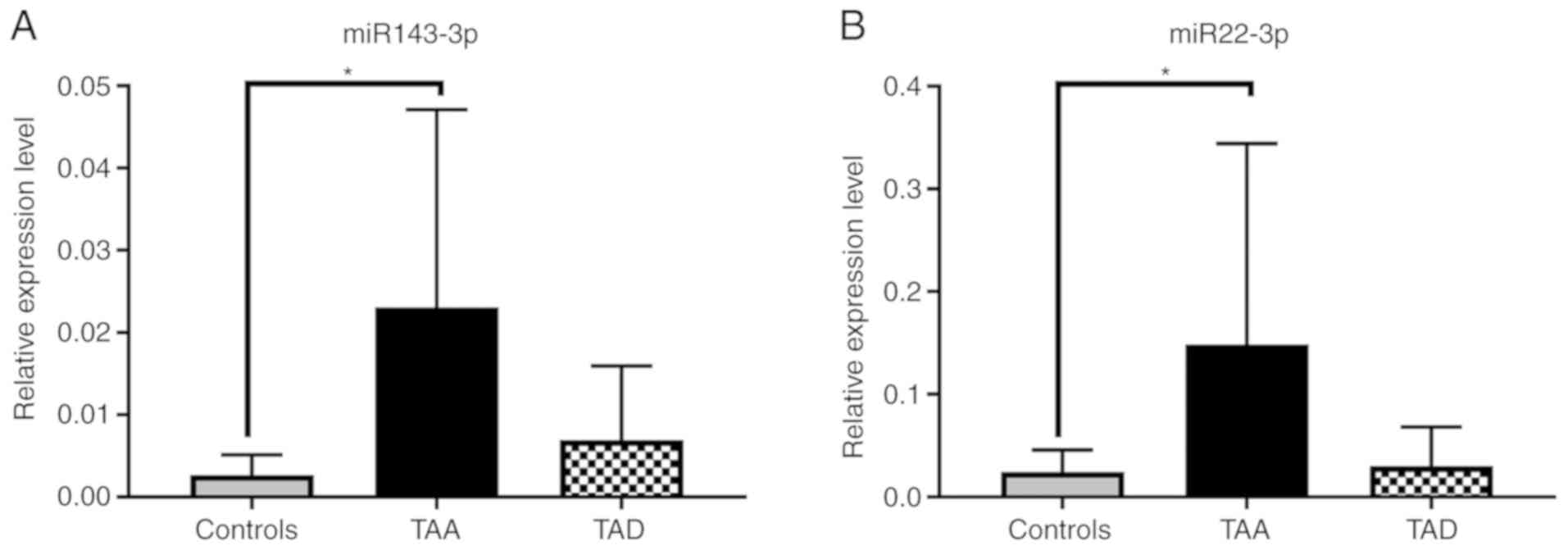
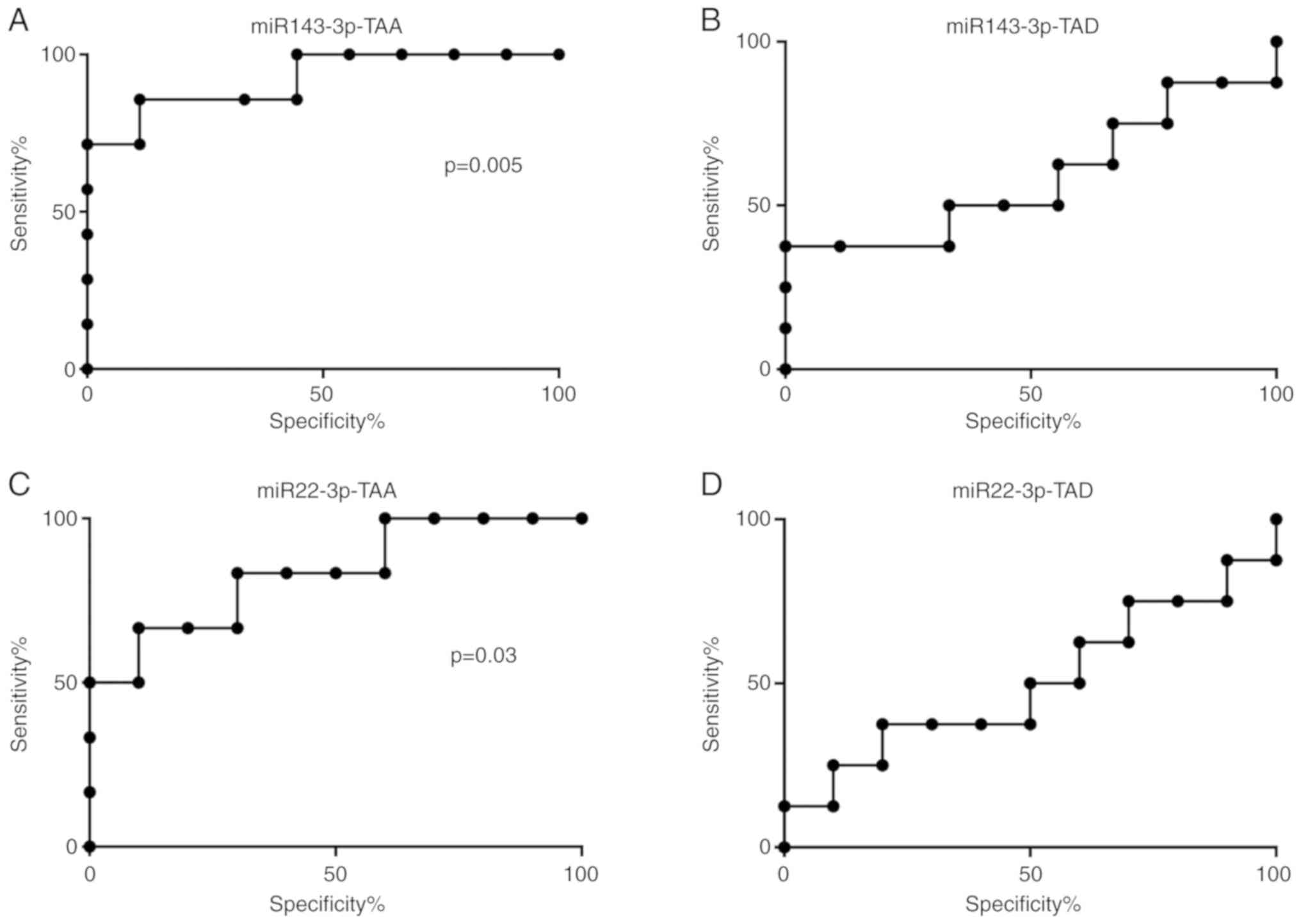
|
1
|
Milewicz DM, Prakash SK and Ramirez F:
Therapeutics targeting drivers of thoracic aortic aneurysms and
acute aortic dissections: Insights from predisposing genes and
mouse models. Annu Rev Med. 68:51–67. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Howard DP, Banerjee A, Fairhead JF,
Perkins J, Silver LE and Rothwell PM; Oxford Vascular Study, :
Population-based study of incidence and outcome of acute aortic
dissection and premorbid risk factor control: 10-year results from
the Oxford Vascular Study. Circulation. 127:2031–2037. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martufi G, Gasser TC, Appoo JJ and Di
Martino ES: Mechano-biology in the thoracic aortic aneurysm: A
review and case study. Biomech Model Mechanobiol. 13:917–928. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liao M, Zou S, Weng J, Hou L, Yang L, Zhao
Z, Bao J and Jing Z: A microRNA profile comparison between thoracic
aortic dissection and normal thoracic aorta indicates the potential
role of microRNAs in contributing to thoracic aortic dissection
pathogenesis. J Vasc Surg. 53:1341–1349.e3. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ikonomidis JS, Ivey CR, Wheeler JB,
Akerman AW, Rice A, Patel RK, Stroud RE, Shah AA, Hughes CG,
Ferrari G, et al: Plasma biomarkers for distinguishing etiologic
subtypes of thoracic aortic aneurysm disease. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 145:1326–1333. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu R, Lo L, Lay AJ, Zhao Y, Ting KK,
