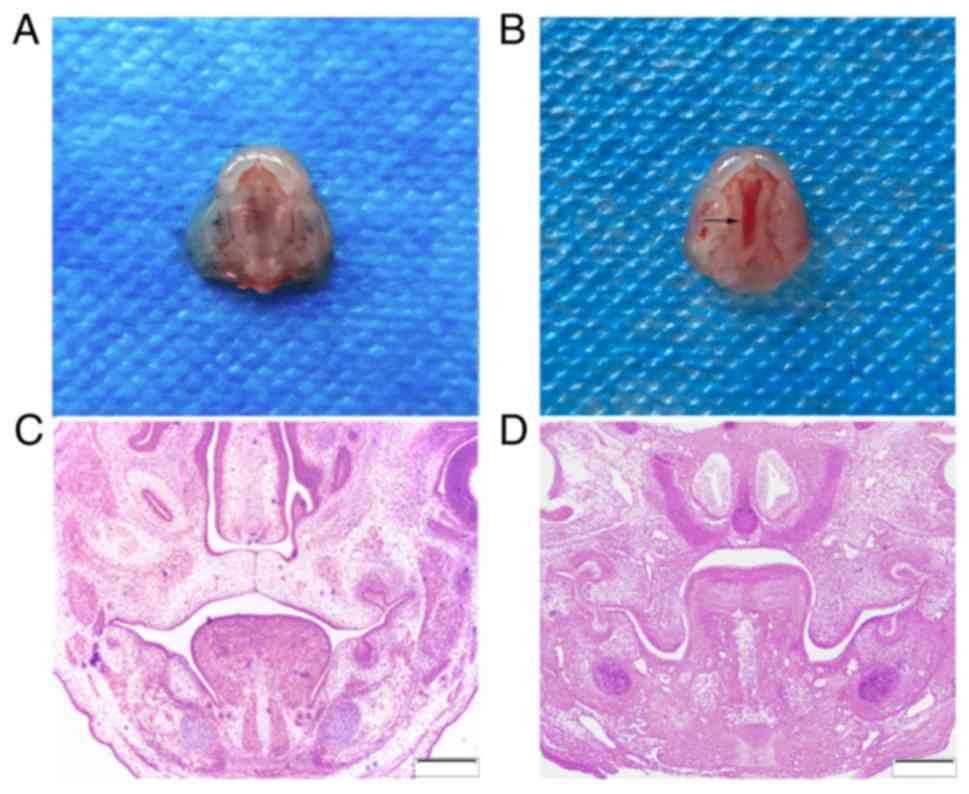
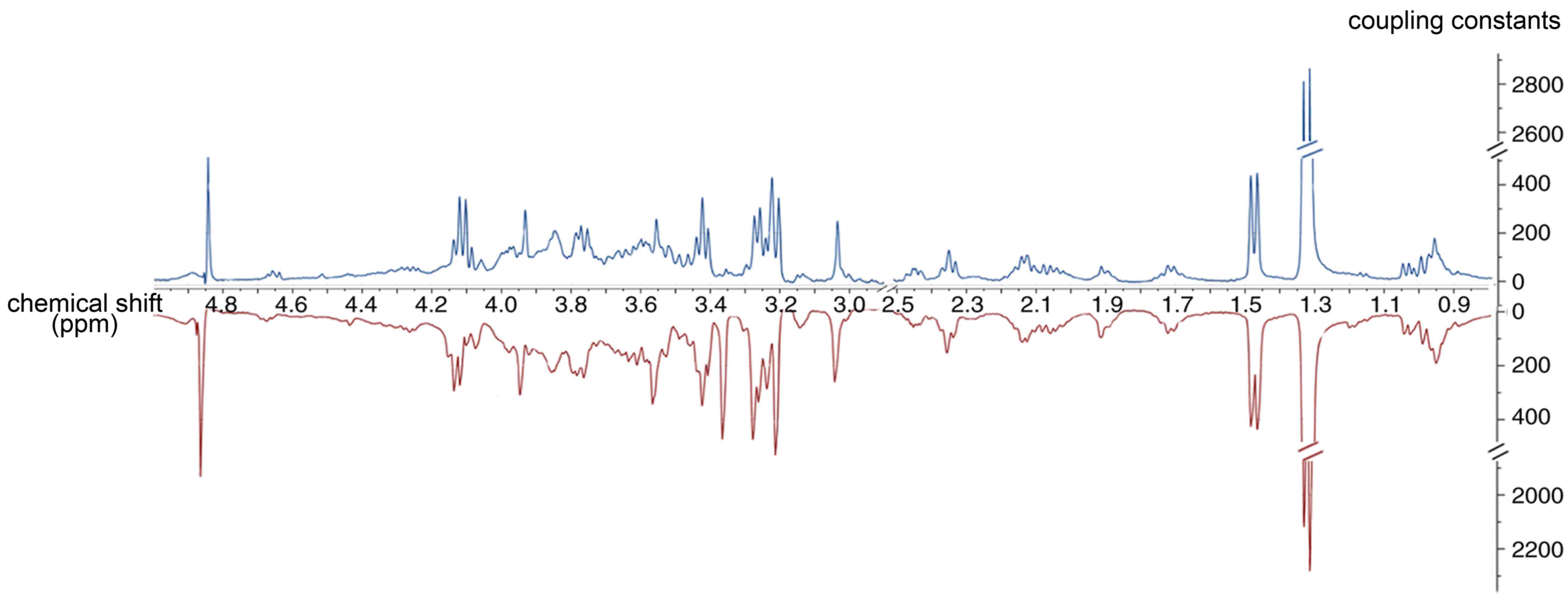
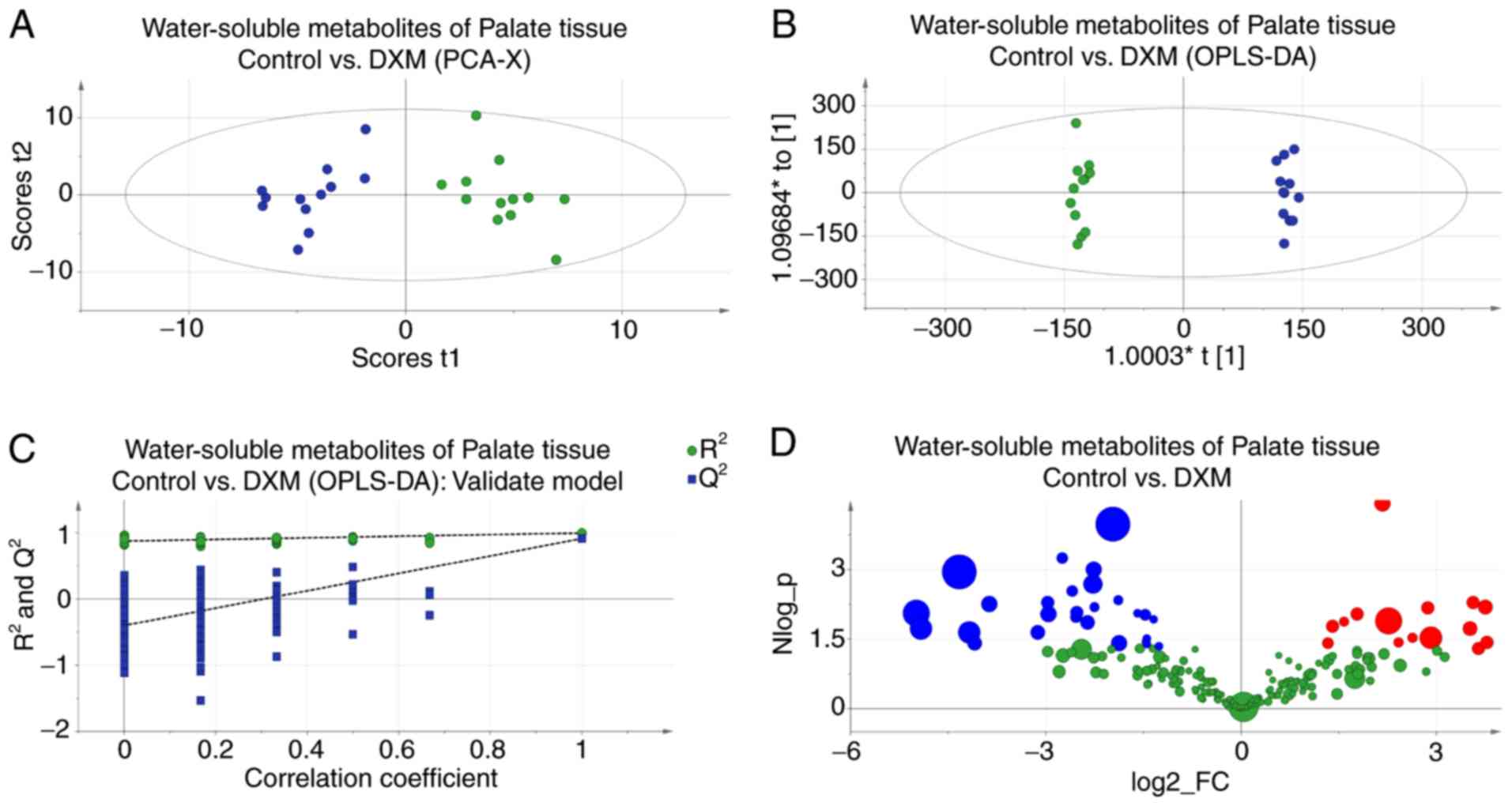
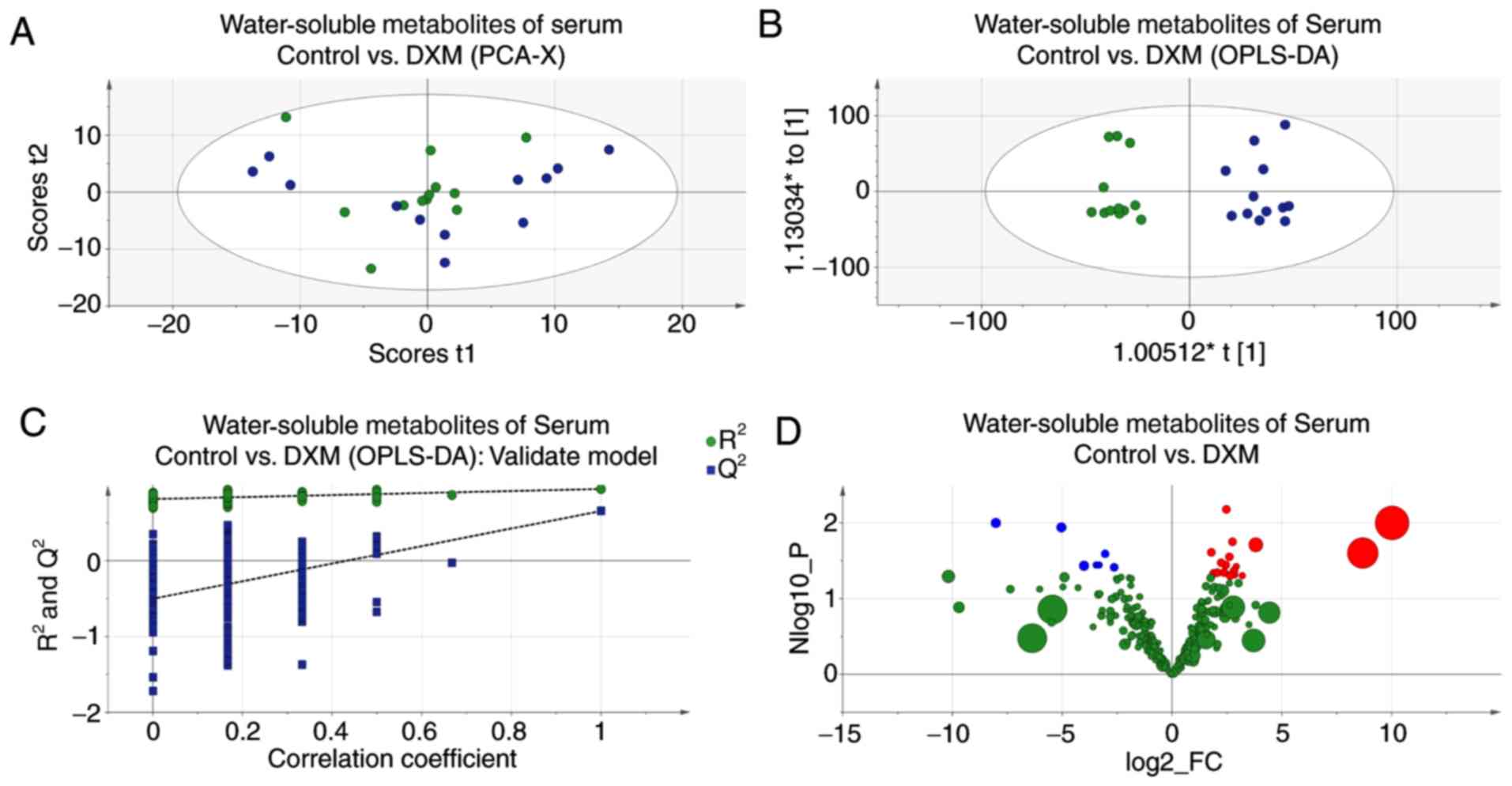
|
1
|
Mossey PA, Little J, Munger RG, Dixon MJ
and Shaw WC: Cleft lip and palate. Lancet. 374:1773–1785. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Watkins SE, Meyer RE, Strauss RP and
Aylsworth AS: Classification, epidemiology, and genetics of
orofacial clefts. Clin Plast Surg. 41:149–163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tang Q, Li L, Jin C, Lee JM and Jung HS:
Role of region-distinctive expression of Rac1 in regulating
fibronectin arrangement during palatal shelf elevation. Cell Tissue
Res. 361:857–868. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bush JO and Jiang R: Palatogenesis:
Morphogenetic and molecular mechanisms of secondary palate
