|
1
|
McDonald JW and Sadowsky C: Spinal-cord
injury. Lancet. 359:417–425. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sharif-Alhoseini M and Rahimi-Movaghar V:
Animal models in traumatic spinal cord injury. Top Paraplegia.
2014.
|
|
3
|
Gao L, Sun Y, Li J, Bai F and Li P:
Effects of electroacupuncture in different time on variations of
fractional anisotropy mean value of diffusion tensor tractogra-phy
in spinal cord injured rats. Chin J Rehabil Theory Prac.
20:728–733. 2014.
|
|
4
|
Majdan M, Plancikova D, Nemcovska E,
Krajcovicova L, Brazinova A and Rusnak M: Mortality due to
traumatic spinal cord injuries in Europe: A cross-sectional and
pooled analysis of population-wide data from 22 countries. Scand J
Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 25:642017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Blight AR, Leroy EC Jr and Heyes MP:
Quinolinic acid accumulation in injured spinal cord: Time course,
distribution, and species differences between rat and guinea pig. J
Neurotrauma. 14:89–98. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
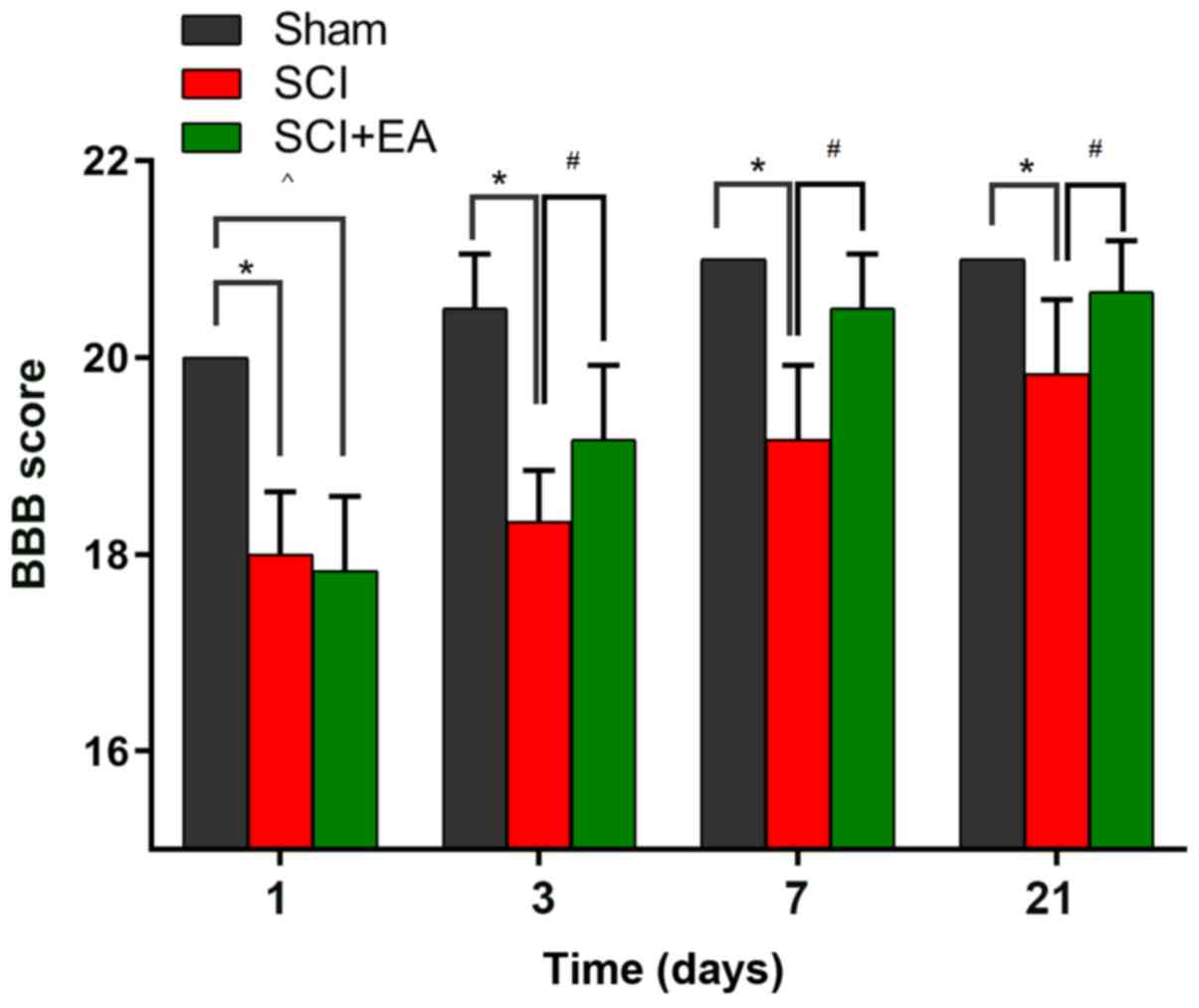
|
|
6
|
Hall ED and Springer JE: Neuroprotection
and acute spinal cord injury: A reappraisal. NeuroRx. 1:80–100.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
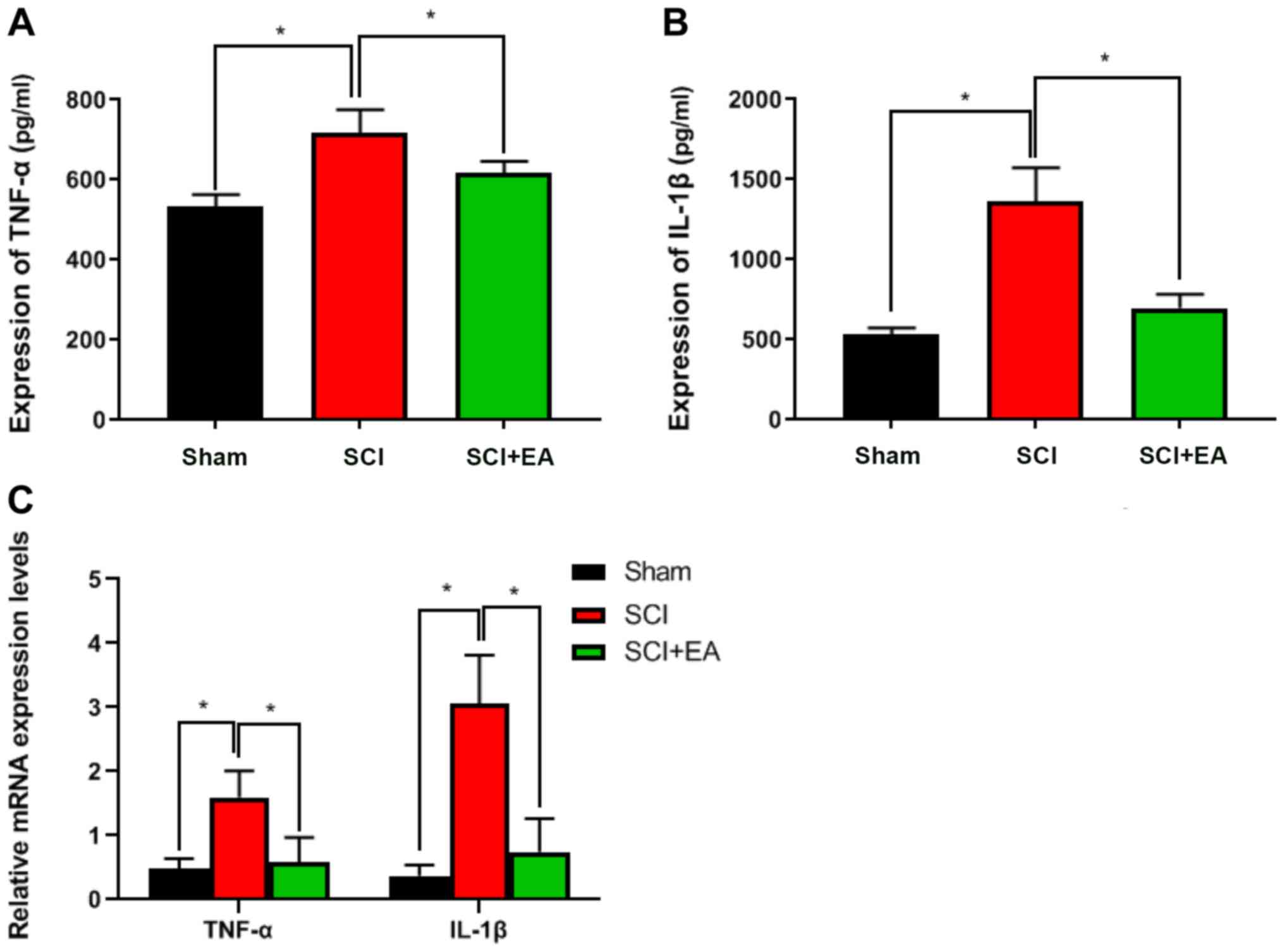
|
|
7
|
Tator CH: Update on the pathophysiology
and pathology of acute spinal cord injury. Brain Pathol. 5:407–413.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
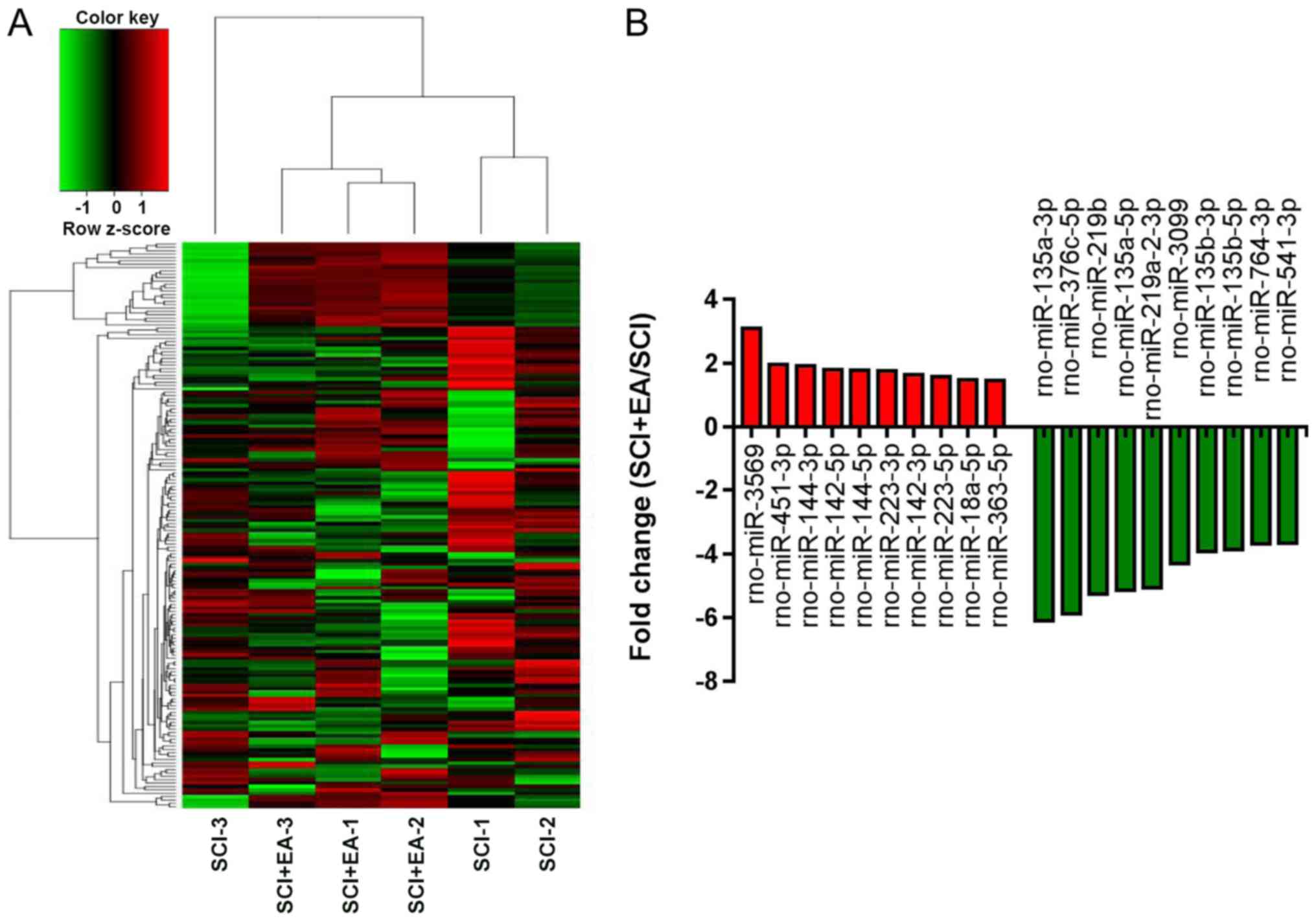
8
|
