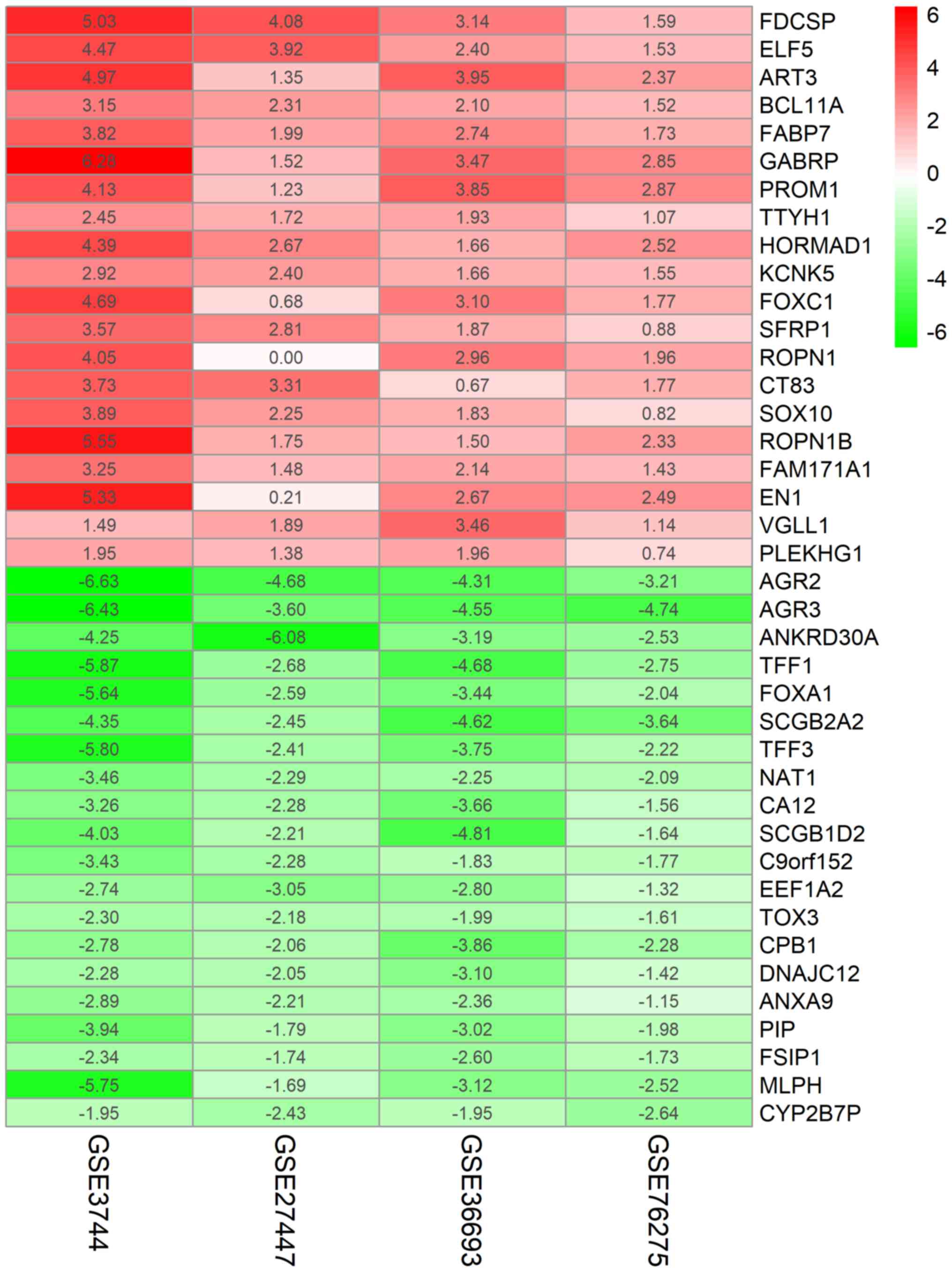
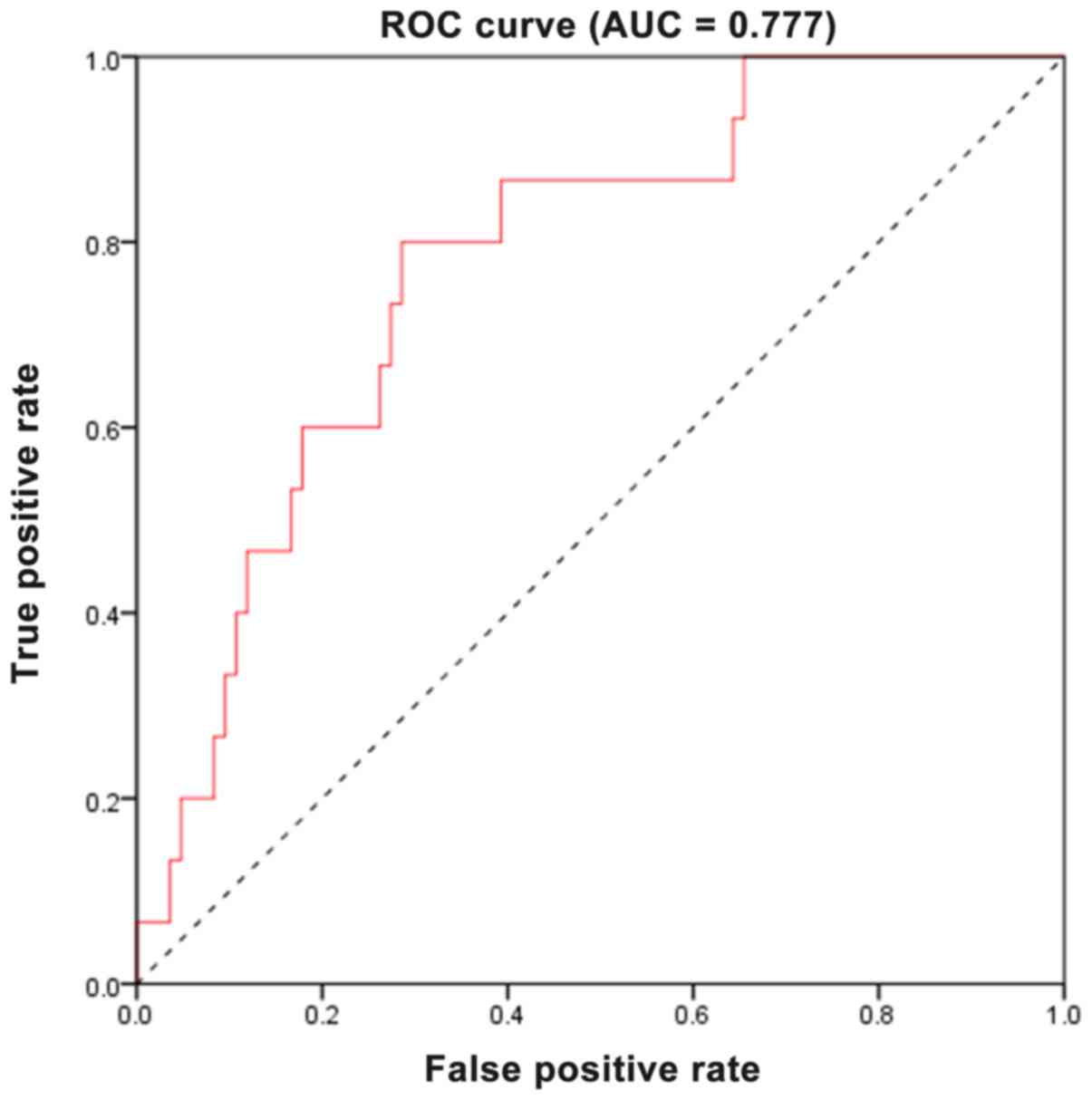
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:7–30. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Foulkes WD, Smith IE and Reis-Filho JS:
Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 363:1938–1948. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI, Hanna WM,
Kahn HK, Sawka CA, Lickley LA, Rawlinson E, Sun P and Narod SA:
Triple-negative breast cancer: Clinical features and patterns of
recurrence. Clin Cancer Res. 13:4429–4434. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler
LG, Cowan D, Conway K, Karaca G, Troester MA, Tse CK, Edmiston S,
et al: Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina
Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 295:2492–2502. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carey L, Winer E, Viale G, Cameron D and
Gianni L: Triple-negative breast cancer: Disease entity or title of
convenience? Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 7:683–692. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rouzier R, Perou CM, Symmans WF, Ibrahim
N, Cristofanilli M, Anderson K, Hess KR, Stec J, Ayers M, Wagner P,
et al: Breast cancer molecular subtypes respond differently to
preoperative chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5678–5685. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
von Minckwitz G, Untch M, Blohmer JU,
Costa SD, Eidtmann H, Fasching PA, Gerber B, Eiermann W, Hilfrich
J, Huober J, et al: Definition and impact of pathologic complete
response on prognosis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in various
intrinsic breast cancer subtypes. J Clin Oncol. 30:1796–1804. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Byler S, Goldgar S, Heerboth S, Leary M,