development. Development. 139:231–243. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ozmen A, Unek G and Korgun ET: Effect of
glucocorticoids on mechanisms of placental angiogenesis. Placenta.
52:41–48. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bandoli G, Palmsten K, Forbess Smith CJ
and Chambers CD: A review of systemic corticosteroid use in
pregnancy and the risk of select pregnancy and birth outcomes.
Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 43:489–502. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bauer MK, Harding JE, Bassett NS, Breier
BH, Oliver MH, Gallaher BH, Evans PC, Woodall SM and Gluckman PD:
Fetal growth and placental function. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
140:115–120. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jahanbin A, Shadkam E, Miri HH, Shirazi AS
and Abtahi M: Maternal folic acid supplementation and the risk of
oral clefts in offspring. J Craniofac Surg. 29:e534–e541. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Suhl J, Romitti PA, Cao Y, Rocheleau CM,
Burns TL, Conway K, Rajaraman P, Agopian AJ and Stewart P; National
Birth Defects Prevention Study, : Maternal occupational cadmium
exposure and nonsyndromic orofacial clefts. Birth Defects Res.
110:603–609. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Waller DK, Hashmi SS, Hoyt AT, Duong HT,
Tinker SC, Gallaway MS, Olney RS, Finnell RH, Hecht JT and Canfield
MA; National Birth Defects Prevention Study, : Maternal report of
fever from cold or flu during early pregnancy and the risk for
noncardiac birth defects, National Birth Defects Prevention Study,
1997–2011. Birth Defects Res. 110:342–351. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bax BE and Bloxam DL: Energy metabolism
and glycolysis in human placental trophoblast cells during
differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1319:283–292. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Baardman ME, Kerstjens-Frederikse WS,
Berger RM, Bakker MK, Hofstra RM and Plösch T: The role of
maternal-fetal cholesterol transport in early fetal life: Current
insights. Biol Reprod. 88:242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cetin I, Ronzoni S, Marconi AM, Perugino
G, Corbetta C, Battaglia FC and Pardi G: Maternal concentrations
and fetal-maternal concentration differences of plasma amino acids
in normal and intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 174:1575–1583. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dubé E, Gravel A, Martin C, Desparois G,
Moussa I, Ethier-Chiasson M, Forest JC, Giguère Y, Masse A and
Lafond J: Modulation of fatty acid transport and metabolism by
maternal obesity in the human full-term placenta. Biol Reprod.
