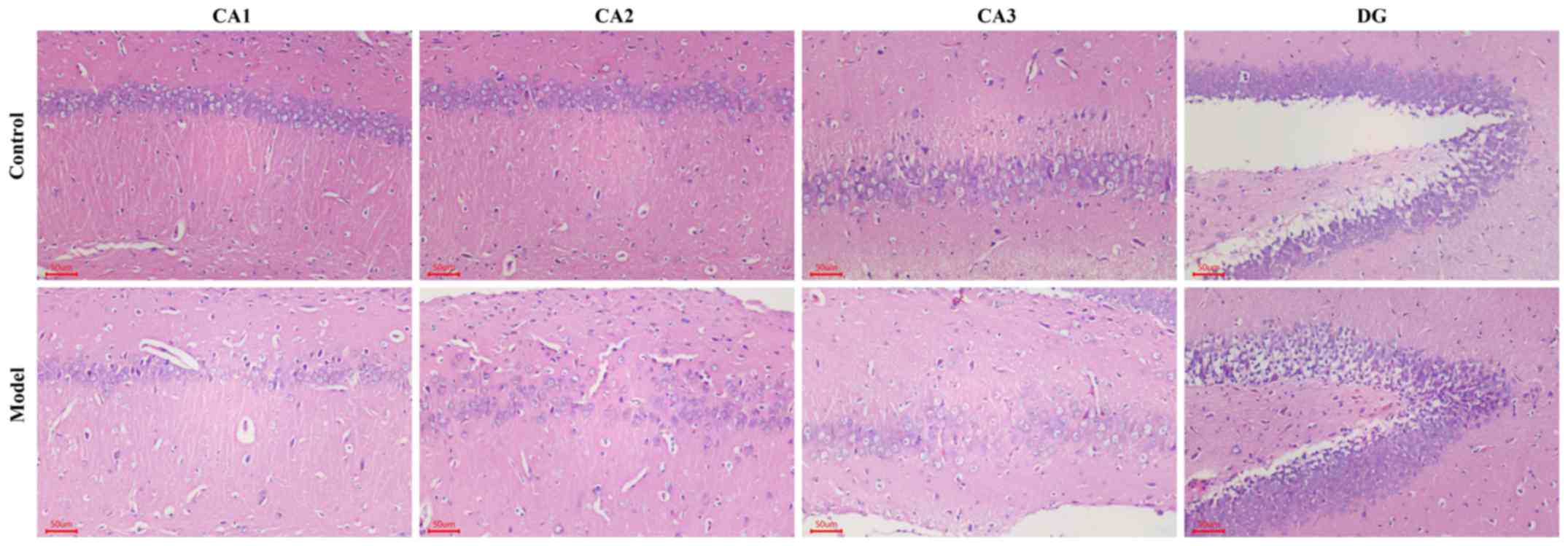
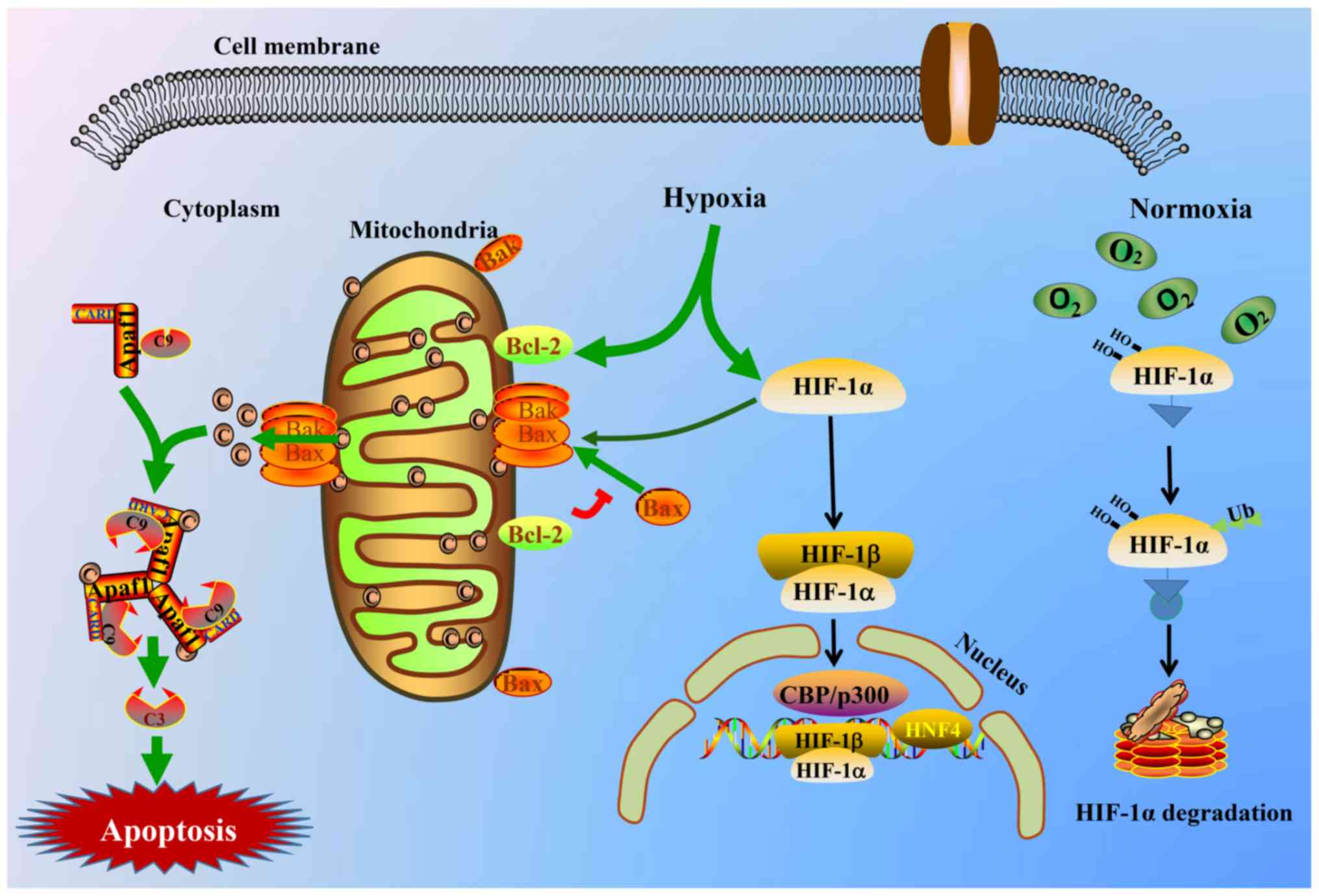
|
1
|
Young AJ, Berryman CE, Kenefick RW,
Derosier AN, Margolis LM, Wilson MA, Carrigan CT, Murphy NE,
Carbone JW, Rood JC, et al: Altitude acclimatization alleviates the
hypoxia-induced suppression of exogenous glucose oxidation during
steady-state aerobic exercise. Front Physiol. 9:8302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gonzalez Garay A, Molano Franco D, Nieto
Estrada VH, Martí-Carvajal AJ and Arevalo-Rodriguez I:
Interventions for preventing high altitude illness: Part 2. Less
commonly-used drugs. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
3:CD0129832018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Paul S, Gangwar A, Bhargava K, Khurana P
and Ahmad Y: Diagnosis and prophylaxis for high-altitude
acclimatization: Adherence to molecular rationale to evade
high-altitude illnesses. Life Sci. 203:171–176. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xiang K, Ouzhuluobu, Peng Y, Yang Z, Zhang
X, Cui C, Zhang H, Li M, Zhang Y, Bianba, et al: Identification of
a Tibetan-specific mutation in the hypoxic gene EGLN1 and its
contribution to high-altitude adaptation. Mol Biol Evol.
30:1889–1898. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang H, He Y, Cui C, Ouzhuluobu,
Baimakangzhuo, Duojizhuoma, Dejiquzong, Bianba, Gonggalanzi, Pan Y,
et al: Cross-altitude analysis suggests a turning point at the
elevation of 4,500 m for polycythemia prevalence in Tibetans. Am J
Hematol. 92:E552–E554. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gonggalanzi, Labasangzhu, Nafstad P,
Stigum H, Wu T, Haldorsen ØD, Ommundsen K and Bjertness E: Acute
mountain sickness among tourists visiting the high-altitude city of
Lhasa at 3658 m above sea level: A cross-sectional study. Arch
Public Health. 74:232016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
West JB: High-altitude medicine. Lancet
Respir Med. 3:12–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Basnyat B and Murdoch DR: High-altitude
illness. Lancet. 361:1967–1974. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Azad P, Stobdan T, Zhou D, Hartley I,
Akbari A, Bafna V and Haddad GG: High-altitude adaptation in
humans: From genomics to integrative physiology. J Mol Med (Berl).