Dong J, Lu M, He X, Xu J, Qin J, Cheng Z,
Liang B, Wang D and Li H: Identifying the role of microRNAs in
spinal cord injury. Neurol Sci. 35:1663–1671. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ning B, Gao L, Liu RH, Liu Y, Zhang NS and
Chen ZY: MicroRNAs in spinal cord injury: Potential roles and
therapeutic implications. Int J Biol Sci. 10:997–1006. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li J, Li L and Shen Y: Protective role of
microRNA-219-5p inhibitor against spinal cord injury via liver
receptor homolog-1/Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway regulation. Exp
Ther Med. 15:3563–3569. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bhalala OG, Srikanth M and Kessler JA: The
emerging roles of microRNAs in CNS injuries. Nat Rev Neurol.
9:328–339. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zheng Q, Zhang D, Yang YU, Cui X, Sun J,
Liang C, Qin H, Yang X, Liu S and Yan Q: MicroRNA-200c impairs
uterine receptivity formation by targeting FUT4 and
1,3-fucosylation. Cell Death Differ. 24:2161–2172. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zeng Y, Liu JX, Yan ZP, Yao XH and Liu XH:
Potential microRNA biomarkers for acute ischemic stroke. Int J Mol
Med. 36:1639–1647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hinkel R, Penzkofer D, Zühlke S, Fischer
A, Husada W, Xu QF, Baloch E, Van RE, Zeiher AM, Kupatt C and
Dimmeler S: Inhibition of microRNA-92a protects against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in a large-animal model. Circulation.
