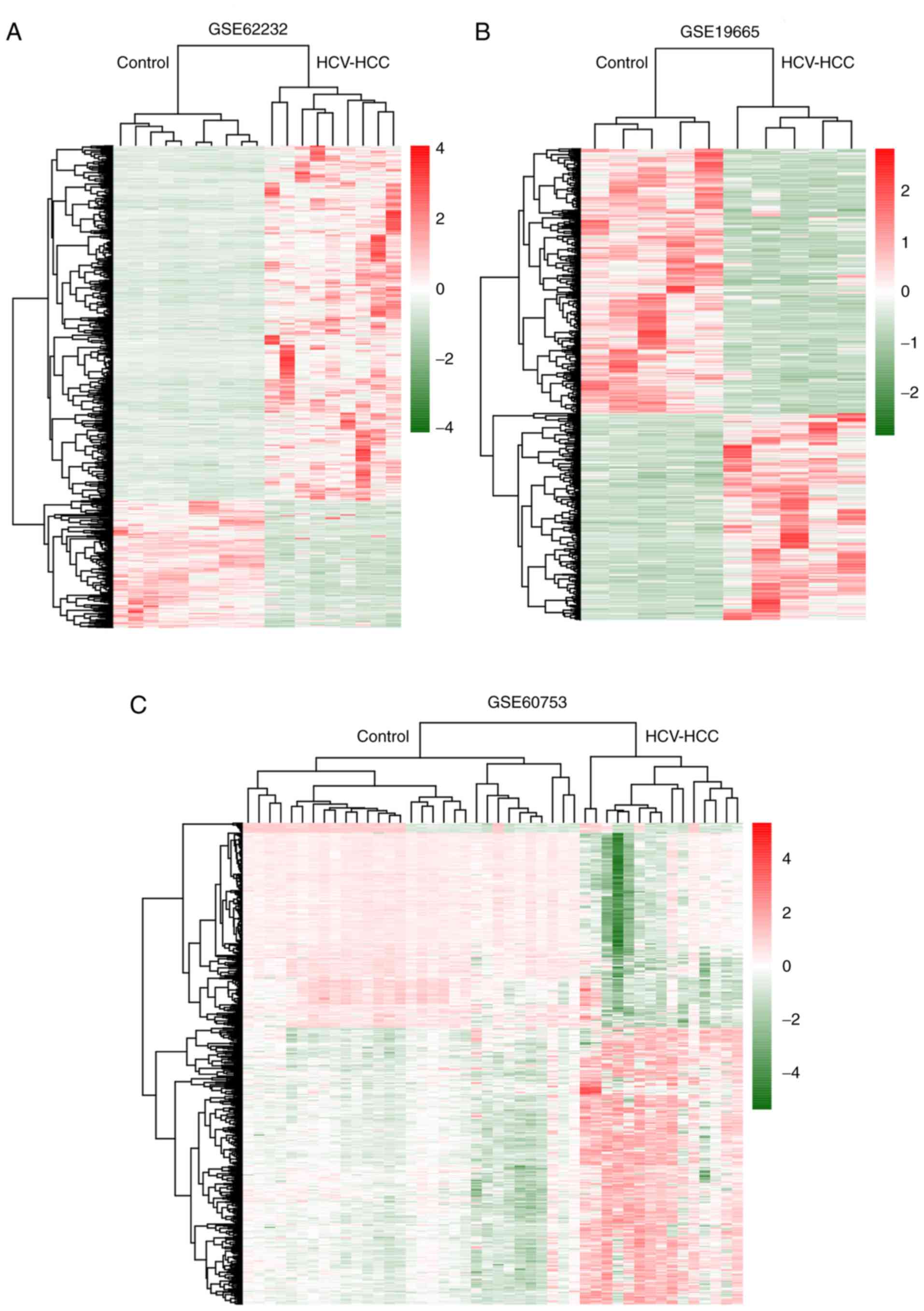
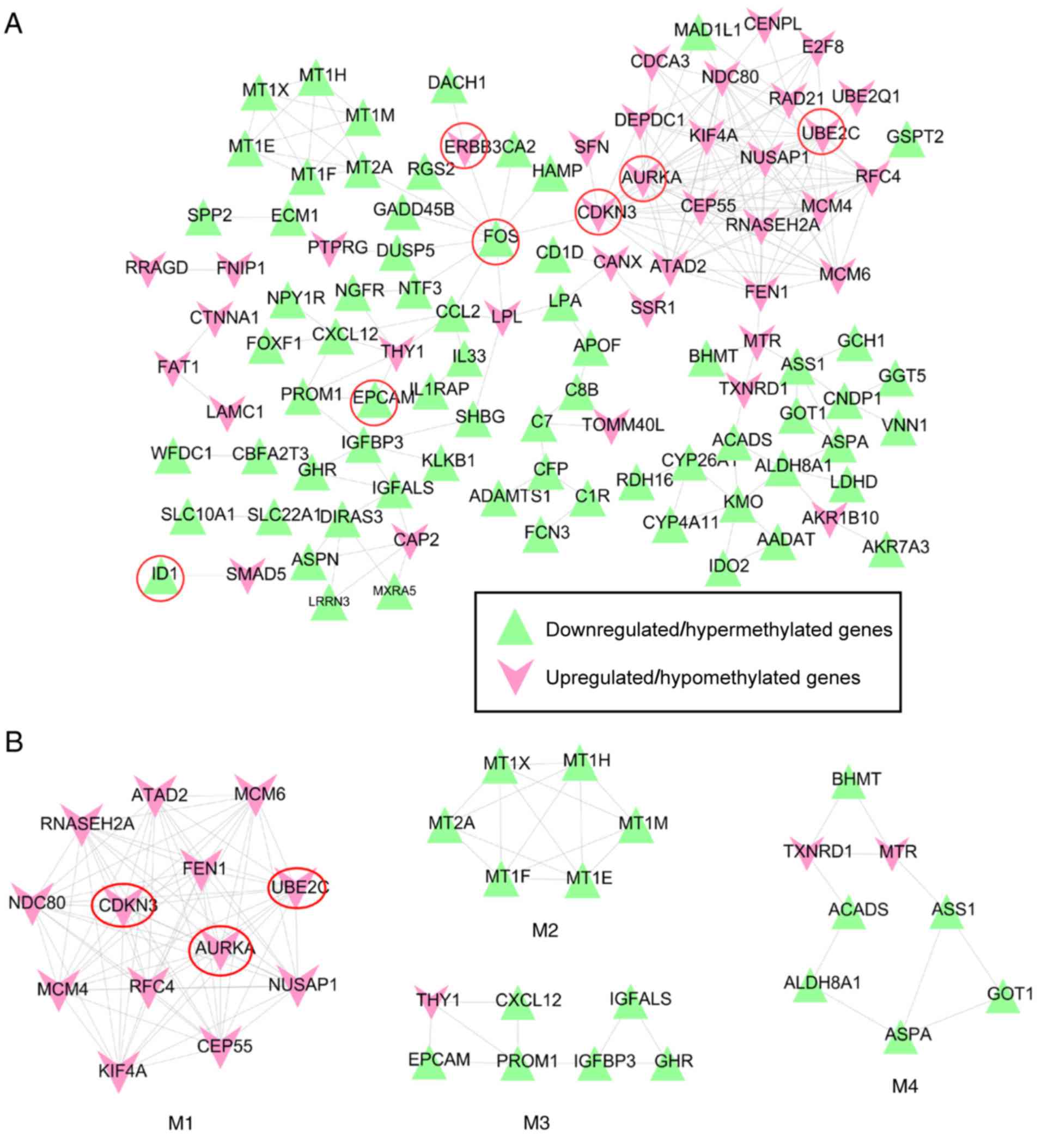
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jing L, Huang L, Yan J, Qiu M and Yan Y:
Liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: Personal experiences
in a series of 1330 consecutive cases in China. ANZ J Surg.
