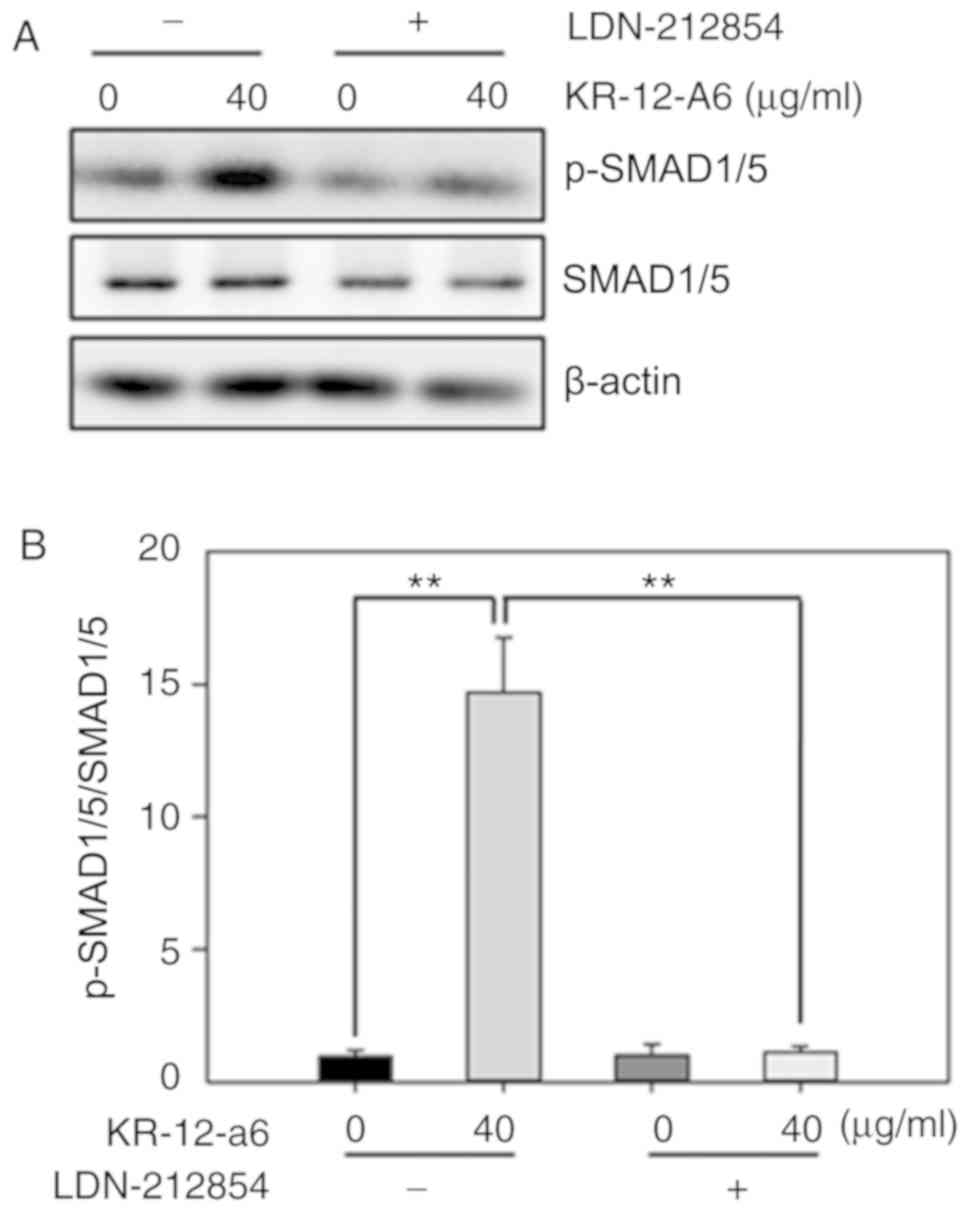
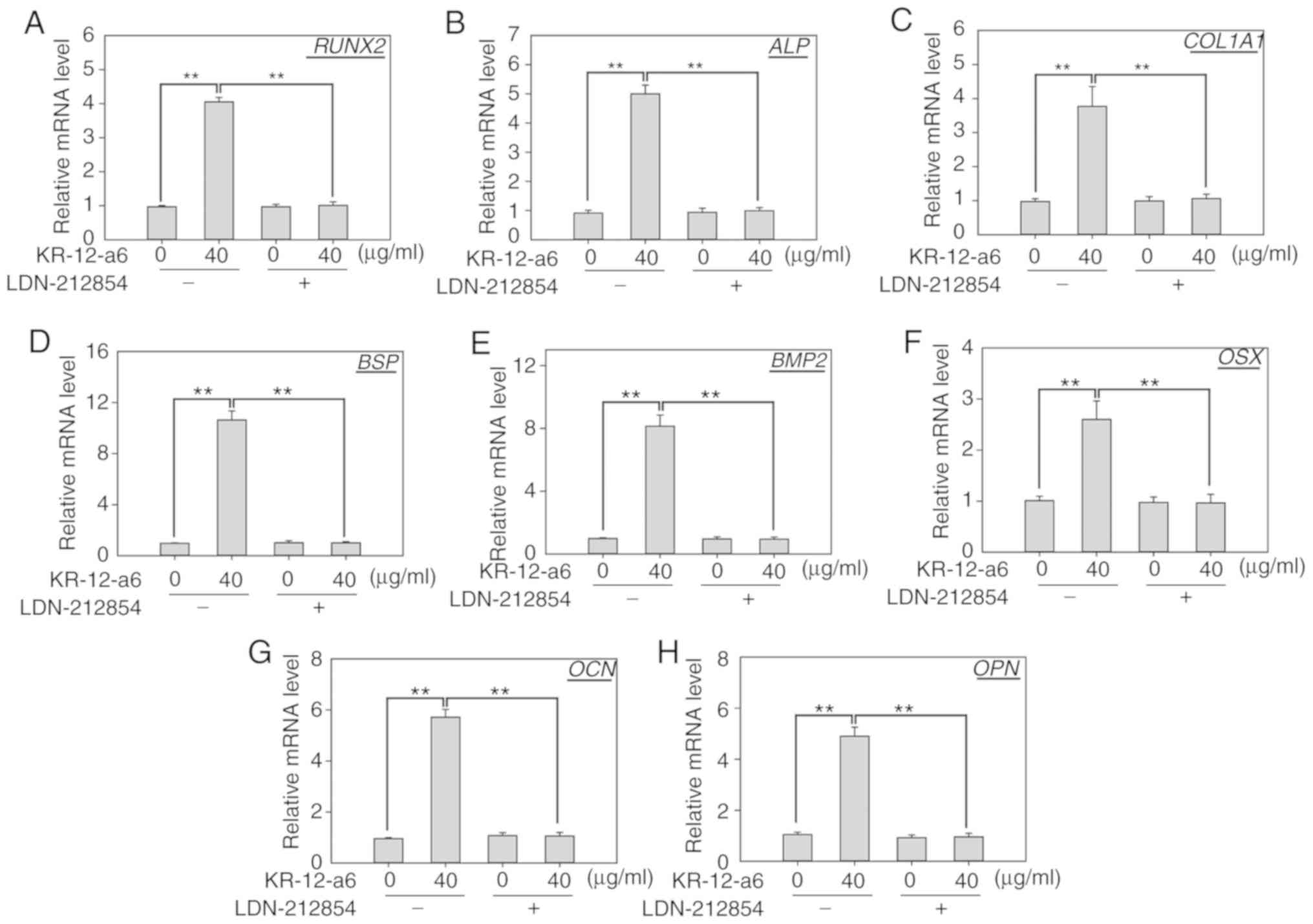
|
1
|
Bechinger B and Gorr SU: Antimicrobial
peptides: Mechanisms of action and resistance. J Dent Res.
96:254–260. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Larrick JW, Hirata M, Balint RF, Lee J,
Zhong J and Wright SC: Human CAP18: A novel antimicrobial
lipopolysaccharide-binding protein. Infect Immun. 63:1291–1297.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cowland JB, Johnsen AH and Borregaard N:
hCAP-18, a cathelin/pro-bactenecin-like protein of human neutrophil
specific granules. FEBS Lett. 368:173–176. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chakraborty K, Ghosh S, Koley H,
Mukhopadhyay AK, Ramamurthy T, Saha DR, Mukhopadhyay D,
Roychowdhury S, Hamabata T, Takeda Y and Das S: Bacterial exotoxins
downregulate cathelicidin (hCAP-18/LL-37) and human beta-defensin 1
(HBD-1) expression in the intestinal epithelial cells. Cell
Microbiol. 10:2520–2537. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Agier J, Brzezińska-Błaszczyk E,
Żelechowska P, Wiktorska M, Pietrzak J and Różalska S: Cathelicidin
LL-37 affects surface and intracellular toll-like receptor
expression in tissue mast cells. J Immunol Res. 2018:73571622018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chamilos G, Gregorio J, Meller S, Lande R,
Kontoyiannis DP, Modlin RL and Gilliet M: Cytosolic sensing of
extracellular self-DNA transported into monocytes by the
antimicrobial peptide LL37. Blood. 120:3699–2707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Agerberth B, Charo J, Werr J, Olsson B,