87:14, 1–11. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gil-Sánchez A, Koletzko B and Larqué E:
Current understanding of placental fatty acid transport. Curr Opin
Clin Nutr Metab Care. 15:265–272. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Paolini CL, Marconi AM, Ronzoni S, Di Noio
M, Fennessey PV, Pardi G and Battaglia FC: Placental transport of
leucine, phenylalanine, glycine, and proline in intrauterine
growth-restricted pregnancies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
86:5427–5432. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Skuladottir H, Wilcox AJ, Ma C, Lammer EJ,
Rasmussen SA, Werler MM, Shaw GM and Carmichael SL: Corticosteroid
use and risk of orofacial clefts. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol
Teratol. 100:499–506. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pinsky L and Digeorge AM: Cleft palate in
the mouse: A teratogenic index of gluocorticoid potency. Science.
147:402–403. 1965. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hu X, Gao JH, Liao YJ, Tang SJ and Lu F:
Dexamethasone alters epithelium proliferation and survival and
suppresses Wnt/β-catenin signaling in developing cleft palate. Food
Chem Toxicol. 56:67–74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lan SJ, Yang XG, Chen Z, Yang TY, Xiang
CH, Zhang D, Li YX and Rong L: Role of GATA-6 and bone
morphogenetic protein-2 in dexamethasone-induced cleft palate
formation in institute of cancer research mice. J Craniofac Surg.
27:1600–1605. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Carmichael SL, Shaw GM, Ma C, Werler MM,
Rasmussen SA and Lammer EJ; National Birth Defects Prevention
Study, : Maternal corticosteroid use and orofacial clefts. Am J
Obstet Gynecol. 197:585.e1–7. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Pratt RM: Receptor-dependent mechanisms of
glucocorticoid and dioxin-induced cleft palate. Environ Health
Perspect. 61:35–40. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Laura H, Wilson SF, Lunte CE and Larive
CK: Concentration profiling in rat tissue by high-resolution
magic-angle spinning NMR spectroscopy: Investigation of a model
drug. Anal Chem. 77:2978–2984. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Holmes E, Nicholls AW, Lindon JC, Connor
SC, Connelly JC, Haselden JN, Damment SJ, Spraul M, Neidig P and
Nicholson JK: Chemometric models for toxicity classification based
on NMR spectra of biofluids. Chem Res Toxicol. 13:471–478. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bogner W, Gruber S, Trattnig S and Chmelik
M: High-resolution mapping of human brain metabolites by free
induction decay (1)H MRSI at 7 T. NMR Biomed. 25:873–882. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin L, Cao B, Xu Z, Sui Y, Chen J, Luan Q,
Yang R, Li S and Li KF: In vivo HMRS and lipidomic profiling
reveals comprehensive changes of hippocampal metabolism during
aging in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 470:9–14. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nassirpour S, Chang P and Henning A: High
and ultra-high resolution metabolite mapping of the human brain
using 1H FID MRSI at 9.4T. Neuroimage. 168:211–221.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rao R, Tkac I, Schmidt AT and Georgieff
MK: Fetal and neonatal iron deficiency causes volume loss and
alters the neurochemical profile of the adult rat hippocampus. Nutr
Neurosci. 14:59–65. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song F, Wu W, Qian Z, Zhang G and Cheng Y:
Assessment of the placenta in intrauterine growth restriction by
diffusion-weighted imaging and proton magnetic resonance
spectroscopy. Reprod Sci. 24:575–581. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou J, Xu B, Huang J, Jia X, Xue J, Shi
X, Xiao L and Li W: 1H NMR-based metabonomic and pattern
recognition analysis for detection of oral squamous cell carcinoma.