95:1269–1282. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Davis C and Hackett P: Advances in the
prevention and treatment of high altitude illness. Emerg Med Clin
North Am. 35:241–260. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Horscroft JA, Kotwica AO, Laner V, West
JA, Hennis PJ, Levett DZH, Howard DJ, Fernandez BO, Burgess SL,
Ament Z, et al: Metabolic basis to Sherpa altitude adaptation. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 114:6382–6387. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ward PA, Blanchard RJ and Bolivar V:
Recognition and alleviation of distress in laboratory animals.
National Academies Press. 44:3802007.
|
|
13
|
Zhang Y, Meng X, Wu W, Lai X, Wang Y,
Zhang J and Wang Z: Duoxuekang, a traditional Tibetan medicine,
reduces hypoxia-induced high-altitude polycythemia in rats. A
Sponsored Supplement to Science. 338:63–64. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Zhang XY, Zhang XJ, Xv J, Jia W, Pu XY,
Wang HY, Liang H, Zhuoma-Lamao and Lu DX: Crocin attenuates acute
hypobaric hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits of rats. Eur J
Pharmacol. 818:300–305. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gong G, Yin L, Yuan L, Sui D, Sun Y, Fu H,
Chen L and Wang X: Ganglioside GM1 protects against high altitude
cerebral edema in rats by suppressing the oxidative stress and
inflammatory response via the PI3K/AKT-Nrf2 pathway. Mol Immunol.
95:91–98. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Song TT, Bi YH, Gao YQ, Huang R, Hao K, Xu
G, Tang JW, Ma ZQ, Kong FP, Coote JH, et al: Systemic
pro-inflammatory response facilitates the development of cerebral
edema during short hypoxia. J Neuroinflammation. 13:63–76. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guo P, Luo H, Fan Y, Luo Y and Zhou Q:
Establishment and evaluation of an experimental animal model of
high altitude cerebral edema. Neurosci Lett. 547:82–86. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gu J, Su S, Guo J, Zhu Y, Zhao M and Duan
JA: Anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic effects of the combination
of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Radix Paeoniae against focal cerebral
ischaemia via TLR4/MyD88/MAPK/NF-κB signalling pathway in MCAO
rats. J Pharm Pharmacol. 70:268–277. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang P, Xie ZD, Xie CN, Lin CW, Wang JL,
Xuan LN, Zhang CW, Wang Y, Huang ZH and Teng HL: AMP-activated
protein kinase-dependent induction of autophagy by erythropoietin
protects against spinal cord injury in rats. CNS Neurosci Ther.
24:1185–1195. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Song H, Konan LM, Cui J, Johnson CE,
Langenderfer M, Grant D, Ndam T, Simonyi A, White T, Demirci U, et
al: Ultrastructural brain abnormalities and associated behavioral
changes in mice after low-intensity blast exposure. Behav Brain
Res. 347:148–157. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kaplan GB, Leite-Morris KA, Wang L,
Rumbika KK, Heinrichs SC, Zeng X, Wu L, Arena DT and Teng YD:
Pathophysiological bases of comorbidity: Traumatic brain injury and
post-traumatic stress disorder. J Neurotrauma. 35:210–225. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mancuso M, Abbruzzese L, Canova S, Landi
G, Rossi S and Santarnecchi E: Transcranial random noise
stimulation does not improve behavioral and neurophysiological
measures in patients with subacute vegetative-unresponsive
wakefulness state (VS-UWS). Front Hum Neurosci. 11:5242017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhao Q, Wang X, Chen A, Cheng X, Zhang G,
Sun J, Zhao Y, Huang Y and Zhu Y: Rhein protects against cerebral
ischemic-/reperfusion-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis in
rats. Int J Mol Med. 41:2802–2812. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ren H, Meng X, Yin J, Sun J, Huang Q and
Yin Z: Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharide peptide attenuates skin
flap ischemia-reperfusion injury in a thioredoxin-dependent manner.
Plast Reconstr Surg. 142:23e–33e. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang X, Rui L, Wang M, Lian H and Cai L:
Sinomenine attenuates chronic intermittent hypoxia-induced lung
injury by inhibiting inflammation and oxidative stress. Med Sci
Monit. 24:1574–1580. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang G, Min D, Yan J, Yang M and Lin G:
Protective role and mechanism of snakegourd peel against myocardial
infarction in rats. Phytomedicine. 42:18–24. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wu H, Luo D, Li C, Zhang H, Shunxian A,
Zhang Y and Sun C: Chicoric acid improves heart and blood responses
to hypobaric hypoxia in tibetan yaks. Am J Chin Med. 46:339–355.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yan YT, Li SD, Li C, Xiong YX, Lu XH, Zhou
XF, Yang LQ, Pu LJ and Luo HY: Panax notoginsenoside saponins Rb1
regulates the expressions of Akt/mTOR/PTEN signals in the
hippocampus after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Behav Brain Res.
