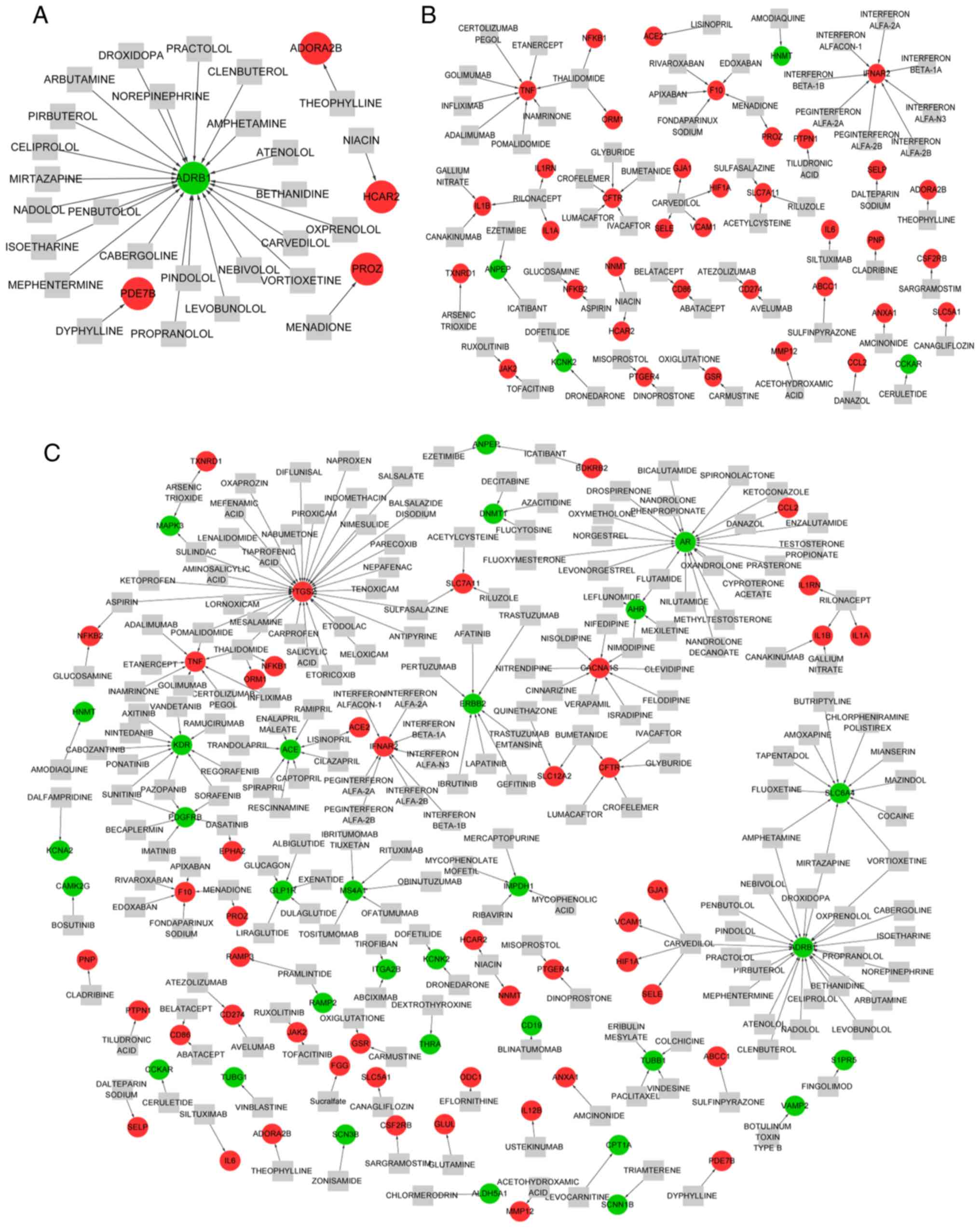
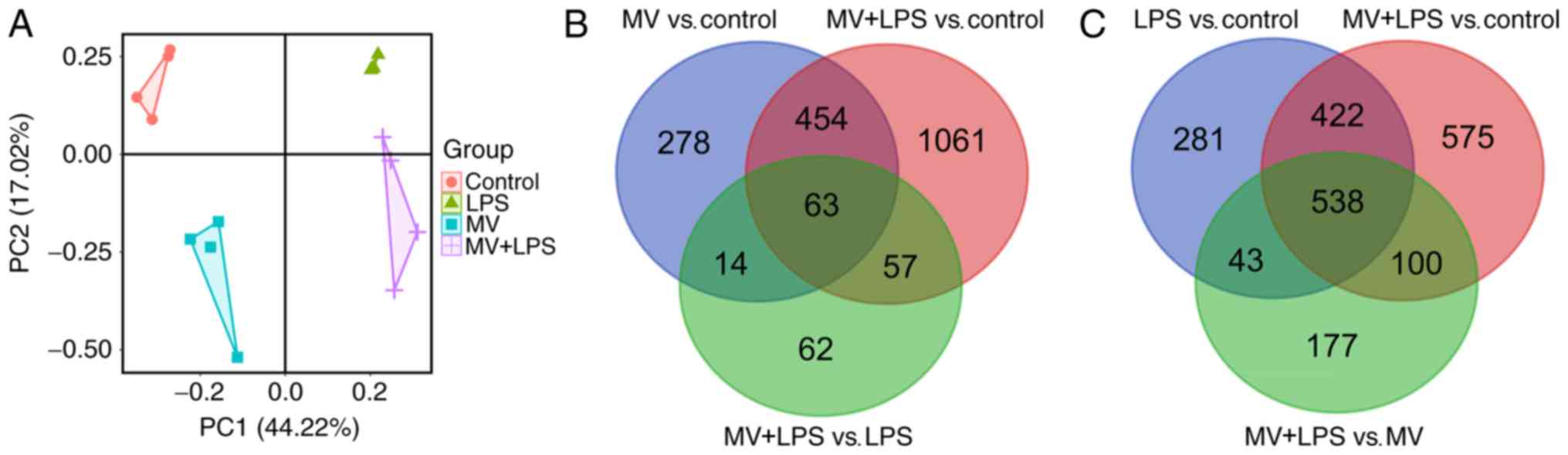
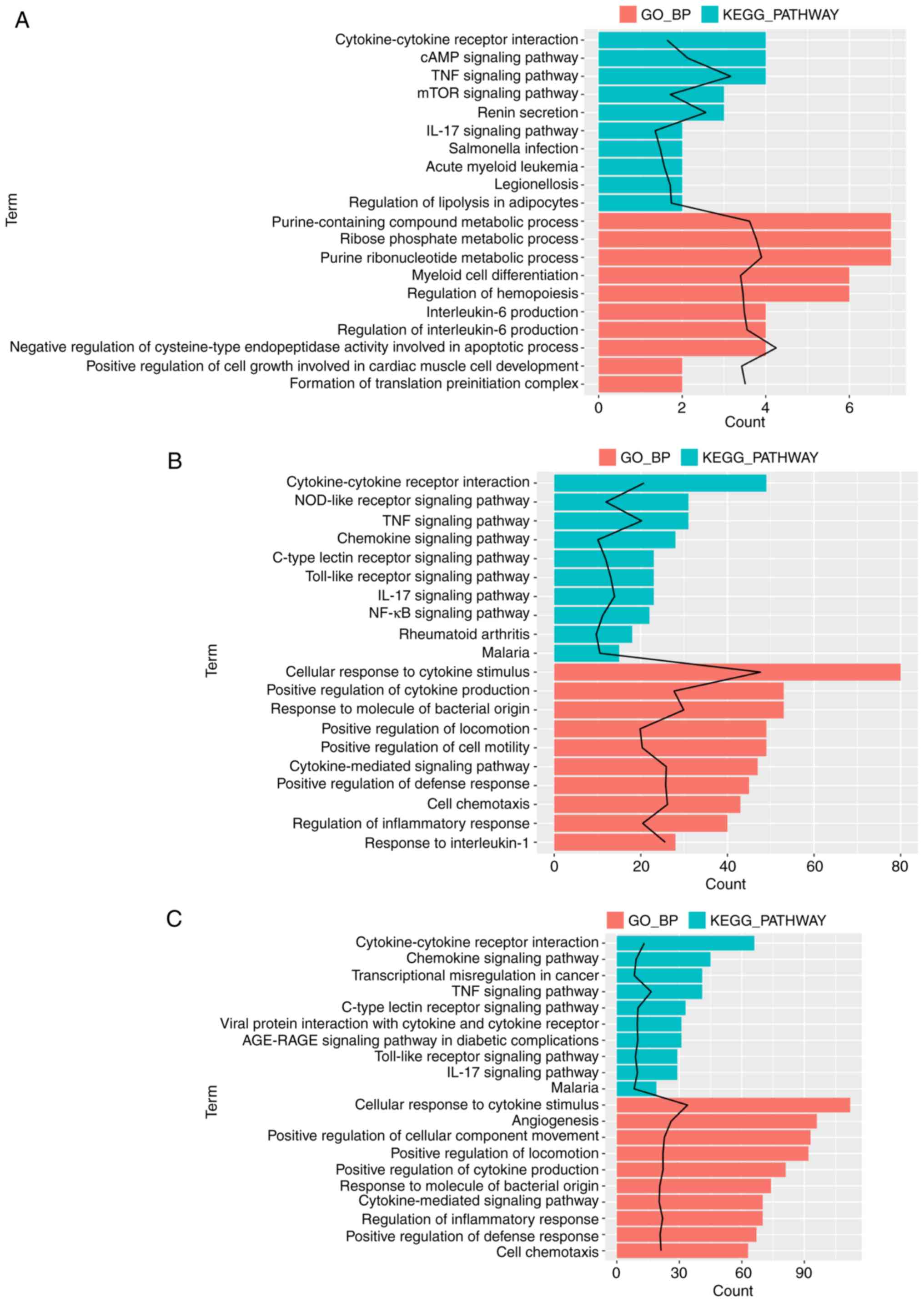
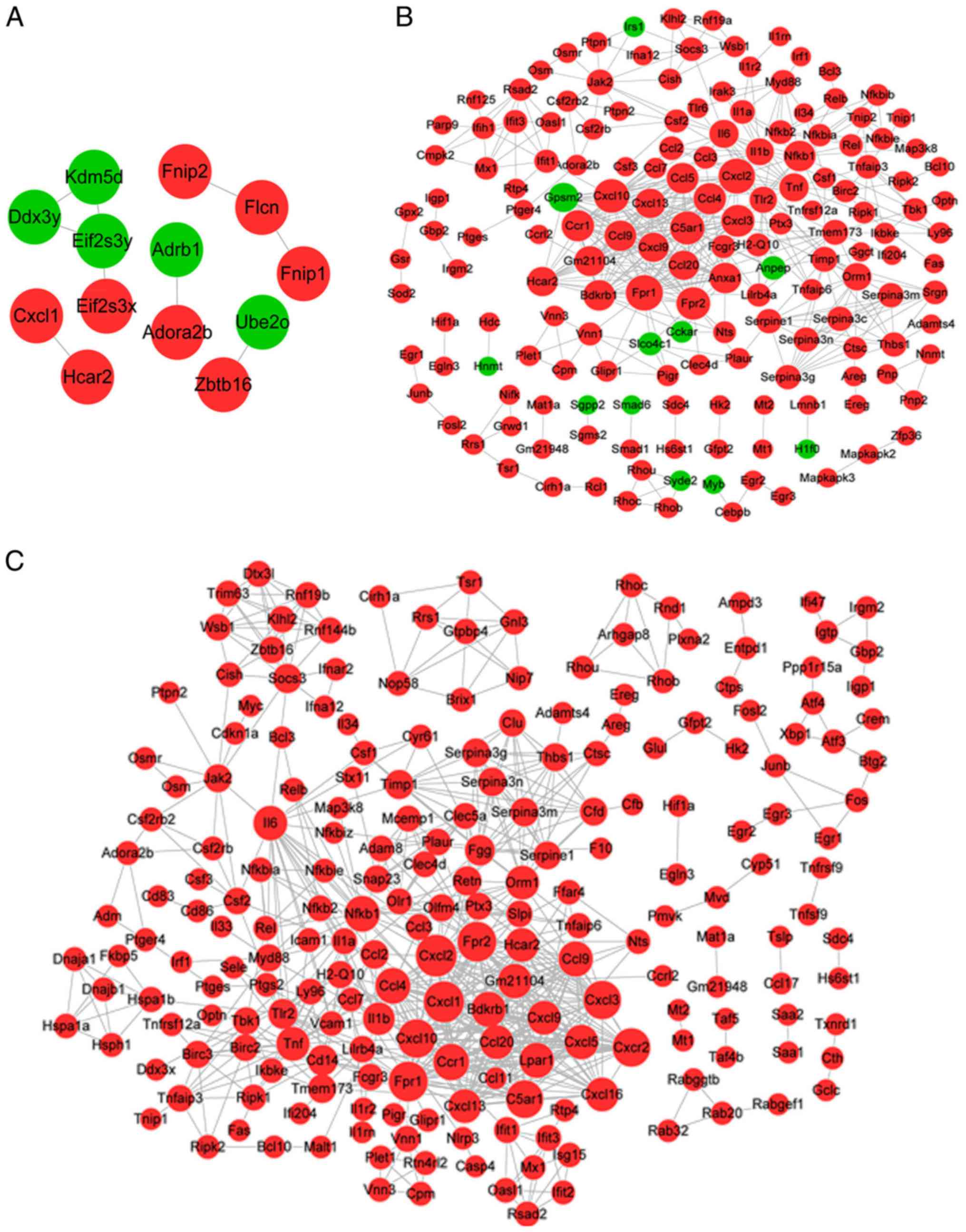
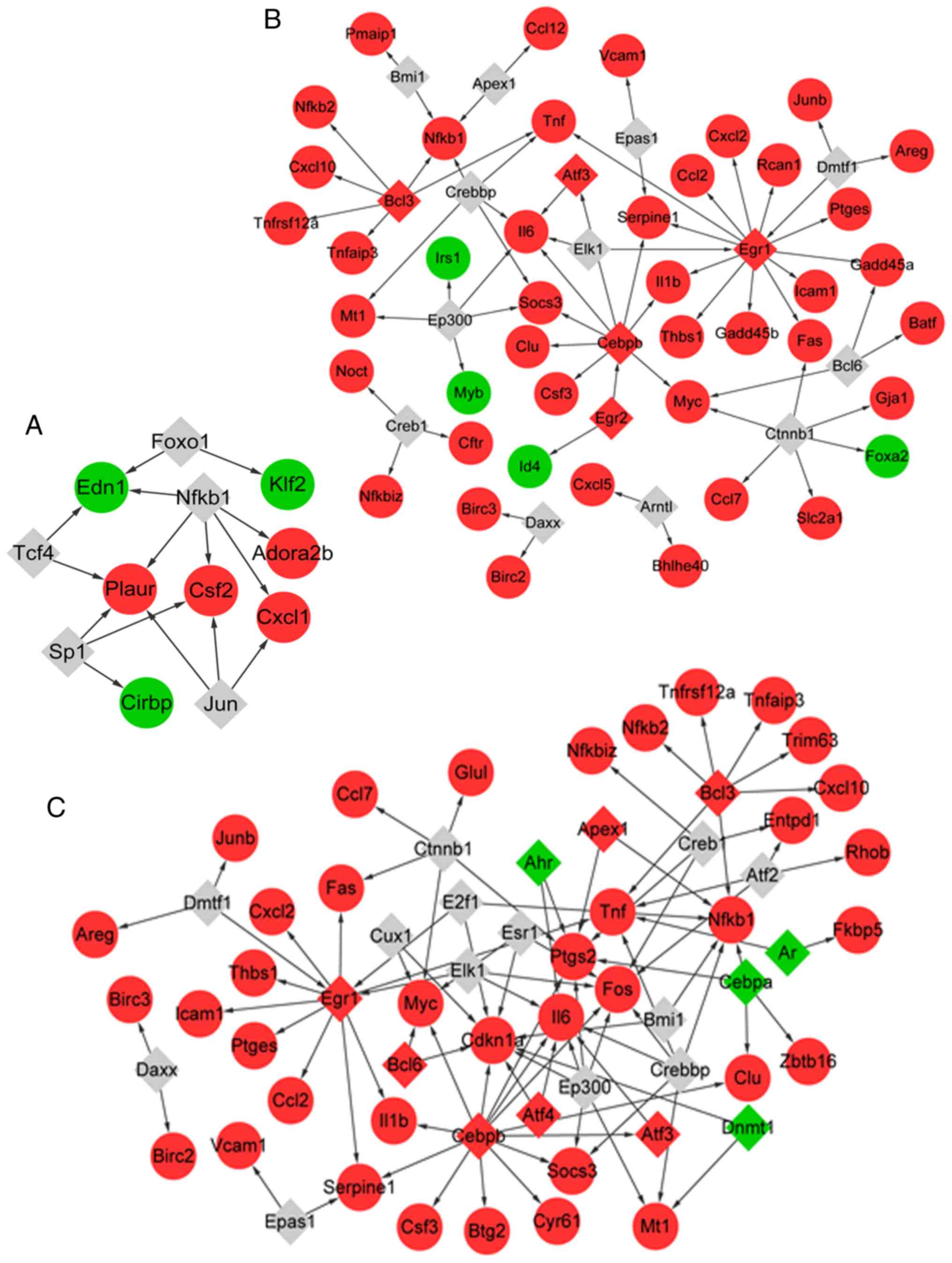
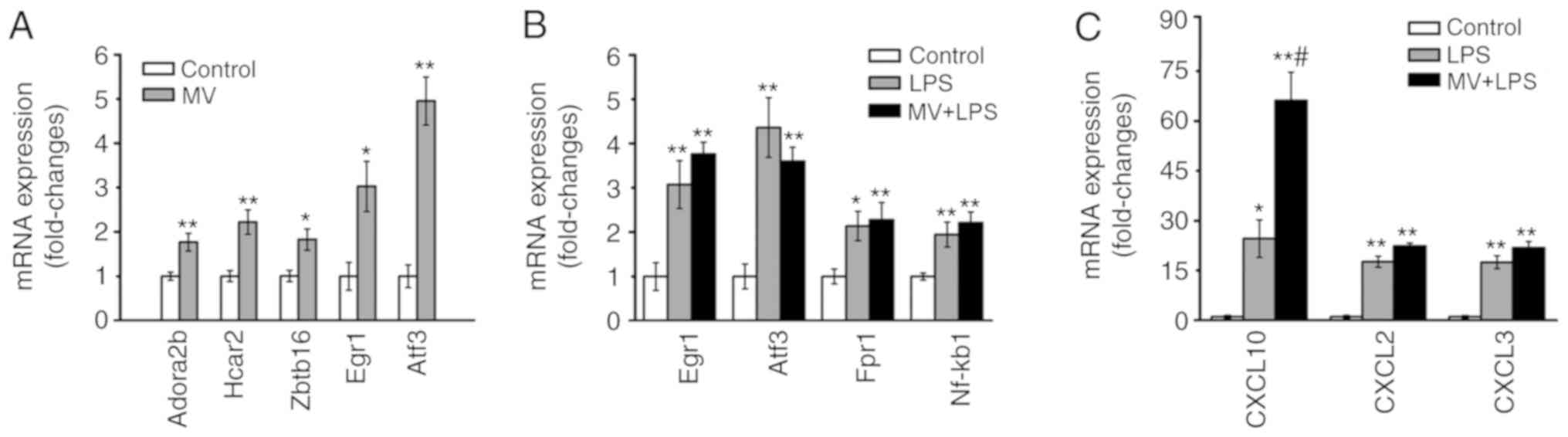
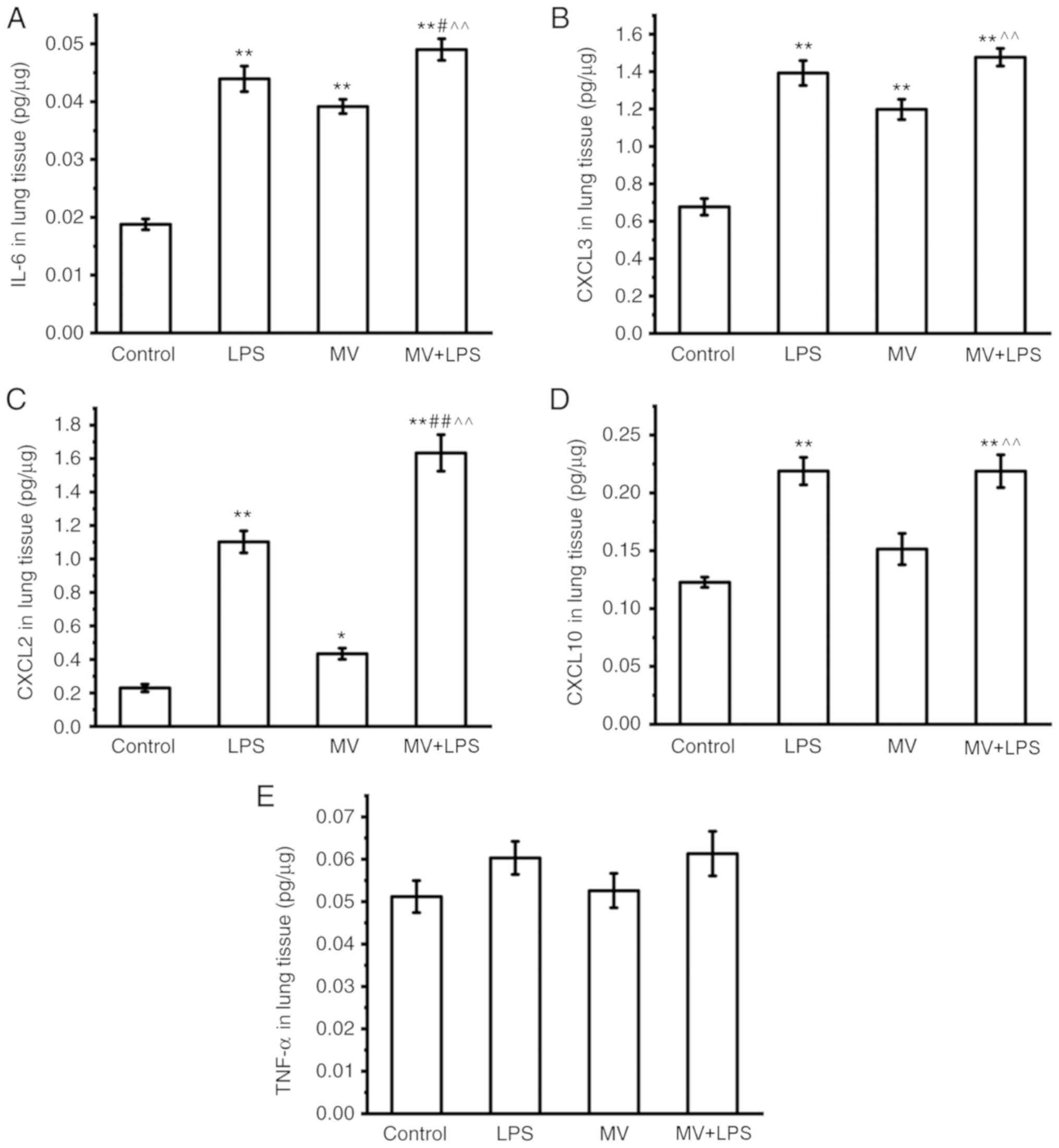
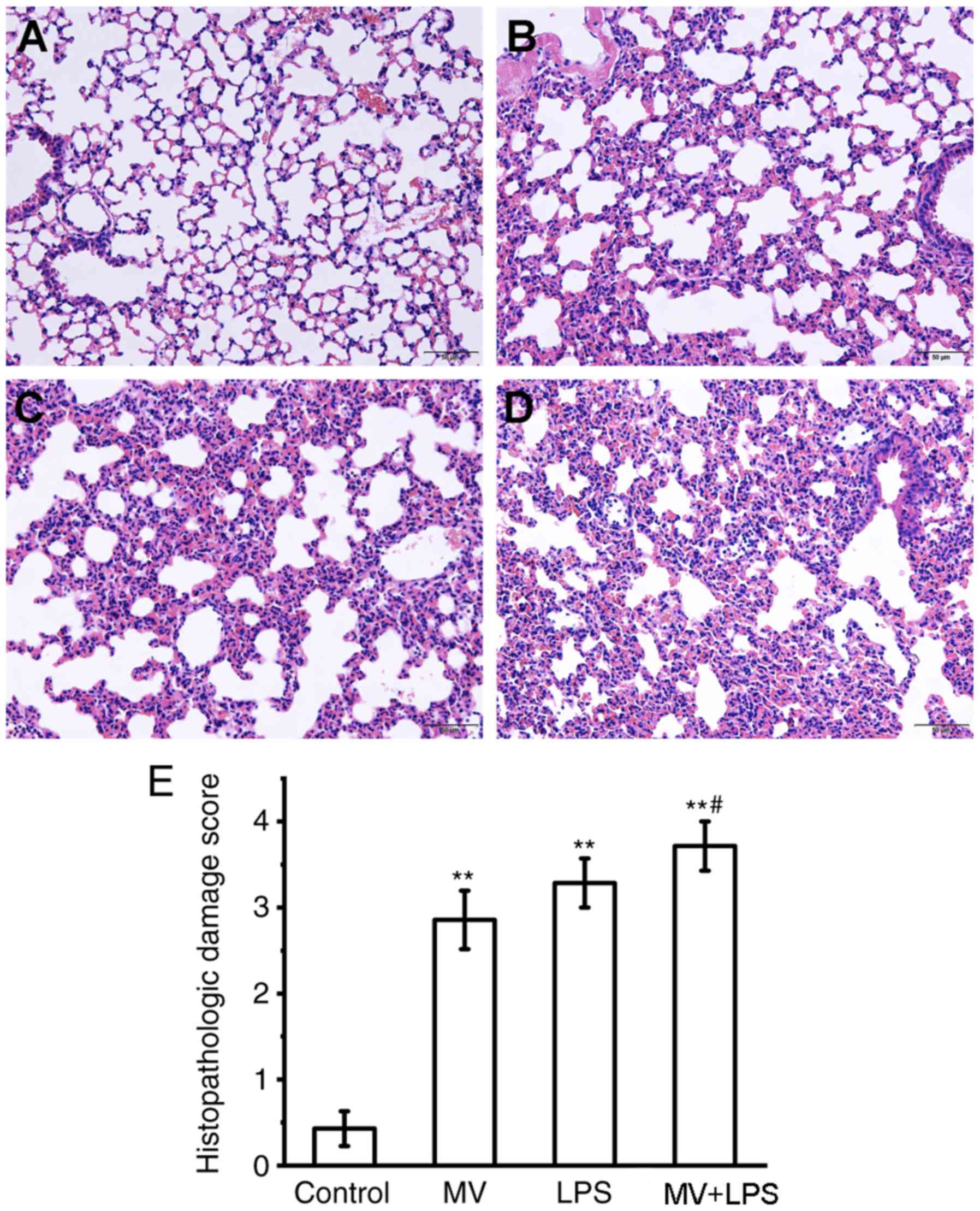
|
1
|
Wang C, Zeng L, Zhang T, Liu J and Wang W:
Casticin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in
mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 789:172–178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zeng M, Sang W, Chen S, Chen R, Zhang H,