Clin Chim Acta. 401:8–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Qin F, Shen Z, Peng L, Wu R, Hu X, Zhang G
and Tang S: Metabolic characterization of all-trans-retinoic acid
(ATRA)-induced craniofacial development of murine embryos using in
vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. PLoS One.
9:e960102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Czeizel AE and Rockenbauer M:
Population-based case-control study of teratogenic potential of
corticosteroids. Teratology. 56:335–340. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
van Runnard Heimel PJ, Franx A, Schobben
AF, Huisjes AJ, Derks JB and Bruinse HW: Corticosteroids,
pregnancy, and hellp syndrome: A review. Obstet Gynecol Surv.
60:57–70. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pradat P, Robert-Gnansia E, Di Tanna GL,
Rosano A, Lisi A and Mastroiacovo P; Contributors to the MADRE
database, : First trimester exposure to corticosteroids and oral
clefts. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 67:968–970. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Regazzi FM, Silva LCG, Lúcio CF, Veiga
GAL, Angrimani DSR, Kishi D, Barbosa MMM and Vannucchi CI:
Influence of prenatal maternal corticosteroid therapy on clinical
and metabolic features and pulmonary function of preterm newborn
puppies. Theriogenology. 97:179–185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schmidt AF, Kemp MW, Rittenschober-Böhm J,
Kannan PS, Usuda H, Saito M, Furfaro L, Watanabe S, Stock S, Kramer
BW, et al: Low-dose betamethasone-acetate for fetal lung maturation
in preterm sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 218:132.e1–132.e9. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Travers CP, Carlo WA, McDonald SA, Das A,
Bell EF, Ambalavanan N, Jobe AH, Goldberg RN, D'Angio CT, Stoll BJ,
et al: Mortality and pulmonary outcomes of extremely preterm
infants exposed to antenatal corticosteroids. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
218:130.e1–130 e13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xiao WL, Liu XY, Liu YS, Zhang DZ and Xue
LF: The relationship between maternal corticosteroid use and
orofacial clefts-a meta-analysis. Reprod Toxicol. 69:99–105. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Mitchell K, Kaul M and Clowse ME: The
management of rheumatic diseases in pregnancy. Scand J Rheumatol.
39:99–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Dobberthien BJ, Tessier AG and Yahya A:
Improved resolution of glutamate, glutamine and γ-aminobutyric acid
with optimized point-resolved spectroscopy sequence timings for
their simultaneous quantification at 9.4 T. NMR Biomed. 31:2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ramadan S Lin A and Stanwell P: Glutamate
and glutamine: A review of in vivo MRS in the human brain. NMR
Biomed. 26:1630–1646. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Meldrum BS: Glutamate as a
neurotransmitter in the brain- review of physiology and pathology.
J Nutr 130 (4S Suppl). 1007S–1015S. 2000.
|
|
43
|
Patel AB, de Graaf RA, Mason GF, Rothman
DL, Shulman RG and Behar KL: The contribution of GABA to glutamate
glutamine cycling and energy metabolism in the rat cortex in vivo.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:5588–5593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mi D, Li Z, Lim L, Li M, Moissidis M, Yang
Y, Gao T, Hu TX, Pratt T, Price DJ, et al: Early emergence of
cortical interneuron diversity in the mouse embryo. Science.
360:81–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li K and Xu E: The role and the mechanism
of gamma-aminobutyric acid during central nervous system
development. Neurosci Bull. 24:195–200. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Asada H, Kawamura Y, Maruyama K, Kume H,
Ding RG, Kanbara N, Kuzume H, Sanbo M, Yagi T and Obata K: Cleft
palate and decreased brain gamma-aminobutyric acid in mice lacking
the 67-kDa isoform of glutamic acid decarboxylase. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 94:6496–6499. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kakizaki T, Oriuchi N and Yanagawa Y:
GAD65/GAD67 double knockout mice exhibit intermediate severity in
both cleft palate and omphalocele compared with GAD67 knockout and
VGAT knockout mice. Neuroscience. 288:86–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Begley JK, Redpath TW, Bolan PJ and
Gilbert FJ: In vivo proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy of
breast cancer: A review of the literature. Breast Cancer Res.
14:2072012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|