88:E713–E717. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Petruzziello A: Epidemiology of Hepatitis
B Virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Open Virol J. 12:26–32. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Moore MS, Bocour A, Tran OC, Qiao B,
Schymura MJ, Laraque F and Winters A: Effect of hepatocellular
carcinoma on mortality among individuals with Hepatitis B or
Hepatitis C infection in New York City, 2001–2012. Open Forum
Infect Dis. 5:ofy1442018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kiran M, Chawla YK and Kaur J: Methylation
profiling of tumor suppressor genes and oncogenes in hepatitis
virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma in northern India. Cancer
Genet Cytogenet. 195:112–119. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zekri AR, Bahnasy AA, Shoeab FE, Mohamed
WS, El-Dahshan DH, Ali FT, Sabry GM, Dasgupta N and Daoud SS:
Methylation of multiple genes in hepatitis C virus associated
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Adv Res. 5:27–40. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramadan RA, Zaki MA, Awad AM and El-Ghalid
LA: Aberrant methylation of promoter region of SPINT2/HAI-2 gene:
An epigenetic mechanism in hepatitis C virus-induced
hepatocarcinogenesis. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers. 19:399–404. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Takagi K, Fujiwara K, Takayama T, Mamiya
T, Soma M and Nagase H: DNA hypermethylation of zygote arrest 1
(ZAR1) in hepatitis C virus positive related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Springerplus. 2:1502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsunedomi R, Iizuka N, Yoshimura K, Iida
M, Tsutsui M, Hashimoto N, Kanekiyo S, Sakamoto K, Tamesa T and Oka
M: ABCB6 mRNA and DNA methylation levels serve as useful biomarkers
for prediction of early intrahepatic recurrence of hepatitis C
virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 42:1551–1559.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mileo AM, Mattarocci S, Matarrese P,
Anticoli S, Abbruzzese C, Catone S, Sacco R, Paggi MG and Ruggieri
A: Hepatitis C virus core protein modulates pRb2/p130 expression in
human hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines through promoter
methylation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 34:1402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Quan H, Zhou F, Nie D, Chen Q, Cai X, Shan
X, Zhou Z, Chen K, Huang A, Li S and Tang N: Hepatitis C virus core
protein epigenetically silences SFRP1 and enhances HCC
aggressiveness by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
Oncogene. 33:2826–2835. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Deng YB, Nagae G, Midorikawa Y, Yagi K,
Tsutsumi S, Yamamoto S, Hasegawa K, Kokudo N, Aburatani H and
Kaneda A: Identification of genes preferentially methylated in
hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci.
101:1501–1510. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang Y, Chen L, Gu J, Zhang H, Yuan J,
Lian Q, Lv G, Wang S, Wu Y, Yang YC, et al: Recurrently deregulated
lncRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 8:144212017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hlady RA, Tiedemann RL, Puszyk W, Zendejas
I, Roberts LR, Choi JH, Liu C and Robertson KD: Epigenetic
signatures of alcohol abuse and hepatitis infection during human
hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncotarget. 5:9425–9443. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: Limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Szekely GJ and Rizzo ML: Hierarchical
clustering via Joint between-within distances: Extending Ward's
minimum variance method. J Classification. 22:151–183. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Liu Y, Sun J and Zhao M: ONGene: A
literature-based database for human oncogenes. J Genet Genomics.
