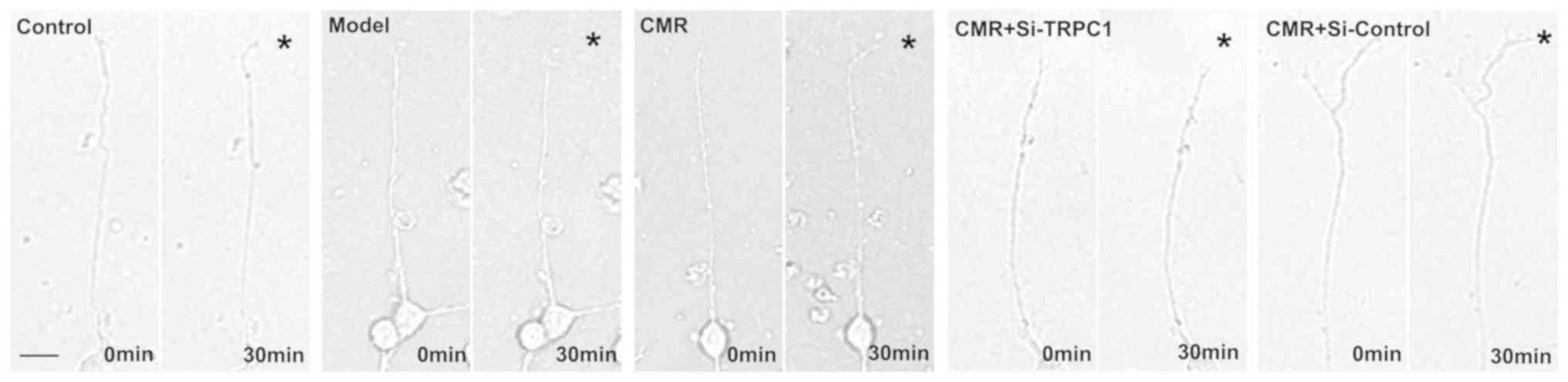
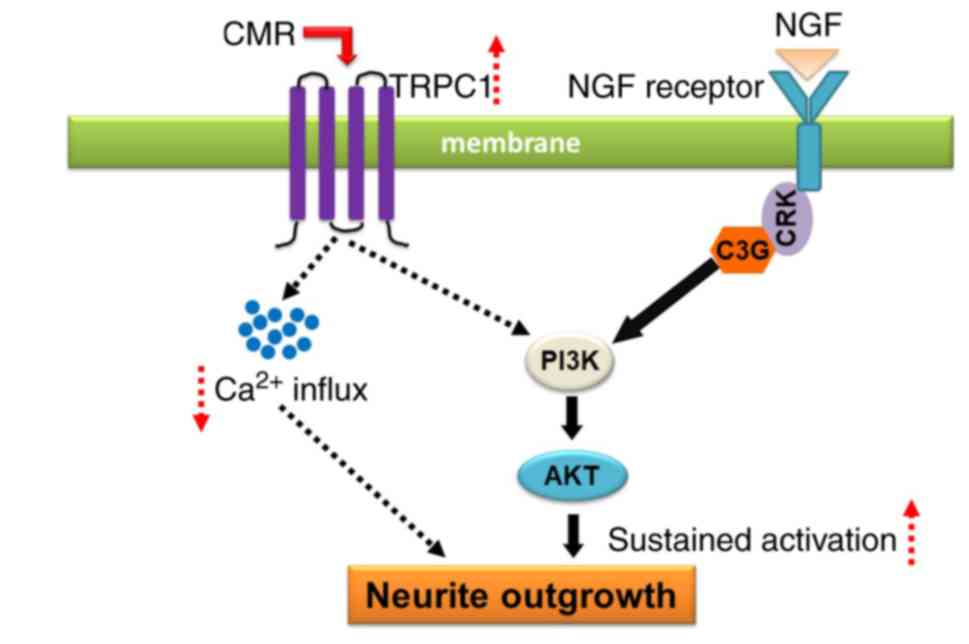
|
1
|
Xiang Y, Zhou Z, Deng C and Leslie RD:
Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults in Asians: Similarities and
differences between east and west. J Diabetes. 5:118–126. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Becker M, Benromano T, Shahar A, Nevo Z
and Pick CG: Changes in the basal membrane of dorsal root ganglia
schwann cells explain the biphasic pattern of the peripheral
neuropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Mol Neurosci.
54:704–713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Xu Q, Pan J, Yu J, Liu X, Liu L, Zuo X, Wu
P, Deng H, Zhang J and Ji A: Meta-analysis of methylcobalamin alone
and in combination with lipoic acid in patients with diabetic
peripheral neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 101:99–105. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gordois A, Scuffham P, Shearer A, Oglesby
A and Tobian JA: The health care costs of diabetic peripheral
neuropathy in the US. Diabetes Care. 26:1790–1795. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
WEI ZX: Experiences in treating diabetic
peripheral neuropathy with traditional Chinese medicine. Chin J
Integr Med. 14:248–250. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Choi HJ, Kim NJ and Kim DH: Inhibitory
effects of crude drugs on alpha-glucosidase. Arch Pharm Res.
