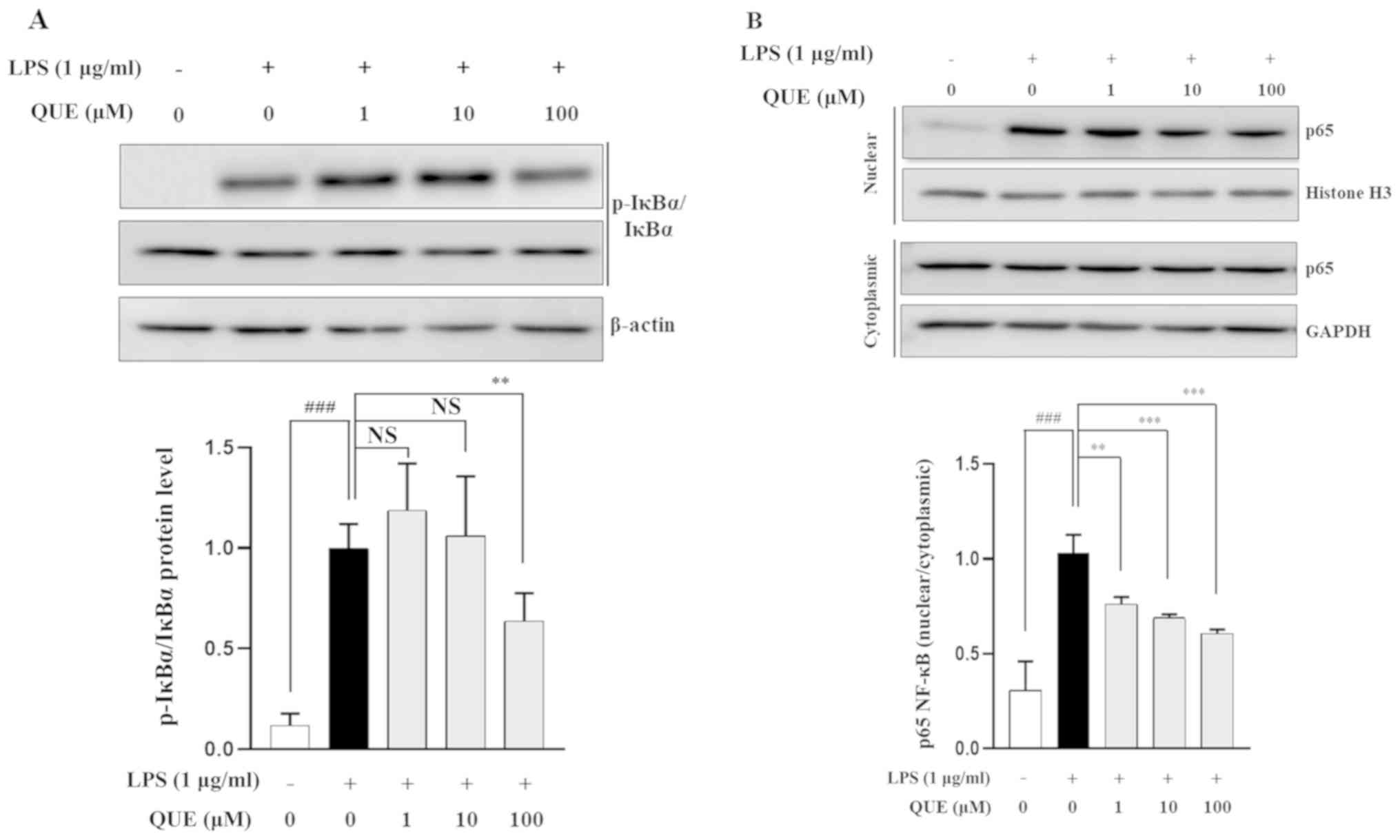
|
1
|
Gori AM, Cesari F, Marcucci R, Giusti B,
Paniccia R, Antonucci E, Gensini GF and Abbate R: The balance
between pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines is associated with
platelet aggregability in acute coronary syndrome patients.
Atherosclerosis. 202:255–262. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fujiwara N and Kobayashi K: Macrophages in
inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:281–286. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aderem A and Ulevitch RJ: Toll-like
receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature.
406:782–787. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fujihara M, Muroi M, Tanamoto K, Suzuki T,
Azuma H and Ikeda H: Molecular mechanisms of macrophage activation
and deactivation by lipopolysaccharide: Roles of the receptor
complex. Pharmacol Ther. 100:171–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kim YH, Lee SH, Lee JY, Choi SW, Park JW
and Kwon TK: Triptolide inhibits murine-inducible nitric oxide
synthase expression by down-regulating lipopolysaccharide-induced
activity of nuclear factor-kappa B and c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase.