Robertson EN, Sherrah AG, Jarrah S, Li H, Zhou Z, et al: ARHGAP18
protects against thoracic aortic aneurysm formation by mitigating
the synthetic and proinflammatory smooth muscle cell phenotype.
Circ Res. 121:512–524. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Boon RA, Seeger T, Heydt S, Fischer A,
Hergenreider E, Horrevoets AJ, Vinciguerra M, Rosenthal N, Sciacca
S, Pilato M, et al: MicroRNA-29 in aortic dilation: Implications
for aneurysm formation. Circ Res. 109:1115–1119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Moushi A, Michailidou K, Soteriou M,
Cariolou M and Bashiardes E: MicroRNAs as possible biomarkers for
screening of aortic aneurysms: A systematic review and validation
study. Biomarkers. 23:253–264. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Wu B, Dong L, Wang C, Wang X and
Shu X: Circulating matrix metalloproteinase patterns in association
with aortic dilatation in bicuspid aortic valve patients with
isolated severe aortic stenosis. Heart Vessels. 31:189–197. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Osaki M, Takeshita F, Sugimoto Y, Kosaka
N, Yamamoto Y, Yoshioka Y, Kobayashi E, Yamada T, Kawai A, Inoue T,
et al: MicroRNA-143 regulates human osteosarcoma metastasis by
regulating matrix metalloprotease-13 expression. Mol Ther.
19:1123–1130. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kim HW and Stansfield BK: Genetic and
epigenetic regulation of aortic aneurysms. Biomed Res Int.
