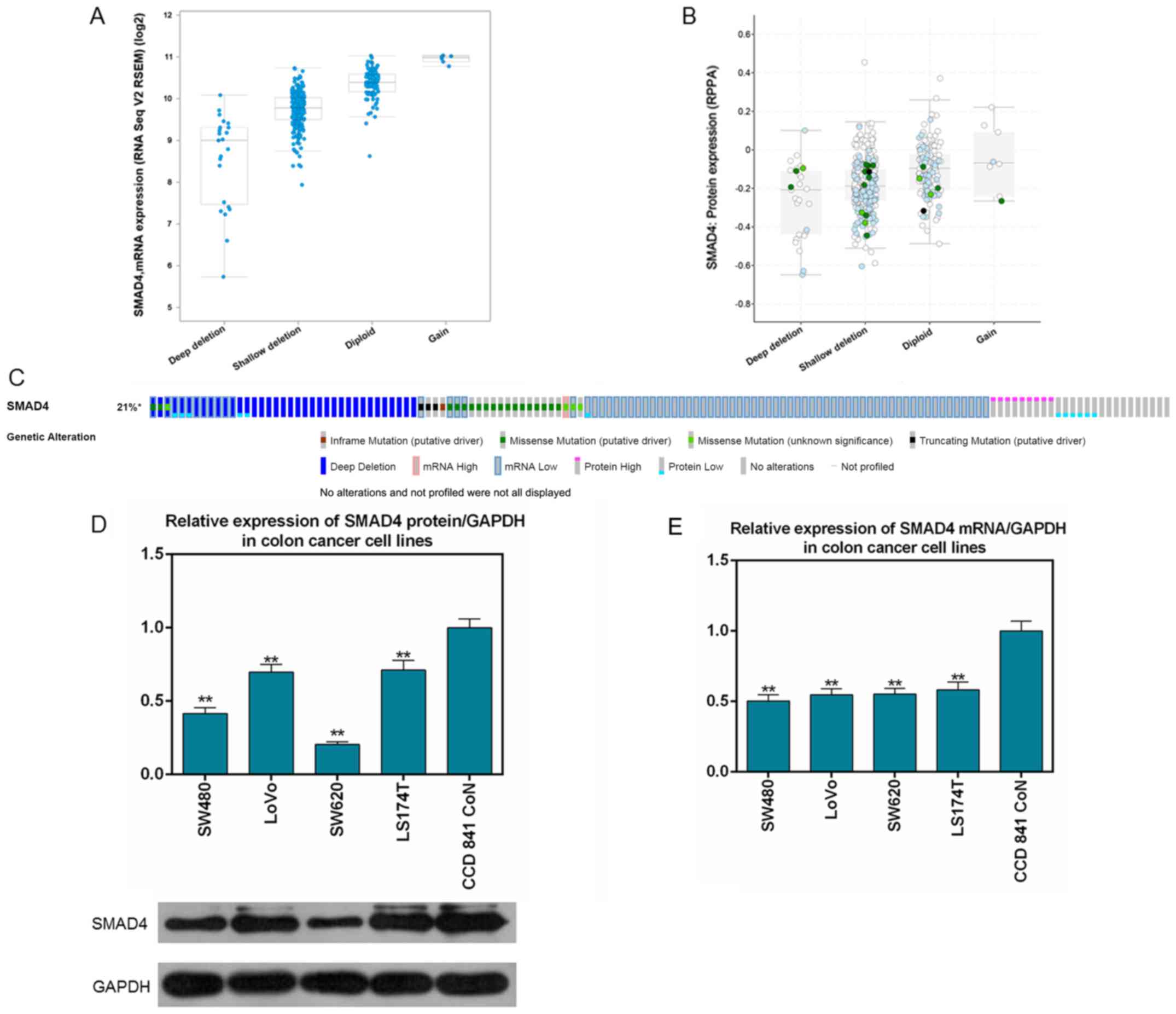
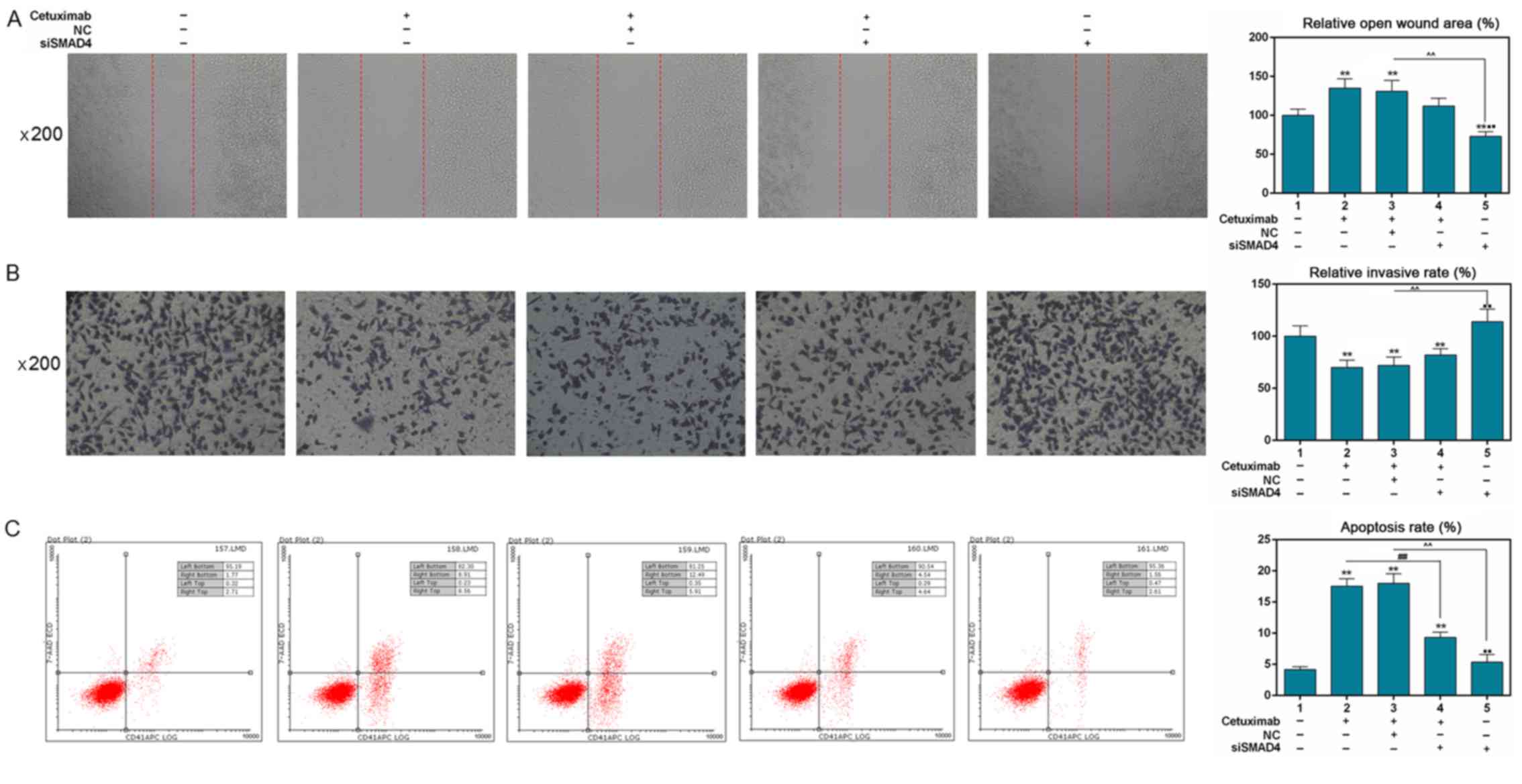
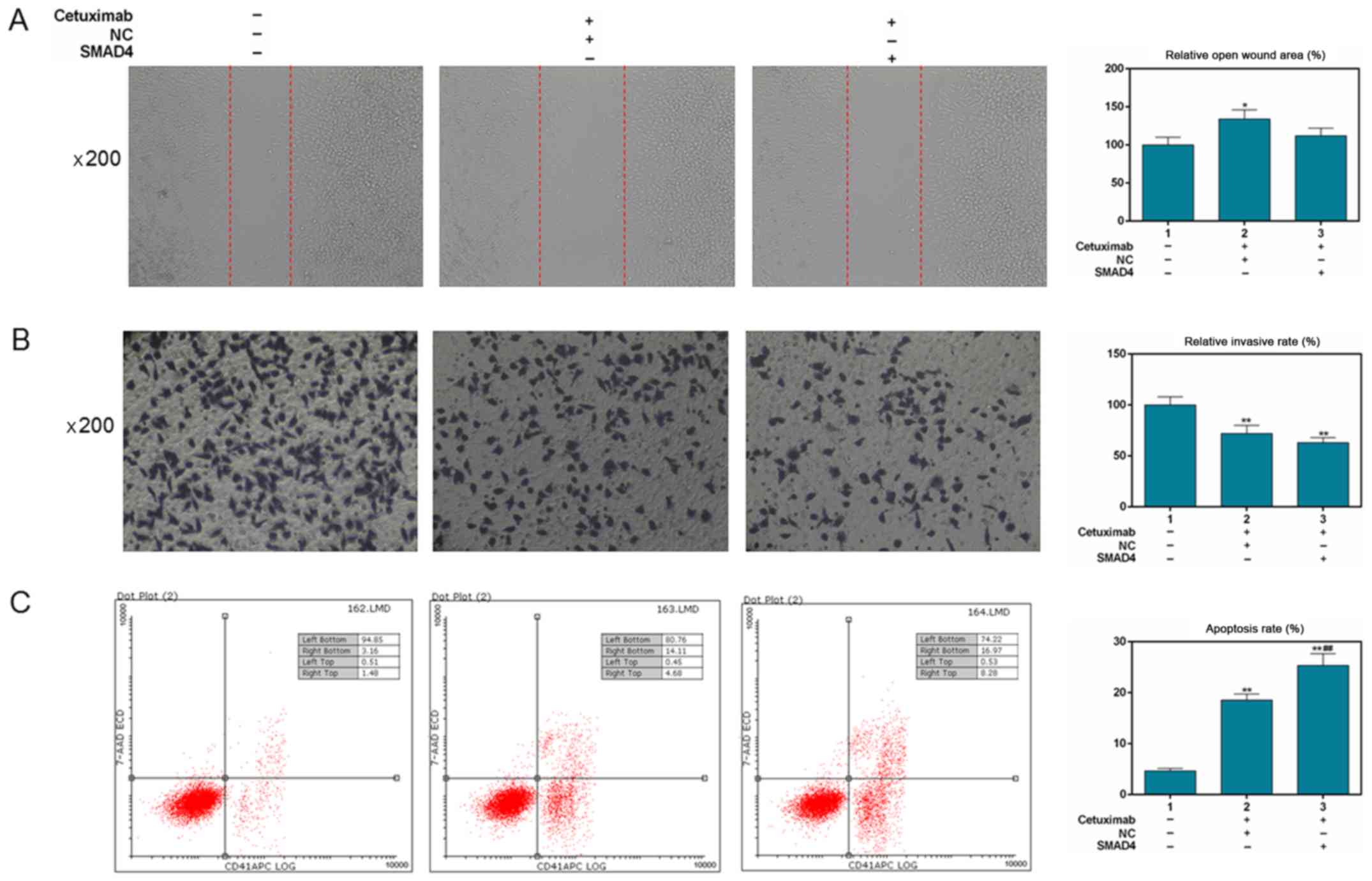
|
1
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
O'Connell MJ, Campbell ME, Goldberg RM,
Grothey A, Seitz JF, Benedetti JK, André T, Haller DG and Sargent
DJ: Survival following recurrence in stage II and III colon cancer:
Findings from the ACCENT data set. J Clin Oncol. 26:2336–2341.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Weitz J, Koch M, Debus J, Höhler T, Galle
PR and Büchler MW: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 365:153–165. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Van Cutsem E, Köhne CH, Láng I, Folprecht
G, Nowacki MP, Cascinu S, Shchepotin I, Maurel J, Cunningham D,
Tejpar S, et al: Cetuximab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and
leucovorin as first-line treatment for metastatic colorectal
cancer: Updated analysis of overall survival according to tumor
KRAS and BRAF mutation status. J Clin Oncol. 29:2011–2019. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Meyerhardt JA and Mayer RJ: Systemic
therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 352:476–487. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat
D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype
C, et al: Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in
irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med.