Housman G, Moulton K and Sarkar S: Genetic and epigenetic aspects
of breast cancer progression and therapy. Anticancer Res.
34:1071–1077. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lehmann BD, Bauer JA, Chen X, Sanders ME,
Chakravarthy AB, Shyr Y and Pietenpol JA: Identification of human
triple-negative breast cancer subtypes and preclinical models for
selection of targeted therapies. J Clin Invest. 121:2750–2767.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Burstein MD, Tsimelzon A, Poage GM,
Covington KR, Contreras A, Fuqua SA, Savage MI, Osborne CK,
Hilsenbeck SG, Chang JC, et al: Comprehensive genomic analysis
identifies novel subtypes and targets of triple-negative breast
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:1688–1698. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Võsa U, Kolde R, Vilo J, Metspalu A and
Annilo T: Comprehensive meta-analysis of microRNA expression using
a robust rank aggregation approach. Methods Mol Biol. 1182:361–373.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kolde R, Laur S, Adler P and Vilo J:
Robust rank aggregation for gene list integration and
meta-analysis. Bioinformatics. 28:573–580. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Shi KQ, Lin Z, Chen XJ, Song M, Wang YQ,
Cai YJ, Yang NB, Zheng MH, Dong JZ, Zhang L and Chen YP:
Hepatocellular carcinoma associated microRNA expression signature:
Integrated bioinformatics analysis, experimental validation and
clinical significance. Oncotarget. 6:25093–25108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chin L, Andersen JN and Futreal PA: Cancer
genomics: From discovery science to personalized medicine. Nat Med.