Xue F, Li Z, Liu Y, Gong Y, Zhang H and Kong X: 4-PBA inhibits
LPS-induced inflammation through regulating ER stress and autophagy
in acute lung injury models. Toxicol Lett. 271:26–37. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Niu X, Liu F, Li W, Zhi W, Zhang H, Wang X
and He Z: Cavidine ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute
lung injury via NF-κB signaling pathway in vivo and in vitro.
Inflammation. 40:1111–1122. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Modrykamien AM and Gupta P: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent).
28:163–171. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gramatté J, Pietzsch J, Bergmann R and
Richter T: Causative treatment of acid aspiration induced acute
lung injury-recent trends from animal experiments and critical
perspective. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 69:187–195. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fanelli V and Ranieri VM: Mechanisms and
clinical consequences of acute lung injury. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 12
(Suppl 1):S3–S8. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao H, Zhao M, Wang Y, Li F and Zhang Z:
Glycyrrhizic acid prevents sepsis-induced acute lung injury and
mortality in rats. J Histochem Cytochem. 64:125–137. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang W, Luo F, Lu Q, Liu J, Li P, Wang X,
Fu Y, Hao K, Yan T and Ding X: The protective effect of Trillin
LPS-induced acute lung injury by the regulations of inflammation
and oxidative state. Chem Biol Interact. 243:127–134. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Zhao C, He W, Wang Z, Fang Q,
Xiao B, Liu Z, Liang G and Yang S: Discovery and evaluation of
asymmetrical monocarbonyl analogs of curcumin as anti-inflammatory
