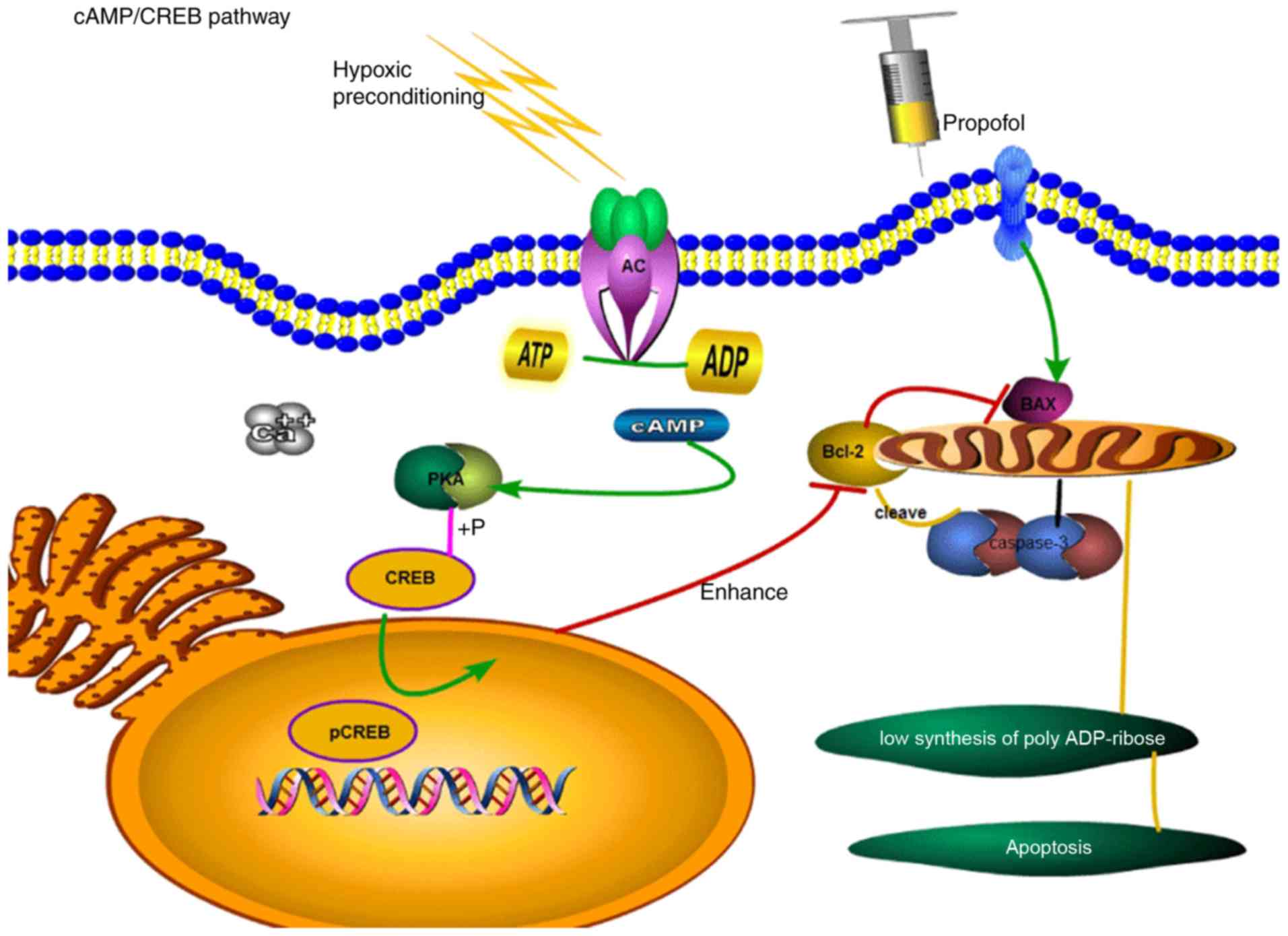
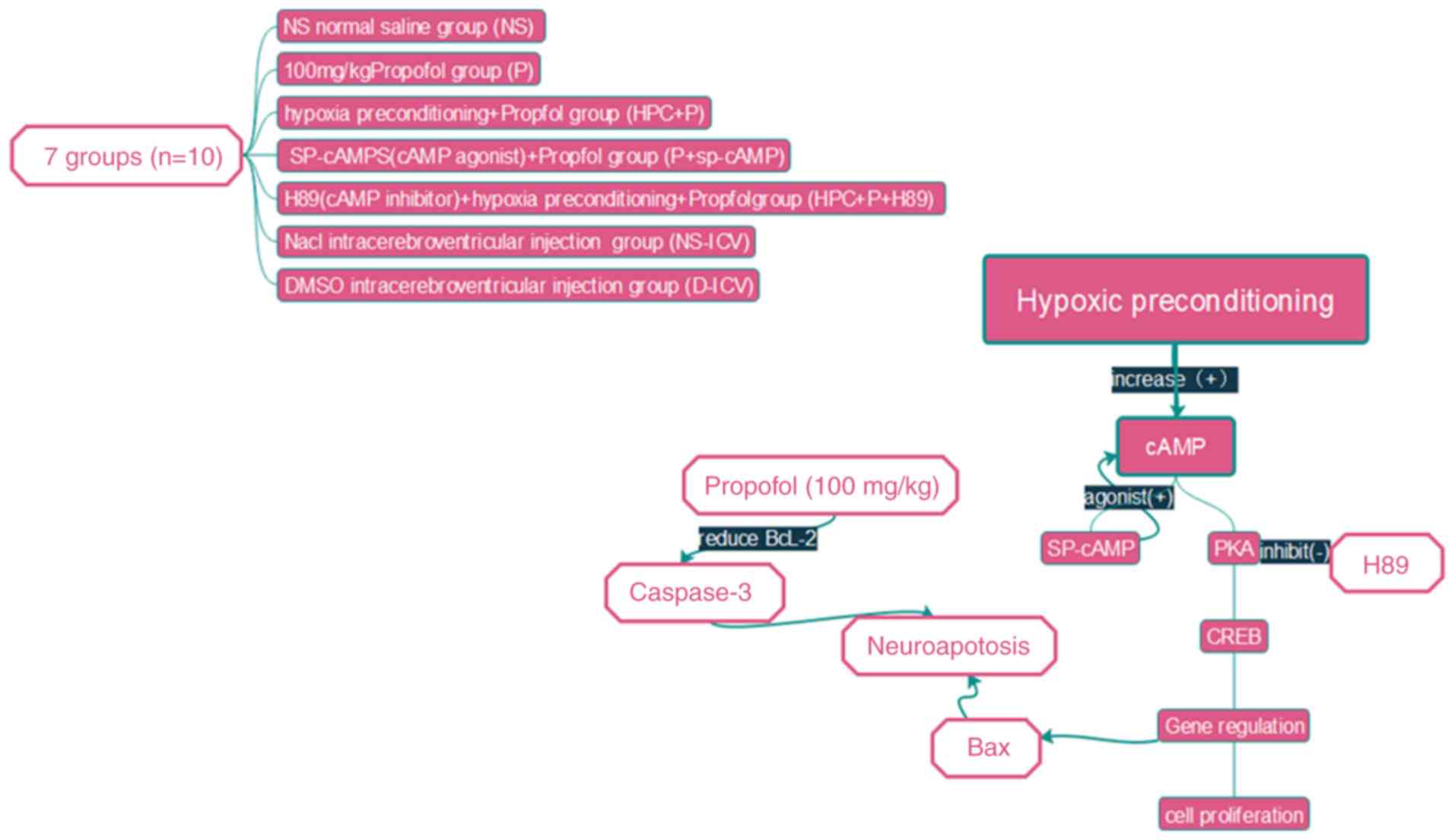
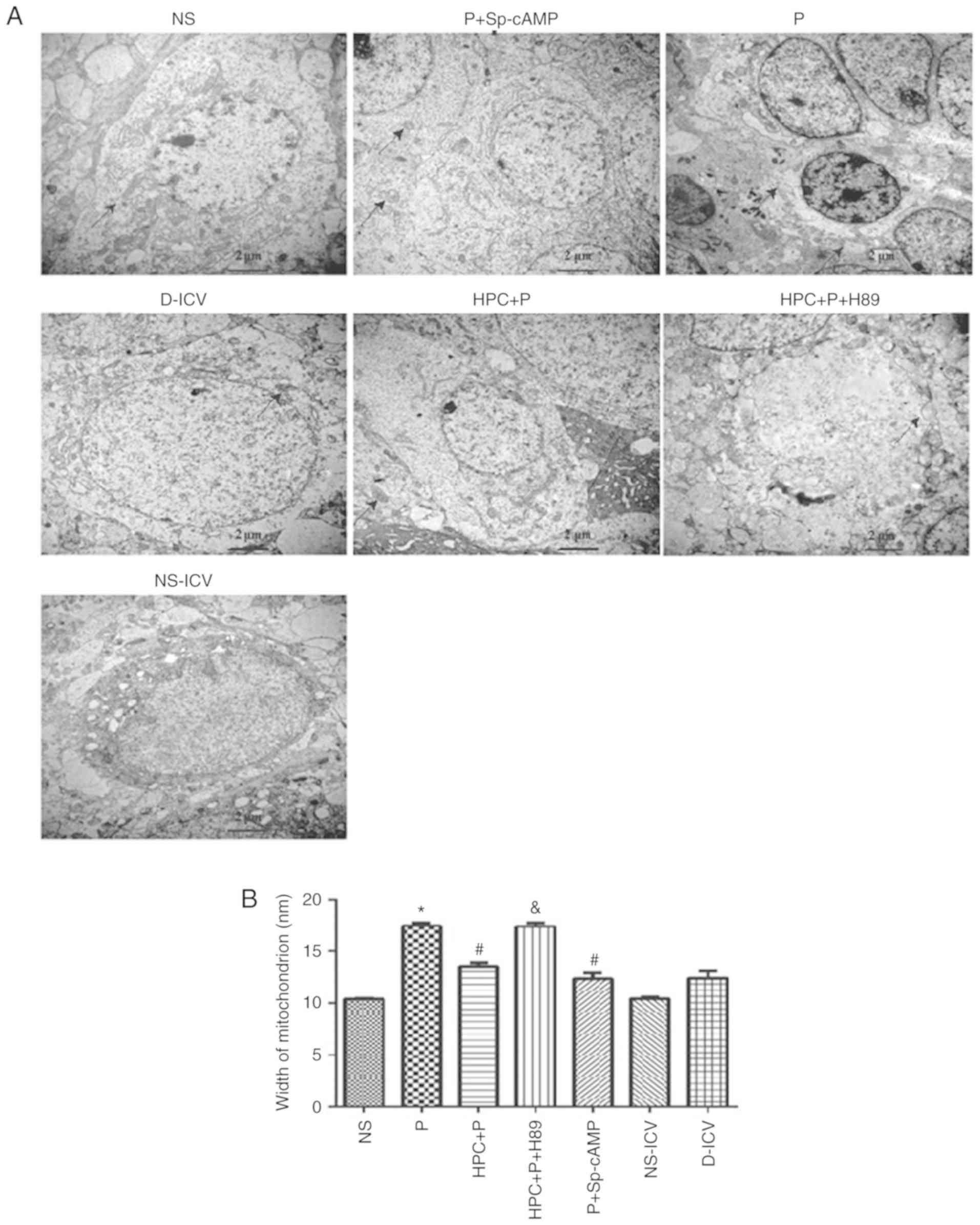
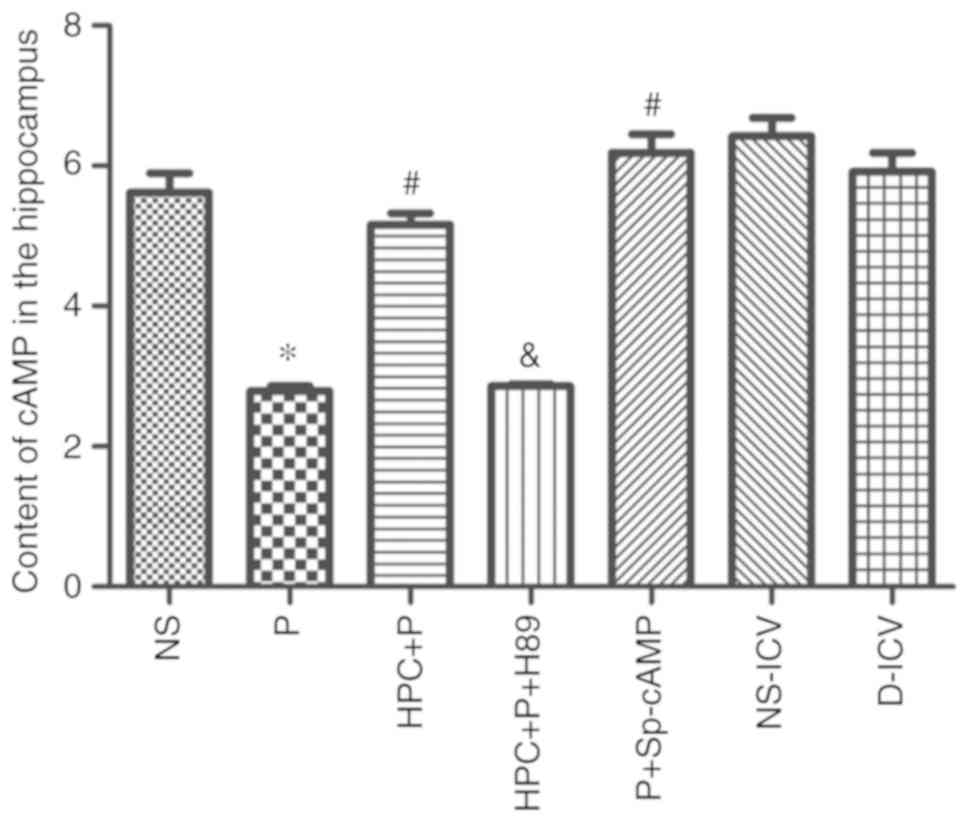
|
1
|
Miner JR and Burton JH: Clinical practice
advisory: Emergency department procedural sedation with propofol.
Ann Emerg Med. 50:182–187, 187.e1. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vasileiou I, Xanthos T, Koudouna E, Perrea
D, Klonaris C, Katsargyris A and Papadimitriou L: Propofol: A
review of its non-anaesthetic effects. Eur J Pharmacol. 605:1–8.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang J, Cottrell JE and Kass IS: Effects