17:297–303. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G,
Rueda OM, Dunning MJ, Speed D, Lynch AG, Samarajiwa S, Yuan Y, et
al: The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast
tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature. 486:346–352. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Perou CM, Sørlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn
M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, Pollack JR, Ross DT, Johnsen H, Akslen LA,
et al: Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature.
406:747–752. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Anders CK and Carey LA: Biology,
metastatic patterns, and treatment of patients with triple-negative
breast cancer. Clin Breast Cancer. 9 (Suppl 2):S73–S81. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kalyuga M, Gallego-Ortega D, Lee HJ, Roden
DL, Cowley MJ, Caldon CE, Stone A, Allerdice SL, Valdes-Mora F,
Launchbury R, et al: ELF5 suppresses estrogen sensitivity and
underpins the acquisition of antiestrogen resistance in luminal
breast cancer. PLoS Biol. 10:e10014612012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Furth PA, Nakles RE, Millman S, Diaz-Cruz
ES and Cabrera MC: Signal transducer and activator of transcription
5 as a key signaling pathway in normal mammary gland developmental
biology and breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 13:2202011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou L, Yan T, Jiang Y, Di G, Shen Z, Shao
Z and Lu J: Prognostic and predictive value of TFF1 for adjuvant
endocrine therapy in Chinese women with early ER positive breast
cancer: Comparing aromatase inhibitors with tamoxifen. Breast.
