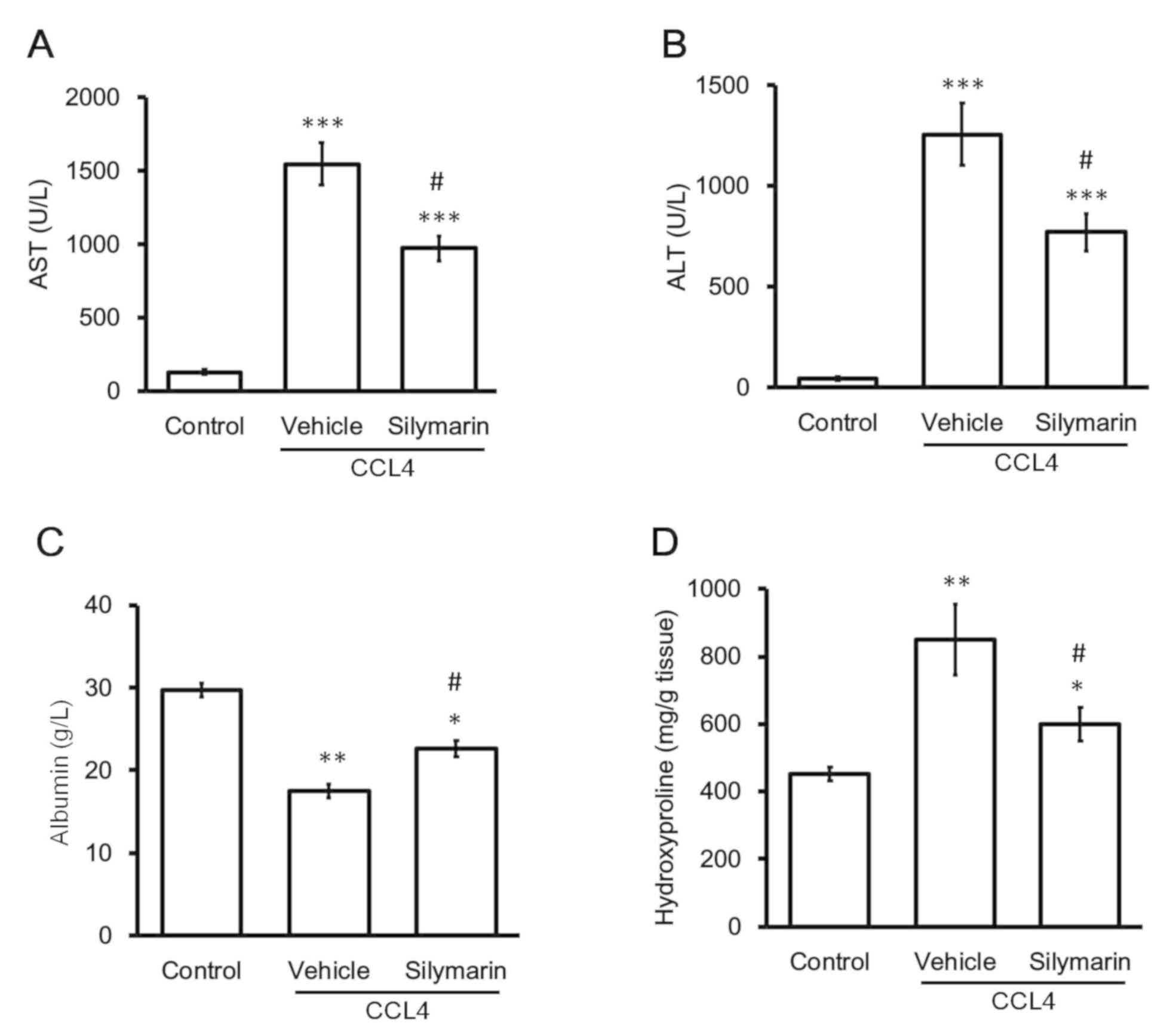
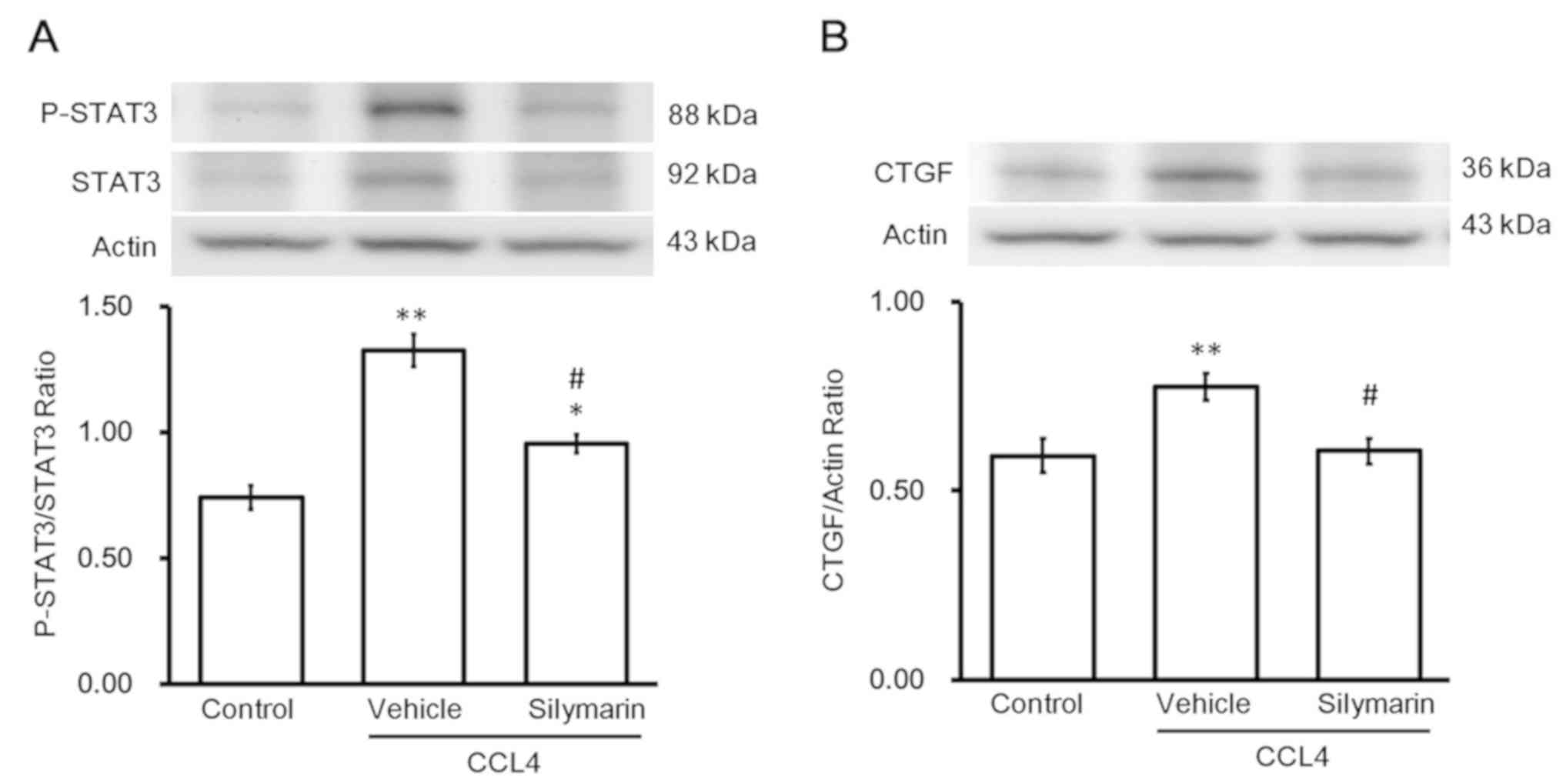
