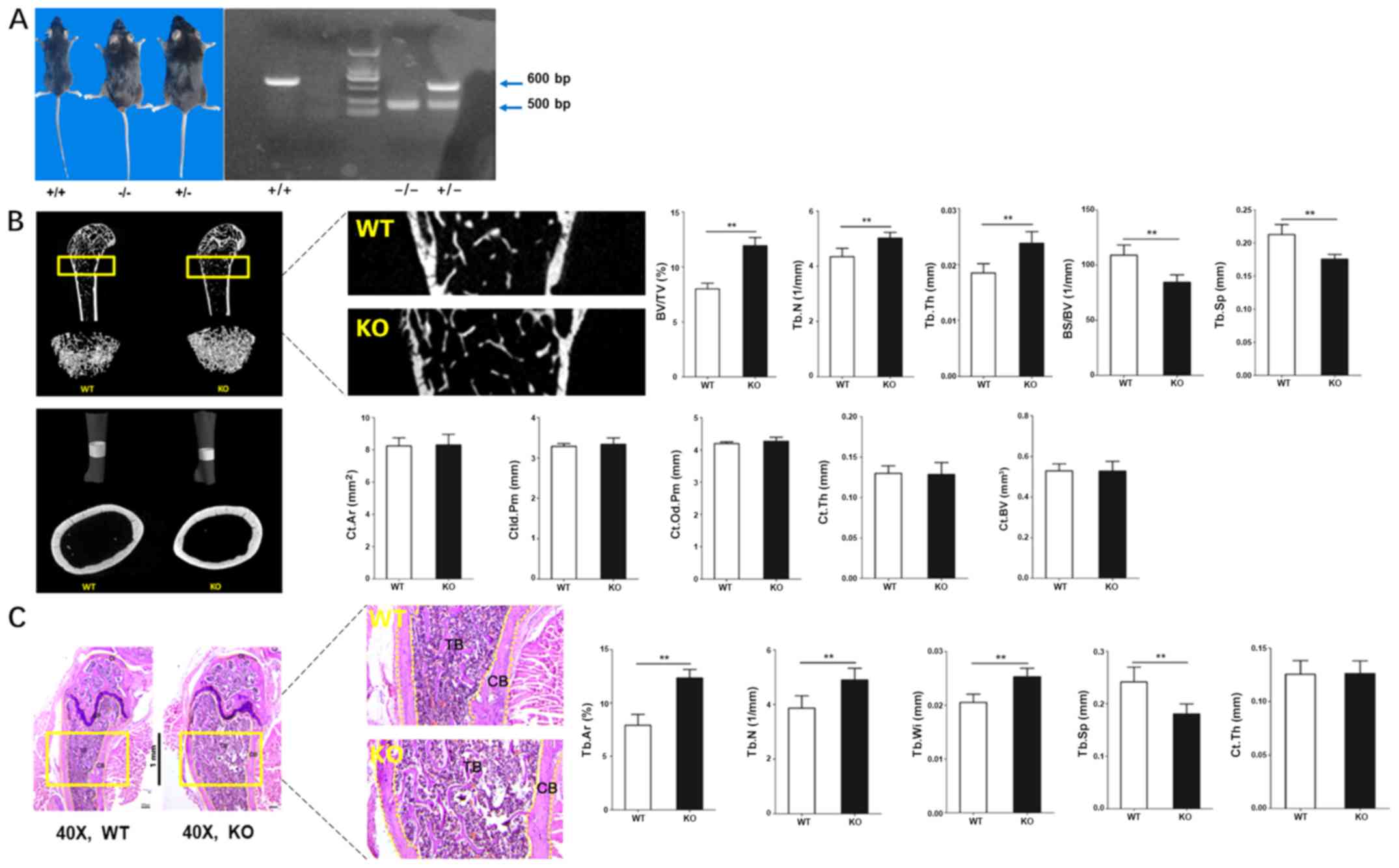
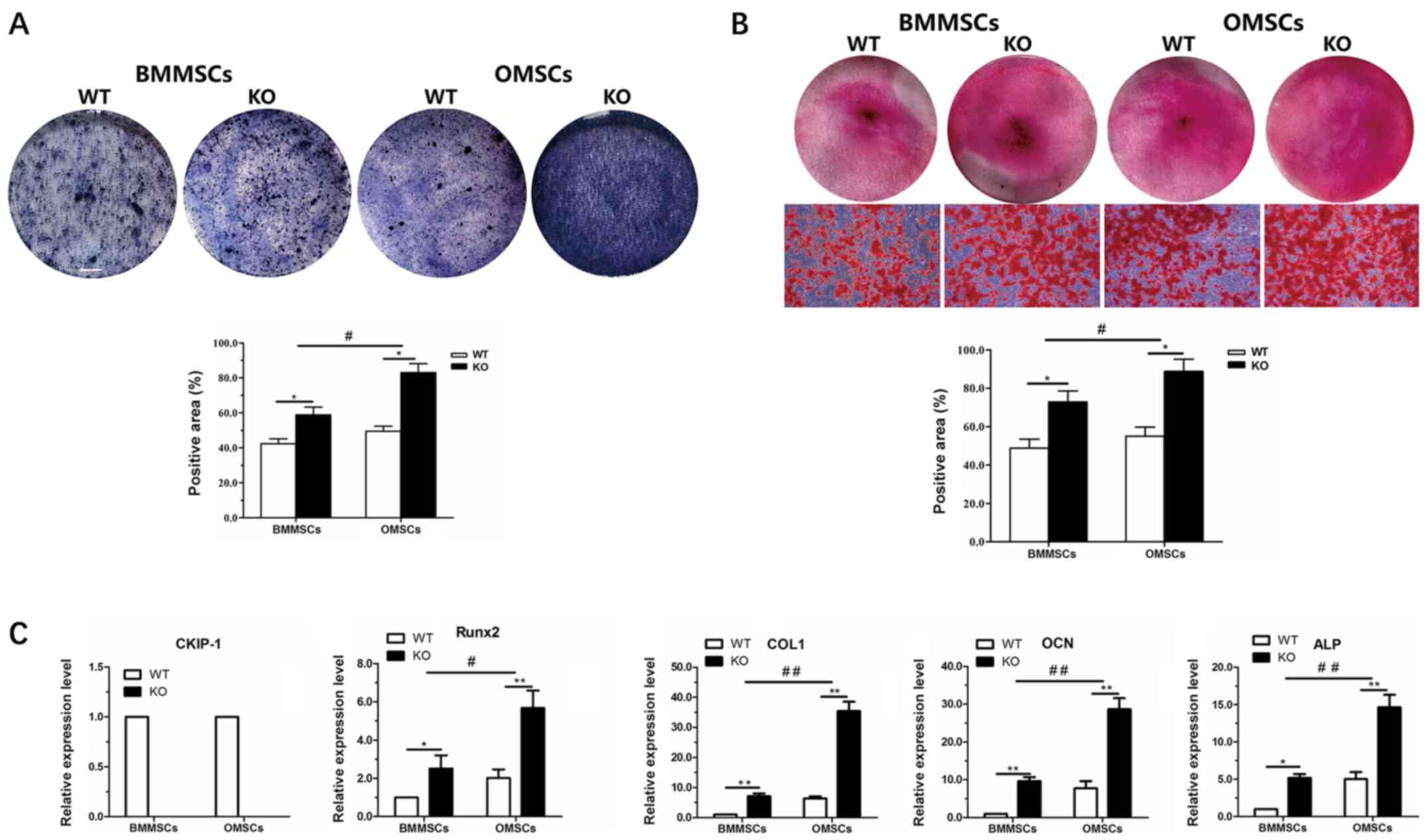
|
1
|
Cicciù M, Cervino G, Herford AS, Famà F,
Bramanti E, Fiorillo L, Lauritano F, Sambataro S, Troiano G and
Laino L: Facial bone reconstruction using both marine or non-marine
bone substitutes: Evaluation of current outcomes in a systematic
literature review. Mar Drugs. 16:E272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Rashidy AA, Roether JA, Harhaus L,
Kneser U and Boccaccini AR: Regenerating bone with bioactive glass
scaffolds: A review of in vivo studies in bone defect models. Acta
Biomater. 62:1–28. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leyendecker A Jr, Pinheiro CG, Fernandes
TL and Bueno DF: The use of human dental pulp stem cells for in
vivo bone tissue engineering: A systematic review. J Tissue Eng.