of desflurane and propofol on electrophysiological parameters
during and recovery after hypoxia in rat hippocampal slice CA1
pyramidal cells. Neuroscience. 160:140–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Creeley C, Dikranian K, Dissen G, Martin
L, Olney J and Brambrink A: Propofol-induced apoptosis of neurones
and oligodendrocytes in fetal and neonatal rhesus macaque brain. Br
J Anaesth. 110 (Suppl 1):i29–i38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ko HM, Kim SY, Joo SH, Cheong JH, Yang SI,
Shin CY and Koo BN: Synergistic activation of
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated glial cells by propofol. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 438:420–426. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun WC and Pei L: rno-miR-665 targets
BCL2L1 (Bcl-xl) and increases vulnerability to propofol in
developing astrocytes. J Neurochem. 138:233–242. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Logan S, Jiang C, Yan Y, Inagaki Y, Arzua
T and Bai X: Propofol alters long non-coding RNA profiles in the
neonatal mouse hippocampus: Implication of novel mechanisms in
anesthetic-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 49:2496–2510. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heckman PRA, Blokland A, Bollen EPP and
Prickaerts J: Phosphodiesterase inhibition and modulation of
corticostriatal and hippocampal circuits: Clinical overview and
translational considerations. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 87:233–254.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang S, Liang Z, Sun W and Pei L:
Repeated propofol anesthesia induced downregulation of hippocampal
miR-132 and learning and memory impairment of rats. Brain Res.