345:83–92. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ramli Y, Alwahdy AS, Kurniawan M, Juliandi
B, Wuyung PE and Susanto YDB: Intravenous versus intraarterial
transplantation of human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells for
brain ischemia in rats. Hayati J Biosci. 24:187–194. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sun J, Wang F, Li H, Zhang H, Jin J, Chen
W, Pang M, Yu J, He Y, Liu J and Liu C: Neuroprotective effect of
sodium butyrate against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in
mice. Biomed Res Int. 2015:3958952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zuo D, Lin L, Liu Y, Wang C, Xu J, Sun F,
Li L, Li Z and Wu Y: Baicalin attenuates ketamine-induced
neurotoxicity in the developing rats: Involvement of PI3K/Akt and
CREB/BDNF/Bcl-2 pathways. Neurotox Res. 30:159–172. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu Z, Wu P, Zuo X, Yu N, Qin Y, Xu Q, He
S, Cen B, Liao W and Ji A: LncRNA-N1LR enhances neuroprotection
against ischemic stroke probably by inhibiting p53 phosphorylation.
Mol Neurobiol. 54:7670–7685. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang JZ, Jing L, Ma Y, Guo FY, Chang Y
and Li PA: Monosialotetrahexosy-1 ganglioside attenuates diabetes-
enhanced brain damage after transient forebrain ischemia and
suppresses phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in the rat brain. Brain Res.
1344:200–208. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bahrami A, Atkin SL, Majeed M and Sahebkar
A: Effects of curcumin on hypoxia-inducible factor as a new
therapeutic target. Pharmacol Res. 137:159–169. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gonzalez FJ, Xie C and Jiang C: The role
of hypoxia-inducible factors in metabolic diseases. Nat Rev
Endocrinol. 15:21–32. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Choudhry H and Harris AL: Advances in
hypoxia-inducible factor biology. Cell Metab. 27:281–298. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
West JB: Physiological effects of chronic
hypoxia. N Engl J Med. 376:1965–1971. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee KE and Simon MC: SnapShot:
Hypoxia-inducible factors. Cell. 163:1288–1288.e1. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
West JB: High altitude medicine. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 186:1229–1237. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zheng KY, Zhang ZX, Guo AJ, Bi CW, Zhu KY,
Xu SL, Zhan JY, Lau DT, Dong TT, Choi RC and Tsim KW: Salidroside
stimulates the accumulation of HIF-1α protein resulted in the
induction of EPO expression: A signaling via blocking the
degradation pathway in kidney and liver cells. Eur J Pharmacol.
679:34–39. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Long Z, Li J and Meng X: The protective
effects of active ingredients isolated from Rhodiola on the
myocardial cell damage induced by hypoxia/glucose deprivation.
Pharmacology and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica. 26:24–25.
2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
42
|
Wang Y, Zhang Y, Feng X, Meng X, Long Y
and Zhang J: Bioactive chemical constituents from Rhodiola
crenulata and effect on hypoxia inducible factor-1α expression.
West China J Pharmaceutical Sci. 24:021–024. 2009.(In Chinese).
|
|
43
|
Hu Y, Lv X, Zhang J and Meng X:
Comparative study on the protective effects of salidroside and
hypoxic preconditioning for attenuating anoxia-induced apoptosis in
pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. Med Sci Monit. 22:4082–4091. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhao Q, Cheng X, Wang X, Wang J, Zhu Y and
Ma X: Neuroprotective effect and mechanism of Mu-Xiang-You-Fang on
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J Ethnopharmacol.
192:140–147. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Qiu J, Zhou XY, Zhou XG, Cheng R, Liu HY
and Li Y: Neuroprotective effects of microRNA-210 against
oxygen-glucose deprivation through inhibition of apoptosis in PC12
cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:1955–1959. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
He M, Lu Y, Xu S, Mao L, Zhang L, Duan W,
Liu C, Pi H, Zhang Y, Zhong M, et al: MiRNA-210 modulates a
nickel-induced cellular energy metabolism shift by repressing the
iron-sulfur cluster assembly proteins ISCU1/2 in Neuro-2a cells.
Cell Death Dis. 5:e10902014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ye Z, Guo Q, Xia P, Wang N, Wang E and
Yuan Y: Sevoflurane postconditioning involves an up-regulation of
HIF-1α and HO-1 expression via PI3K/Akt pathway in a rat model of
focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1463:63–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|