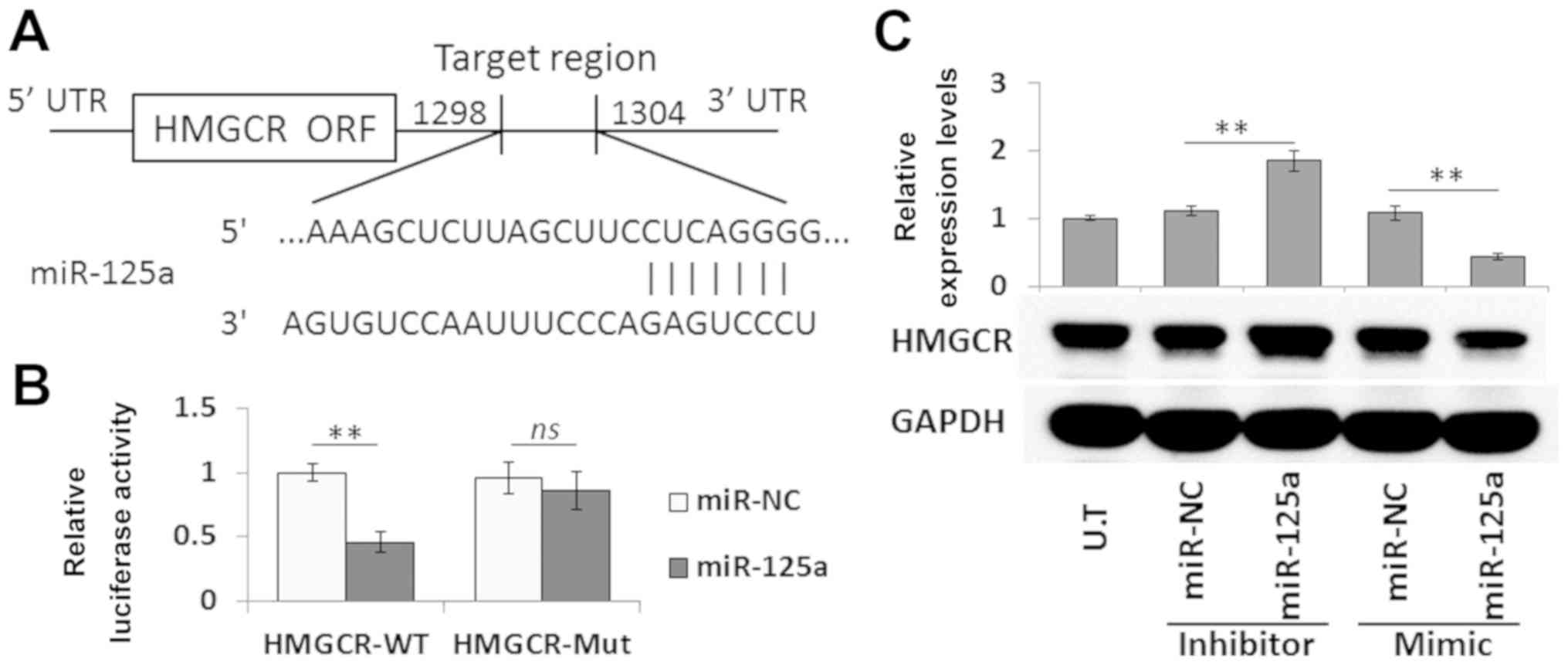
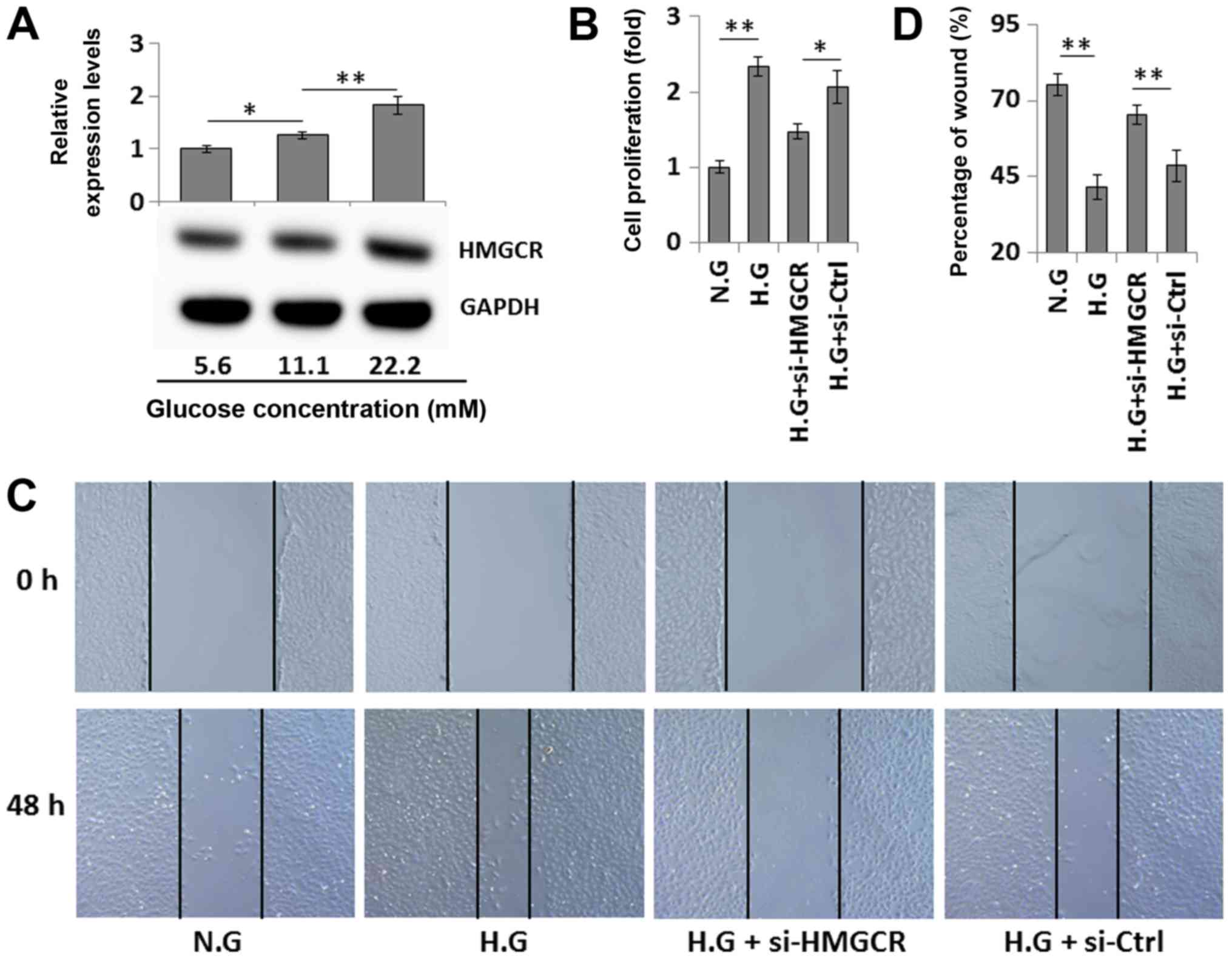
|
1
|
Atkinson MA, Eisenbarth GS and Michels AW:
Type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 383:69–82. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chatterjee S, Khunti K and Davies MJ: Type
2 diabetes. Lancet. 389:2239–2251. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gilbert RE and Krum H: Heart failure in
diabetes: Effects of anti-hyperglycaemic drug therapy. Lancet.
385:2107–2117. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Katakami N: Mechanism of Development of
atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. J
Atheroscler Thromb. 25:27–39. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Low Wang CC, Hess CN, Hiatt WR and
Goldfine AB: Clinical update: Cardiovascular disease in diabetes
mellitus: Atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and heart failure
in type 2 diabetes mellitus-mechanisms, management, and clinical
considerations. Circulation. 133:2459–2502. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shi L, Ji Y, Jiang X, Zhou L, Xu Y, Li Y,
Jiang W, Meng P and Liu X: Liraglutide attenuates high
glucose-induced abnormal cell migration, proliferation, and
apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells by activating the GLP-1
receptor, and inhibiting ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 14:182015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642e552009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ding Y, Sun X and Shan PF: MicroRNAs and
cardiovascular disease in diabetes mellitus. Biomed Res Int.
2017:40803642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rudijanto A: The role of vascular smooth
muscle cells on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Acta Med
Indones. 39:86–93. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chait A and Bornfeldt KE: Diabetes and
atherosclerosis: Is there a role for hyperglycemia? J Lipid Res. 50
(Suppl):S335–S339. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen GP, Zhang XQ, Wu T, Li L, Han J and
Du CQ: Alteration of mevalonate pathway in proliferated vascular
smooth muscle from diabetic mice: Possible role in
high-glucose-induced atherogenic process. J Diabetes Res.
2015:3792872015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Masiello P, Broca C, Gross R, Roye M,
Manteghetti M, Hillaire-Buys D, Novelli M and Ribes G: Experimental
NIDDM: Development of a new model in adult rats administered
streptozotocin and nicotinamide. Diabetes. 47:224–229. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS,
Naylor BA, Treacher DF and Turner RC: Homeostasis model assessment:
Insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma
glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia.
