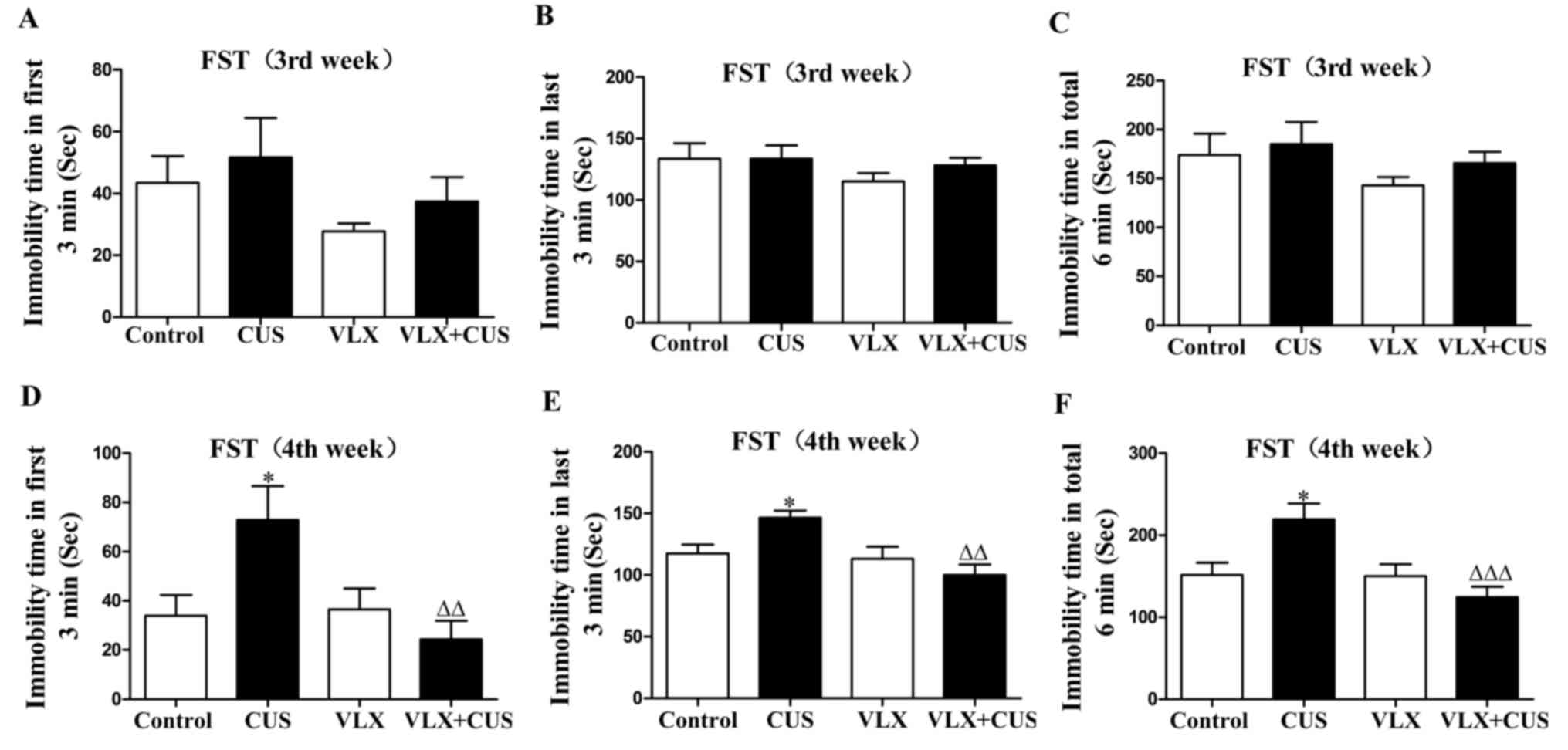
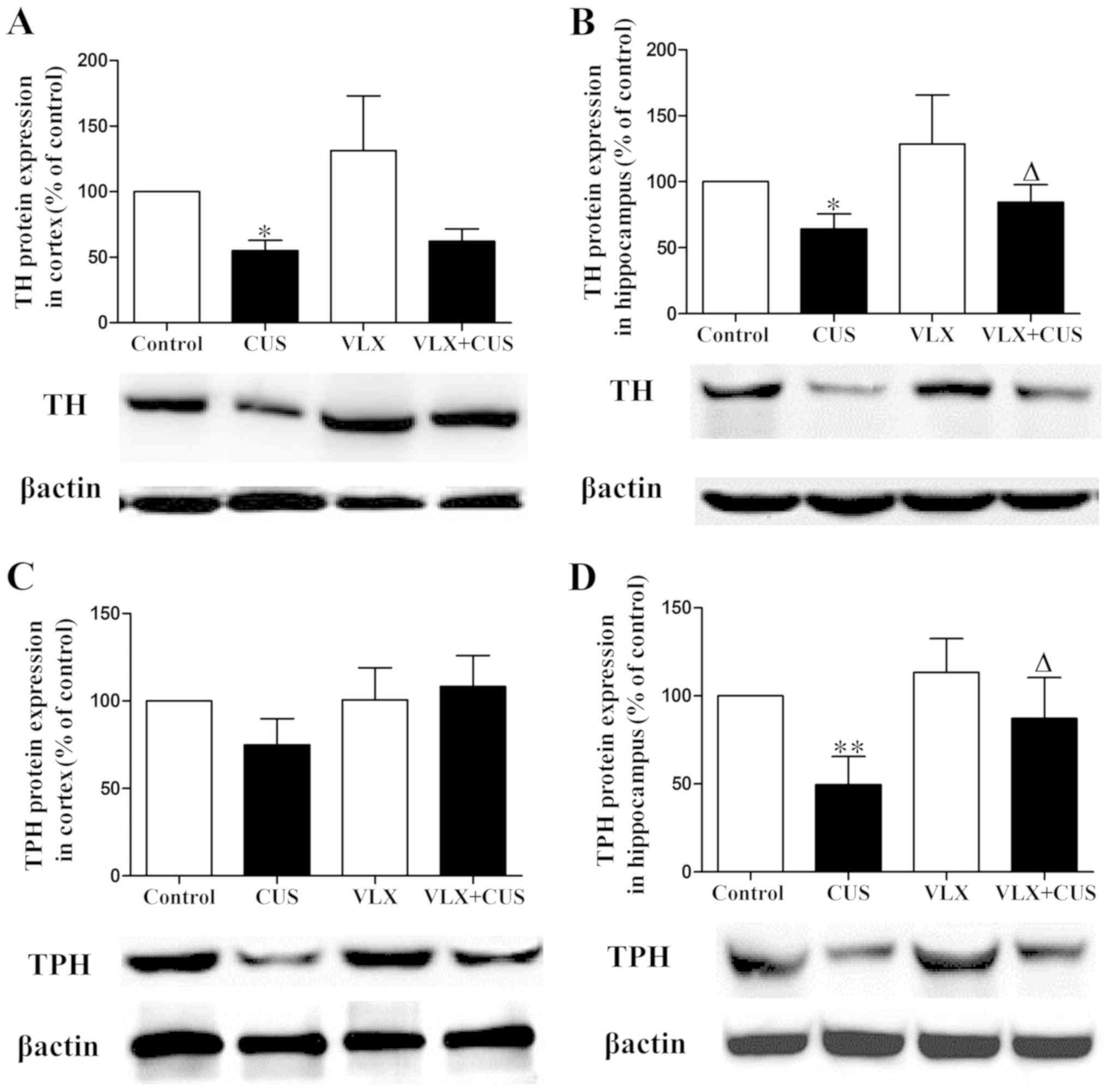
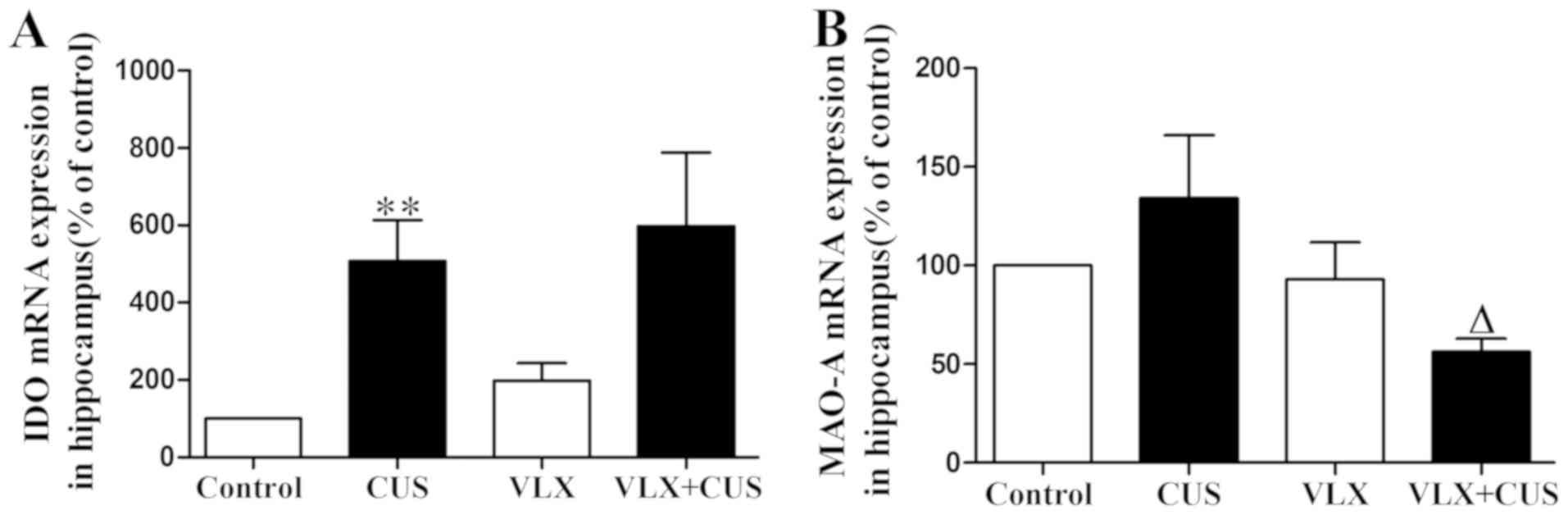
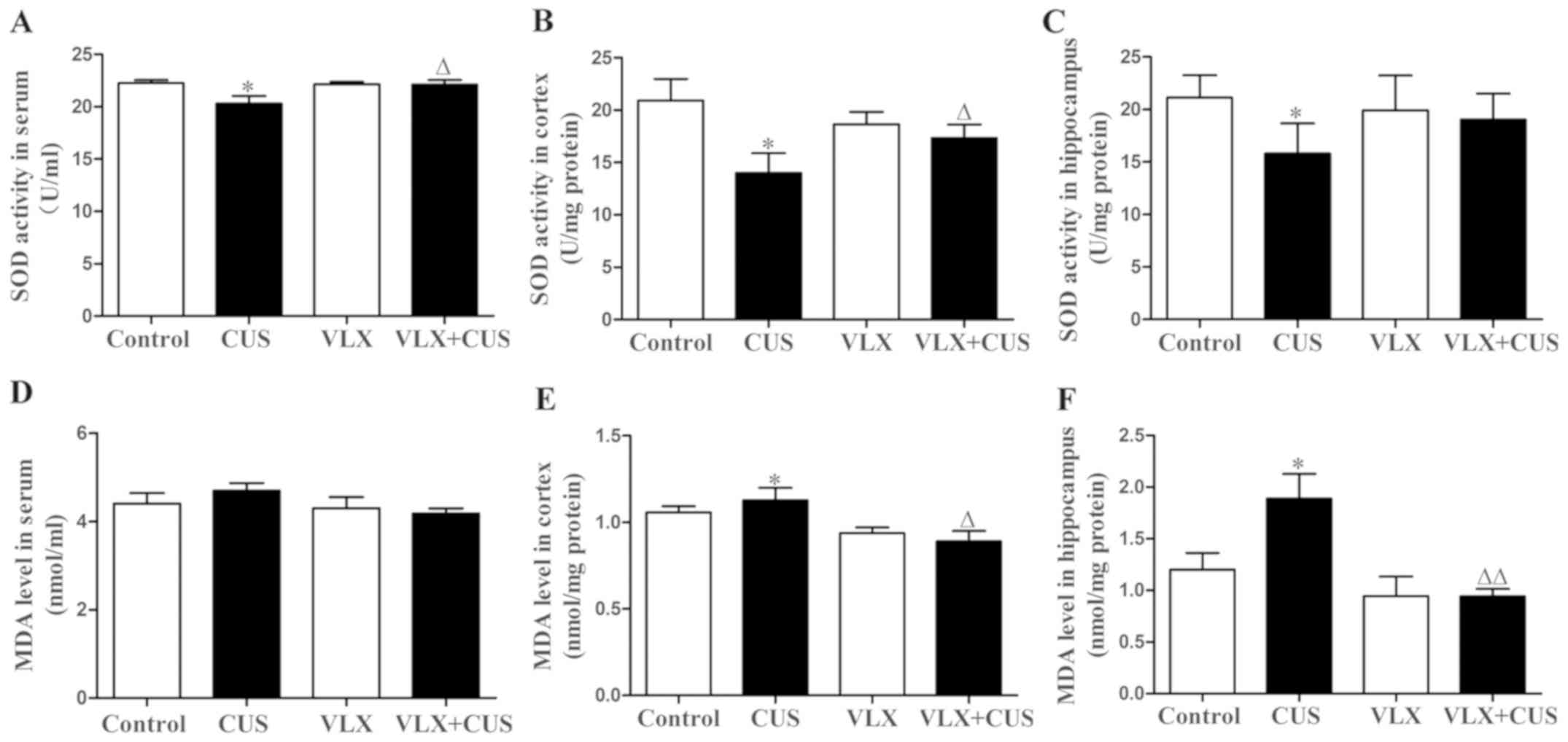
|
1
|
Hamon M and Blier P: Monoamine
neurocircuitry in depression and strategies for new treatments.
Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 45:54–63. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Biegon A and Fieldust S: Reduced tyrosine
hydroxylase immunoreactivity in locus coeruleus of suicide victims.
Synapse. 10:79–82. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dunčko R, Kiss A, Škultétyová I, Rusnák M
and Jezová D: Corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA levels in
response to chronic mild stress rise in male but not in female rats
while tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA levels decrease in both sexes.