Eur J Pharmacol. 494:1–9. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Charo IF and Ransohoff RM: The many roles
of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. N Engl J
Med. 354:610–621. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kiemer AK, Hartung T, Huber C and Vollmar
AM: Phyllanthus amarus has anti-inflammatory potential by
inhibition of iNOS, COX-2, and cytokines via the NF-kappaB pathway.
J Hepatol. 38:289–297. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhai XT, Zhang ZY, Jiang CH, Chen JQ, Ye
JQ, Jia XB, Yang Y, Ni Q, Wang SX, Song J, et al: Nauclea
officinalis inhibits inflammation in LPS-mediated RAW 264.7
macrophages by suppressing the NF-κB signaling pathway. J
Ethnopharmacol. 183:159–165. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He J, Lu X, Wei T, Dong Y, Cai Z, Tang L
and Liu M: Asperuloside and asperulosidic acid exert an
anti-inflammatory effect via suppression of the NF-κB and MAPK
signaling pathways in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 Macrophages Int J Mol
Sci. 19:2027. 2018.
|
|
10
|
Havsteen B: Flavonoids, a class of natural
products of high pharmacological potency. Biochem Pharmacol.
32:1141–1148. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Middleton E Jr, Kandaswami C and
Theoharides TC: The effects of plant flavonoids on mammalian cells:
Implications for inflammation, heart disease, and cancer. Pharmacol
Rev. 52:673–751. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim HP, Son KH, Chang HW and Kang SS:
Anti-inflammatory plant flavonoids and cellular action mechanisms.
J Pharmacol Sci. 96:229–245. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gil B, Sanz MJ, Terencio MC, Ferrándiz ML,
Bustos G, Payá M, Gunasegaran R and Alcaraz MJ: Effects of
flavonoids on Naja naja and human recombinant synovial
phospholipases A2 and inflammatory responses in mice. Life Sci.
54:PL333–PL338. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Manthey DE and Teichman J:
Nephrolithiasis. Emerg Med Clin North Am. 19633–654. (viii)2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu YQ, Zhou CH, Tao J and Li SN:
Antagonistic effects of nobiletin, a polymethoxyflavonoid, on
eosinophilic airway inflammation of asthmatic rats and relevant
mechanisms. Life Sci. 78:2689–2696. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xu JJ, Liu Z, Tang W, Wang GC, Chung HY,
Liu QY, Zhuang L, Li MM and Li YL: Tangeretin from citrus
reticulate inhibits respiratory syncytial virus replication and
associated inflammation in vivo. J Agric Food Chem. 63:9520–9527.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kanes K, Tisserat B, Berhow M and
Vandercook C: Phenolic composition of various tissues of Rutaceae
species. Phytochemistry. 32:967–974. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rouseff RL and Ting SV: Quantitation of
polymethoxylated flavones in orange juice by high-performance
liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A. 176:75–87. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li S, Lo CY and Ho CT: Hydroxylated
polymethoxyflavones and methylated flavonoids in sweet orange
(Citrus sinensis) peel. J Agric Food Chem. 54:4176–4185.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Itoh T, Ohguchi K, Iinuma M, Nozawa Y and
Akao Y: Inhibitory effects of polymethoxy flavones isolated from
Citrus reticulate on degranulation in rat basophilic
leukemia RBL-2H3: Enhanced inhibition by their combination. Bioorg
Med Chem. 16:7592–7598. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Akao Y, Itoh T, Ohguchi K, Iinuma M and
Nozawa Y: Interactive effects of polymethoxy flavones from Citrus
on cell growth inhibition in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells.
Bioorg Med Chem. 16:2803–2810. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ko HC, Jang MG, Kang CH, Lee NH, Kang SI,
Lee SR, Park DB and Kim SJ: Preparation of a polymethoxyflavone
rich fraction (PRF) of Citrus sunki Hort. ex Tanaka and its
antiproliferative effects. Food Chem. 123:484–488. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Guo S, Qiu P, Xu G, Wu X, Dong P, Yang G,
Zheng J, McClements DJ and Xiao H: Synergistic anti-inflammatory
effects of nobiletin and sulforaphane in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. J Agric Food Chem.
60:2157–2164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Harasstani OA, Moin S, Tham CL, Liew CY,
Ismail N, Rajajendram R, Harith HH, Zakaria ZA, Mohamad AS,
Sulaiman MR, et al: Flavonoid combinations cause synergistic
inhibition of proinflammatory mediator secretion from
lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Inflamm Res.
