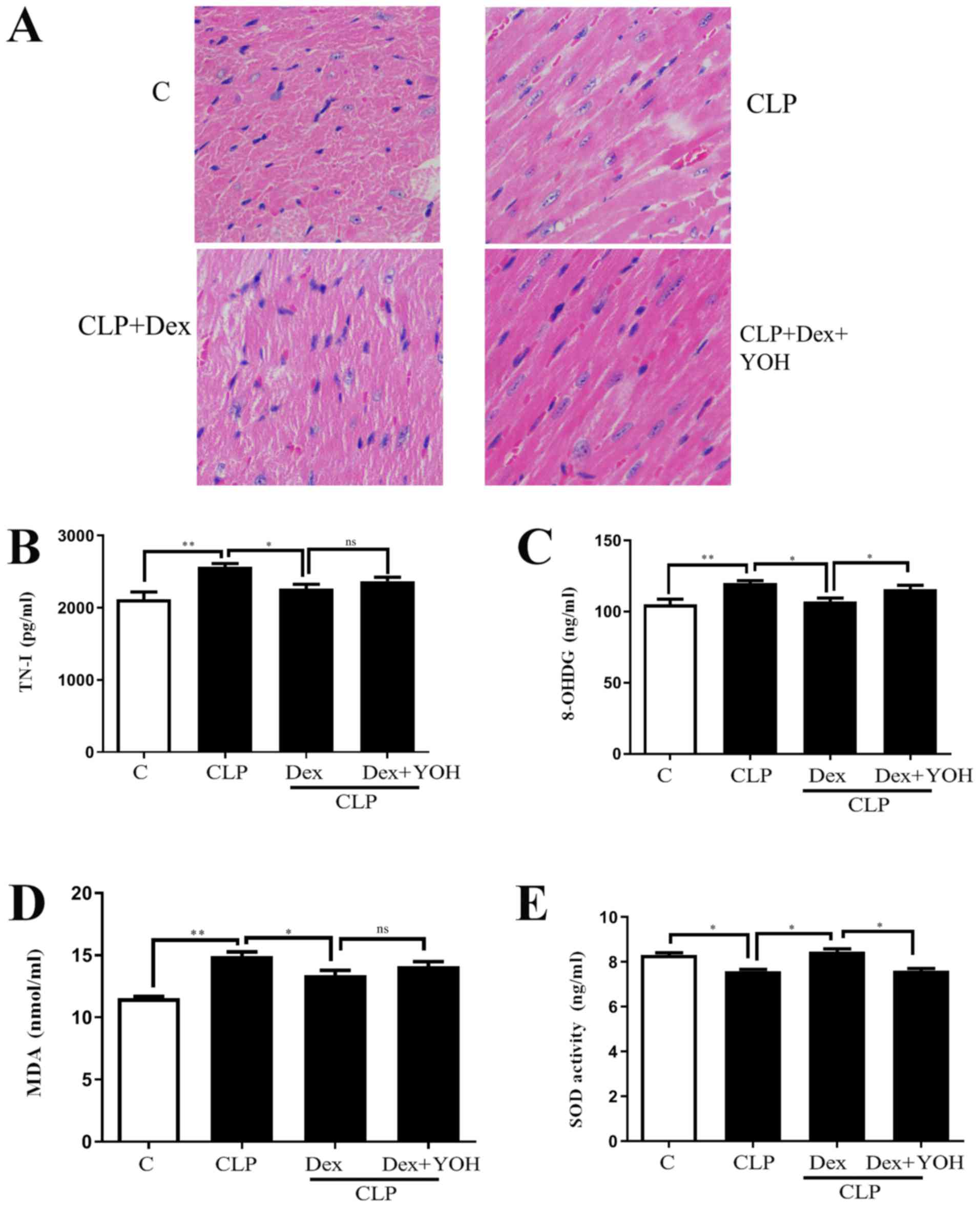
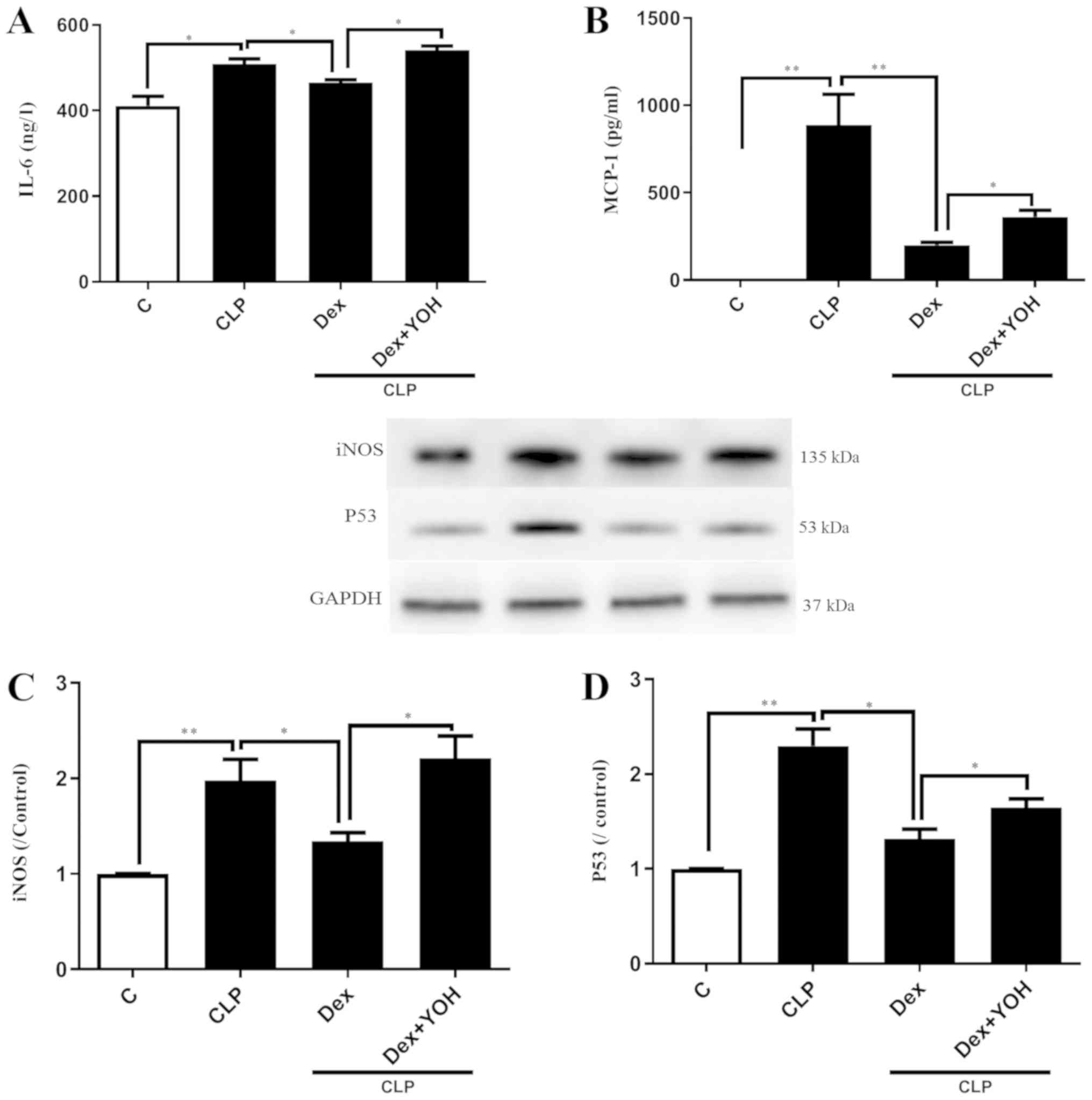
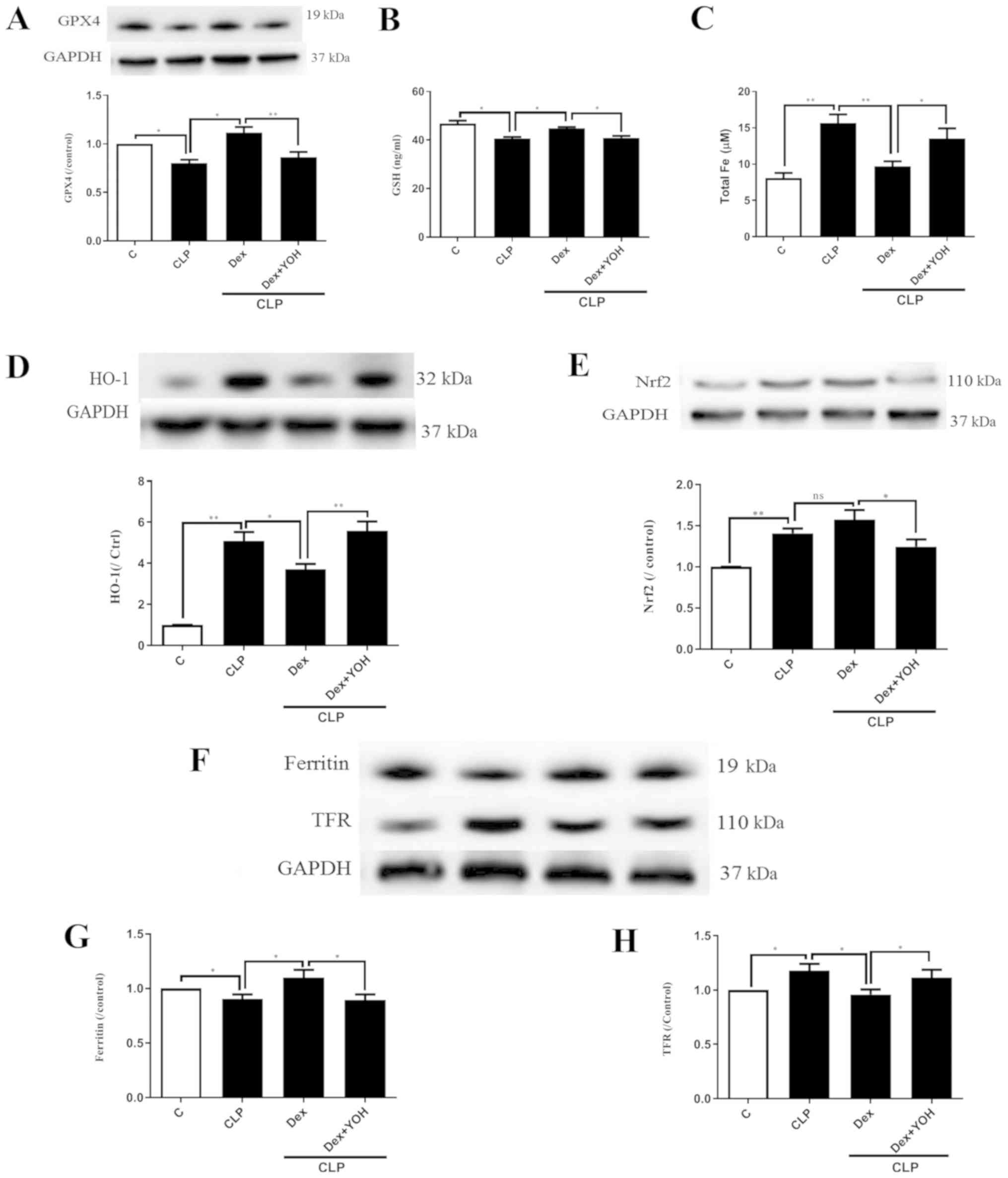
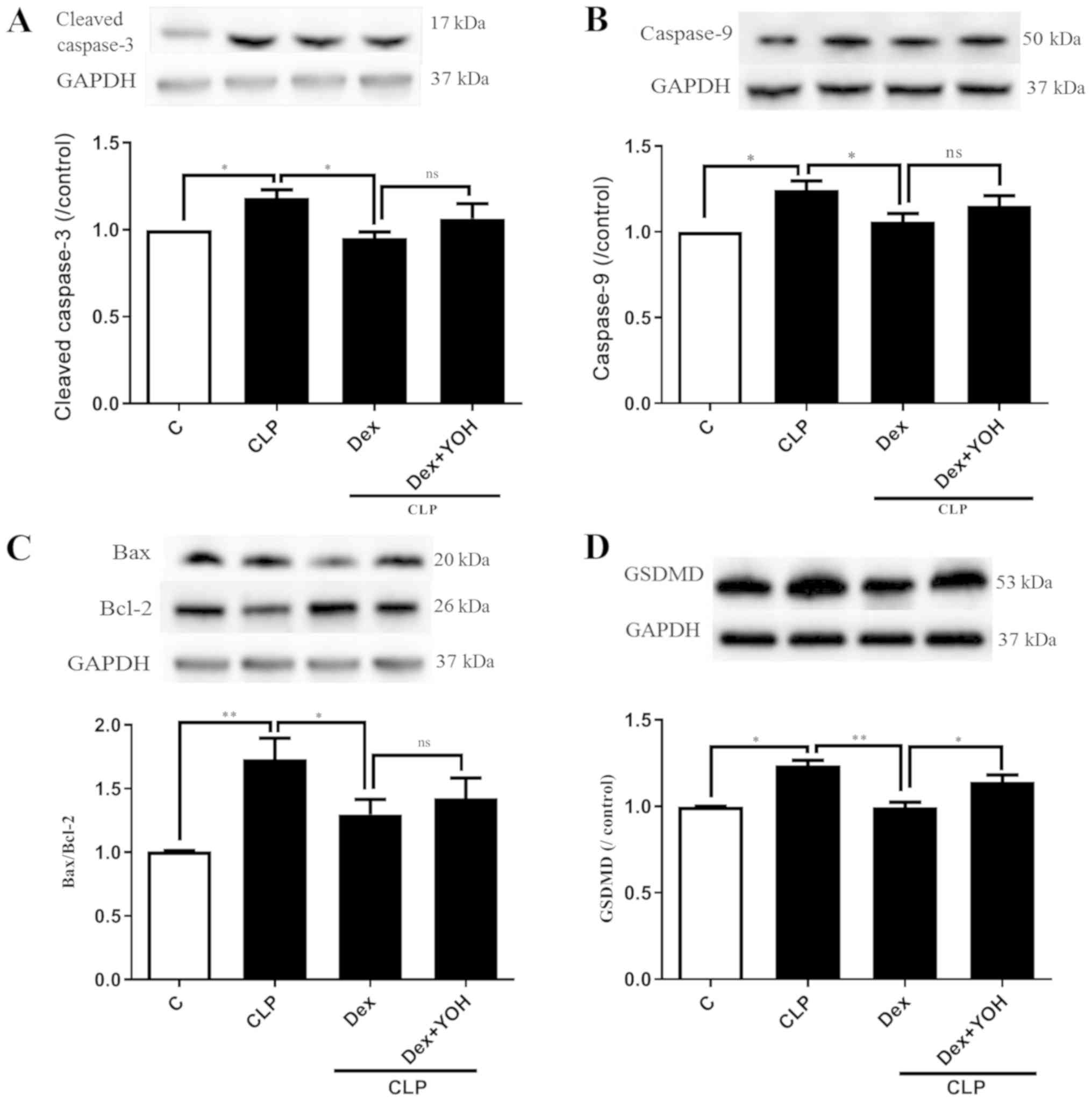
|
1
|
Sun X, Dai Y, Tan G, Liu Y and Li N:
Integration analysis of m(6)A-SNPs and eQTLs associated with sepsis
reveals platelet degranulation and staphylococcus aureus infection
are mediated by m(6)A mRNA methylation. Front Genet. 11:72020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parrillo JE: The cardiovascular
pathophysiology of sepsis. Annu Rev Med. 40:469–485. 1989.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ernsberger P, Giuliano R, Willette RN and
Reis DJ: Role of imidazole receptors in the vasodepressor response
to clonidine analogs in the rostral ventrolateral medulla. J
Pharmacol Exp Ther. 253:408–418. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barr J, Fraser GL, Puntillo K, Ely EW,
Gélinas C, Dasta JF, Davidson JE, Devlin JW, Kress JP, Joffe AM, et
al: Clinical practice guidelines for the management of pain,
agitation, and delirium in adult patients in the intensive care
unit. Crit Care Med. 41:263–306. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Taniguchi T, Kidani Y, Kanakura H,
Takemoto Y and Yamamoto K: Effects of dexmedetomidine on mortality
rate and inflammatory responses to endotoxin-induced shock in rats.
