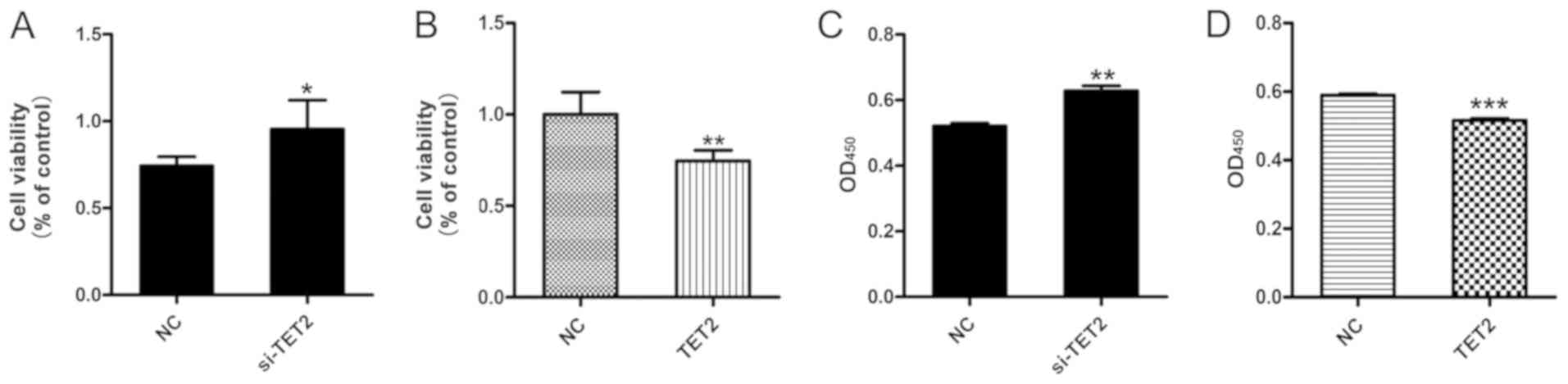
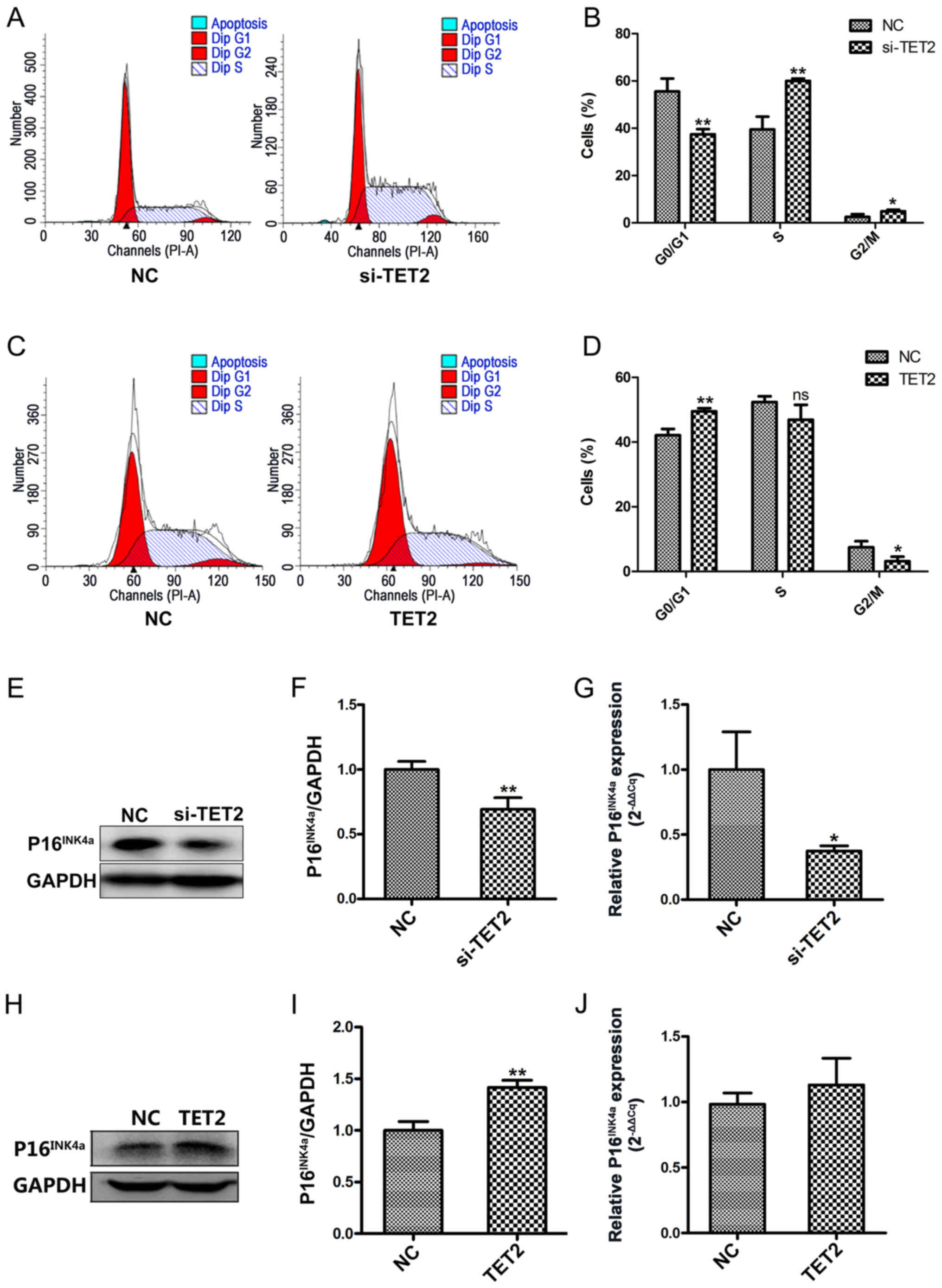
|
1
|
Shen J, Abu-Amer Y, O'Keefe RJ and
McAlinden A: Inflammation and epigenetic regulation in
osteoarthritis. Connect Tissue Res. 58:49–63. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu X and Zhang Y: TET-mediated active DNA
demethylation: Mechanism, function and beyond. Nat Rev Genet.
18:517–534. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Li D, Guo B, Wu H, Tan L and Lu Q: TET
family of dioxygenases: Crucial roles and underlying mechanisms.
Cytogenet Genome Res. 146:171–180. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hu L, Li Z, Cheng J, Rao Q, Gong W, Liu M,
Shi YG, Zhu J, Wang P and Xu Y: Crystal structure of TET2-DNA
complex: Insight into TET-mediated 5mC oxidation. Cell.
155:1545–1555. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ichiyama K, Chen T, Wang X, Yan X, Kim BS,
Tanaka S, Ndiaye-Lobry D, Deng Y, Zou Y, Zheng P, et al: The
methylcytosine dioxygenase Tet2 promotes DNA demethylation and
activation of cytokine gene expression in T cells. Immunity.
42:613–626. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pastor WA, Aravind L and Rao A: TETonic
shift: Biological roles of TET proteins in DNA demethylation and
transcription. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 14:341–356. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ito S, Shen L, Dai Q, Wu SC, Collins LB,
Swenberg JA, He C and Zhang Y: Tet proteins can convert
5-methylcytosine to 5-formylcytosine and 5-carboxylcytosine.
Science. 333:1300–1303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rasmussen KD and Helin K: Role of TET