Psychoneuroendocrinology. 26:77–89. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Heydendael W and Jacobson L: Widespread
hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical axis-relevant and
mood-relevant effects of chronic fluoxetine treatment on
glucocorticoid receptor gene expression in mice. Eur J Neurosci.
31:892–902. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Avgustinovich DF, Alekseenko OV,
Bakshtanovskaia IV, Koriakina LA, Lipina TV, Tenditnik MV, Bondar'
NP, Kovalenko IL and Kudriavtseva NN: Dynamic changes of brain
serotonergic and dopaminergic activities during development of
anxious depression: Experimental study. Usp Fiziol Nauk. 35:19–40.
2004.(In Russian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Savelieva KV, Zhao S, Pogorelov VM, Rajan
I, Yang Q, Cullinan E and Lanthorn TH: Genetic disruption of both
tryptophan hydroxylase genes dramatically reduces serotonin and
affects behavior in models sensitive to antidepressants. PLoS One.
3:e33012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang FZ, Wu Y, Zhang WG, Cai YY and Shi
SX: Estradiol or fluoxetine alters depressive behavior and
tryptophan hydroxylase in rat raphe. Neuroreport. 21:309–312. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shishkina GT, Kalinina TS and Dygalo NN:
Up-regulation of tryptophan hydroxylase-2 mRNA in the rat brain by
chronic fluoxetine treatment correlates with its antidepressant
effect. Neuroscience. 150:404–412. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim SW, Park SY and Hwang O: Up-regulation
of tryptophan hydroxylase expression and serotonin synthesis by
sertraline. Mol Pharmacol. 61:778–785. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin Y, Wang N, Zhang X, Han X, Zhai X and
Lu Y: IDO and TDO as a potential therapeutic target in different
types of depression. Metab Brain Dis. 33:1787–1800. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Christmas DM, Potokar J and Davies SJ: A
biological pathway linking inflammation and depression: Activation
of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.
7:431–439. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Samelson-Jones BJ and Yeh SR: Interactions
between nitric oxide and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase. Biochemistry.
45:8527–8538. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Myint AM and Kim YK: Cytokine-serotonin
interaction through IDO: A neurodegeneration hypothesis of
depression. Med Hypotheses. 61:519–525. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dantzer R, O'Connor JC, Freund GG, Johnson
RW and Kelley KW: From inflammation to sickness and depression:
When the immune system subjugates the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci.
