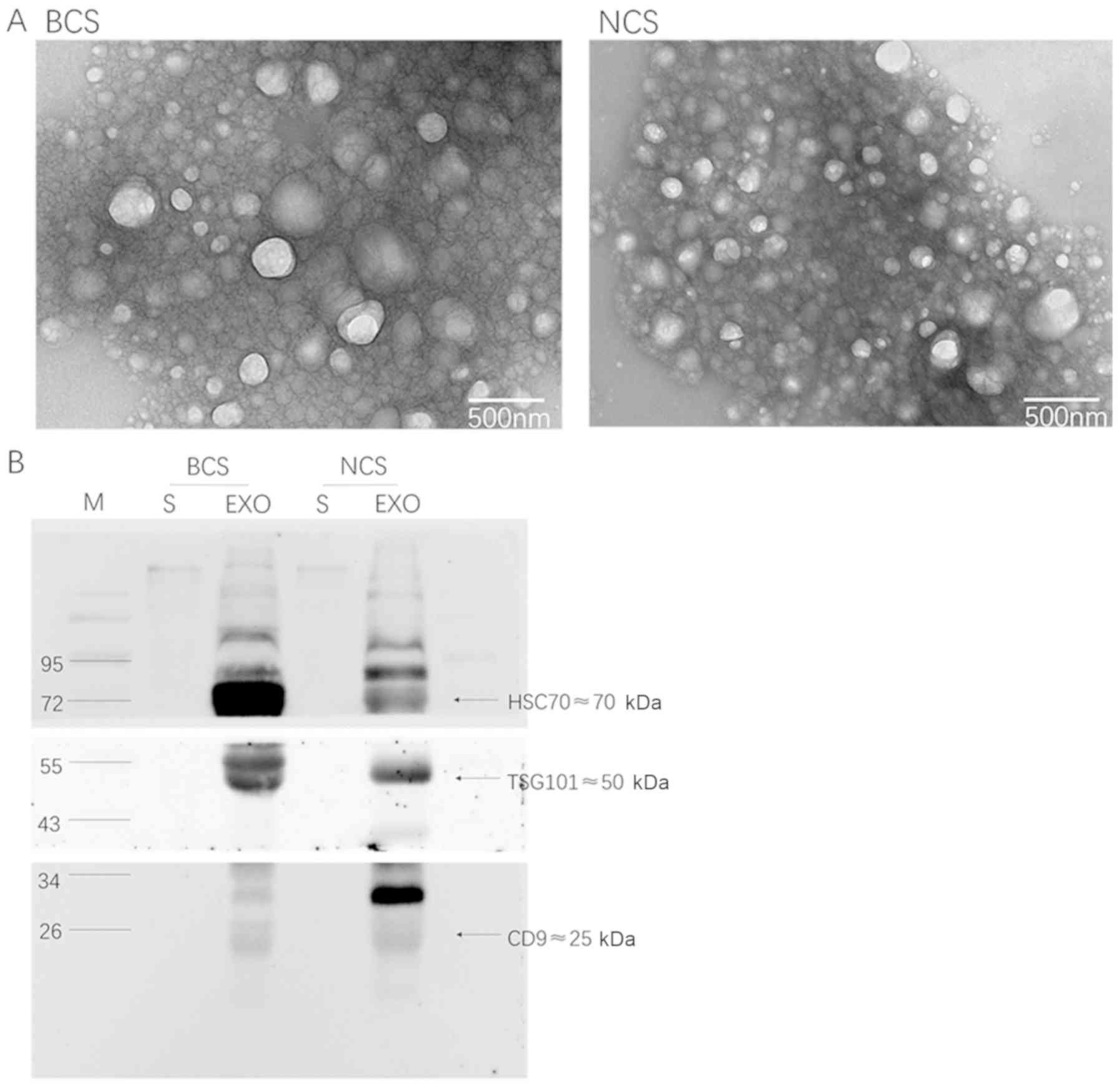
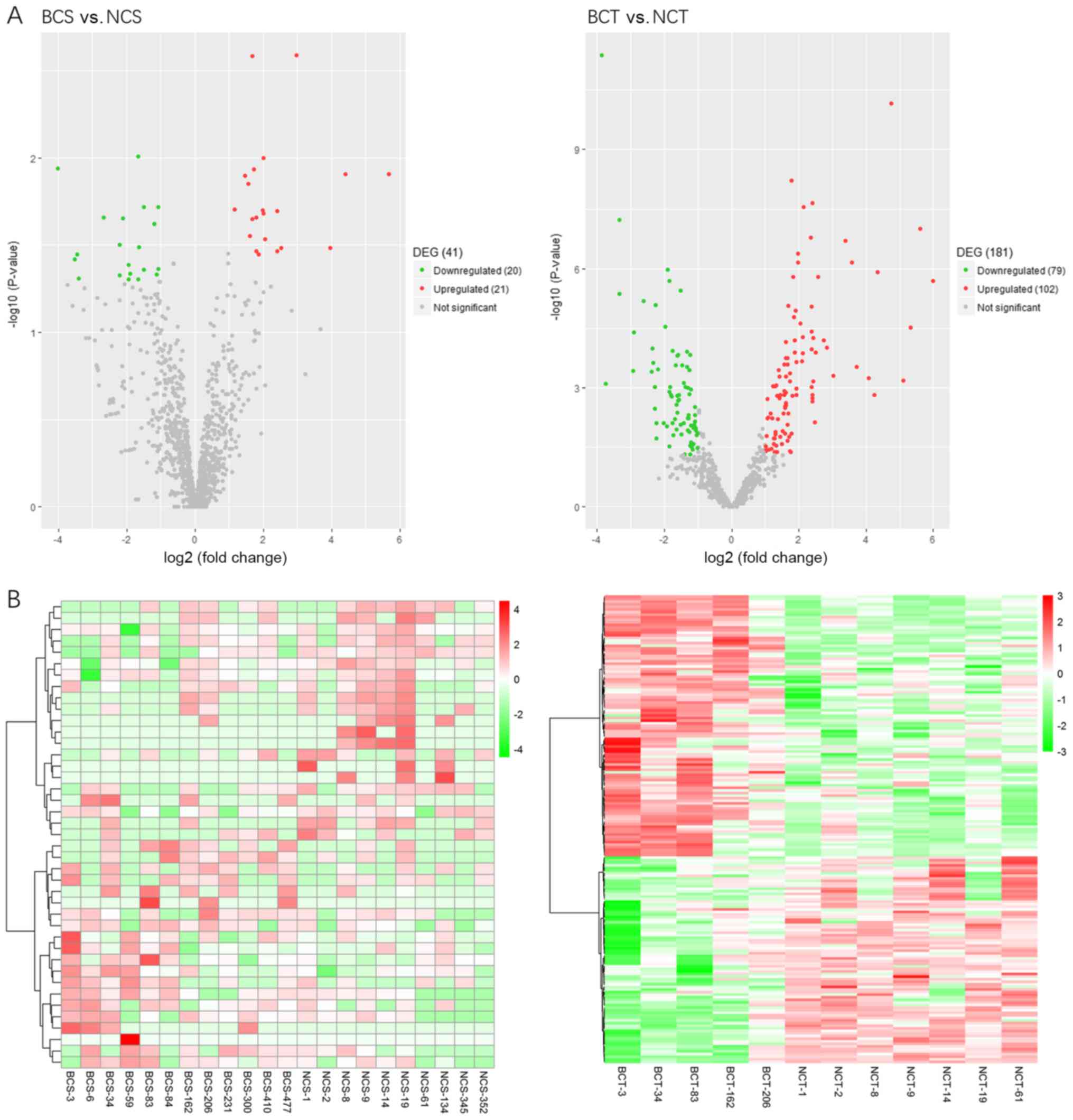
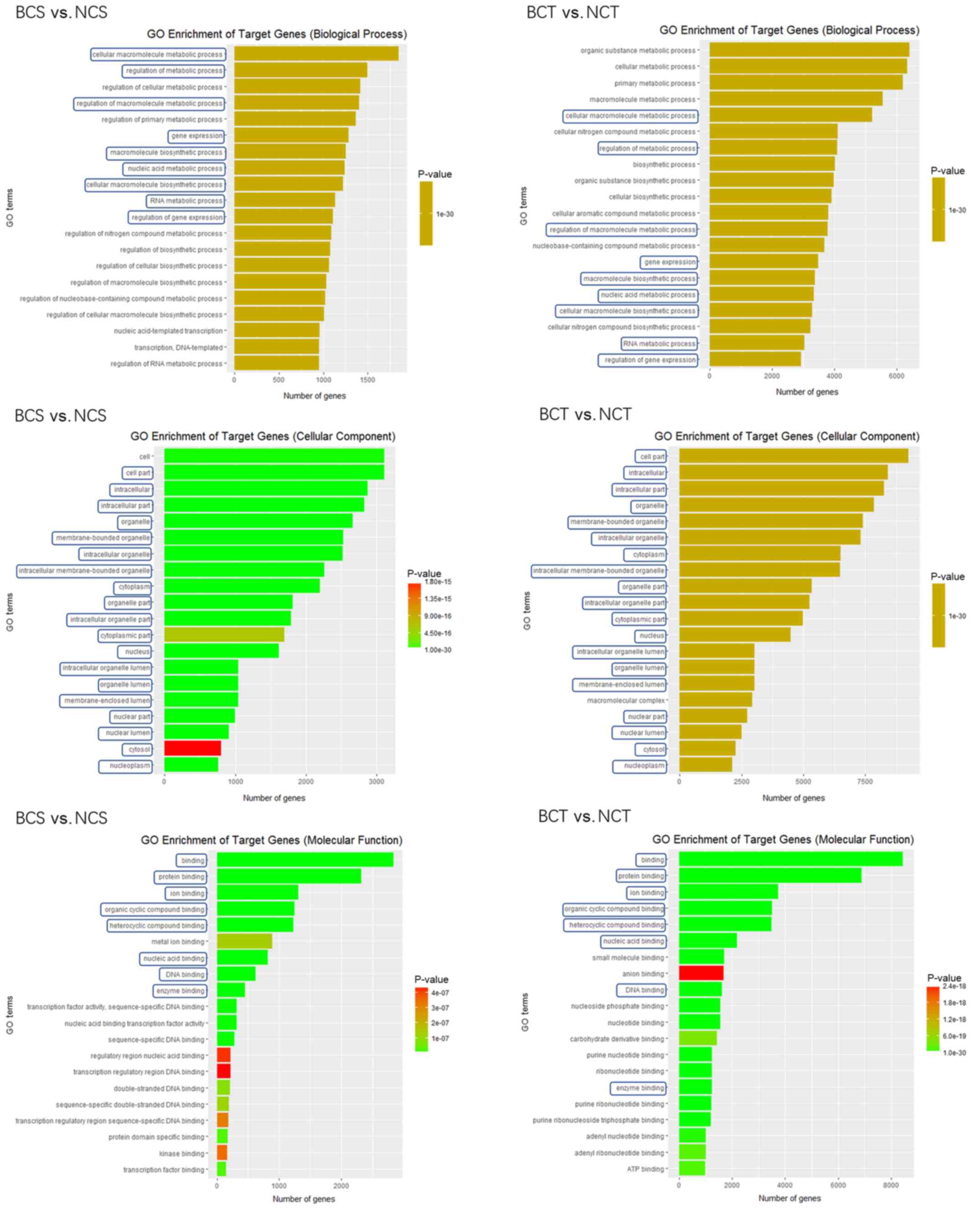