Crit Care Med. 32:1322–1326. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Venn RM, Bradshaw CJ, Spencer R, Brealey
D, Caudwell E, Naughton C, Vedio A, Singer M, Feneck R, Treacher D,
et al: Preliminary UK experience of dexmedetomidine, a novel agent
for postoperative sedation in the intensive care unit. Anaesthesia.
54:1136–1142. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kong W, Kang K, Gao Y, Liu H, Meng X, Yang
S, Yu K and Zhao M: Dexmedetomidine alleviates LPS-induced septic
cardiomyopathy via the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in
mice. Am J Transl Res. 9:5040–5047. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ji F, Li Z, Nguyen H, Young N, Shi P,
Fleming N and Liu H: Perioperative dexmedetomidine improves
outcomes of cardiac surgery. Circulation. 127:1576–1584. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dolma S, Lessnick SL, Hahn WC and
Stockwell BR: Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents
using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor
cells. Cancer Cell. 3:285–296. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fang X, Wang H, Han D, Xie E, Yang X, Wei
J, Gu S, Gao F, Zhu N, Yin X, et al: Ferroptosis as a target for
protection against cardiomyopathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:2672–2680. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao M, Monian P, Quadri N, Ramasamy R and
Jiang X: Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol
Cell. 59:298–308. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun
X, Kang R and Tang D: Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death
Differ. 23:369–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhu H, Santo A, Jia Z and Robert Li Y:
GPx4 in bacterial infection and polymicrobial sepsis: Involvement
of ferroptosis and pyroptosis. React Oxyg Species (Apex).
7:154–160. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhou B, Zhang JY, Liu XS, Chen HZ, Ai YL,
Cheng K, Sun RY, Zhou D, Han J and Wu Q: Tom20 senses
iron-activated ROS signaling to promote melanoma cell pyroptosis.
Cell Res. 28:1171–1185. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dixon SJ and Stockwell BR: The role of
iron and reactive oxygen species in cell death. Nat Chem Biol.
10:9–17. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Baba Y, Higa JK, Shimada BK, Horiuchi KM,
Suhara T, Kobayashi M, Woo JD, Aoyagi H, Marh KS, Kitaoka H and
Matsui T: Protective effects of the mechanistic target of rapamycin
against excess iron and ferroptosis in cardiomyocytes. Am J Physiol
Heart Circ Physiol. 314:H659–H668. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou B, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ,
Kroemer G and Tang D: Ferroptosis is a type of autophagy-dependent
cell death. Semin Cancer Biol. Mar 14–2019.doi:
10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.03.002 (Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jin X, Xu Z, Cao J, Yan R, Xu R, Ran R, Ma
Y, Cai W, Fan R, Zhang Y, et al: HO-1/EBP interaction alleviates
cholesterol-induced hypoxia through the activation of the AKT and
Nrf2/mTOR pathways and inhibition of carbohydrate metabolism in
cardiomyocytes. Int J Mol Med. 39:1409–1420. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Andreas M, Oeser C, Kainz FM, Shabanian S,
Aref T, Bilban M, Messner B, Heidtmann J, Laufer G, Kocher A and
Wolzt M: Intravenous heme arginate induces HO-1 (Heme Oxygenase-1)
in the human heart. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 38:2755–2762.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kwon MY, Park E, Lee SJ and Chung SW: Heme
oxygenase-1 accelerates erastin-induced ferroptotic cell death.