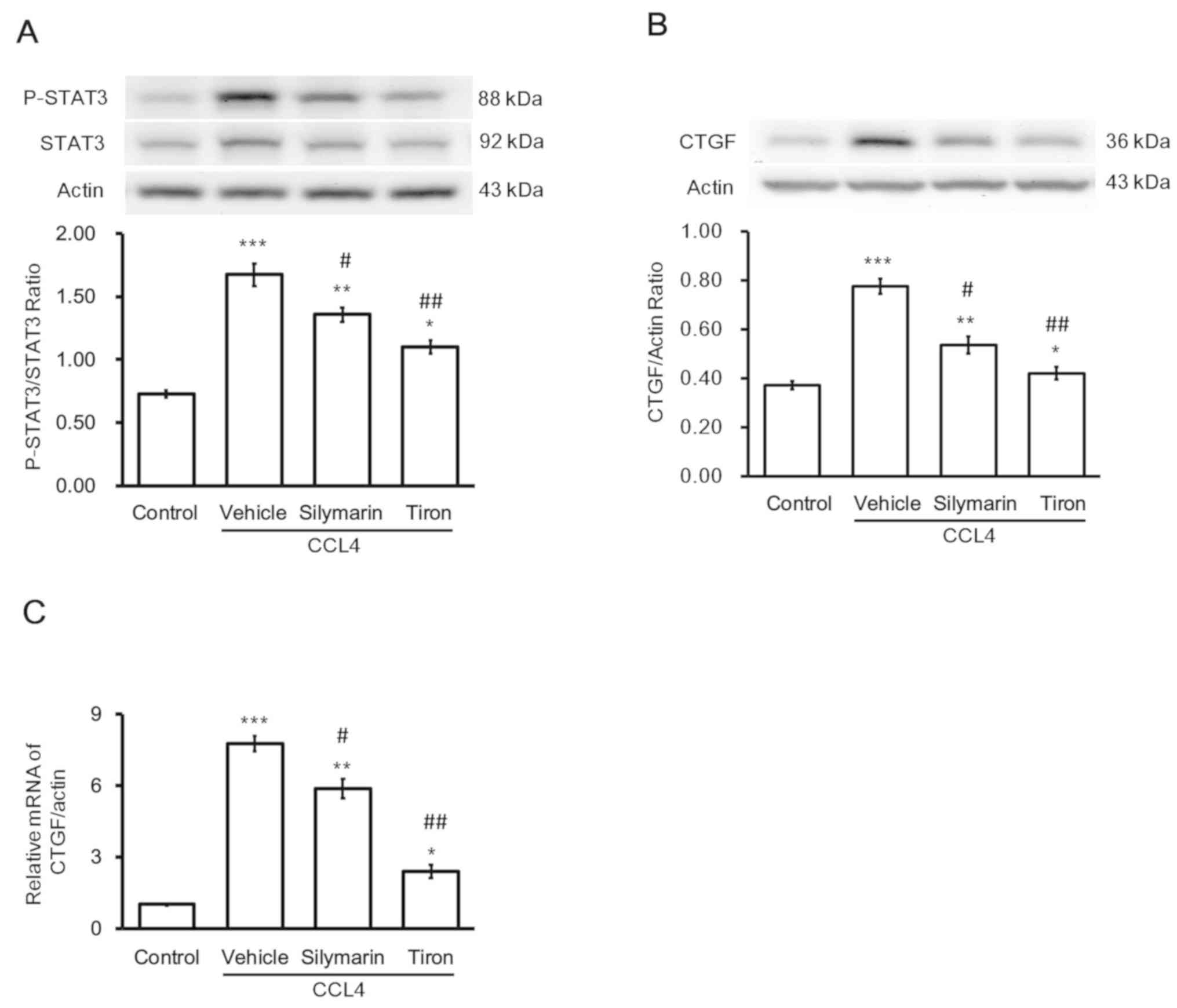
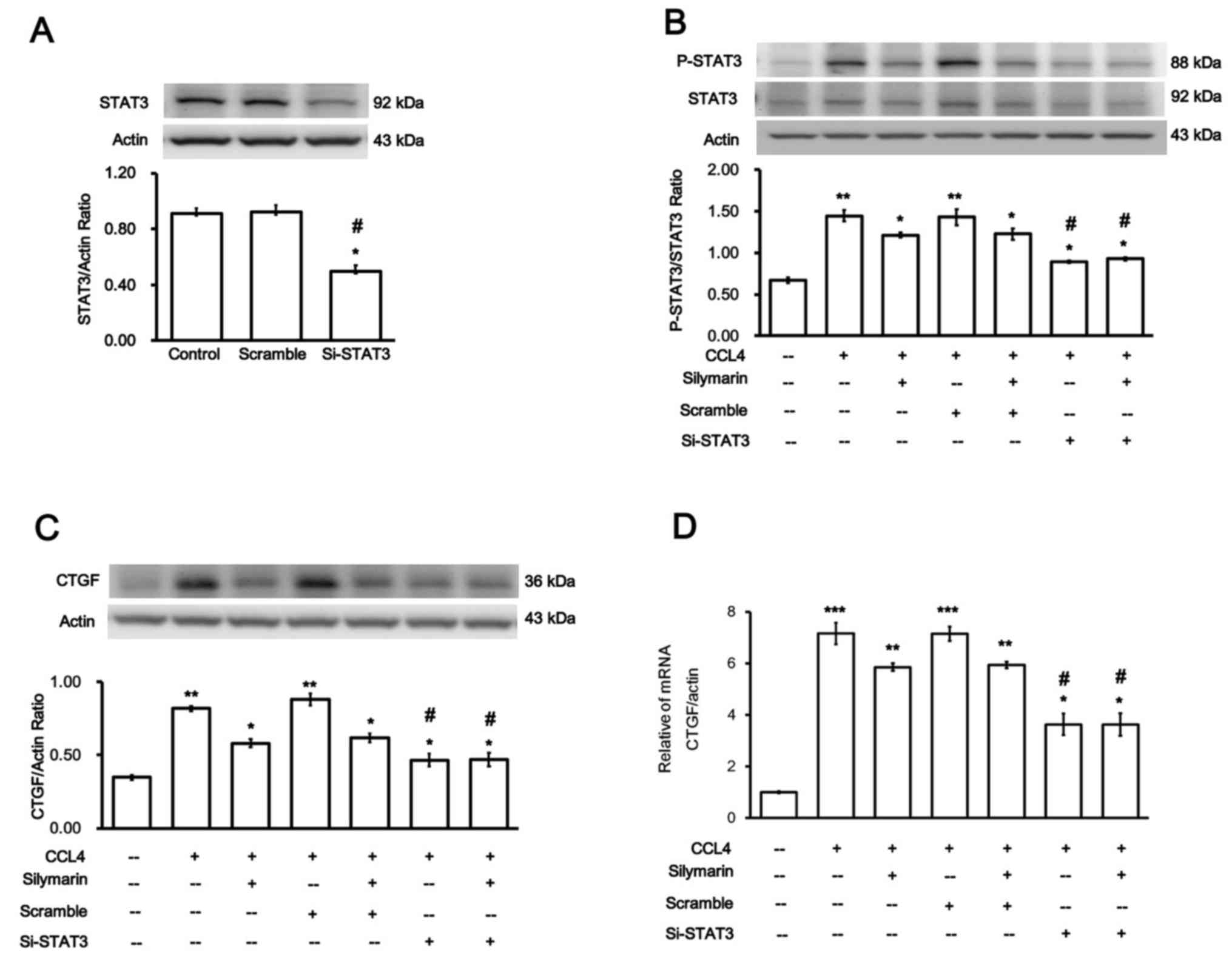
|
1
|
Pari L and Sankaranarayanan C: Beneficial
effects of thymoquinone on hepatic key enzymes in
streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic rats. Life Sci.