23:261–266. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen F, Nakashima N, Kimura I and Kimura
M: Hypoglycemic activity and mechanisms of extracts from mulberry
leaves (folium mori) and cortex mori radicis in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Yakugaku Zasshi. 115:476–482.
1995.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lian J, Chen J, Yuan Y, Chen J, Daud M,
Sayed M, Luo L, Zhu Y, Li S and Bu S: Cortex mori radicis extract
attenuates myocardial damages in diabetic rats by regulating ERS.
Biomed Pharmacother. 90:777–785. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yin N, Hong X, Han Y, Duan Y, Zhang Y and
Chen Z: Cortex mori radicis extract induces neurite outgrowth in
PC12 cells activating ERK signaling pathway via inhibiting Ca(2+)
influx. Int J Clin Exp Med. 8:5022–5032. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hwang SH, Kang IJ and Lim SS: Antidiabetic
effect of fresh nopal (opuntia ficus-indica) in low-dose
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats fed a high-fat diet. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017:43807212017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lee MS, Park WS, Kim YH, Kwon SH, Jang YJ,
Han D, Morita K and Her S: Antidepressant-like effects of Cortex
Mori Radicis extract via bidirectional phosphorylation of
glucocorticoid receptors in the hippocampus. Behav Brain Res.
236:56–61. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yue HY, Yin C, Hou JL, Zeng X, Chen YX,
Zhong W, Hu PF, Deng X, Tan YX, Zhang JP, et al: Hepatocyte nuclear
factor 4alpha attenuates hepatic fibrosis in rats. Gut. 59:236–246.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wesche-Soldato DE, Chung CS, Lomas-Neira
J, Doughty LA, Gregory SH and Ayala A: In vivo delivery of
caspase-8 or Fas siRNA improves the survival of septic mice. Blood.
106:2295–2301. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Taiana MM, Lombardi R, Porretta-Serapiglia
C, Ciusani E, Oggioni N, Sassone J, Bianchi R and Lauria G:
Neutralization of schwann cell-secreted VEGF is protective to in
vitro and in vivo experimental diabetic neuropathy. PLoS One.
9:e1084032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao F, Xiang HC, Li HP, Jia M, Pan XL, Pan
HL and Li M: Electroacupuncture inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome
activation through CB2 receptors in inflammatory pain. Brain Behav
Immun. 67:91–100. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gasperini R, Choi-Lundberg D, Thompson MJ,
Mitchell CB and Foa L: Homer regulates calcium signaling in growth
cone turning. Neural Dev. 4:292009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Coppey LJ, Shevalye H, Obrosov A, Davidson
EP and Yorek MA: Determination of peripheral neuropathy in high-fat
fed low-dose streptozotocin treated female C57BI/6J mice and
Sprague-Dawley rats. J Diabetes Investig. 9:1033–1040. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schmidt RE, Parvin CA and Green KG:
Synaptic ultrastructural alterations anticipate the development of
neuroaxonal dystrophy in sympathetic ganglia of aged and diabetic
mice. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 67:1166–1186. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang X, Yao W, Liu H, Gao Y, Liu R and Xu
L: Tangluoning, a traditional Chinese medicine, attenuates in vivo
and in vitro diabetic peripheral neuropathy through modulation of
PERK/Nrf2 pathway. Sci Rep. 7:10142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kang TH, Moon E, Hong BN, Choi SZ, Son M,
Park JH and Kim SY: Diosgenin from Dioscorea nipponica ameliorates
diabetic neuropathy by inducing nerve growth factor. Biol Pharm
Bull. 34:1493–1498. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim HJ, Lee HJ, Jeong SJ, Lee HJ, Kim SH
and Park EJ: Cortex mori radicis extract exerts antiasthmatic
effects via enhancement of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells
and inhibition of Th2 cytokines in a mouse asthma model. J
Ethnopharmacol. 138:40–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
You S and Kim GH: Protective effect of
Mori Cortex radicis extract against high glucose-induced oxidative
stress in PC12 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 83:1893–1900.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Y, Chen Z, Ye R, He Y, Li Y and Qiu
X: Protective effect of jiaweibugan decoction against diabetic
peripheral neuropathy. Neural Regen Res. 8:1113–1121.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim KJ, Namgung U and Cho CS: Protective
effects of bogijetong decoction and its selected formula on
neuropathic insults in streptozotocin-induced diabetic animals.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017:42963182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sarina, Yagi Y, Nakano O, Hashimoto T,
Kimura K, Asakawa Y, Zhong M, Narimatsu S and Gohda E: Induction of
neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells by artemisinin through activation
of ERK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Brain Res. 1490:61–71.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang D, Chan JD, Nogi T and Marchant JS:
Opposing roles of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in neuronal control
of regenerative patterning. J Neurosci. 31:15983–15995. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Balasubramanyam M, Balaji RA, Subashini B
and Mohan V: Evidence for mechanistic alterations of Ca2+
homeostasis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Exp Diabetes Res.