enzymes in DNA methylation, development, and cancer. Genes Dev.
30:733–750. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He YF, Li BZ, Li Z, Liu P, Wang Y, Tang Q,
Ding J, Jia Y, Chen Z, Li L, et al: Tet-mediated formation of
5-carboxylcytosine and its excision by TDG in mammalian DNA.
Science. 333:1303–1307. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weber AR, Krawczyk C, Robertson AB,
Kuśnierczyk A, Vågbø CB, Schuermann D, Klungland A and Schär P:
Biochemical reconstitution of TET1-TDG-BER-dependent active DNA
demethylation reveals a highly coordinated mechanism. Nat Commun.
7:108062016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Q, Zhao K, Shen Q, Han Y, Gu Y, Li
X, Zhao D, Liu Y, Wang C, Zhang X, et al: Tet2 is required to
resolve inflammation by recruiting Hdac2 to specifically repress
IL-6. Nature. 525:389–393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Yao B, Chen L, Kang Y, Li Y, Cheng
Y, Li L, Lin L, Wang Z, Wang M, et al: Ten-eleven translocation 2
interacts with forkhead box O3 and regulates adult neurogenesis.
Nat Commun. 8:159032017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sun H, Miao Z, Wang H, Tao Y, Yang J, Cai
J, Wang J and Wang Y: DNA hydroxymethylation mediated traumatic
spinal injury by influencing cell death-related gene expression. J
Cell Biochem. 119:9295–9302. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Uchiyama R, Uhara H, Uchiyama A, Ogawa E,
Takazawa Y, Ashida A, Koga H, Hayashi K, Kiniwa Y and Okuyama R:
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine as a useful marker to differentiate between
malignant melanomas and benign melanocytic nevi. J Dermatol Sci.