1670:156–164. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kajimoto M, Atkinson DB, Ledee DR, Kayser
EB, Morgan PG, Sedensky MM, Isern NG, Des Rosiers C and Portman MA:
Propofol compared with isoflurane inhibits mitochondrial metabolism
in immature swine cerebral cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
34:514–521. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cui Y, Ling-Shan G, Yi L, Xing-Qi W,
Xue-Mei Z and Xiao-Xing Y: Repeated administration of propofol
upregulated the expression of c-Fos and cleaved-caspase-3 proteins
in the developing mouse brain. Indian J Pharmacol. 43:648–651.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lv J, Liang Y, Tu Y, Chen J and Xie Y:
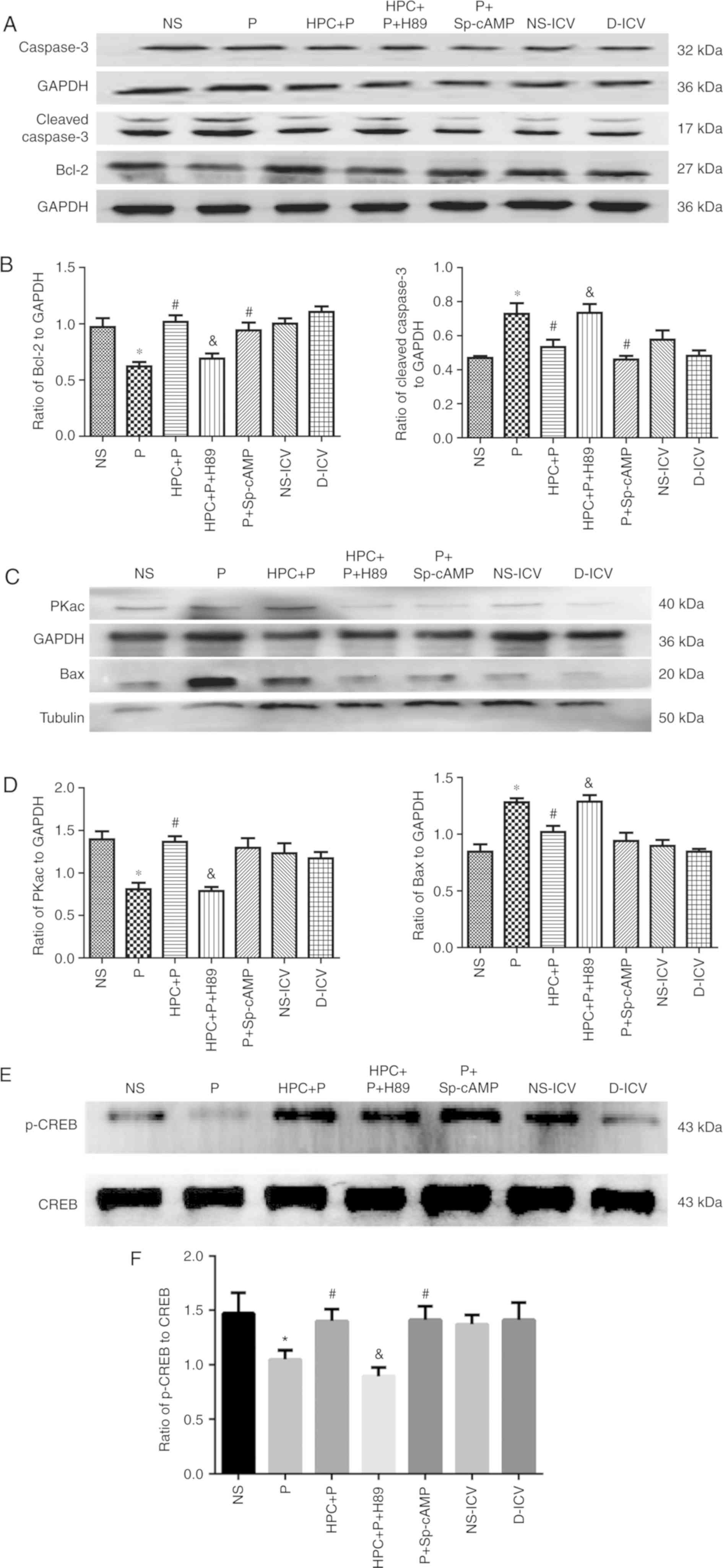
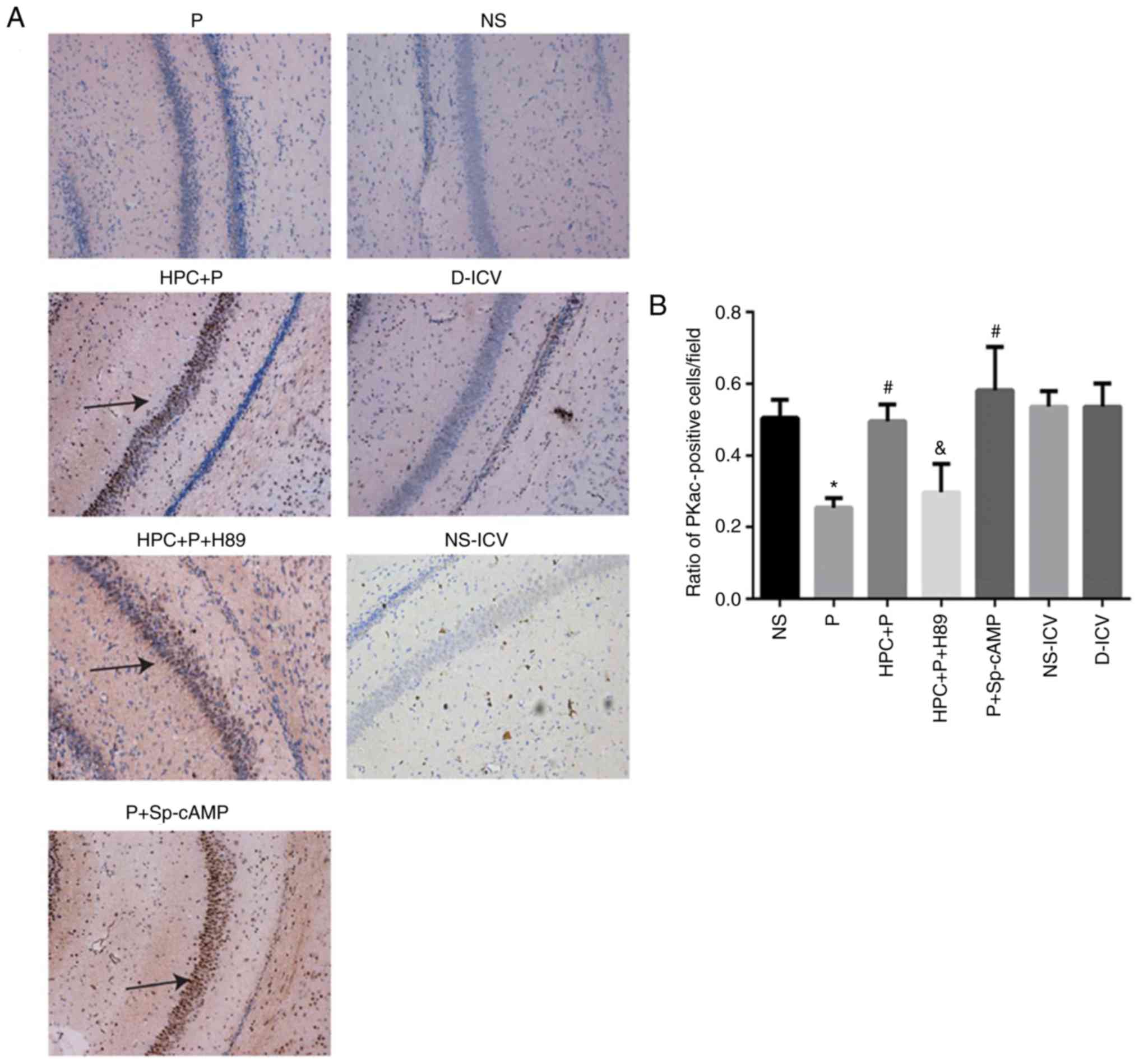
Hypoxic preconditioning reduces propofol-induced neuroapoptosis via
regulation of Bcl-2 and Bax and downregulation of activated
caspase-3 in the hippocampus of neonatal rats. Neurol Res.