44:119–121. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43
(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y and Wu FX:
CytoNCA: A cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation
of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 127:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maere S, Heymans K and Kuiper M: BiNGO: A
Cytoscape plugin to assess overrepresentation of Gene Ontology
categories in Biological Networks. Bioinformatics. 21:3448–3449.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pontén F, Jirström K and Uhlen M: The
human protein atlas-a tool for pathology. J Pathol. 216:387–393.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Irshad M, Gupta P and Irshad K: Molecular
basis of hepatocellular carcinoma induced by hepatitis C virus
infection. World J Hepatol. 9:1305–1314. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moustafa S, Karakasiliotis I and Mavromara
P: Hepatitis C virus core+1/ARF protein modulates Cyclin D1/pRb
pathway and promotes carcinogenesis. J Virol. 92(pii): e02036–17.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bassiouny AEE, Nosseir MM, Zoheiry MK,
Ameen NA, Abdelhadi AM, Ibrahim IM, Zada S, El-Deen AH and
El-Bassiouni NE: Differential expression of cell cycle regulators
in HCV-infection and related hepatocellular carcinoma. World J
Hepatol. 2:32–41. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kufer TA, Silljé HH, Körner R, Gruss OJ,
Meraldi P and Nigg EA: Human TPX2 is required for targeting
Aurora-A kinase to the spindle. J Cell Biol. 158:617–623. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Benten D, Keller G, Quaas A, Schrader J,
Gontarewicz A, Balabanov S, Braig M, Wege H, Moll J, Lohse AW and
Brummendorf TH: Aurora kinase inhibitor PHA-739358 suppresses
growth of hepatocellular carcinoma in vitro and in a xenograft
mouse model. Neoplasia. 11:934–944. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang G, Chang B, Yang F, Guo X, Cai KQ,
Xiao X, Wang H, Sen S, Hung MC, Mills GB, et al: Aurora Kinase A
promotes ovarian tumorigenesis through dysregulation of the cell
cycle and suppression of BRCA2. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3171–3181.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhou N, Singh K, Mir MC, Parker Y, Lindner
D, Dreicer R, Ecsedy JA, Zhang Z, The BT, Almasan A and Hansel DE:
The investigational Aurora kinase A inhibitor MLN8237 induces
defects in cell viability and cell cycle progression in malignant
bladder cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Clin Cancer Res.
19:1717–1728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li JP, Yang YX, Liu QL, Pan ST, He ZX,
Zhang X, Yang T, Chen XW, Dong W, Qiu JX and Zhou SF: The
investigational Aurora kinase A inhibitor alisertib (MLN8237)
induces cell cycle G2/M arrest, apoptosis, and autophagy via p38
MAPK and Akt/mTOR signaling pathways in human breast cancer cells.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:1627–1652. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu Q, Yu X, Zhou ZW, Zhou C, Chen XW and
Zhou SF: Inhibition of Aurora A Kinase by alisertib induces
autophagy and cell cycle arrest and increases chemosensitivity in
human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 17:386–401. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhu Q, Yu X, Zhou ZW, Luo M, Zhou C, He
ZX, Chen Y and Zhou SF: A quantitative proteomic response of
hepatocellular carcinoma Hep3B cells to danusertib, a pan-Aurora
kinase inhibitor. J Cancer. 9:2061–2071. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chen C, Song G, Xiang J, Zhang H, Zhao S
and Zhan Y: AURKA promotes cancer metastasis by regulating
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell properties
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
486:514–520. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mohiuddin MK, Chava S, Upendrum P, Latha
M, Zubeda S, Kumar A, Ahuja YR, Hasan Q and Mohan V: Role of Human
papilloma virus infection and altered methylation of specific genes
in esophageal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4187–4193. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Watanabe T, Hiasa Y, Tokumoto Y, Hirooka
M, Abe M, Ikeda Y, Matsuura B, Chung RT and Onji M: Protein Kinase
R modulates c-Fos and c-Jun signaling to promote proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma with Hepatitis C virus infection. PLoS
One. 8:e677502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Oliveiraferrer L, Rößler K, Haustein V,
Schröder C, Wicklein D, Maltseva D, Khaustova N, Samatov T,
Tonevitsky A, Mahner S, et al: c-FOS suppresses ovarian cancer
progression by changing adhesion. Br J Cancer. 110:753–763. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guo JC, Li J, Zhao YP, Zhou L, Cui QC,
Zhou WX, Zhang TP and You L: Expression of c-fos was associated
with clinicopathologic characteristics and prognosis in pancreatic
cancer. PLoS One. 10:e01203322015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|