9:46–56. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dobos N, deVries EF, Kema IP, Patas K,
Prins M, Nijholt IM, Dierckx RA, Korf J, den Boer JA, Luiten PG and
Eisel UL: The role of indoleamine 2, 3- dioxygenase in a mouse
model of neuroinflammation-induced depression. J Alzheimers Dis.
28:905–915. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Stefanescu C and Ciobica A: The relevance
of oxidative stress status in first episode and recurrent
depression. J Affect disord. 143:34–38. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Naoi M, Maruyama W and Shamoto-Nagai M:
Type A monoamine oxidase and serotonin are coordinately involved in
depressive disorders: From neurotransmitter imbalance to impaired
neurogenesis. J Neural Transmission (Vienna). 125:53–66. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Buckholtz JW and Meyer-Lindenberg A: MAOA
and the neurogenetic architecture of human aggression. Trends
Neurosci. 31:120–129. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Meyer JH, Ginovart N, Boovariwala A,
Sagrati S, Hussey D, Garcia A, Young T, Praschak-Rieder N, Wilson
AA and Houle S: Elevated monoamine oxidase a levels in the brain:
An explanation for the monoamine imbalance of major depression.
Arch Gen Psychiatry. 63:1209–1216. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grunewald M, Johnson S, Lu D, Wang Z,
Lomberk G, Albert PR, Stockmeier CA, Meyer JH, Urrutia R, Miczek
KA, et al: Mechanistic role for a novel glucocorticoid-KLF11
(TIEG2) protein pathway in stress-induced monoamine oxidase A
expression. J Biol Chem. 287:24195–24206. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bonnet U: Moclobemide: Therapeutic use and
clinical studies. CNS Drug Rev. 9:97–140. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Elhwuegi AS: Central monoamines and their
role in major depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol
Psychiatry. 28:435–451. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ye Y, Wang G, Wang H and Wang X:
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) infusion restored
astrocytic plasticity in the hippocampus of a rat model of
depression. Neurosci Lett. 503:15–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Grundmann O, Lv Y, Kelber O and Butterweck
V: Mechanism of St. John's wort extract (STW3-VI)during chronic
restraint stress is mediated by the interrelationship of the
immune, oxidative defense, and neuroendocrine system.
Neuropharmacology. 58:767–773. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Makino M, Kitano Y, Komiyama C and
Takasuna K: Human interferon-alpha increases immobility in the
forced swimming test in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl).
148:106–110. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M and Ahmad N: Dose
translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J.
22:659–661. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Watanabe Y, Asami Y, Hirano Y, Kuribayashi
K, Itamura R and Imaeda T: Factors impacting the efficacy of
venlafaxine extended release 75–225 mg/day in patients with major
depressive disorder: Exploratory post hoc subgroup analyses of a
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study in Japan.
Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 14:1261–1272. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Szkutnik-Fiedler D, Kus K, Balcerkiewicz
M, Grześkowiak E, Nowakowska E, Burda K, Ratajczak P and Sadowski
C: Concomitant use of tramadol and venlafaxine–evaluation of
antidepressant-like activity and other behavioral effects in rats.
Pharmacol Rep. 64:1350–1358. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yilmaz N, Demirdas A, Yilmaz M, Sutcu R,
Kirbas A, Cure MC and Eren I: Effects of venlafaxine and
escitalopram treatments on NMDA receptors in the rat depression
model. J Membr Biol. 242:145–151. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao Y, Ma R, Shen J, Su H, Xing D and Du
L: A mouse model of depression induced by repeated corticosterone
injections. Eur J Pharmacol. 581:113–120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brady LS, Gold PW, Herkenham M, Lynn AB
and Whitfield HJ Jr: The antidepressants fluoxetine, idazoxan and
phenelzine alter corticotropin-releasing hormone and tyrosine
hydroxylase mRNA levels in rat brain: Therapeutic implications.
Brain Res. 572:117–125. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sung YH, Shin MS, Cho S, Baik HH, Jin BK,
Chang HK, Lee EK and Kim CJ: Depression-like state in maternal rats
induced by repeated separation of pups is accompanied by a decrease
of cell proliferation and an increase of apoptosis in the
hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 470:86–90. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhao X, Seese RR, Yun K, Peng T and Wang
Z: The role of galanin system in modulating depression, anxiety,
and addiction-like behaviors after chronic restraint stress.