128:1066–1075. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Beermann J, Piccoli MT, Viereck J and Thum
T: Non-coding RNAs in development and disease: Background,
mechanisms, and therapeutic approaches. Physiol Rev. 96:1297–1325.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Liu N,
Williams AH, McAnally J, Gerard RD, Richardson JA and Olson EN: A
signature pattern of stress-responsive microRNAs that can evoke
cardiac hypertrophy and heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:18255–18260. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhao Y, Ransom JF, Li A, Vedantham V, von
Drehle M, Muth AN, Tsuchihashi T, McManus MT, Schwartz RJ and
Srivastava D: Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction,
and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1-2. Cell. 129:303–317. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bala S, Marcos M and Szabo G: Emerging
role of microRNAsin liver diseases. World J Gastroenterol.
15:5633–5640. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Krutzfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev
KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M and Stoffel M: Silencing of microRNAs in
vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature. 438:685–689. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jackson AL, Burchard J, Leake D, Reynolds
A, Schelter J, Guo J, Johnson JM, Lim L, Karpilow J, Nichols K, et
al: Position-specific chemical modification of siRNAs reduces
‘off-target’ transcript silencing. RNA. 12:1197–1205. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rao P, Benito E and Fischer A: MicroRNAs
as biomarkers for CNS disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 6:392013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang W, Kwon EJ and Tsai LH: MicroRNAs in
learning, memory, and neurological diseases. Learn Mem. 19:359–368.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang T, Ni SF, Luo Z, Lang Y, Hu J and Lu
H: The protective effect of microRNA-21 in neurons after spinal
cord injury. Spinal Cord. 57:141–149. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao L, Dai C, Feng Z, Zhang L and Zhang Z:
MiR-137 inhibited inflammatory response and apoptosis after spinal
cord injury via targeting of MK2. J Cell Biochem. 119:3280–3292.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bao N, Fang B, Lv H, Jiang Y, Chen F, Wang
Z and Ma H: Upregulation of miR-199a-5p protects spinal cord
against ischemia/reperfusion-induced injury via downregulation of
ECE1 in rat. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 38:1293–1303. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Obermair FJ, Schröter A and Thallmair M:
Endogenous neural progenitor cells as therapeutic target after
spinal cord injury. Physiology (Bethesda). 23:296–304.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yan Q, Ruan JW, Ding Y, Li WJ, Li Y and
Zeng YS: Electro-acupuncture promotes differentiation of
mesenchymal stem cells, regeneration of nerve fibers and partial
functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Exp Toxicol Pathol.