85:830–834. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nguyen-Lefebvre AT and Horuzsko A: Kupffer
cell metabolism and function. J Enzymol Metab. 1(pii):
1012015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mello T, Zanieri F, Ceni E and Galli A:
Oxidative stress in the healthy and wounded hepatocyte: A cellular
organelles perspective. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:83274102016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gressner OA, Weiskirchen R and Gressner
AM: Biomarkers of hepatic fibrosis, fibrogenesis and genetic
pre-disposition pending between fiction and reality. J Cell Mol
Med. 11:1031–1051. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Higuchi H and Gores GJ: Mechanisms of
liver injury: An overview. Curr Mol Med. 3:483–490. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Canbay A, Friedman S and Gores GJ:
Apoptosis: The nexus of liver injury and fibrosis. Hepatology.
39:273–278. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang X and Wu B: Critical issues in the
diagnosis and treatment of liver cirrhosis. Gastroenterol Rep
(Oxf). 7:227–230. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pinzani M and Rombouts K: Liver fibrosis:
From the bench to clinical targets. Dig Liver Dis. 36:231–242.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gressner AM, Weiskirchen R, Breitkopf K
and Dooley S: Roles of TGF-beta in hepatic fibrosis. Front Biosci.
7:d793–d807. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sugimoto H, Yang C, LeBleu VS, Soubasakos
MA, Giraldo M, Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: BMP-7 functions as a novel
hormone to facilitate liver regeneration. FASEB J. 21:256–264.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schuster N and Krieglstein K: Mechanisms
of TGF-beta-mediated apoptosis. Cell Tissue Res. 307:1–14. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Arnott JA, Lambi AG, Mundy C, Hendesi H,
Pixley RA, Owen TA, Safadi FF and Popoff SN: The role of connective
tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) in skeletogenesis. Crit Rev
Eukaryot Gene Expr. 21:43–69. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Abreu JG, Ketpura NI, Reversade B and De
Robertis EM: Connective-tissue growth factor (CTGF) modulates cell
signalling by BMP and TGF-beta. Nat Cell Biol. 4:599–604. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gressner OA, Lahme B, Demirci I, Gressner
AM and Weiskirchen R: Differential effects of TGF-beta on
connective tissue growth factor (CTGF/CCN2) expression in hepatic
stellate cells and hepatocytes. J Hepatol. 47:699–710. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gressner AM, Yagmur E, Lahme B, Gressner O
and Stanzel S: Connective tissue growth factor in serum as a new
candidate test for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Clin Chem.
52:1815–1817. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Meindl-Beinker NM and Dooley S:
Transforming growth factor-beta and hepatocyte transdifferentiation
in liver fibrogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 23 (Suppl
1):S122–S127. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Williams AT and Burk RF: Carbon
tetrachloride hepatotoxicity: An example of free radical-mediated
injury. Semin Liver Dis. 10:279–284. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Manibusan MK, Odin M and Eastmond DA:
Postulated carbon tetrachloride mode of action: A review. J Environ
Sci Health C Environ Carcinog Ecotoxicol Rev. 25:185–209. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Planaguma A, Claria J, Miquel R,
López-Parra M, Titos E, Masferrer JL, Arroyo V and Rodés J: The
selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor SC-236 reduces liver fibrosis
by mechanisms involving non-parenchymal cell apoptosis and
PPARgamma activation. FASEB J. 19:1120–1122. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Badr G, Sayed EA, Waly H, Hassan KA,
Mahmoud MH and Selamoglu Z: The therapeutic mechanisms of Propolis
against CCl4-mediated liver injury by mediating
apoptosis of activated hepatic stellate cells and improving the
hepatic architecture through PI3K/AKT/mTOR, TGF-beta/Smad2,
Bcl2/BAX/P53 and iNOS signaling pathways. Cell Physiol Biochem.
53:301–322. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dong S, Chen QL, Song YN, Sun Y, Wei B, Li
XY, Hu YY, Liu P and Su SB: Mechanisms of CCl4-induced
liver fibrosis with combined transcriptomic and proteomic analysis.