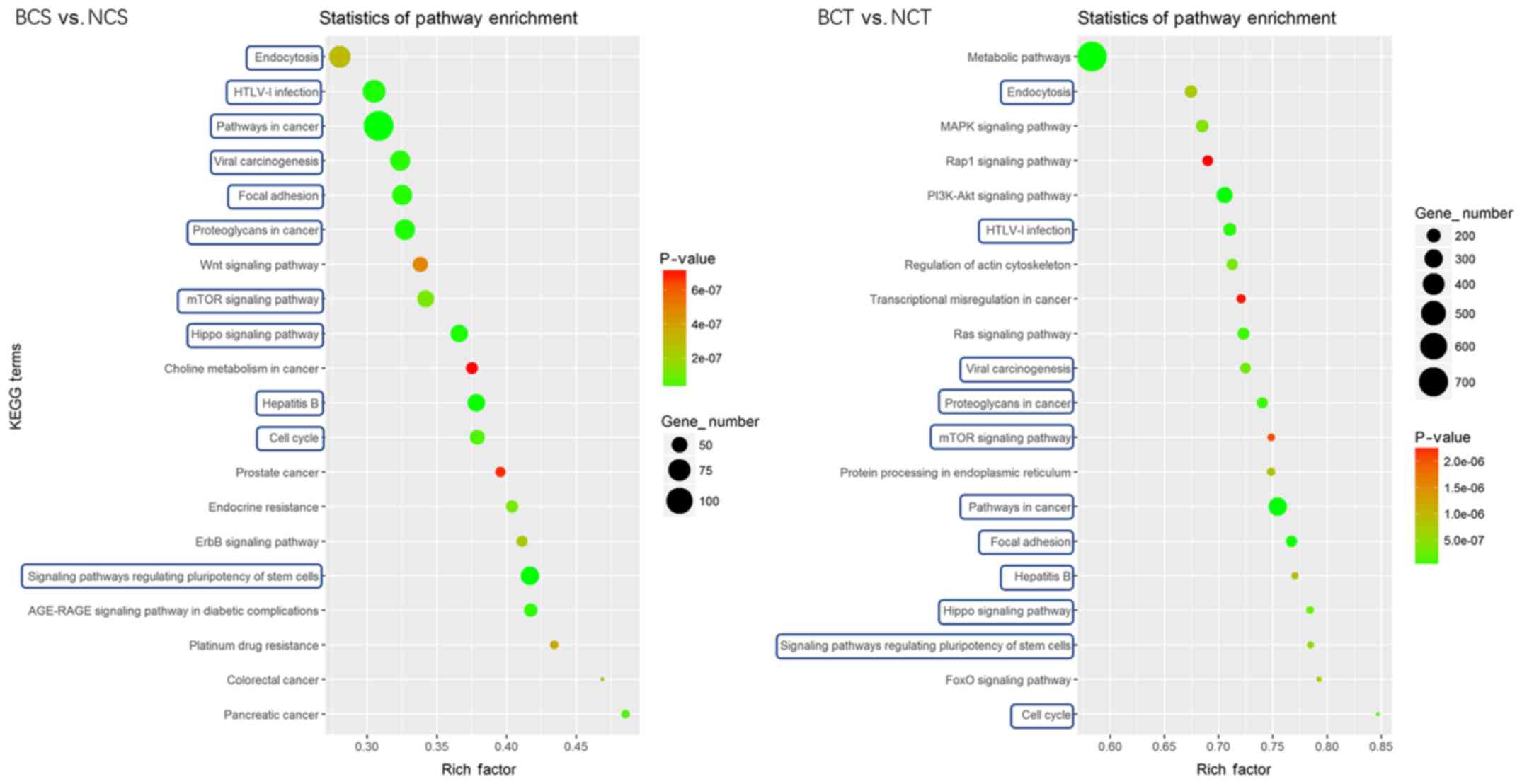
|
1
|
Harbeck N and Gnant M: Breast cancer.
Lancet. 389:1134–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bertoli G, Cava C and Castiglioni I:
MicroRNAs: New biomarkers for diagnosis, prognosis, therapy
prediction and therapeutic tools for breast cancer. Theranostics.