28:412–419. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hwang HW and Mendell JT: MicroRNAs in cell
proliferation, cell death, and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer.
96:776–780. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ye D, Zhang T, Lou G and Liu Y: Role of
miR-223 in the pathophysiology of liver diseases. Exp Mol Med.
50:1282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Maegdefessel L, Rayner KJ and Leeper NJ:
MicroRNA regulation of vascular smooth muscle function and
phenotype: Early career committee contribution. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 35:2–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Santovito D, Egea V and Weber C: Small but
smart: MicroRNAs orchestrate atherosclerosis development and
progression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1861 (12 Pt B). 2075–2086.
2016.
|
|
20
|
Ji R, Cheng Y, Yue J, Yang J, Liu X, Chen
H, Dean DB and Zhang C: MicroRNA expression signature and
antisense-mediated depletion reveal an essential role of MicroRNA
in vascular neointimal lesion formation. Circ Res. 100:1579–1588.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu X, Cheng Y, Zhang S, Lin Y, Yang J and
Zhang C: A necessary role of miR-221 and miR-222 in vascular smooth
muscle cell proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia. Circ Res.
104:476–487. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leeper NJ, Raiesdana A, Kojima Y, Chun HJ,
Azuma J, Maegdefessel L, Kundu RK, Quertermous T, Tsao PS and Spin
JM: MicroRNA-26a is a novel regulator of vascular smooth muscle
cell function. J Cell Physiol. 226:1035–1043. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu J, Li L, Yun HF and Han YS: MiR-138
promotes smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration in db/db
mice through down-regulation of SIRT1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
463:1159–1164. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cordes KR, Sheehy NT, White MP, Berry EC,
Morton SU, Muth AN, Lee TH, Miano JM, Ivey KN and Srivastava D:
miR-145 and miR-143 regulate smooth muscle cell fate and
plasticity. Nature. 460:705–710. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Torella D, Iaconetti C, Catalucci D,
Ellison GM, Leone A, Waring CD, Bochicchio A, Vicinanza C, Aquila
I, Curcio A, et al: MicroRNA-133 controls vascular smooth muscle
cell phenotypic switch in vitro and vascular remodeling in vivo.
Circ Res. 109:880–893. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang J, Chen L, Ding J, Fan Z, Li S, Wu H,
Zhang J, Yang C, Wang H, Zeng P and Yang J: MicroRNA-24 inhibits
high glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation and
migration by targeting HMGB1. Gene. 586:268–273. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chen M, Zhang Y, Li W and Yang J:
MicroRNA-145 alleviates high glucose-induced proliferation and
migration of vascular smooth muscle cells through targeting ROCK1.
Biomed Pharmacother. 99:81–86. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bi Q, Tang S, Xia L, Du R, Fan R, Gao L,
Jin J, Liang S, Chen Z, Xu G, et al: Ectopic expression of MiR-125a
inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of hepatocellular
carcinoma by targeting MMP11 and VEGF. PLoS One. 7:e401692012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sun YM, Lin KY and Chen YQ: Diverse
functions of miR-125 family in different cell contexts. J Hematol
Oncol. 6:62013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang Y, Zhang D, Lv J, Wang S and Zhang
Q: MiR-125a-5p suppresses bladder cancer progression through
targeting FUT4. Biomed Pharmacother. 108:1039–1047. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cai M, Chen Q, Shen J, Lv C and Cai L:
Epigenetic silenced miR-125a-5p could be self-activated through
targeting Suv39H1 in gastric cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 22:4721–4731.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yan L, Yu MC, Gao GL, Liang HW, Zhou XY,
Zhu ZT, Zhang CY, Wang YB and Chen X: MiR-125a-5p functions as a
tumour suppressor in breast cancer by downregulating BAP1. J Cell
Biochem. 119:8773–8783. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Goldstein JL and Brown MS: Regulation of
the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 343:425–430. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Buhaescu I and Izzedine H: Mevalonate
pathway: A review of clinical and therapeutical implications. Clin
Biochem. 40:575–584. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han J, Jiang DM, Du CQ and Hu SJ:
Alteration of enzyme expressions in mevalonate pathway: Possible
role for cardiovascular remodeling in spontaneously hypertensive
rats. Circ J. 75:1409–1417. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chen GP, Zhang XQ, Wu T, Han J and Ye D:
Inhibition of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase attenuates high
glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation. Mol Med
Rep. 15:3153–3160. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|