Idali F, Lindbom L, Kiessling R, Jörnvall H, Wigzell H and
Gudmundsson GH: The human antimicrobial and chemotactic peptides
LL-37 and alpha-defensins are expressed by specific lymphocyte and
monocyte populations. Blood. 96:3086–3093. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dorschner RA, Pestonjamasp VK, Tamakuwala
S, Ohtake T, Rudisill J, Nizet V, Agerberth B, Gudmundsson GH and
Gallo RL: Cutaneous injury induces the release of cathelicidin
anti-microbial peptides active against group A
Streptococcus. J Invest Dermatol. 117:91–97. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duplantier AJ and van Hoek ML: The human
cathelicidin antimicrobial peptide LL-37 as a potential treatment
for polymicrobial infected wounds. Front Immunol. 4:1432013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang G: Structures of human host defense
cathelicidin LL-37 and its smallest antimicrobial peptide KR-12 in
lipid micelles. J Biol Chem. 283:32637–32643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mishra B, Epand RF, Epand RM and Wang G:
Structural location determines functional roles of the basic amino
acids of KR-12, the smallest antimicrobial peptide from human
cathelicidin LL-37. RSC Adv. Nov 14–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
doi: 10.1039/C3RA42599A. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Rico-Mata R, De Leon-Rodriguez LM and
Avila EE: Effect of antimicrobial peptides derived from human
cathelicidin LL-37 on Entamoeba histolytica trophozoites.
