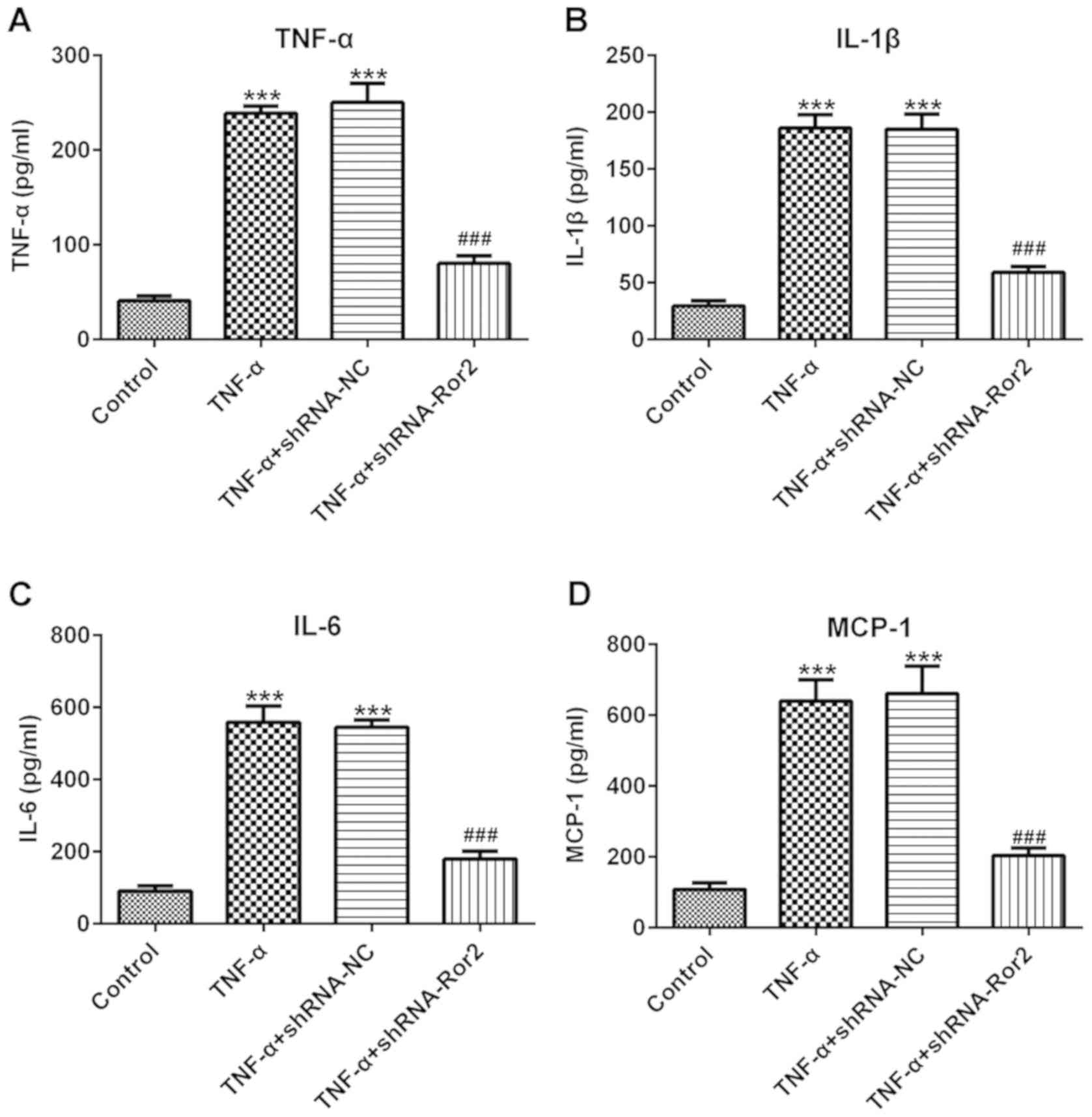
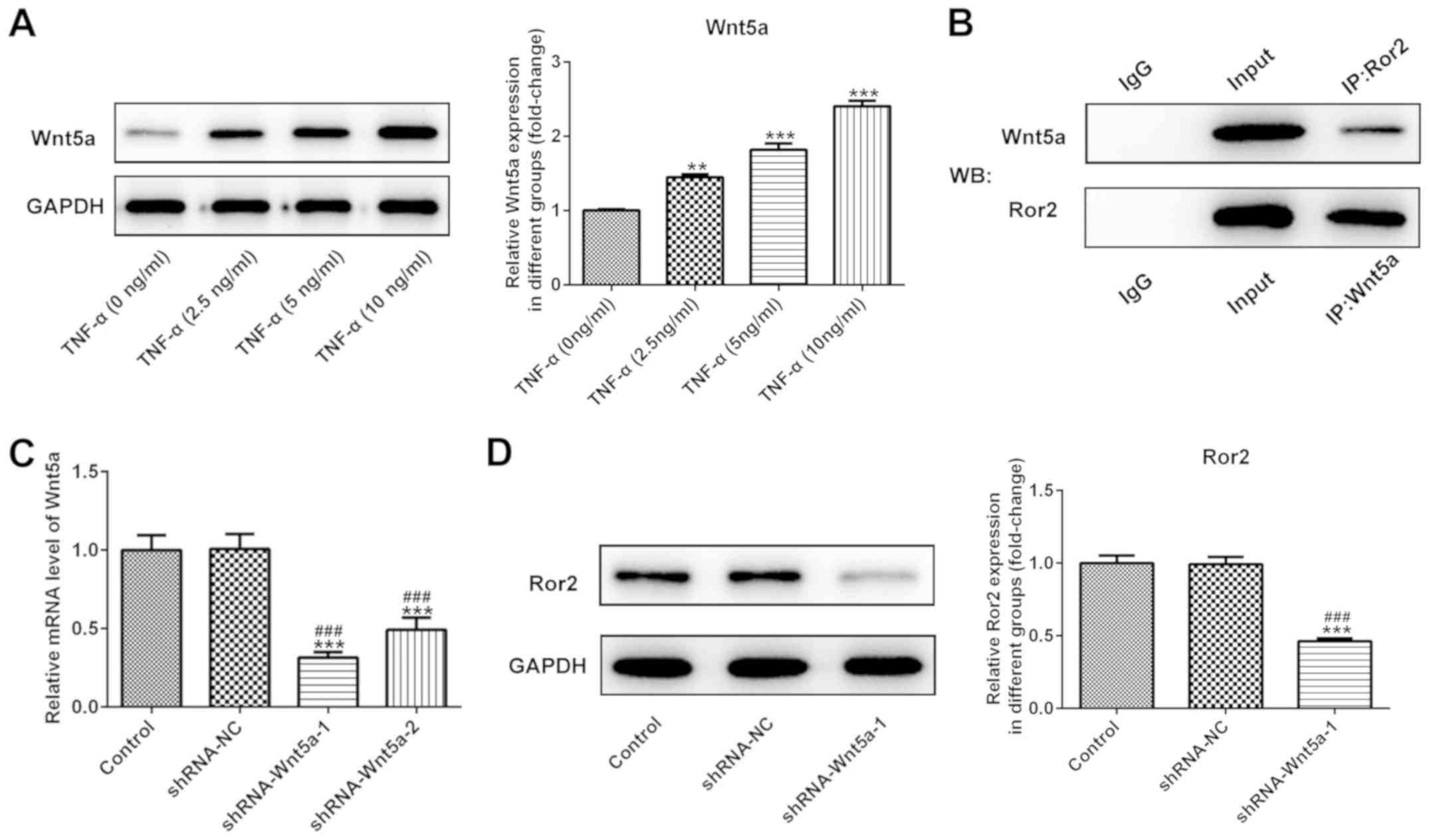
|
1
|
Schaftenaar F, Frodermann V, Kuiper J and
Lutgens E: Atherosclerosis: The interplay between lipids and immune
cells. Curr Opin Lipidol. 27:2981–215. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Libby P, Ridker PM and Hansson GK:
Progress and challenges in translating the biology of
atherosclerosis. Nature. 473:317–325. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gisterå A and Hansson GK: The immunology
of atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:368–380. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wolf D and Ley K: Immunity and
Inflammation in Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 124:315–327. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gimbrone MA Jr and García-Cardeña G:
Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and the Pathobiology of
Atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 118:620–636. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sitia S, Tomasoni L, Atzeni F, Ambrosio G,
Cordiano C, Catapano A, Tramontana S, Perticone F, Naccarato P,
Camici P, et al: From endothelial dysfunction to atherosclerosis.