1:275–287. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Verkhratsky A and Fernyhough P:
Mitochondrial malfunction and Ca2+ dyshomeostasis drive neuronal
pathology in diabetes. Cell Calcium. 44:112–122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cao XH, Byun HS, Chen SR and Pan HL:
Diabetic neuropathy enhances voltage-activated Ca2+ channel
activity and its control by M4 muscarinic receptors in primary
sensory neurons. J Neurochem. 119:594–603. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Chandramoorthy HC, Bin-Jaliah I, Karari H,
Rajagopalan P, Ahmed Shariff ME, Al-Hakami A, Al-Humayad SM,
Baptain FA, Ahmed HS, Yassin HZ and Haidara MA: MSCs ameliorates
DPN induced cellular pathology via [Ca2+]i homeostasis and
scavenging the pro-inflammatory cytokines. J Cell Physiol.
233:1330–1341. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Louhivuori LM: Calcium a key player in
early neural development and migration: TRPCs and VGCCs.
Argumentation. 1:201–207. 2015.
|
|
33
|
Li M, Chen C, Zhou Z, Xu S and Yu Z: A
TRPC1-mediated increase in store-operated Ca2+ entry is required
for the proliferation of adult hippocampal neural progenitor cells.
Cell Calcium. 51:486–496. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kruglikov I, Gryshchenko O, Shutov L,
Kostyuk E, Kostyuk P and Voitenko N: Diabetes-induced abnormalities
in ER calcium mobilization in primary and secondary nociceptive
neurons. Pflugers Arch. 448:395–401. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song E, Lee SK, Wang J, Ince N, Ouyang N,
Min J, Chen J, Shankar P and Lieberman J: RNA interference
targeting Fas protects mice from fulminant hepatitis. Nat Med.
9:347–351. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vigont V, Kolobkova Y, Skopin A, Zimina O,
Zenin V, Glushankova L and Kaznacheyeva E: Both Orai1 and TRPC1 are
involved in excessive store-operated calcium entry in striatal
neurons expressing mutant huntingtin Exon 1. Front Physiol.
6:3372015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chen HC, Wang CH, Shih CP, Chueh SH, Liu
SF, Chen HK and Lin YC: TRPC1 is required for survival and
proliferation of cochlear spiral ganglion stem/progenitor cells.
Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 79:2290–2294. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shim S, Yuan JP, Kim JY, Zeng W, Huang G,
Milshteyn A, Kern D, Muallem S, Ming GL and Worley PF:
Peptidyl-prolyl isomerase FKBP52 controls chemotropic guidance of
neuronal growth cones via regulation of TRPC1 channel opening.
Neuron. 64:471–483. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Heo DK, Chung WY, Park HW, Yuan JP, Min GL
and Kim JY: Opposite regulatory effects of TRPC1 and TRPC5 on
neurite outgrowth in PC12 cells. Cell Signal. 24:899–906. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang D, Freedman BI, Flekac M, Santos E,
Hicks PJ, Bowden DW, Efendic S, Brismar K and Gu HF: Evaluation of
genetic association and expression reduction of TRPC1 in the
development of diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. 29:244–251.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Krout D, Schaar A, Sun Y, Sukumaran P,
Roemmich JN, Singh BB and Claycombe-Larson KJ: The TRPC1
Ca2+-permeable channel inhibits exercise-induced
protection against high-fat diet-induced obesity and type II
diabetes. J Biol Chem. 292:20799–20807. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yu JS and Cui W: Proliferation, survival
and metabolism: The role of PI3K/AKT/mTOR signalling in
pluripotency and cell fate determination. Development.
17:3050–3060. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Li R, Li Y, Wu Y, Zhao Y, Chen H, Yuan Y,
Xu K, Zhang H, Lu Y, Wang J, et al: Heparin-poloxamer
thermosensitive hydrogel loaded with bFGF and NGF enhances
peripheral nerve regeneration in diabetic rats. Biomaterials.
168:24–37. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chen L, Gong HY and Xu L: PVT1 protects
diabetic peripheral neuropathy via PI3K/AKT pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 22:6905–6911. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang YP, Liu SY, Sun QY, Ren J, Liu HX
and Li H: Proanthocyanidin B2 attenuates high-glucose-induced
neurotoxicity of dorsal root ganglion neurons through the PI3K/Akt
signaling pathway. Neural Regen Res. 13:1628–1636. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|