40:767–773. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Baillieul S, Chacaroun S, Doutreleau S,
Detante O, Pépin JL and Verges S: Hypoxic conditioning and the
central nervous system: A new therapeutic opportunity for brain and
spinal cord injuries? Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 242:1198–1206. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Okuda S, Sufu-Shimizu Y, Kato T, Fukuda M,
Nishimura S, Oda T, Kobayashi S, Yamamoto T, Morimoto S and Yano M:
CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation of RyR2 plays a crucial role in
aberrant Ca2+ release as an arrhythmogenic substrate in
cardiac troponin T-related familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 496:1250–1256. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang C, Du F, Cang J and Xue Z: Pink1
attenuates propofol-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in
developing neurons. J Anesth. 32:62–69. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wei ZZ, Zhu YB, Zhang JY, McCrary MR, Wang
S, Zhang YB, Yu SP and Wei L: Priming of the cells: Hypoxic
preconditioning for stem cell therapy. Chin Med J (Engl).
130:2361–2374. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tsui YP, Mung AK, Chan YS, Shum DK and
Shea GK: Hypoxic preconditioning of marrow-derived progenitor cells
as a source for the generation of mature schwann cells. J Vis Exp.
Jun 14–2017.doi: 10.3791/55794. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lv J, Wei Y, Chen Y, Zhang X, Gong Z,
Jiang Y, Gong Q, Zhou L, Wang H and Xie Y: Dexmedetomidine
attenuates propofol-induce neuroapoptosis partly via the activation
of the PI3k/Akt/GSK3β pathway in the hippocampus of neonatal rats.
Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 52:121–128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhong Y, Liang Y, Chen J, Li L, Qin Y,
Guan E, He D, Wei Y, Xie Y and Xiao Q: Propofol inhibits
proliferation and induces neuroapoptosis of hippocampal neurons in
vitro via downregulation of NF-κB p65 and Bcl-2 and upregulation of
caspase-3. Cell Biochem Funct. 32:720–729. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Galluzzi L and Vanpouille-Box C: BAX and
BAK at the gates of innate immunity. Trends Cell Biol. 28:343–345.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rahmani M, Nkwocha J, Hawkins E, Pei X,
Parker RE, Kmieciak M, Leverson JD, Sampath D, Ferreira-Gonzalez A
and Grant S: Cotargeting BCL-2 and PI3K induces BAX-dependent
mitochondrial apoptosis in AML cells. Cancer Res. 78:3075–3086.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ma ZW and Liu DX: Humanin decreases
mitochondrial membrane permeability by inhibiting the membrane
association and oligomerization of Bax and Bid proteins. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 39:1012–1021. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu C, Li X, Guo P and Wang J:
Hypoxia-induced activation of JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway promotes
trophoblast cell viability and angiogenesis in preeclampsia. Med
Sci Monit. 23:4909–4917. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Karen T, Schlager GW, Bendix I, Sifringer
M, Herrmann R, Pantazis C, Enot D, Keller M, Kerner T and
Felderhoff-Mueser U: Effect of propofol in the immature rat brain
on short- and long-term neurodevelopmental outcome. PLoS One.
8:e644802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Stetler RA, Leak RK, Gan Y, Li P, Zhang F,
Hu X, Jing Z, Chen J, Zigmond MJ and Gao Y: Preconditioning
provides neuroprotection in models of CNS disease: Paradigms and
clinical significance. Prog Neurobiol. 114:58–83. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bao D, Zhao W, Dai C, Wan H and Cao Y: H89
dihydrochloride hydrate and calphostin C lower the body temperature
through TRPV1. Mol Med Rep. 17:1599–1608. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoo SB, Lee S, Lee JY, Kim BT, Lee JH and
Jahng JW: cAMP/PKA agonist restores the fasting-induced
down-regulation of nNOS expression in the paraventricular nucleus.