Autoimmun Rev. 9:830–834. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Förstermann U, Xia N and Li H: Roles of
vascular oxidative stress and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of
atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 120:713–735. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Eelen G, de Zeeuw P, Simons M and
Carmeliet P: Endothelial cell metabolism in normal and diseased
vasculature. Circ Res. 116:1231–1244. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cochain C and Zernecke A: Macrophages in
vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Pflugers Arch.
469:485–499. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nusse R and Clevers H: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling, disease, and emerging therapeutic modalities. Cell.
169:985–999. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Matthijs Blankesteijn W and Hermans KC:
Wnt signaling in atherosclerosis. Eur J Pharmacol. 763((Pt A)):
122–130. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Krishna SM, Seto SW, Jose RJ, Li J, Morton
SK, Biros E, Wang Y, Nsengiyumva V, Lindeman JH, Loots GG, et al:
Wnt signaling pathway inhibitor sclerostin inhibits angiotensin
II-induced aortic aneurysm and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 37:553–566. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Christman MA II, Goetz DJ, Dickerson E,
McCall KD, Lewis CJ, Benencia F, Silver MJ, Kohn LD and Malgor R:
Wnt5a is expressed in murine and human atherosclerotic lesions. Am
J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 294:H2864–H2870. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Malgor R, Bhatt PM, Connolly BA, Jacoby
DL, Feldmann KJ, Silver MJ, Nakazawa M, McCall KD and Goetz DJ:
Wnt5a, TLR2 and TLR4 are elevated in advanced human atherosclerotic
lesions. Inflamm Res. 63:277–285. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bhatt PM and Malgor R: Wnt5a: A player in
the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis and other inflammatory
disorders. Atherosclerosis. 237:155–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou XL, Zhang CJ, Peng YN, Wang Y, Xu HJ
and Liu CM: ROR2 modulates neuropathic pain via phosphorylation of
NMDA receptor subunit GluN2B in rats. Br J Anaesth. 123:e239–e248.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gordon MD and Nusse R: Wnt signaling:
Multiple pathways, multiple receptors, and multiple transcription
factors. J Biol Chem. 281:22429–22433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yu J, Chen L, Cui B, Widhopf GF II, Shen
Z, Wu R, Zhang L, Zhang S, Briggs SP and Kipps TJ: Wnt5a induces
ROR1/ROR2 heterooligomerization to enhance leukemia chemotaxis and
proliferation. J Clin Invest. 126:585–598. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Arabzadeh S, Hossein G, Salehi-Dulabi Z
and Zarnani AH: WNT5A-ROR2 is induced by inflammatory mediators and
is involved in the migration of human ovarian cancer cell line
SKOV-3. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 21:92016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sato A, Kayama H, Shojima K, Matsumoto S,
Koyama H, Minami Y, Nojima S, Morii E, Honda H, Takeda K, et al:
The Wnt5a-Ror2 axis promotes the signaling circuit between
interleukin-12 and interferon-γ in colitis. Sci Rep. 5:105362015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ackers I, Szymanski C, Duckett KJ, Consitt
LA, Silver MJ and Malgor R: Blocking Wnt5a signaling decreases CD36
expression and foam cell formation in atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc
Pathol. 34:1–8. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pan W, Yu H, Huang S and Zhu P:
Resveratrol Protects against TNF-α-Induced Injury in Human
Umbilical Endothelial Cells through Promoting Sirtuin-1-Induced
Repression of NF-KB and p38 MAPK. PLoS One. 11:e01470342016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li Y, Sun J, Gu L and Gao X: Protective
effect of CTRP6 on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by
attenuating inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis in PC12
cells. Mol Med Rep. 22:344–352. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kim DH, Lee SM, Lee YJ, Yoon JJ, Tan R, Yu
YC, Kang DG and Lee HS: Effect of Paeotang on tumor necrosis factor
α-induced vascular inflammation in human umbilical vein endothelial
cells. Chin J Integr Med. doi.10.1007/s11655-017-2759-3.