Exp Parasitol. 133:300–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Feng X, Sambanthamoorthy K, Palys T and
Paranavitana C: The human antimicrobial peptide LL-37 and its
fragments possess both antimicrobial and antibiofilm activities
against multidrug-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii.
Peptides. 49:131–137. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Luo Y, McLean DT, Linden GJ, McAuley DF,
McMullan R and Lundy FT: The naturally occurring host defense
peptide, LL-37, and its truncated mimetics KE-18 and KR-12 have
selected biocidal and antibiofilm activities against Candida
albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli in
vitro. Front Microbiol. 8:5442017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jacob B, Park IS, Bang JK and Shin SY:
Short KR-12 analogs designed from human cathelicidin LL-37
possessing both antimicrobial and antiendotoxic activities without
mammalian cell toxicity. J Pept Sci. 19:700–707. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Geurts J, Hohnen A, Vranken T and Moh P:
Treatment strategies for chronic osteomyelitis in low- and
middle-income countries: Systematic review. Trop Med Int Health.
22:1054–1062. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mortazavi MM, Khan MA, Quadri SA, Suriya
SS, Fahimdanesh KM, Fard SA, Hassanzadeh T, Taqi MA, Grossman H and
Tubbs RS: Cranial osteomyelitis: A comprehensive review of modern
therapies. World Neurosurg. 111:142–153. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fily F, Ronat JB, Malou N, Kanapathipillai
R, Seguin C, Hussein N, Fakhri RM and Langendorf C: Post-traumatic
osteomyelitis in Middle East war-wounded civilians: Resistance to
first-line antibiotics in selected bacteria over the decade
2006–2016. BMC Infect Dis. 19:1032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ince A, Schütze N, Karl N, Löhr JF and
Eulert J: Gentamicin negatively influenced osteogenic function in
vitro. Int Orthop. 31:223–228. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mantripragada VP and Jayasuriya AC: Effect
of dual delivery of antibiotics (vancomycin and cefazolin) and
BMP-7 from chitosan microparticles on Staphylococcus
epidermidis and pre-osteoblasts in vitro. Mater Sci Eng C Mater
Biol Appl. 67:409–417. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choe H, Narayanan AS, Gandhi DA, Weinberg
A, Marcus RE, Lee Z, Bonomo RA and Greenfield EM: Immunomodulatory
peptide IDR-1018 decreases implant infection and preserves
osseointegration. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 473:2898–2907. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zou W, Greenblatt MB, Brady N, Lotinun S,
Zhai B, de Rivera H, Singh A, Sun J, Gygi SP, Baron R, et al: The
microtubule-associated protein DCAMKL1 regulates osteoblast
function via repression of Runx2. J Exp Med. 210:1793–1806. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mansour A, Abou-Ezzi G, Sitnicka E,
Jacobsen SE, Wakkach A and Blin-Wakkach C: Osteoclasts promote the
formation of hematopoietic stem cell niches in the bone marrow. J
Exp Med. 209:537–549. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Crane JL and Cao X: Bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells and TGF-β signaling in bone remodeling. J
Clin Invest. 124:466–472. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li B: MicroRNA regulation in osteogenic
and adipogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells and
its application in bone regeneration. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther.
13:26–30. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bidwell JP, Alvarez MB, Hood M Jr and
Childress P: Functional impairment of bone formation in the
pathogenesis of osteoporosis: The bone marrow regenerative
competence. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 11:117–125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shen GS, Zhou HB, Zhang H, Chen B, Liu ZP,
Yuan Y, Zhou XZ and Xu YJ: The GDF11-FTO-PPARγ axis controls the
shift of osteoporotic MSC fate to adipocyte and inhibits bone
formation during osteoporosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1864:3644–3654. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pavone V, Testa G, Giardina SMC, Vescio A,
Restivo DA and Sessa G: Pharmacological therapy of osteoporosis: A
systematic current review of literature. Front Pharmacol.
8:8032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Faber C, Stallmann HP, Lyaruu DM, Joosten
U, von Eiff C, van NieuwAmerongen A and Wuisman PI: Comparable
efficacies of the antimicrobial peptide human lactoferrin 1–11 and
gentamicin in a chronic methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus
aureus osteomyelitis model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother.
49:2438–2444. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xing K, Huang G, Hua S, Xu G and Li M:
Systematic review of randomized controlled trials on antibiotic
treatment for osteomyelitis in diabetes. Diabet Med. 36:546–556.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sierra JM, Fusté E, Rabanal F, Vinuesa T
and Viñas M: An overview of antimicrobial peptides and the latest
advances in their development. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 17:663–676.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|