J Toxicol Sci. 41:561–572. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tzeng JI, Chen MF, Chung HH and Cheng JT:
Silymarin decreases connective tissue growth factor to improve
liver fibrosis in rats treated with carbon tetrachloride. Phytother
Res. 27:1023–1028. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang H, Lafdil F, Kong X and Gao B: Signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 in liver diseases: A
novel therapeutic target. Int J Biol Sci. 7:536–550. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao B, Wang H, Lafdil F and Feng D: STAT
proteins-key regulators of anti-viral responses, inflammation, and
tumorigenesis in the liver. J Hepatol. 57:430–441. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nieto N: Oxidative-stress and IL-6 mediate
the fibrogenic effects of [corrected] Kupffer cells on stellate
cells. Hepatology. 44:1487–1501. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Su TH, Shiau CW, Jao P, Liu CH, Liu CJ,
Tai WT, Jeng YM, Yang HC, Tseng TC, Huang HP, et al: Sorafenib and
its derivative SC-1 exhibit antifibrotic effects through signal
transducer and activator of transcription 3 inhibition. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 112:7243–7248. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hui J, Gao J, Wang Y, Zhang J, Han Y, Wei
L, Liu Xiaochuang and Wu J: Panax notoginseng saponins ameliorates
experimental hepatic fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell
proliferation by inhibiting the Jak2/Stat3 pathways. J Tradit Chin
Med. 36:217–224. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qu W, Huang H, Li K and Qin C:
Danshensu-mediated protective effect against hepatic fibrosis
induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Pathol Biol (Paris).
62:348–353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Surai PF: Silymarin as a natural
antioxidant: An overview of the current evidence and perspectives.
Antioxidants (Basel). 4:204–247. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen X, Ying X, Zhang W, Chen Y, Shi C,
Hou Y and Zhang Y: The hepatoprotective effect of fraxetin on
carbon tetrachloride induced hepatic fibrosis by antioxidative
activities in rats. Int Immunopharmacol. 17:543–547. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Abdel-Moneim AM, Al-Kahtani MA, El-Kersh
MA and Al-Omair MA: Free Radical-scavenging, Anti-
inflammatory/Anti-Fibrotic and Hepatoprotective Actions of Taurine
and silymarin against CCl4 induced rat liver damage.
PLoS One. 10:e01445092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kuo SC, Li Y, Cheng KC, Niu CS, Cheng JT
and Niu HS: Increase in renal erythropoietin receptors in diabetic
rats is mainly mediated by hyperglycemia associated with the
STAT3/GATA-1 signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 96:1094–1102.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang R, Wang J, Song F, Li S and Yuan Y:
Tanshinol ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis in
rats through the regulation of Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-κB/IκBα signaling
pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther. 12:1281–1292. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsai JH, Liu JY, Wu TT, Ho PC, Huang CY,
Shyu JC, Hsieh YS, Tsai CC and Liu YC: Effects of silymarin on the
resolution of liver fibrosis induced by carbon tetrachloride in
rats. J Viral Hepat. 15:508–514. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu Y, Wen PH, Zhang XX, Dai Y and He Q:
Breviscapine ameliorates CCl4-induced liver injury in
mice through inhibiting inflammatory apoptotic response and ROS
generation. Int J Mol Med. 42:755–768. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morgan A, Ibrahim MA, Galal MK, Ogaly HA
and Abd-Elsalam RM: Innovative perception on using Tiron to
modulate the hepatotoxicity induced by titanium dioxide
nanoparticles in male rats. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:553–561. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Schust J, Sperl B, Hollis A, Mayer TU and
Berg T: Stattic: A small-molecule inhibitor of STAT3 activation and
dimerization. Chem Biol. 13:1235–1242. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
El-Lakkany NM, Hammam OA, El-Maadawy WH,
Badawy AA, Ain-Shoka AA and Ebeid FA:
Anti-inflammatory/anti-fibrotic effects of the hepatoprotective
silymarin and the schistosomicide praziquantel against Schistosoma
mansoni-induced liver fibrosis. Parasit Vectors. 5:92012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu Y, Liu H, Meyer C, Li J, Nadalin S,
Königsrainer A, Weng H, Dooley S and ten Dijke P: Transforming
growth factor-β (TGF-β)-mediated connective tissue growth factor
(CTGF) expression in hepatic stellate cells requires Stat3
signaling activation. J Biol Chem. 288:30708–30719. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ha HL, Shin HJ, Feitelson MA and Yu DY:
Oxidative stress and antioxidants in hepatic pathogenesis. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:6035–6043. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Shaker E, Mahmoud H and Mnaa S: Silymarin,
the antioxidant component and Silybum marianum extracts prevent
liver damage. Food Chem Toxicol. 48:803–806. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Huo HZ, Wang B, Liang YK, Bao YY and Gu Y:
Hepatoprotective and antioxidant effects of licorice extract
against CCl(4)-induced oxidative damage in rats. Int J Mol Sci.