2017:72685212017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jancík S, Drábek J, Radzioch D and Hajdúch
M: Clinical relevance of KRAS in human cancers. J Biomed
Biotechnol. 2010:1509602010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li Y and Maegdefessel L: Non-coding RNA
contribution to thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysm disease
development and progression. Front Physiol. 8:4292017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ignatieva E, Kostina D, Irtyuga O,
Uspensky V, Golovkin A, Gavriliuk N, Moiseeva O, Kostareva A and
Malashicheva A: Mechanisms of smooth muscle cell differentiation
are distinctly altered in thoracic aortic aneurysms associated with
bicuspid or tricuspid aortic valves. Front Physiol. 8:5362017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Erbel R, Aboyans V, Boileau C, Bossone E,
Bartolomeo RD, Eggebrecht H, Evangelista A, Falk V, Frank H,
Gaemperli O, et al: 2014 ESC Guidelines on the diagnosis and
treatment of aortic diseases: Document covering acute and chronic
aortic diseases of the thoracic and abdominal aorta of the adult.
The Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Aortic Diseases
of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J.
35:2873–2926. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kent KC: Clinical practice. Abdominal
aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 371:2101–2108. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Burillo E, Lindholt JS, Molina-Sánchez P,
Jorge I, Martinez-Pinna R, Blanco-Colio LM, Tarin C, Torres-Fonseca
MM, Esteban M, Laustsen J, et al: ApoA-I/HDL-C levels are inversely
associated with abdominal aortic aneurysm progression. Thromb
Haemost. 113:1335–1346. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gawinecka J, Schönrath F and von
Eckardstein A: Acute aortic dissection: Pathogenesis, risk factors
and diagnosis. Swiss Med Wkly. 147:w144892017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Turchinovich A, Weiz L, Langheinz A and
Burwinkel B: Characterization of extracellular circulating
microRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 39:7223–7233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Patuzzo C, Pasquali A, Malerba G, Trabetti
E, Pignatti P, Tessari M and Faggian G: Preliminary microRNA
analysis of non syndromic thoracic aortic aneurysms. Balkan J Med
Genet. 15 (Suppl):S51–S55. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Licholai S, Blaż M, Kapelak B and Sanak M:
Unbiased profile of MicroRNA expression in ascending aortic
aneurysm tissue appoints molecular pathways contributing to the
pathology. Ann Thorac Surg. 102:1245–1252. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rangrez AY, Massy ZA, Metzinger-Le Meuth V
and Metzinger L: miR-143 and miR-145: Molecular keys to switch the
phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Cardiovasc Genet.
4:197–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cordes KR, Sheehy NT, White MP, Berry EC,
Morton SU, Muth AN, Lee TH, Miano JM, Ivey KN and Srivastava D:
miR-145 and miR-143 regulate smooth muscle cell fate and
plasticity. Nature. 460:705–710. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Climent M, Quintavalle M, Miragoli M, Chen
J, Condorelli G and Elia L: TGFβ triggers miR-143/145 transfer from
smooth muscle cells to endothelial cells, thereby modulating vessel
stabilization. Circ Res. 116:1753–1764. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song B and Ju J: Impact of miRNAs in
gastrointestinal cancer diagnosis and prognosis. Expert Rev Mol
Med. 12:e332010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang J, Lu L and Huang K: miR-143 inhibits
osteosarcoma cell proliferation by downregulating K-ras expression.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 9:3436–3441. 2016.
|
|
28
|
Yu ML, Wang JF, Wang GK, You XH, Zhao XX,
Jing Q and Qin YW: Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation is
influenced by let-7d microRNA and its interaction with KRAS. Circ
J. 75:703–709. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Inoue T and Node K: Molecular basis of
restenosis and novel issues of drug-eluting stents. Circ J.
73:615–621. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Roberts OL, Holmes K, Müller J, Cross DA
and Cross MJ: ERK5 is required for VEGF-mediated survival and
tubular morphogenesis of primary human microvascular endothelial
cells. J Cell Sci. 123:3189–3200. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang F, Chen Q, He S, Yang M, Maguire EM,
An W, Afzal TA, Luong LA, Zhang L and Xiao Q: miR-22 is a novel
mediator of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotypic modulation and
neointima formation. Circulation. 137:1824–1841. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Long X, Cowan SL and Miano JM:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase 14 is a novel negative regulatory
switch for the vascular smooth muscle cell contractile gene
program. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:378–386. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhao H, Wen G, Huang Y, Yu X, Chen Q,
Afzal TA, Luong le A, Zhu J, Ye S, Zhang L and Xiao Q: MicroRNA-22
regulates smooth muscle cell differentiation from stem cells by
targeting methyl CpG-binding protein 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 35:918–929. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dhingra R and Vasan RS: Age as a risk
factor. Med Clin North Am. 96:87–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|