351:337–345. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Misale S, Di Nicolantonio F,
Sartore-Bianchi A, Siena S and Bardelli A: Resistance to anti-EGFR
therapy in colorectal cancer: From heterogeneity to convergent
evolution. Cancer Discov. 4:1269–1280. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bronte G, Silvestris N, Castiglia M,
Galvano A, Passiglia F, Sortino G, Cicero G, Rolfo C, Peeters M,
Bazan V, et al: New findings on primary and acquired resistance to
anti-EGFR therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer: Do all roads
lead to RAS? Oncotarget. 6:24780–24796. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Demagny H and De Robertis EM: Point
mutations in the tumor suppressor Smad4/DPC4 enhance its
phosphorylation by GSK3 and reversibly inactivate TGF-β signaling.
Mol Cell Oncol. 3:e10251812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Inamoto S, Itatani Y, Yamamoto T,
Minamiguchi S, Hirai H, Iwamoto M, Hasegawa S, Taketo MM, Sakai Y
and Kawada K: Loss of SMAD4 promotes colorectal cancer progression
by accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells through the
CCL15-CCR1 chemokine axis. Clin Cancer Res. 22:492–501. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Voorneveld PW, Kodach LL, Jacobs RJ, Liv
N, Zonnevylle AC, Hoogenboom JP, Biemond I, Verspaget HW, Hommes
DW, de Rooij K, et al: Loss of SMAD4 alters BMP signaling to
promote colorectal cancer cell metastasis via activation of Rho and
ROCK. Gastroenterology. 147:196–208.e113. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu L, Nie J, Chen L, Dong G, Du X, Wu X,
Tang Y and Han W: The oncogenic role of microRNA-130a/301a/454 in
human colorectal cancer via targeting Smad4 expression. PLoS One.
8:e555322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Alazzouzi H, Alhopuro P, Salovaara R,
Sammalkorpi H, Järvinen H, Mecklin JP, Hemminki A, Schwartz S Jr,
Aaltonen LA and Arango D: SMAD4 as a prognostic marker in
colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 11:2606–2611. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Alhopuro P, Alazzouzi H, Sammalkorpi H,
Dávalos V, Salovaara R, Hemminki A, Järvinen H, Mecklin JP,
Schwartz S Jr, Aaltonen LA and Arango D: SMAD4 levels and response
to 5-fluorouracil in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
11:6311–6316. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Losi L, Bouzourene H and Benhattar J: Loss
of Smad4 expression predicts liver metastasis in human colorectal
cancer. Oncol Rep. 17:1095–1099. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Miyaki M, Iijima T, Konishi M, Sakai K,
Ishii A, Yasuno M, Hishima T, Koike M, Shitara N, Iwama T, et al:
Higher frequency of Smad4 gene mutation in human colorectal cancer
with distant metastasis. Oncogene. 18:3098–3103. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shintani Y, Okimura A, Sato K, Nakagiri T,
Kadota Y, Inoue M, Sawabata N, Minami M, Ikeda N, Kawahara K, et
al: Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a determinant of
sensitivity to chemoradiotherapy in non-small cell lung cancer. Ann
Thorac Surg. 92:1794–1804. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tomono T, Yano K and Ogihara T:
Snail-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition enhances
P-gp-mediated multidrug resistance in HCC827 cells. J Pharm Sci.