59:711–721. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fan GW, Gao XM, Wang H, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Hu
LM, Su YF, Kang LY and Zhang BL: The anti-inflammatory activities
of Tanshinone IIA, an active component of TCM, are mediated by
estrogen receptor activation and inhibition of iNOS. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 113:275–280. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Feng CG, Kullberg MC, Jankovic D, Cheever
AW, Caspar P, Coffman RL and Sher A: Transgenic mice expressing
human interleukin-10 in the antigen-presenting cell compartment
show increased susceptibility to infection with Mycobacterium avium
associated with decreased macrophage effector function and
apoptosis. Infect Immun. 70:6672–6679. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rao KM, Meighan T and Bowman L: Role of
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in the production of
inflammatory mediators: Differences between primary rat alveolar
macrophages and macrophage cell lines. J Toxicol Environ Health A.
65:757–768. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nogata Y, Sakamoto K, Shiratsuchi H, Ishii
T, Yano M and Ohta H: Flavonoid composition of fruit tissues of
citrus species. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 70:178–192. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lai CS, Li S, Chai CY, Lo CY, Ho CT, Wang
YJ and Pan MH: Inhibitory effect of citrus
5-hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone on
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol 13-acetate-induced skin inflammation and
tumor promotion in mice. Carcinogenesis. 28:2581–2588. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li S, Sang S, Pan MH, Lai CS, Lo CY, Yang
CS and Ho CT: Anti-inflammatory property of the urinary metabolites
of nobiletin in mouse. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 17:5177–5181. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pan MH, Lai YS, Lai CS, Wang YJ, Li S, Lo
CY, Dushenkov S and Ho CT:
5-Hydroxy-3,6,7,8,3′,4′-hexamethoxyflavone induces apoptosis
through reactive oxygen species production, growth arrest and DNA
damage-inducible gene 153 expression, and caspase activation in
human leukemia cells. J Agric Food Chem. 55:5081–5091. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Son ES, Kim SH, Ryter SW, Yeo EJ, Kyung
SY, Kim YJ, Jeong SH, Lee CS and Park JW: Quercetogetin protects
against cigarette smoke extract-induced apoptosis in epithelial
cells by inhibiting mitophagy. Toxicol In Vitro. 48:170–178. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Palmer RM, Ashton DS and Moncada S:
Vascular endothelial cells synthesize nitric oxide from L-arginine.
Nature. 333:664–666. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Griswold DE and Adams JL: Constitutive
cyclooxygenase (COX-1) and inducible cyclooxygenase (COX-2):
Rationale for selective inhibition and progress to date. Med Res
Rev. 16:181–206. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Karin M and Greten FR: NF-κB: Linking
inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression.
Nat Rev Immunol. 5:749–759. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Viatour P, Merville MP, Bours V and
Chariot A: Phosphorylation of NF-κB and IκB proteins: Implications
in cancer and inflammation. Trends Biochem Sci. 30:43–52. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li Y, Gong Q, Guo W, Kan X, Xu D, Ma H, Fu
S and Liu J: Farrerol relieve lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced
mastitis by inhibiting AKT/NF-κB p65, ERK1/2 and P38 signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 19:17702018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Arthur JSC and Ley SC: Mitogen-activated
protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:679–692.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Johnson GL and Lapadat R:
Mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways mediated by ERK, JNK, and
p38 protein kinases. Science. 298:1911–1912. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Uto T, Fujii M and Hou DX:
6-(Methylsulfinyl)hexyl isothiocyanate suppresses inducible nitric
oxide synthase expression through the inhibition of Janus kinase
2-mediated JNK pathway in lipopolysaccharide-activated murine
macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol. 70:1211–1221. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yoon WJ, Moon JY, Song G, Lee YK, Han MS,
Lee JS, Ihm BS, Lee WJ, Lee NH and Hyun CG: Artemisia fukudo
essential oil attenuates LPS-induced inflammation by suppressing
NF-κB and MAPK activation in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Food Chem
Toxicol. 48:1222–1229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cruz CD, Neto FL, Castro-Lopes J, McMahon
SB and Cruz F: Inhibition of ERK phosphorylation decreases
nociceptive behaviour in monoarthritic rats. Pain. 116:411–419.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Goodridge HS, Harnett W, Liew FY and
Harnett MM: Differential regulation of interleukin-12 p40 and p35
induction via Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent and
-independent mechanisms and the implications for bioactive IL-12
and IL-23 responses. Immunology. 109:415–425. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Korb A, Tohidast-Akrad M, Cetin E, Axmann
R, Smolen J and Schett G: Differential tissue expression and
activation of p38 MAPK alpha, beta, gamma, and delta isoforms in
rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 54:2745–2756. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Dong C, Davis RJ and Flavell RA: MAP
kinases in the immune response. Annu Rev Immunol. 20:55–72. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|