5:1122–1143. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Opstal-van Winden AW, Rodenburg W,
Pennings JL, van Oostrom CT, Beijnen JH, Peeters PH, van Gils CH
and de Vries A: A bead-based multiplexed immunoassay to evaluate
breast cancer biomarkers for early detection in pre-diagnostic
serum. Int J Mol Sci. 13:13587–13604. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sinn P, Aulmann S, Wirtz R, Schott S,
Marmé F, Varga Z, Lebeau A, Kreipe H and Schneeweiss A: Multigene
assays for classification, prognosis, and prediction in breast
cancer: A critical review on the background and clinical utility.
Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. 73:932–940. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Herranz H and Cohen SM: MicroRNAs and gene
regulatory networks: Managing the impact of noise in biological
systems. Genes Dev. 24:1339–1344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ashby J, Flack K, Jimenez LA, Duan Y,
Khatib AK, Somlo G, Wang SE, Cui X and Zhong W: Distribution
profiling of circulating microRNAs in serum. Anal Chem.
86:9343–9349. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Arroyo JD, Chevillet JR, Kroh EM, Ruf IK,
Pritchard CC, Gibson DF, Mitchell PS, Bennett CF,
Pogosova-Agadjanyan EL, Stirewalt DL, et al: Argonaute2 complexes
carry a population of circulating microRNAs independent of vesicles
in human plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:5003–5008. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Desrochers LM, Antonyak MA and Cerione RA:
Extracellular vesicles: Satellites of information transfer in
cancer and stem cell biology. Dev Cell. 37:301–309. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tomasetti M, Lee W, Santarelli L and
Neuzil J: Exosome-derived microRNAs in cancer metabolism: Possible
implications in cancer diagnostics and therapy. Exp Mol Med.
49:e2852017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Graveel CR, Calderone HM, Westerhuis JJ,
Winn ME and Sempere LF: Critical analysis of the potential for
microRNA biomarkers in breast cancer management. Breast Cancer
(Dove Med Press). 7:59–79. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hannafon BN, Trigoso YD, Calloway CL, Zhao
YD, Lum DH, Welm AL, Zhao ZJ, Blick KE, Dooley WC and Ding WQ:
Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res. 18:902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gao Y, Cai Q, Huang Y, Li S, Yang H, Sun
L, Chen K and Wang Y: MicroRNA-21 as a potential diagnostic
biomarker for breast cancer patients: A pooled analysis of
individual studies. Oncotarget. 7:34498–34506. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shimomura A, Shiino S, Kawauchi J,
Takizawa S, Sakamoto H, Matsuzaki J, Ono M, Takeshita F, Niida S,
Shimizu C, et al: Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting
breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 107:326–334. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Eichelser C, Stuckrath I, Muller V,
Milde-Langosch K, Wikman H, Pantel K and Schwarzenbach H: Increased
serum levels of circulating exosomal microRNA-373 in
receptor-negative breast cancer patients. Oncotarget. 5:9650–9663.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xiao CL, Mai ZB, Lian XL, Zhong JY, Jin
JJ, He QY and Zhang G: FANSe2: A robust and cost-efficient
alignment tool for quantitative next-generation sequencing
applications. PLoS One. 9:e942502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K,
Schaeffer L and Wold B: Mapping and quantifying mammalian
transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Methods. 5:621–628. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bloom JS, Khan Z, Kruglyak L, Singh M and
Caudy AA: Measuring differential gene expression by short read
sequencing: Quantitative comparison to 2-channel gene expression
microarrays. BMC Genomics. 10:2212009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie C, Mao X, Huang J, Ding Y, Wu J, Dong
S, Kong L, Gao G, Li CY and Wei L: KOBAS 2.0: A web server for
annotation and identification of enriched pathways and diseases.