106:2642–2649. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi Q, Diao Y, Jin F and Ding Z:
Antimetastatic effects of Aidi on human esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma by inhibiting epithelialmesenchymal transition and
angiogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 18:131–138. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zheng J, Zhang M, Zhang L, Ding X, Li W
and Lu S: HSPC159 promotes proliferation and metastasis via
inducing EMT and activating PI3K/Akt pathway in breast cancer.
Cancer Sci. 109:2153–2163. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kalluri R: EMT: When epithelial cells
decide to become mesenchymal-like cells. J Clin Invest.
119:1417–1419. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Greenburg G and Hay ED: Epithelia
suspended in collagen gels can lose polarity and express
characteristics of migrating mesenchymal cells. J Cell Biol.
95:333–339. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Brabletz T, Hlubek F, Spaderna S,
Schmalhofer O, Hiendlmeyer E, Jung A and Kirchner T: Invasion and
metastasis in colorectal cancer: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition,
mesenchymal-epithelial transition, stem cells and beta-catenin.
Cells Tissues Organs. 179:56–65. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Polyak K and Weinberg RA: Transitions
between epithelial and mesenchymal states: Acquisition of malignant
and stem cell traits. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:265–273. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moon SU, Kang MH, Sung JH, Kim JW, Lee JO,
Kim YJ, Lee KW, Bang SM, Lee JS and Kim JH: Effect of Smad3/4 on
chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol
Rep. 33:185–192. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang B, Zhang B, Chen X, Bae S, Singh K,
Washington MK and Datta PK: Loss of Smad4 in colorectal cancer
induces resistance to 5-fluorouracil through activating Akt
pathway. Br J Cancer. 110:946–957. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Papageorgis P, Cheng K, Ozturk S, Gong Y,
Lambert AW, Abdolmaleky HM, Zhou JR and Thiagalingam S: Smad4
inactivation promotes malignancy and drug resistance of colon
cancer. Cancer Res. 71:998–1008. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun C, Wang FJ, Zhang HG, Xu XZ, Jia RC,
Yao L and Qiao PF: miR-34a mediates oxaliplatin resistance of
colorectal cancer cells by inhibiting macroautophagy via
transforming growth factor-β/Smad4 pathway. World J Gastroenterol.
23:1816–1827. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhao S, Venkatasubbarao K, Lazor JW,
Sperry J, Jin C, Cao L and Freeman JW: Inhibition of STAT3 Tyr705
phosphorylation by Smad4 suppresses transforming growth factor
beta-mediated invasion and metastasis in pancreatic cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 68:4221–4228. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang H, Rajan S, Liu G and Chakrabarty S:
Transforming growth factor beta suppresses beta-catenin/Wnt
signaling and stimulates an adhesion response in human colon
carcinoma cells in a Smad4/DPC4 independent manner. Cancer Lett.
264:281–287. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Barros R, Pereira B, Duluc I, Azevedo M,
Mendes N, Camilo V, Jacobs RJ, Paulo P, Santos-Silva F, van
Seuningen I, et al: Key elements of the BMP/SMAD pathway
co-localize with CDX2 in intestinal metaplasia and regulate CDX2
expression in human gastric cell lines. J Pathol. 215:411–420.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang S, Zhang F, Miao L, Zhang H, Fan Z,
Wang X and Ji G: Lentiviral-mediated Smad4 RNAi induced
anti-proliferation by p16 up-regulation and apoptosis by caspase 3
down-regulation in hepatoma SMMC-7721 cells. Oncol Rep.