Neuroscience. 246:82–93. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Abumaria N, Rygula R, Hiemke C, Fuchs E,
Havemann-Reinecke U, Rüther E and Flügge G: Effect of chronic
citalopram on serotonin-related and stress-regulated genes in the
dorsal raphe nucleus of the rat. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol.
17:417–429. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Klomp A, Václavů L, Meerhoff GF, Reneman L
and Lucassen PJ: Effects of chronic fluoxetine treatment on
neurogenesis and tryptophan hydroxylase expression in adolescent
and adult rats. PLoS One. 9:e976032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Maes M, Leonard BE, Myint AM, Kubera M and
Verkerk R: The new ‘5-HT’ hypothesis of depression: Cell-mediated
immune activation induces indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase, which leads
to lower plasma tryptophan and an increased synthesis of
detrimental tryptophan catabolites (TRYCATs), both of which
contribute to the onset of depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol
Biol Psychiatry. 35:702–721. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Liu YN, Peng YL, Liu L, Wu TY, Zhang Y,
Lian YJ, Yang YY, Kelley KW, Jiang CL and Wang YX: TNFα mediates
stress-induced depression by upregulating indoleamine 2,
3-dioxygenase in a mouse model of unpredictable chronic mild
stress. Eur Cytokine Netw. 26:15–25. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Raison CL, Dantzer R, Kelley KW, Lawson
MA, Woolwine BJ, Vogt G, Spivey JR, Saito K and Miller AH: CSF
concentrations of brain tryptophan and kynurenines during immune
stimulation with IFN-alpha: Relationship to CNS immune responses
and depression. Mol Psychiatry. 15:393–403. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mohamed BM, Aboul-Fotouh S, Ibrahim EA,
Shehata H, Mansour AA, Yassin NA, El-Eraky W and Abdel-Tawab AM:
Effects of pentoxifylline, 7-nitroindazole, and imipramine on tumor
necrosis factor-α and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase enzyme activity
in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of chronic
mild-stress-exposed rats. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 9:697–708.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Thomas J, Khanam R and Vohora D:
Augmentation of antidepressant effects of venlafaxine by
agomelatine in mice are independent of kynurenine pathway.
Neurochem Int. 99:103–109. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Schulze TG, Müller DJ, Krauss H, Scherk H,
Ohlraun S, Syagailo YV, Windemuth C, Neidt H, Grässle M,
Papassotiropoulos A, et al: Association between a functional
polymorphism in the monoamine oxidase A gene promoter and major
depressive disorder. Am J Med Genet. 96:801–803. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Duncan J, Johnson S and Ou XM: Monoamine
oxidases in major depressive disorder and alcoholism. Drug Discov
Ther. 6:112–122. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mattson MP, Maudsley S and Martin B: BDNF
and 5-HT: A dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and
neurodegenerative disorders. Trends Neurosci. 27:588–594. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Doyle A, Hucklebridge F, Evans P and Clow
A: Salivary monoamine oxidase A and B inhibitory activities
correlate with stress. Life Sci. 59:1357–1362. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Filipenko ML, Beilina AG, Alekseyenko OV,
Dolgov VV and Kudryavtseva NN: Repeated experience of social
defeats increases serotonin transporter and monoamine oxidase A
mRNA levels in raphe nuclei of male mice. Neurosci Lett. 321:25–28.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Sacher J, Wilson AA, Houle S, Rusjan P,
Hassan S, Bloomfield PM, Stewart DE and Meyer JH: Elevated brain
monoamine oxidase A binding in the early postpartum period. Arch
Gen Psychiatry. 67:468–474. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rekkas PV, Wilson AA, Lee VW, Yogalingam
P, Sacher J, Rusjan P, Houle S, Stewart DE, Kolla NJ, Kish S, et
al: Greater monoamine oxidase a binding in perimenopausal age as
measured with carbon 11-labeled harmine positron emission
tomography. JAMA Psychiatry. 71:873–879. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Fisar Z, Hroudová J and Raboch J:
Inhibition of monoamine oxidase activity by antidepressants and
mood stabilizers. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 31:645–656.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|