Nucleic Acids Res. (39): (Web Server Issue). W316–W322. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Herrera-Perez Z, Gretz N and Dweep H: A
comprehensive review on the genetic regulation of cisplatin-induced
nephrotoxicity. Curr Genomics. 17:279–293. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wong NW, Chen Y, Chen S and Wang X:
OncomiR: An online resource for exploring pan-cancer microRNA
dysregulation. Bioinformatics. 34:713–715. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rajkumar AP, Qvist P, Lazarus R, Lescai F,
Ju J, Nyegaard M, Mors O, Børglum AD, Li Q and Christensen JH:
Experimental validation of methods for differential gene expression
analysis and sample pooling in RNA-seq. BMC Genomics. 16:5482015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
de Souza Rocha Simonini P, Breiling A,
Gupta N, Malekpour M, Youns M, Omranipour R, Malekpour F, Volinia
S, Croce CM, Najmabadi H, et al: Epigenetically deregulated
microRNA-375 is involved in a positive feedback loop with estrogen
receptor alpha in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 70:9175–9184.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zou Q, Yi W, Huang J, Fu F, Chen G and
Zhong D: MicroRNA-375 targets PAX6 and inhibits the viability,
migration and invasion of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells. Exp Ther
Med. 14:1198–1204. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fu H, Fu L, Xie C, Zuo WS, Liu YS, Zheng
MZ and Yu JM: miR-375 inhibits cancer stem cell phenotype and
tamoxifen resistance by degrading HOXB3 in human ER-positive breast
cancer. Oncol Rep. 37:1093–1099. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schrauder MG, Strick R, Schulz-Wendtland
R, Strissel PL, Kahmann L, Loehberg CR, Lux MP, Jud SM, Hartmann A,
Hein A, et al: Circulating micro-RNAs as potential blood-based
markers for early stage breast cancer detection. PLoS One.
7:e297702012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yamamoto Y, Yoshioka Y, Minoura K,
Takahashi RU, Takeshita F, Taya T, Horii R, Fukuoka Y, Kato T,
Kosaka N and Ochiya T: An integrative genomic analysis revealed the
relevance of microRNA and gene expression for drug-resistance in
human breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 10:1352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Srivastava N, Manvati S, Srivastava A, Pal
R, Kalaiarasan P, Chattopadhyay S, Gochhait S, Dua R and Bamezai
RN: miR-24-2 controls H2AFX expression regardless of gene copy
number alteration and induces apoptosis by targeting antiapoptotic
gene BCL-2: A potential for therapeutic intervention. Breast Cancer
Res. 13:R392011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lee YM, Lee JY, Ho CC, Hong QS, Yu SL,
Tzeng CR, Yang PC and Chen HW: miRNA-34b as a tumor suppressor in
estrogen-dependent growth of breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer
Res. 13:R1162011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ke H, Zhao L, Feng X, Xu H, Zou L, Yang Q,
Su X, Peng L and Jiao B: NEAT1 is required for survival of breast
cancer cells through fus and mir-548. Gene Regul Syst Bio.
10:11–17. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi Y, Qiu M, Wu Y and Hai L: miR-548-3p
functions as an anti-oncogenic regulator in breast cancer. Biomed
Pharmacother. 75:111–116. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lv ZD, Kong B, Liu XP, Jin LY, Dong Q, Li
FN and Wang HB: miR-655 suppresses epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by targeting Prrx1 in triple-negative breast cancer. J
Cell Mol Med. 20:864–873. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Liang HQ, Wang RJ, Diao CF, Li JW, Su JL
and Zhang S: The PTTG1-targeting miRNAs miR-329, miR-300, miR-381,
and miR-655 inhibit pituitary tumor cell tumorigenesis and are
involved in a p53/PTTG1 regulation feedback loop. Oncotarget.
6:29413–29427. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
An N, Luo X, Zhang M and Yu R:
MicroRNA-376b promotes breast cancer metastasis by targeting Hoxd10
directly. Exp Ther Med. 13:79–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li LJ, Huang Q, Zhang N, Wang GB and Liu
YH: miR-376b-5p regulates angiogenesis in cerebral ischemia. Mol
Med Rep. 10:527–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|