agents. Drug Des Devel Ther. 8:373–382. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen WY, Huang YC, Yang ML, Lee CY, Chen
CJ, Yeh CH, Pan PH, Horng CT, Kuo WH and Kuan YH: Protective effect
of rutin on LPS-induced acute lung injury via down-regulation of
MIP-2 expression and MMP-9 activation through inhibition of Akt
phosphorylation. Int Immunopharmacol. 22:409–413. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen Y, Zhou X and Rong L: Analysis of
mechanical ventilation and lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung
injury using DNA microarray analysis. Mol Med Rep. 11:4239–4245.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen H, Bai C and Wang X: The value of the
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury model in respiratory
medicine. Expert Rev Respir Med. 4:773–783. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang A, Pan W, Lv J and Wu H: Protective
effect of Amygdalin on LPS-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting
NF-κB and NLRP3 signaling pathways. Inflammation. 40:745–751. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pedrazza L, Cunha AA, Luft C, Nunes NK,
Schimitz F, Gassen RB, Breda RV, Donadio MV, de Souza Wyse AT,
Pitrez PMC, et al: Mesenchymal stem cells improves survival in
LPS-induced acute lung injury acting through inhibition of NETs
formation. J Cell Physiol. 232:3552–3564. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bouferrache K and Vieillard-Baron A: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome, mechanical ventilation, and right
ventricular function. Curr Opin Crit Care. 17:30–35. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gordo-Vidal F and Enciso-Calderón V: Acute
respiratory distress syndrome, mechanical ventilation and right
ventricular function. Med Intensiva. 36:138–142. 2012.(In Spanish).