Oncotarget. 6:24393–24403. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
NaveenKumar SK, Hemshekhar M, Kemparaju K
and Girish KS: Hemin-induced platelet activation and ferroptosis is
mediated through ROS-driven proteasomal activity and inflammasome
activation: Protection by melatonin. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1865:2303–2316. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Liu XR, Li T, Cao L, Yu YY, Chen LL, Fan
XH, Yang BB and Tan XQ: Dexmedetomidine attenuates
H2O2-induced neonatal rat cardiomyocytes
apoptosis through mitochondria- and ER-medicated oxidative stress
pathways. Mol Med Rep. 17:7258–7264. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qiu R, Yao W, Ji H, Yuan D, Gao X, Sha W,
Wang F, Huang P and Hei Z: Dexmedetomidine restores septic renal
function via promoting inflammation resolution in a rat sepsis
model. Life Sci. 204:1–8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xu L, Bao H, Si Y and Wang X: Effects of
dexmedetomidine on early and late cytokines during polymicrobial
sepsis in mice. Inflamm Res. 62:507–514. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen JH, Yu GF, Jin SY, Zhang WH, Lei DX,
Zhou SL and Song XR: Activation of alpha2 adrenoceptor attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced hepatic injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
8:10752–10759. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhao W, Jia L, Yang HJ, Xue X, Xu WX, Cai
JQ, Guo RJ and Cao CC: Taurine enhances the protective effect of
Dexmedetomidine on sepsis-induced acute lung injury via balancing
the immunological system. Biomed Pharmacother. 103:1362–1368. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rinaldi B, Di Filippo C, Capuano A,
Donniacuo M, Sodano L, Ferraraccio F, Rossi F and D'Amico M:
Adiponectin elevation by telmisartan ameliorates ischaemic
myocardium in Zucker diabetic fatty rats with metabolic syndrome.
Diabetes Obes Metab. 14:320–328. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Szekely L, Vijay P, Sharp TG, Bando K and
Brown JW: Correlation of plasma adrenomedullin to myocardial
preservation during open-heart surgery. Pediatr Cardiol.
21:228–233. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shi J, Gao W and Shao F: Pyroptosis:
Gasdermin-mediated programmed necrotic cell death. Trends Biochem
Sci. 42:245–254. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mantzarlis K, Tsolaki V and Zakynthinos E:
Role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsis
and potential therapies. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:59852092017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee WJ, Chen YL, Chu YW and Chien DS:
Comparison of glutathione peroxidase-3 protein expression and
enzyme bioactivity in normal subjects and patients with sepsis.
Clin Chim Acta. 489:177–182. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang Y, Mao X, Chen H, Feng J, Yan M, Wang
Y and Yu Y: Dexmedetomidine alleviates LPS-induced apoptosis and
inflammation in macrophages by eliminating damaged mitochondria via
PINK1 mediated mitophagy. Int Immunopharmacol. 73:471–481. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaludercic N and Di Lisa F: Mitochondrial
ROS formation in the pathogenesis of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Front
Cardiovasc Med. 7:122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ighodaro OM: Molecular pathways associated
with oxidative stress in diabetes mellitus. Biomed Pharmacother.
108:656–662. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jin JK, Blackwood EA, Azizi K, Thuerauf
DJ, Fahem AG, Hofmann C, Kaufman RJ, Doroudgar S and Glembotski CC:
ATF6 decreases myocardial ischemia/reperfusion damage and links ER
stress and oxidative stress signaling pathways in the heart. Circ
Res. 120:862–875. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Catalao CHR, Santos-Júnior NN, da Costa
LHA, Souza AO, Alberici LC and Rocha MJA: Brain oxidative stress
during experimental sepsis is attenuated by simvastatin
administration. Mol Neurobiol. 54:7008–7018. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Droge W: Free radicals in the
physiological control of cell function. Physiol Rev. 82:47–95.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Webster NR and Nunn JF: Molecular
structure of free radicals and their importance in biological
reactions. Br J Anaesth. 60:98–108. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Arcangeli A, D'Alò C and Gaspari R:
Dexmedetomidine use in general anaesthesia. Curr Drug Targets.