63:151–156. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jiang SH, Tu WZ, Zou EM, Hu J, Wang S, Li
JR, Wang WS, He R, Cheng RD and Liao WJ: Neuroprotective effects of
different modalities of acupuncture on traumatic spinal cord injury
in rats. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2014:4315802014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Park JH, Han JB, Kim SK, Park JH, Go DH,
Sun B and Min BI: Spinal GABA receptors mediate the suppressive
effect of electroacupuncture on cold allodynia in rats. Brain Res.
1322:24–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Aloe L and Manni L: Low-frequency
electro-acupuncture reduces the nociceptive response and the pain
mediator enhancement induced by nerve growth factor. Neurosci Lett.
449:173–177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park JH, Kim SK, Kim HN, Sun B, Koo S,
Choi SM, Bae H and Min BI: Spinal cholinergic mechanism of the
relieving effects of electroacupuncture on cold and warm allodynia
in a rat model of neuropathic pain. J Physiol Sci. 59:291–298.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Min YJ, Cheng LH and Gao J: Comparative
observations on three-unblocking acupuncture for the treatment of
spinal cord injury in convalescent patients with paraplegia.
Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi. 32:1010–1013. 2013.
|
|
33
|
Huang C, Wang Y, Han JS and Wan Y:
Characteristics of electroacupuncture-induced analgesia in mice:
Variation with strain, frequency, intensity and opioid involvement.
Brain Res. 945:20–25. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lao L, Zhang RX, Zhang G, Wang X, Berman
BM and Ren K: A para-metric study of electroacupuncture on
persistent hyperalgesia and Fos protein expression in rats. Brain
Res. 1020:18–29. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin JG, Lo MW, Wen YR, Hsieh CL, Tsai SK
and Sun WZ: The effect of high and low frequency electroacupuncture
in pain after lower abdominal surgery. Pain. 99:509–514. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang JF, Li SS and Wu YC: Recovery of
spinal cord injury following electroacupuncture in rats through
enhancement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol Med Rep. 16:2185–2190.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Filipp ME, Travis BJ, Henry SS, Idzikowski
EC, Magnuson SA, Loh MY, Hellenbrand DJ and Hanna AS: Differences
in neuroplasticity after spinal cord injury in varying animal
models and humans. Neural Regen Res. 14:7–19. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC: A
sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field
testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ramayo-Caldas Y, Mach N, Esteve-Codina A,
Corominas J, Castelló A, Ballester M, Estellé J, Ibáñez-Escriche N,
Fernández AI, Pérez-Enciso M and Folch JM: Liver transcriptome
profile in pigs with extreme phenotypes of intramuscular fatty acid
composition. BMC Genomics. 13:5472012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wright GW and Simon RM: A random variance
model for detection of differential gene expression in small
microarray experiments. Bioinformatics. 19:2448–2455. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Turner DA: Miranda: A non-strict
functional language with polymorphic types. Proc of a conference on
functional programming languages and computer architecture. 1–16.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Krüger J and Rehmsmeier M: RNAhybrid:
MicroRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids
Res. 34((Web Server issue)): W451–W454. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Deng G, Gao Y, Cen Z, He J, Cao B, Zeng G
and Zong S: miR-136-5p regulates the inflammatory response by
targeting the IKKβ/NF-κB/A20 pathway after spinal cord injury. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 50:512–524. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Knierim E, Hirata H, Wolf NI,
Morales-Gonzalez S, Schottmann G, Tanaka Y, Rudnik-Schöneborn S,
Orgeur M, Zerres K, Vogt S, et al: Mutations in subunits of the
activating signal cointegrator 1 complex are associated with