20:1053–1059. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Druliner BR, Ruan X, Sicotte H, O'Brien D,
Liu H, Kocher JA and Boardman L: Early genetic aberrations in
patients with sporadic colorectal cancer. Mol Carcinog. 57:114–124.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Al-Shamsi HO, Jones J, Fahmawi Y, Dahbour
I, Tabash A, Abdel-Wahab R, Abousamra AO, Shaw KR, Xiao L, Hassan
MM, et al: Molecular spectrum of KRAS, NRAS, BRAF, PIK3CA, TP53,
and APC somatic gene mutations in Arab patients with colorectal
cancer: Determination of frequency and distribution pattern. J
Gastrointest Oncol. 7:882–902. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Müller MF, Ibrahim AE and Arends MJ:
Molecular pathological classification of colorectal cancer.
Virchows Arch. 469:125–134. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mehrvarz Sarshekeh A, Advani S, Overman
MJ, Manyam G, Kee BK, Fogelman DR, Dasari A, Raghav K, Vilar E,
Manuel S, et al: Association of SMAD4 mutation with patient
demographics, tumor characteristics, and clinical outcomes in
colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 12:e01733452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang C, Zhou Y, Ruan R, Zheng M, Han W and
Liao L: High expression of COUP-TF II cooperated with negative
Smad4 expression predicts poor prognosis in patients with
colorectal cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:7112–7121.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mei Z, Shao YW, Lin P, Cai X, Wang B, Ding
Y, Ma X, Wu X, Xia Y, Zhu D, et al: SMAD4 and NF1 mutations as
potential biomarkers for poor prognosis to cetuximab-based therapy
in Chinese metastatic colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer.
18:4792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang B, Leng C, Wu C, Zhang Z, Dou L, Luo
X, Zhang B and Chen X: Smad4 sensitizes colorectal cancer to
5-fluorouracil through cell cycle arrest by inhibiting the
PI3K/Akt/CDC2/survivin cascade. Oncol Rep. 35:1807–1815. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ozawa H, Ranaweera RS, Izumchenko E,
Makarev E, Zhavoronkov A, Fertig EJ, Howard JD, Markovic A, Bedi A,
Ravi R, et al: SMAD4 loss is associated with cetuximab resistance
and induction of MAPK/JNK activation in head and neck cancer cells.
Clin Cancer Res. 23:5162–5175. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Cheng H, Fertig EJ, Ozawa H, Hatakeyama H,
Howard JD, Perez J, Considine M, Thakar M, Ranaweera R, Krigsfeld G
and Chung CH: Decreased SMAD4 expression is associated with
induction of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cetuximab
resistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biol
Ther. 16:1252–1258. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang F, Xia X, Yang C, Shen J, Mai J, Kim
HC, Kirui D, Kang Y, Fleming JB, Koay EJ, et al: SMAD4 gene
mutation renders pancreatic cancer resistance to radiotherapy
through promotion of autophagy. Clin Cancer Res. 24:3176–3185.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sun FD, Wang PC, Luan RL, Zou SH and Du X:
MicroRNA-574 enhances doxorubicin resistance through
down-regulating SMAD4 in breast cancer cells. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol
Sci. 22:1342–1350. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shiou SR, Singh AB, Moorthy K, Datta PK,
Washington MK, Beauchamp RD and Dhawan P: Smad4 regulates claudin-1
expression in a transforming growth factor-beta-independent manner
in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res. 67:1571–1579. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xiao DS, Wen JF, Li JH, Hu ZL, Zheng H and
Fu CY: Effect of deleted pancreatic cancer locus 4 gene
transfection on biological behaviors of human colorectal carcinoma
cells. World J Gastroenterol. 11:348–352. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu SQ, Xu CY, Wu WH, Fu ZH, He SW, Qin MB
and Huang JA: Sphingosine kinase 1 promotes the metastasis of
colorectal cancer by inducing the epithelialmesenchymal transition
mediated by the FAK/AKT/MMPs axis. Int J Oncol. 54:41–52.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Thiery JP and Chopin D: Epithelial cell
plasticity in development and tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis
Rev. 18:31–42. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Potts JD and Runyan RB:
Epithelial-mesenchymal cell transformation in the embryonic heart
can be mediated, in part, by transforming growth factor beta. Dev
Biol. 134:392–401. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Brown CB, Boyer AS, Runyan RB and Barnett
JV: Requirement of type III TGF-beta receptor for endocardial cell
transformation in the heart. Science. 283:2080–2082. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Proetzel G, Pawlowski SA, Wiles MV, Yin M,
Boivin GP, Howles PN, Ding J, Ferguson MW and Doetschman T:
Transforming growth factor-beta 3 is required for secondary palate
fusion. Nat Genet. 11:409–414. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Kaartinen V, Voncken JW, Shuler C,
Warburton D, Bu D, Heisterkamp N and Groffen J: Abnormal lung
development and cleft palate in mice lacking TGF-beta 3 indicates
defects of epithelial-mesenchymal interaction. Nat Genet.
11:415–421. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Oft M, Peli J, Rudaz C, Schwarz H, Beug H
and Reichmann E: TGF-beta1 and Ha-Ras collaborate in modulating the
phenotypic plasticity and invasiveness of epithelial tumor cells.
Genes Dev. 10:2462–2477. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Battifora H: Spindle cell carcinoma:
Ultrastructural evidence of squamous origin and collagen production
by the tumor cells. Cancer. 37:2275–2282. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Buchmann A, Ruggeri B, Klein-Szanto AJ and
Balmain A: Progression of squamous carcinoma cells to spindle
carcinomas of mouse skin is associated with an imbalance of H-ras
alleles on chromosome 7. Cancer Res. 51:4097–4101. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Geiger T, Sabanay H, Kravchenko-Balasha N,
Geiger B and Levitzki A: Anomalous features of EMT during
keratinocyte transformation. PLoS One. 3:e15742008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Huber MA, Kraut N and Beug H: Molecular
requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor
progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 17:548–558. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Larue L and Bellacosa A:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: Role
of phosphatidylinositol 3′ kinase/AKT pathways. Oncogene.
24:7443–7454. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Thompson EW, Newgreen DF and Tarin D:
Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: A role for
epithelial-mesenchymal transition? Cancer Res. 65:5991–5995. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Fuchs BC, Fujii T, Dorfman JD, Goodwin JM,
Zhu AX, Lanuti M and Tanabe KK: Epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition and integrin-linked kinase mediate sensitivity to
epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in human hepatoma
cells. Cancer Res. 68:2391–2399. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu Y, Li Y, Wang R, Qin S, Liu J, Su F,
Yang Y, Zhao F, Wang Z and Wu Q: MiR-130a-3p regulates cell
migration and invasion via inhibition of Smad4 in gemcitabine
resistant hepatoma cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:192016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wen Z, Feng S, Wei L, Wang Z, Hong D and
Wang Q: Evodiamine, a novel inhibitor of the Wnt pathway, inhibits
the self-renewal of gastric cancer stem cells. Int J Mol Med.
36:1657–1663. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Della Corte CM, Bellevicine C, Vicidomini
G, Vitagliano D, Malapelle U, Accardo M, Fabozzi A, Fiorelli A,
Fasano M, Papaccio F, et al: SMO gene amplification and activation
of the hedgehog pathway as novel mechanisms of resistance to
anti-epidermal growth factor receptor drugs in human lung cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 21:4686–4697. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Güngör C, Zander H, Effenberger KE,
Vashist YK, Kalinina T, Izbicki JR, Yekebas E and Bockhorn M: Notch
signaling activated by replication stress-induced expression of
midkine drives epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 71:5009–5019.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|