10:687–695. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fu C, Dai X, Yang Y, Lin M, Cai Y and Cai
S: Dexmedetomidine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury by inhibiting oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction
and apoptosis in rats. Mol Med Rep. 15:131–138. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sha J, Zhang H, Zhao Y, Feng X, Hu X, Wang
C, Song M and Fan H: Dexmedetomidine attenuates
lipopolysaccharide-induced liver oxidative stress and cell
apoptosis in rats by increasing GSK-3β/MKP-1/Nrf2 pathway activity
via the α2 adrenergic receptor. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
364:144–152. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yazar E, Er A, Uney K, Bulbul A, Avci GE,
Elmas M and Tras B: Effects of drugs used in endotoxic shock on
oxidative stress and organ damage markers. Free Radic Res.
44:397–402. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fearnhead HO, Vandenabeele P and Vanden
Berghe T: How do we fit ferroptosis in the family of regulated cell
death? Cell Death Differ. 24:1991–1998. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu H and Sun A: Programmed necrosis in
heart disease: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 116:125–134. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Mughal W, Dhingra R and Kirshenbaum LA:
Striking a balance: Autophagy, apoptosis, and necrosis in a normal
and failing heart. Curr Hypertens Rep. 14:540–547. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Konstantinidis K, Whelan RS and Kitsis RN:
Mechanisms of cell death in heart disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 32:1552–1562. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Galluzzi L, Kepp O, Krautwald S, Kroemer G
and Linkermann A: Molecular mechanisms of regulated necrosis. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 35:24–32. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li Z, Jia Y, Feng Y, Cui R, Miao R, Zhang
X, Qu K, Liu C and Zhang J: Methane alleviates sepsis-induced
injury by inhibiting pyroptosis and apoptosis: In vivo and in vitro
experiments. Aging (Albany NY). 11:1226–1239. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Fu Q, Wu J, Zhou XY, Ji MH, Mao QH, Li Q,
Zong MM, Zhou ZQ and Yang JJ: NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway-induced
pyroptosis mediated cognitive deficits in a mouse model of
sepsis-associated encephalopathy. Inflammation. 42:306–318. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Patel S: Inflammasomes, the cardinal
pathology mediators are activated by pathogens, allergens and
mutagens: A critical review with focus on NLRP3. Biomed
Pharmacother. 92:819–825. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Zhou W, Chen C, Chen Z, Liu L, Jiang J, Wu
Z, Zhao M and Chen Y: NLRP3: A novel mediator in cardiovascular
disease. J Immunol Res. 2018:57021032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Bruni A, Bornstein S, Linkermann A and
Shapiro AMJ: Regulated cell death seen through the lens of islet
transplantation. Cell Transplant. 27:890–901. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Li C, Lönn ME, Xu X, Maghzal GJ, Frazer
DM, Thomas SR, Halliwell B, Richardson DR, Anderson GJ and Stocker
R: Sustained expression of heme oxygenase-1 alters iron homeostasis
in nonerythroid cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 53:366–374. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Soares MP, Seldon MP, Gregoire IP,
Vassilevskaia T, Berberat PO, Yu J, Tsui TY and Bach FH: Heme
oxygenase-1 modulates the expression of adhesion molecules
associated with endothelial cell activation. J Immunol.
172:3553–3563. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mao X, Wang T, Liu Y, Irwin MG, Ou JS,
Liao XL, Gao X, Xu Y, Ng KF, Vanhoutte PM and Xia Z:
N-acetylcysteine and allopurinol confer synergy in attenuating
myocardial ischemia injury via restoring HIF-1α/HO-1 signaling in
diabetic rats. PLoS One. 8:e689492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hu XB, Xi ZY, Liu LQ, Kang K, Li WH, Shen
YX, Kang F and Li J: Dexmedetomidine promotes SH-SY5Y cell
resistance against impairment of iron overload by inhibiting NF-κB
Pathways. Neurochem Res. 44:959–967. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zhang F, Ding T, Yu L, Zhong Y, Dai H and
Yan M: Dexmedetomidine protects against oxygen-glucose
deprivation-induced injury through the I2 imidazoline
receptor-PI3K/AKT pathway in rat C6 glioma cells. J Pharm
Pharmacol. 64:120–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|