Jan 17–2018.(Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1177/2041731417752766.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Buduru SD, Gulei D, Zimta AA, Tigu AB,
Cenariu D and Berindan-Neagoe I: The potential of different origin
stem cells in modulating oral bone regeneration processes. Cells.
8:E292019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
He S, Yang S, Zhang Y, Li X, Gao D, Zhong
Y, Cao L, Ma H, Liu Y, Li G, et al: LncRNA ODIR1 inhibits
osteogenic differentiation of hUC-MSCs through the
FBXO25/H2BK120ub/H3K4me3/OSX axis. Cell Death Dis. 10:9472019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carthew J, Donderwinkel I, Shrestha S,
Truong VX, Forsythe JS and Frith JE: In situ miRNA delivery from a
hydrogel promotes osteogenesis of encapsulated mesenchymal stromal
cells. Acta Biomater. 101:249–261. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ouyang Z, Tan T, Zhang X, Wan J, Zhou Y,
Jiang G, Yang D, Guo X and Liu T: CircRNA hsa_circ_0074834 promotes
the osteogenesis-angiogenesis coupling process in bone mesenchymal
stem cells (BMSCs) by acting as a ceRNA for miR-942-5p. Cell Death
Dis. 10:9322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhou J and Zhao L: Multifunction Sr, Co
and F co-doped microporous coating on titanium of antibacterial,
angiogenic and osteogenic activities. Sci Rep. 6:290692016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Prasopthum A, Cooper M, Shakesheff KM and
Yang J: Three-dimensional printed scaffolds with controlled
micro-/nanoporous surface topography direct chondrogenic and
osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. ACS Appl
Mater Interfaces. 11:18896–18906. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Aghajani F, Hooshmand T, Khanmohammadi M,
Khanjani S, Edalatkhah H, Zarnani A-H and Kazemnejad S: Comparative
immunophenotypic characteristics, proliferative features, and
osteogenic differentiation of stem cells isolated from human
permanent and deciduous teeth with bone marrow. Mol Biotechnol.
58:415–427. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Isobe Y, Koyama N, Nakao K, Osawa K, Ikeno
M, Yamanaka S, Okubo Y, Fujimura K and Bessho K: Comparison of
human mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, synovial
fluid, adult dental pulp, and exfoliated deciduous tooth pulp. Int
J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 45:124–131. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peng L, Jia Z, Yin X, Zhang X, Liu Y, Chen
P, Ma K and Zhou C: Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells
from bone marrow, cartilage, and adipose tissue. Stem Cells Dev.
17:761–773. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lotfy A, Salama M, Zahran F, Jones E,
Badawy A and Sobh M: Characterization of mesenchymal stem cells
derived from rat bone marrow and adipose tissue: A comparative
study. Int J Stem Cells. 7:135–142. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khalilifar MA, Baghaban Eslaminejad MR,
Ghasemzadeh M, Hosseini S and Baharvand H: In vitro and in vivo
comparison of different types of rabbit mesenchymal stem cells for
cartilage repair. Cell J. 21:150–160. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lloyd B, Tee BC, Headley C, Emam H,
Mallery S and Sun Z: Similarities and differences between porcine
mandibular and limb bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Arch Oral
Biol. 77:1–11. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chai Y and Maxson RE Jr: Recent advances
in craniofacial morphogenesis. Dev Dyn. 235:2353–2375. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lu K, Yin X, Weng T, Xi S, Li L, Xing G,
Cheng X, Yang X, Zhang L and He F: Targeting WW domains linker of
HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf1 for activation by CKIP-1. Nat
Cell Biol. 10:994–1002. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou ZC, Che L, Kong L, Lei DL, Liu R and
Yang XJ: CKIP-1 silencing promotes new bone formation in rat
mandibular distraction osteogenesis. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol
Oral Radiol. 123:e1–e9. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo Z, Li H, Li X, Yu X, Wang H, Tang P
and Mao N: In vitro characteristics and in vivo immunosuppressive
activity of compact bone-derived murine mesenchymal progenitor
cells. Stem Cells. 24:992–1000. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu H, Guo ZK, Jiang XX, Li H, Wang XY,
Yao HY, Zhang Y and Mao N: A protocol for isolation and culture of
mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact bone. Nat Protoc.