|
|
26
|
Choe JY, Park KY, Lee SJ, Park SH and Kim
SK: Rebamipide inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α-induced
interleukin-8 expression by suppressing the NF-κB signal pathway in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Inflamm Res. 59:1019–1026.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang CJ, Zhu N, Liu Z, Shi Z, Long J, Zu
XY, Tang ZW, Hu ZY, Liao DF and Qin L: Wnt5a/Ror2 pathway
contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis and
inflammatory response in atherosclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Cell Biol Lipids. 1865:1585472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
DiDonato JA, Mercurio F and Karin M: NF-κB
and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol Rev.
246:379–400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen XJ, Zhang WN, Chen B, Xi WD, Lu Y,
Huang JY, Wang YY, Long J, Wu SF, Zhang YX, et al:
Homoharringtonine deregulates MYC transcriptional expression by
directly binding NF-κB repressing factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:2220–2225. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Brentnall M, Rodriguez-Menocal L, De
Guevara RL, Cepero E and Boise LH: Caspase-9, caspase-3 and
caspase-7 have distinct roles during intrinsic apoptosis. BMC Cell
Biol. 14:322013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lamkanfi M and Kanneganti TD: Caspase-7: A
protease involved in apoptosis and inflammation. Int J Biochem Cell
Biol. 42:21–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bhatt PM, Lewis CJ, House DL, Keller CM,
Kohn LD, Silver MJ, McCall KD, Goetz DJ and Malgor R: Increased
Wnt5a mRNA expression in advanced atherosclerotic lesions, and
oxidized LDL treated human monocyte-derived macrophages. Open Circ
Vasc J. 5:1–7. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Flores-Hernández E, Velázquez DM,
Castañeda-Patlán MC, Fuentes-García G, Fonseca-Camarillo G,
Yamamoto-Furusho JK, Romero-Avila MT, García-Sáinz JA and
Robles-Flores M: Canonical and non-canonical Wnt signaling are
simultaneously activated by Wnts in colon cancer cells. Cell
Signal. 72:1096362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takeuchi S, Takeda K, Oishi I, Nomi M,
Ikeya M, Itoh K, Tamura S, Ueda T, Hatta T, Otani H, et al: Mouse
Ror2 receptor tyrosine kinase is required for the heart development
and limb formation. Genes Cells. 5:71–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Witte F, Chan D, Economides AN, Mundlos S
and Stricker S: Receptor tyrosine kinase-like orphan receptor 2
(ROR2) and Indian hedgehog regulate digit outgrowth mediated by the
phalanx-forming region. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:14211–14216.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dai B, Yan T and Zhang A: ROR2 receptor
promotes the migration of osteosarcoma cells in response to Wnt5a.
Cancer Cell Int. 17:1122017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Henry CE, Llamosas E, Daniels B, Coopes A,
Tang K and Ford CE: ROR1 and ROR2 play distinct and opposing roles
in endometrial cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 148:576–584. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Debebe Z and Rathmell WK: Ror2 as a
therapeutic target in cancer. Pharmacol Ther. 150:143–148. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Takahashi D, Suzuki H, Kakei Y, Yamakoshi
K, Minami Y, Komori T and Nishita M: Expression of Ror2 associated
with fibrosis of the submandibular gland. Cell Struct Funct.
42:159–167. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Murphy JM, Jeong K, Rodriguez YAR, Kim JH,
Ahn EE and Lim SS: FAK and Pyk2 activity promote TNF-α and
IL-1β-mediated pro-inflammatory gene expression and vascular
inflammation. Sci Rep. 9:76172019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Liu JB, Jia L, Li BR, Lan LZ, Ge Q, Zhen
HT and Deng HC: Adiponectin suppresses inflammatory responses at
the early phase of atherosclerosis in hyperglycemic rats. Mol Med
Rep. 3:323–328. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bergenfelz C, Medrek C, Ekström E,
Jirström K, Janols H, Wullt M, Bredberg A and Leandersson K: Wnt5a
induces a tolerogenic phenotype of macrophages in sepsis and breast
cancer patients. J Immunol. 188:5448–5458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|