12:6529–6543. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Han YH and Park WH: Tiron, a ROS
scavenger, protects human lung cancer Calu-6 cells against
antimycin A-induced cell death. Oncol Rep. 21:253–261.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chiu YH, Ku PM, Cheng YZ, Li Y, Cheng JT
and Niu HS: Phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 induced by hyperglycemia is different with that
induced by lipopolysaccharide or erythropoietin via receptorcoupled
signaling in cardiac cells. Mol Med Rep. 17:1311–1320.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pan Y, Zhou F, Zhang R and Claret FX:
Stat3 inhibitor Stattic exhibits potent antitumor activity and
induces chemo- and radio-sensitivity in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
PLoS One. 8:e545652013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang CM, Hsu CT, Niu HS, Chang CH, Cheng
JT and Shieh JM: Lung damage induced by hyperglycemia in diabetic
rats: The role of signal transducer and activator of transcription
3 (STAT3). J Diabetes Complications. 30:1426–1433. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Heidelberger S, Zinzalla G, Antonow D,
Essex S, Basu BP, Palmer J, Husby J, Jackson PJ, Rahman KM,
Wilderspin AF, et al: Investigation of the protein alkylation sites
of the STAT3:STAT3 inhibitor Stattic by mass spectrometry. Bioorg
Med Chem Lett. 23:4719–4722. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Szelag M, Sikorski K, Czerwoniec A,
Szatkowska K, Wesoly J and Bluyssen HA: In silico simulations of
STAT1 and STAT3 inhibitors predict SH2 domain cross-binding
specificity. Eur J Pharmacol. 720:38–48. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Boengler K, Ungefug E, Heusch G and Schulz
R: The STAT3 inhibitor stattic impairs cardiomyocyte mitochondrial
function through increased reactive oxygen species formation. Curr
Pharm Des. 19:6890–6895. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sanseverino I, Purificato C, Gauzzi MC and
Gessani S: Revisiting the specificity of small molecule inhibitors:
The example of stattic in dendritic cells. Chem Biol. 19:1213–1216.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Miller AM, Wang H, Bertola A, Park O,
Horiguchi N, Ki SH, Yin S, Lafdil F and Gao B:
Inflammation-associated interleukin-6/signal transducer and
activator of transcription 3 activation ameliorates alcoholic and
nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases in interleukin-10-deficient mice.
Hepatology. 54:846–856. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Jung JE, Lee HG, Cho IH, Chung DH, Yoon
SH, Yang YM, Lee JW, Choi S, Park JW, Ye SK and Chung MH: STAT3 is
a potential modulator of HIF-1-mediated VEGF expression in human
renal carcinoma cells. FASEB J. 19:1296–1298. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang Z, Li J, Xiao W, Long J and Zhang H:
The STAT3 inhibitor S3I-201 suppresses fibrogenesis and
angiogenesis in liver fibrosis. Lab Invest. 98:1600–1613. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Wang Y, Gao J, Zhang D, Zhang J, Ma J and
Jiang H: New insights into the antifibrotic effects of sorafenib on
hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis. J Hepatol. 53:132–144.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Deng YR, Ma HD, Tsuneyama K, Yang W, Wang
YH, Lu FT, Liu CH, Liu P, He XS, Diehl AM, et al: STAT3-mediated
attenuation of CCl4-induced mouse liver fibrosis by the
protein kinase inhibitor sorafenib. J Autoimmun. 46:25–34. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|