prenatal spinal muscular atrophy and congenital bone fractures. Am
J Human Genet. 98:473–489. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Matsuda M, Kanno H, Sugaya T, Yamaya S,
Yahata K, Handa K, Shindo T, Shimokawa H, Ozawa H and Itoi E:
Low-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy promotes BDNF
expression and improves functional recovery after spinal cord
injury in rats. Exp Neurol. 328:1132512020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Saugstad JA: MicroRNAs as effectors of
brain function with roles in ischemia and injury, neuroprotection,
and neurodegeneration. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 30:1564–1576.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yip PK, Bowes AL, Hall JCE, Burguillos MA,
Ip THR, Baskerville T, Liu ZH, Mohamed MAEK, Getachew F, Lindsay
AD, et al: Docosahexaenoic acid reduces microglia phagocytic
activity via miR-124 and induces neuroprotection in rodent models
of spinal cord contusion injury. Human Mol Genet. 28:2427–2448.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yan L, Shi E, Jiang X, Shi J, Gao S and
Liu H: Inhibition of microRNA-204 conducts neuroprotection against
spinal cord ischemia. Ann Thorac Surg. 107:76–83. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Min YJ, Ding LLQ, Cheng LH, Xiao WP, He
XW, Zhang H, Min ZY and Pei J: Effect of electroacupuncture on the
mRNA and protein expression of Rho-A and Rho-associated kinase II
in spinal cord injury rats. Neural Regen Res. 12:110–116. 2017.
|
|
54
|
Yunta M, Nieto-Díaz M, Esteban FJ,
Caballero-López M, Navarro-Ruíz R, Reigada D, Pita-Thomas DW, del
Águila A, Muñoz-Galdeano T and Maza RM: MicroRNA dysregulation in
the spinal cord following traumatic injury. PLoS One. 7:e345342012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Strickland ER, Hook MA, Balaraman S, Huie
JR, Grau JW and Miranda RC: MicroRNA dysregulation following spinal
cord contusion: Implications for neural plasticity and repair.
Neuroscience. 186:146–160. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Xing SM, Wang J, He X, Lai J, Shen L, Chen
D, Fu K and Tan J: Identification of disease-related miRNAs based
on co-expression network in spinal cord injury. Int Neurosci.
125:270–276. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Wei H, Wang C, Zhang C, Li P, Wang F and
Zhang Z: Comparative profiling of microRNA expression between
neural stem cells and motor neurons in embryonic spinal cord in
rat. Int J Dev Neurosci. 28:545–551. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Izumi B, Nakasa T, Tanaka N, Nakanishi K,
Kamei N, Yamamoto R, Nakamae T, Ohta R, Fujioka Y, Yamasaki K and
Ochi M: MicroRNA-223 expression in neutrophils in the early phase
of secondary damage after spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett.
492:114–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
He J, Zhao J, Peng X, Shi X, Zong S and
Zeng G: molecular mechanism of MiR-136-5p targeting NF-κB/A20 in
the IL-17-mediated inflammatory response after spinal cord injury.
Cell Physiol Biochem. 44:1224–1241. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Zhang Z, Wan F, Zhuang Q, Zhang Y and Xu
Z: Suppression of miR-127 protects PC-12 cells from LPS-induced
inflammatory injury by downregulation of PDCD4. Biomed
Pharmacother. 96:1154–1162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Ahn KS, Sethi G and Aggarwal BB: Nuclear
factor-kappa B: From clone to clinic. Curr Mol Med. 7:619–637.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wang C, Wang Q, Lou Y, Xu J, Feng Z, Chen
Y, Tang Q, Zheng G, Zhang Z, Wu Y, et al: Salidroside attenuates
neuroinflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal
cord injury through microglia polarization regulation. J Cell Mol
Med. 22:1148–1166. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Zhang W, Wu Q, Zhang Y,
Liu Y, Guan Y and Chen X: Melatonin improves functional recovery in
female rats after acute spinal cord injury by modulating
polarization of spinal microglial/macrophages. J Neurosci Res.
97:733–743. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|