5:550–560. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Short BJ, Brouard N and Simmons PJ:
Prospective isolation of mesenchymal stem cells from mouse compact
bone. Methods Mol Biol. 482:259–268. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang J, Xu S, Shen M, Cheng B, Li Y, Liu
X, Qin D, Bellare A and Kong L: Osteogenic activity of titanium
surfaces with hierarchical micro-/nano-structures obtained by
hydrofluoric acid treatment. Int J Nanomedicine. 12:1317–1328.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Song W, Ma Z, Zhang Y and Yang C:
Autophagy plays a dual role during intracellular siRNA delivery by
lipoplex and polyplex nanoparticles. Acta Biomater. 58:196–204.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) methods Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop DJ and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular
Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhang L, Wu K, Song W, Xu H, An R, Zhao L,
Liu B and Zhang Y: Chitosan/siCkip-1 biofunctionalized titanium
implant for improved osseointegration in the osteoporotic
condition. Sci Rep. 5:108602015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang X, Wang Q, Wan Z, Li J, Liu L and
Zhang X: CKIP-1 knockout offsets osteoporosis induced by simulated
microgravity. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 122:140–148. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhang L, Xing G, Tie Y, Tang Y, Tian C, Li
L, Sun L, Wei H, Zhu Y and He F: Role for the pleckstrin homology
domain-containing protein CKIP-1 in AP-1 regulation and apoptosis.
EMBO J. 24:766–778. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aghaloo TL, Chaichanasakul T, Bezouglaia
O, Kang B, Franco R, Dry SM, Atti E and Tetradis S: Osteogenic
potential of mandibular vs. long-bone marrow stromal cells. J Dent
Res. 89:1293–1298. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yamaza T, Ren G, Akiyama K, Chen C, Shi Y
and Shi S: Mouse mandible contains distinctive mesenchymal stem
cells. J Dent Res. 90:317–324. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Karaplis AC: Embryonic development of bone
and regulation of intramembranous and endochondral bone formation.
In: Principles of Bone Biology. Academic Press. (Cambridge, MA).
53–84. 2002.
|
|
32
|
Helms JA and Schneider RA: Cranial
skeletal biology. Nature. 423:326–331. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Leucht P, Kim JB, Amasha R, James AW,
Girod S and Helms JA: Embryonic origin and Hox status determine
progenitor cell fate during adult bone regeneration. Development.
135:2845–2854. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Scott MA, Levi B, Askarinam A, Nguyen A,
Rackohn T, Ting K, Soo C and James AW: Brief review of models of
ectopic bone formation. Stem Cells Dev. 21:655–667. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gallinetti S, Canal C, Ginebra MP and
Ferreira J: Development and characterization of biphasic
hydroxyapatite/β-TCP cements. J Am Ceram Soc. 97:1065–1073. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Valentim RMB, Andrade SMC, Dos Santos MEM,
Santos A, Pereira V, dos Santos I, Dias C and dos Reis M: Composite
based on biphasic calcium phosphate (HA/β-TCP) and nanocellulose
from the açaí tegument. Materials (Basel). 11:E22132018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ishack S, Mediero A, Wilder T, Ricci JL
and Cronstein BN: Bone regeneration in critical bone defects using
three-dimensionally printed β-tricalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite
scaffolds is enhanced by coating scaffolds with either dipyridamole
or BMP-2. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 105:366–375. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|