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 16:333–337. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Laycock JF, Hubbard JI, Schwartz JH,
Stanton BA and Valtin H: The cAMP agonist Sp-cAMPS stimulates
osmotic water transport across rat inner medullary collecting duct
cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 689:606–608. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Singh R, Letai A and Sarosiek K:
Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: The balancing act of
BCL-2 family proteins. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:175–193. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
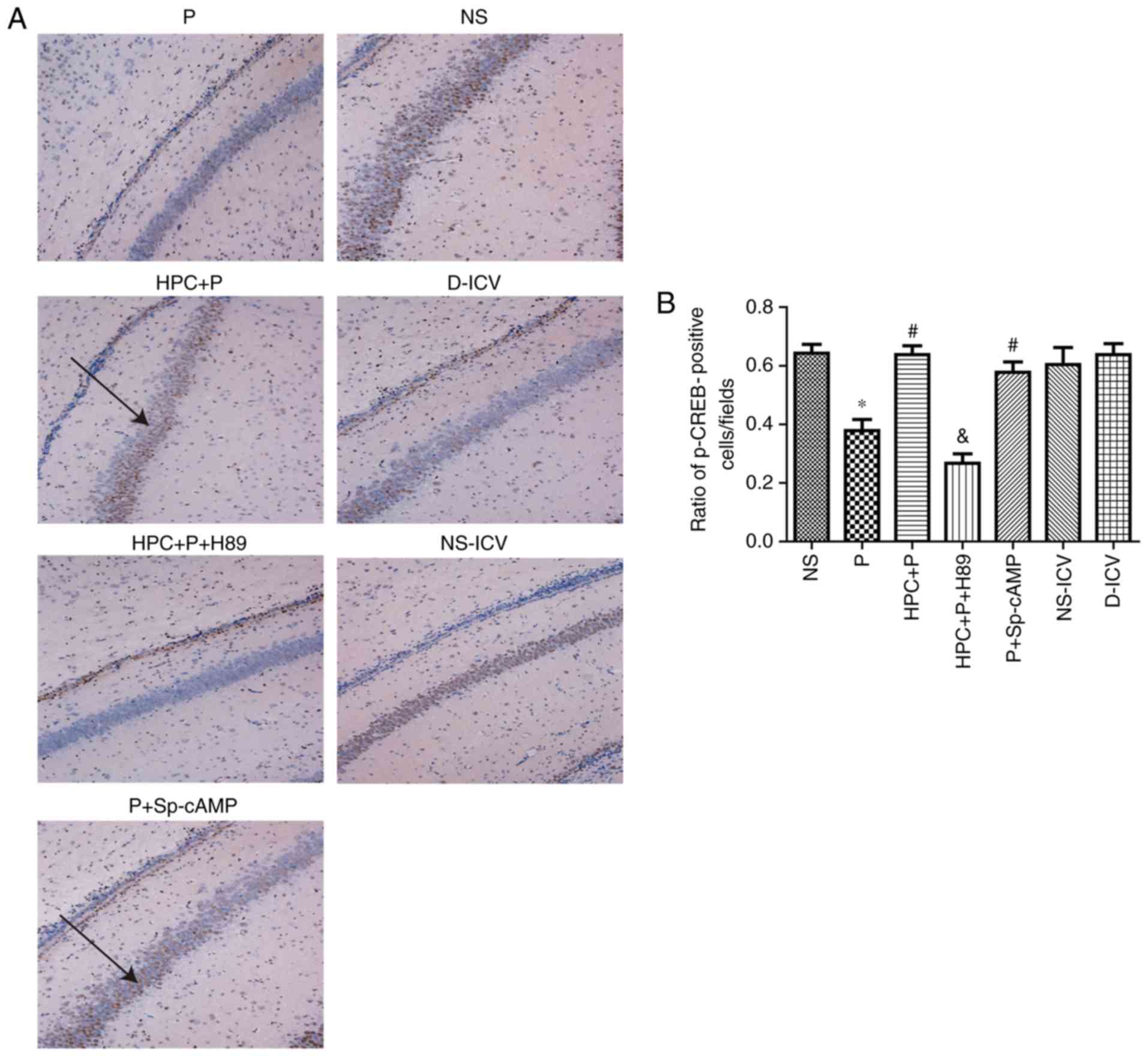
Lonze BE and Ginty DD: Function and
regulation of CREB family transcription factors in the nervous
system. Neuron. 35:605–623. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|