20:15–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Prest SJ, May FE and Westley BR: The
estrogen-regulated protein, TFF1, stimulates migration of human
breast cancer cells. FASEB J. 16:592–594. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
May FE and Westley BR: TFF3 is a valuable
predictive biomarker of endocrine response in metastatic breast
cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 22:465–479. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ishibashi Y, Ohtsu H, Ikemura M, Kikuchi
Y, Niwa T, Nishioka K, Uchida Y, Miura H, Aikou S, Gunji T, et al:
Serum TFF1 and TFF3 but not TFF2 are higher in women with breast
cancer than in women without breast cancer. Sci Rep. 7:48462017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Abramson VG, Lehmann BD, Ballinger TJ and
Pietenpol JA: Subtyping of triple-negative breast cancer:
Implications for therapy. Cancer. 121:8–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Podo F, Buydens LM, Degani H, Hilhorst R,
Klipp E, Gribbestad IS, Van Huffel S, van Laarhoven HW, Luts J,
Monleon D, et al: Triple-negative breast cancer: Present challenges
and new perspectives. Mol Oncol. 4:209–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liedtke C, Mazouni C, Hess KR, André F,
Tordai A, Mejia JA, Symmans WF, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Hennessy B,
Green M, et al: Response to neoadjuvant therapy and long-term
survival in patients with triple-negative breast cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 26:1275–1281. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Iwamoto T, Bianchini G, Booser D, Qi Y,
Coutant C, Shiang CY, Santarpia L, Matsuoka J, Hortobagyi GN,
Symmans WF, et al: Gene pathways associated with prognosis and
chemotherapy sensitivity in molecular subtypes of breast cancer. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 103:264–272. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tan L, Song X, Sun X, Wang N, Qu Y and Sun
Z: ART3 regulates triple-negative breast cancer cell function via
activation of Akt and ERK pathways. Oncotarget. 7:46589–46602.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu RZ, Graham K, Glubrecht DD, Lai R,
Mackey JR and Godbout R: A fatty acid-binding protein 7/RXRβ
pathway enhances survival and proliferation in triple-negative
breast cancer. J Pathol. 228:310–321. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Watkins J, Weekes D, Shah V, Gazinska P,
Joshi S, Sidhu B, Gillett C, Pinder S, Vanoli F, Jasin M, et al:
Genomic complexity profiling reveals that HORMAD1 overexpression
contributes to homologous recombination deficiency in
triple-negative breast cancers. Cancer Discov. 5:488–505. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fritzsche FR, Dahl E, Pahl S, Burkhardt M,
Luo J, Mayordomo E, Gansukh T, Dankof A, Knuechel R, Denkert C, et
al: Prognostic relevance of AGR2 expression in breast cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 12:1728–1734. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wright TM, Wardell SE, Jasper JS, Stice
JP, Safi R, Nelson ER and McDonnell DP: Delineation of a
FOXA1/ERalpha/AGR2 regulatory loop that is dysregulated in
endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer. Mol Cancer Res.
12:1829–1839. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Soutto M, Peng D, Katsha A, Chen Z,
Piazuelo MB, Washington MK, Belkhiri A, Correa P and El-Rifai W:
Activation of β-catenin signalling by TFF1 loss promotes cell
proliferation and gastric tumorigenesis. Gut. 64:1028–1039. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Buache E, Etique N, Alpy F, Stoll I,
Muckensturm M, Reina-San-Martin B, Chenard MP, Tomasetto C and Rio
MC: Deficiency in trefoil factor 1 (TFF1) increases tumorigenicity
of human breast cancer cells and mammary tumor development in
TFF1-knockout mice. Oncogene. 30:3261–3273. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|