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nieman GF, Gatto LA, Bates JH and Habashi
NM: Mechanical ventilation as a therapeutic tool to reduce ARDS
incidence. Chest. 148:1396–1404. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mekontso Dessap A, Boissier F, Charron C,
Bégot E, Repessé X, Legras A, Brun-Buisson C, Vignon P and
Vieillard-Baron A: Acute cor pulmonale during protective
ventilation for acute respiratory distress syndrome: Prevalence,
predictors, and clinical impact. Intensive Care Med. 42:862–870.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brochard L, Slutsky A and Pesenti A:
Mechanical ventilation to minimize progression of lung injury in
acute respiratory failure. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 195:438–442.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sadowitz B, Jain S, Kollisch-Singule M,
Satalin J, Andrews P, Habashi N, Gatto LA and Nieman G: Preemptive
mechanical ventilation can block progressive acute lung injury.
World J Crit Care Med. 5:74–82. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chian CF, Chiang CH, Chuang CH, Liu SL and
Tsai AC: SN50, a cell-permeable-inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB,
attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in an isolated and
perfused rat lung model. Shock. 46:194–201. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Slutsky AS and Ranieri VM:
Ventilator-induced lung injury. N Engl J Med. 369:2126–2136. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Smith LS, Gharib SA, Frevert CW and Martin
TR: Effects of age on the synergistic interactions between
lipopolysaccharide and mechanical ventilation in mice. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 43:475–486. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
The R Development Core Team, . R: A
language and environment for statistical computing. 2014.
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dong WW, Liu YJ, Lv Z, Mao YF, Wang YW,
Zhu XY and Jiang L: Lung endothelial barrier protection by
resveratrol involves inhibition of HMGB1 release and HMGB1-induced
mitochondrial oxidative damage via an Nrf2-dependent mechanism.
Free Radic Biol Med. 88:404–416. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Li TJ, Zhao LL, Qiu J, Zhang HY, Bai GX
and Chen L: Interleukin-17 antagonist attenuates lung inflammation
through inhibition of the ERK1/2 and NF-κB pathway in LPS-induced
acute lung injury. Mol Med Rep. 16:2225–2232. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Patel BV, Wilson MR, O'Dea KP and Takata
M: TNF-induced death signaling triggers alveolar epithelial
dysfunction in acute lung injury. J Immunol. 190:4274–4282. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Puneet P, Moochhala S and Bhatia M:
Chemokines in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Am J Physiol
Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 288:L3–L15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bhatia M, Zemans RL and Jeyaseelan S: Role
of chemokines in the pathogenesis of acute lung injury. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 46:566–572. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang W, Yang P, Zhong Y, Zhao Z, Xing L,
Zhao Y, Zou Z, Zhang Y, Li C, Li T, et al: Monoclonal antibody
against CXCL-10/IP-10 ameliorates influenza A (H1N1) virus induced
acute lung injury. Cell Res. 23:577–580. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bao Z, Ye Q, Gong W, Xiang Y and Wan H:
Humanized monoclonal antibody against the chemokine CXCL-8 (IL-8)
effectively prevents acute lung injury. Int Immunopharmacol.
10:259–263. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yang J, Tian H and Huang X: Tephrosin
attenuates sepsis induced acute lung injury in rats by impeding
expression of ICAM-1 and MIP-2. Microb Pathog. 117:93–99. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lai C, Wang K, Zhao Z, Zhang L, Gu H, Yang
P and Wang X: C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) mediates acute
lung injury induced by lethal influenza H7N9 virus. Front
Microbiol. 8:5872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Boucher A, Lemay A and Akoum A: Effect of
hormonal agents on monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression by
endometrial epithelial cells of women with endometriosis. Fertil
Steril. 74:969–975. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jolicoeur C, Lemay A and Akoum A:
Comparative effect of danazol and a GnRH agonist on monocyte
chemotactic protein-1 expression by endometriotic cells. Am J
Reprod Immunol. 45:86–93. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Vecchio EA, White PJ and May LT: The
adenosine A2B G protein-coupled receptor: Recent advances and
therapeutic implications. Pharmacol Ther. 198:20–33. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Eckle T, Grenz A, Laucher S and Eltzschig
HK: A2B adenosine receptor signaling attenuates acute lung injury
by enhancing alveolar fluid clearance in mice. J Clin Invest.
118:3301–3315. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Holgate ST: The Quintiles Prize Lecture
2004. The identification of the adenosine A2B receptor as a novel
therapeutic target in asthma. Br J Pharmacol. 145:1009–1015. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Philipp S, Yang XM, Cui L, Davis AM,
Downey JM and Cohen MV: Postconditioning protects rabbit hearts
through a protein kinase C-adenosine A2b receptor cascade.
Cardiovasc Res. 70:308–314. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|