73:161–163. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benhadou F, Mintoff D and Del Marmol V:
Psoriasis: Keratinocytes or immune cells - Which is the trigger?
Dermatology. 235:91–100. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bitschar K, Wolz C, Krismer B, Peschel A
and Schittek B: Keratinocytes as sensors and central players in the
immune defense against Staphylococcus aureus in the skin. J
Dermatol Sci. 87:215–220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Asahina R and Maeda S: A review of the
roles of keratinocyte-derived cytokines and chemokines in the
pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis in humans and dogs. Vet Dermatol.
28:16–e5. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fogel O, Richard-Miceli C and Tost J:
Epigenetic changes in chronic inflammatory diseases. Adv Protein
Chem Struct Biol. 106:139–189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Liu X, Liu N and Chen H:
Prediction of crucial epigenetically-associated, differentially
expressed genes by integrated bioinformatics analysis and the
identification of S100A9 as a novel biomarker in psoriasis. Int J
Mol Med. 45:93–102. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Poole CJ, Lodh A, Choi JH and van Riggelen
J: MYC deregulates TET1 and TET2 expression to control global DNA
(hydroxy)methylation and gene expression to maintain a neoplastic
phenotype in T-ALL. Epigenetics Chromatin. 12:412019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chiba S: Dysregulation of TET2 in
hematologic malignancies. Int J Hematol. 105:17–22. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Raghuraman S, Donkin I, Versteyhe S,
Barrès R and Simar D: The emerging role of epigenetics in
inflammation and immunometabolism. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
27:782–795. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang X, Liu X, Duan X, Zhu K, Zhang S, Gan
L, Liu N, Jaypaul H, Makamure JT, Ming Z, et al: Ten-eleven
translocation-2 regulates DNA hydroxymethylation status and
psoriasiform dermatitis progression in mice. Acta Derm Venereol.
98:585–593. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng X and Blumenthal RM: Mammalian DNA
methyltransferases: A structural perspective. Structure.
16:341–350. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ko M, An J, Bandukwala HS, Chavez L, Aijö
T, Pastor WA, Segal MF, Li H, Koh KP, Lähdesmäki H, et al:
Modulation of TET2 expression and 5-methylcytosine oxidation by the
CXXC domain protein IDAX. Nature. 497:122–126. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Prikrylova T, Robertson J, Ferrucci F,
Konorska D, Aanes H, Manaf A, Zhang B, Vågbø CB, Kuśnierczyk A,
Gilljam KM, et al: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine marks mammalian origins
acting as a barrier to replication. Sci Rep. 9:110652019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chrysanthou S, Senner CE, Woods L,
Fineberg E, Okkenhaug H, Burge S, Perez-Garcia V and Hemberger M: A
critical role of TET1/2 proteins in cell-cycle progression of
trophoblast stem cells. Stem Cell Reports. 10:1355–1368. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shimozaki K: Ten-eleven translocation 1
and 2 confer overlapping transcriptional programs for the
proliferation of cultured adult neural stem cells. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 37:995–1008. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mahfoudhi E, Talhaoui I, Cabagnols X,
Della Valle V, Secardin L, Rameau P, Bernard OA, Ishchenko AA,
Abbes S, Vainchenker W, et al: TET2-mediated
5-hydroxymethylcytosine induces genetic instability and
mutagenesis. DNA Repair (Amst). 43:78–88. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
O'Neill CJ and McCluggage WG: p16
expression in the female genital tract and its value in diagnosis.
Adv Anat Pathol. 13:8–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Aagaard L, Lukas J, Bartkova J, Kjerulff
AA, Strauss M and Bartek J: Aberrations of p16Ink4 and
retinoblastoma tumour-suppressor genes occur in distinct sub-sets
of human cancer cell lines. Int J Cancer. 61:115–120. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Stylianou E: Epigenetics of chronic
inflammatory diseases. J Inflamm Res. 12:1–14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lagos C, Carvajal P, Castro I, Jara D,
González S, Aguilera S, Barrera MJ, Quest AFG, Bahamondes V, Molina
C, et al: Association of high 5-hydroxymethylcytosine levels with
Ten Eleven Translocation 2 overexpression and inflammation in
Sjögren's syndrome patients. Clin Immunol. 196:85–96. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang X, Feng Z, Li Q, Yi B and Xu Q: DNA
methylcytosine dioxygenase ten-eleven translocation 2 enhances
lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine expression in human dental pulp
cells by regulating MyD88 hydroxymethylation. Cell Tissue Res.
373:477–485. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|