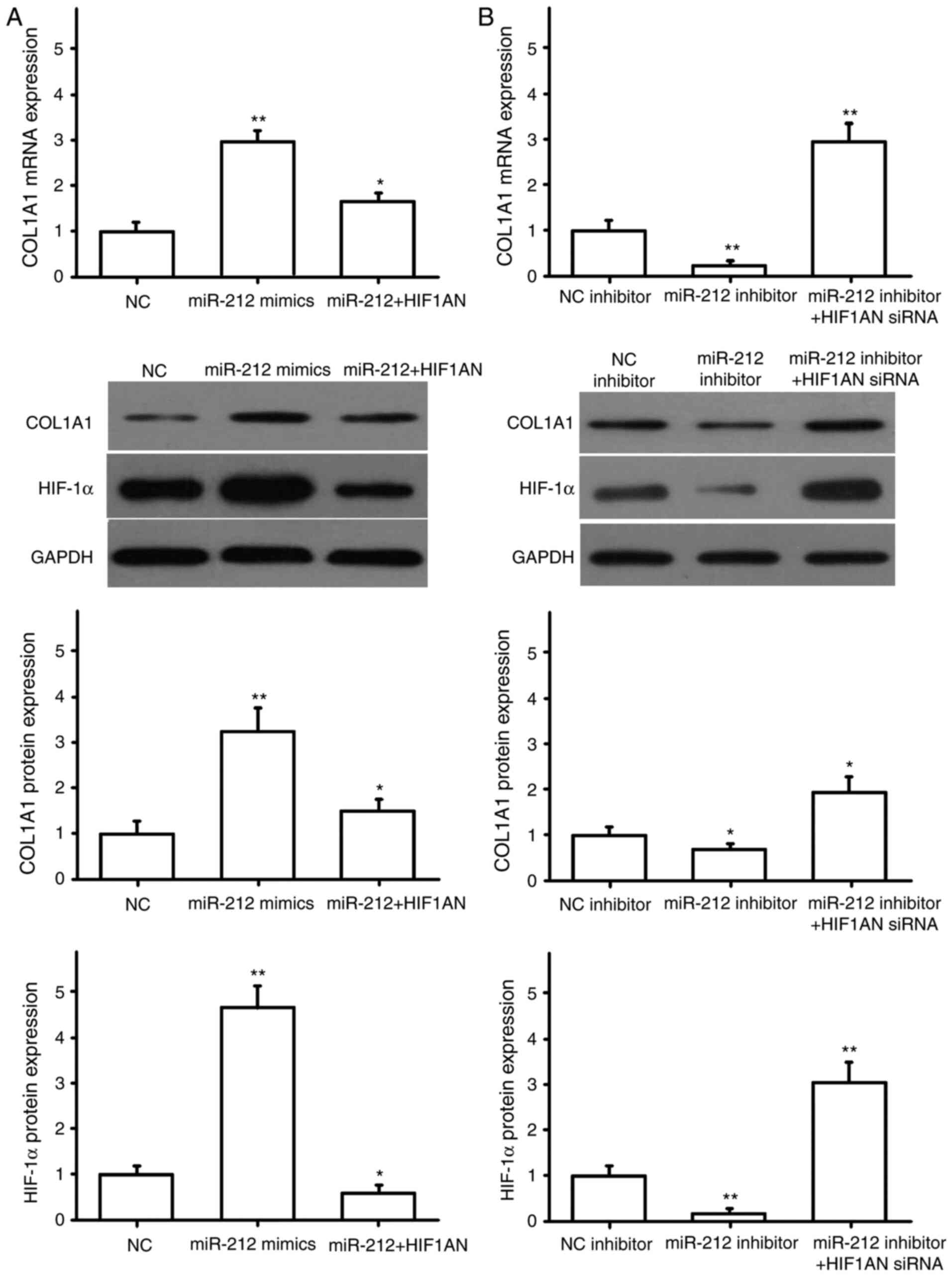
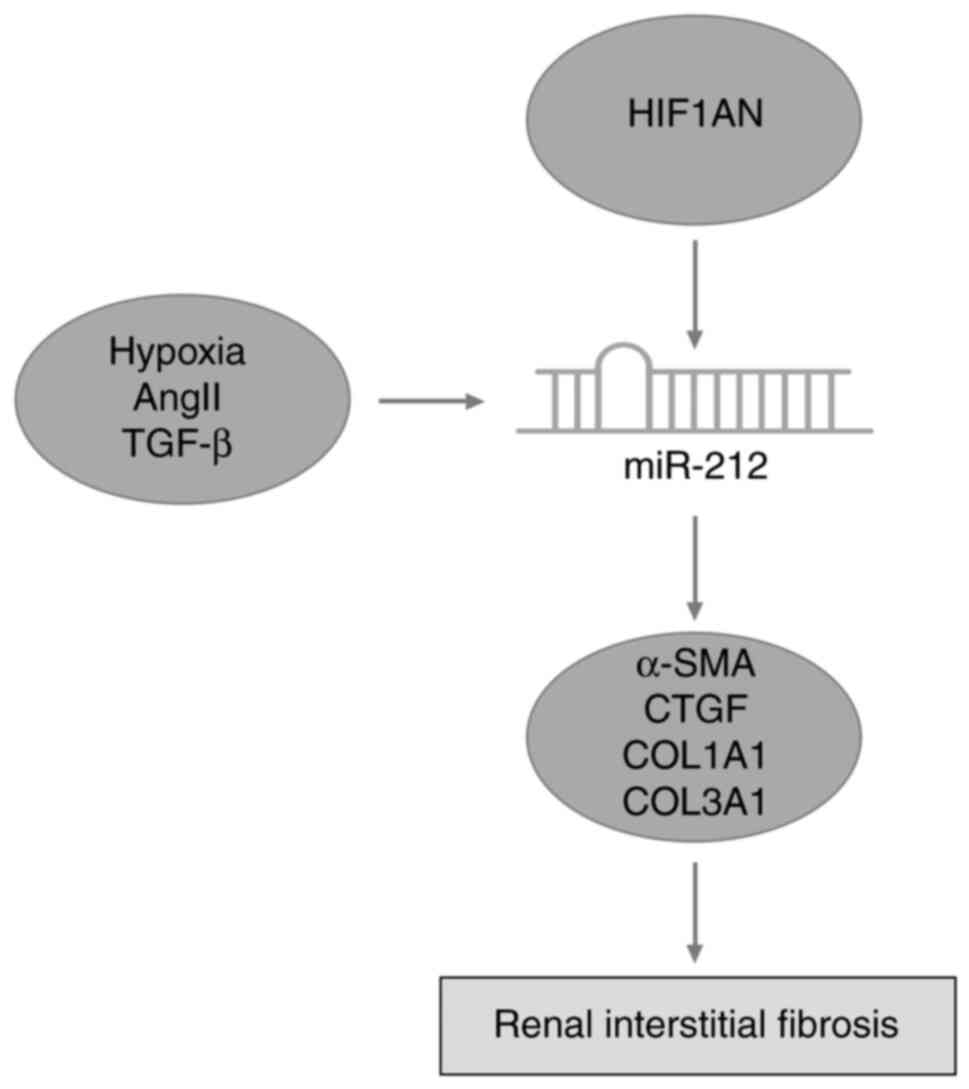
|
1
|
Perico N and Remuzzi G: Chronic kidney
disease: A research and public health priority. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 27 (Suppl 3):iii19–iii26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lin Z, Gong Q, Zhou Z, Zhang W, Liao S,
Liu Y, Yan X, Pan X, Lin S and Li X: Increased plasma CXCL16 levels
in patients with chronic kidney diseases. Eur J Clin Invest.
41:836–845. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grgic I, Duffield JS and Humphreys BD: The
origin of interstitial myofibroblasts in chronic kidney disease.
Pediatr Nephrol. 27:183–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hayer MK, Price AM, Liu B, Baig S, Ferro
CJ, Townend JN, Steeds RP and Edwards NC: Diffuse myocardial
interstitial fibrosis and dysfunction in early chronic kidney
disease. Am J Cardiol. 121:656–660. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou TB, Qin YH, Lei FY, Huang WF and
Drummen GPC: Prohibitin attenuates oxidative stress and
extracellular matrix accumulation in renal interstitial fibrosis
disease. PLoS One. 8:e771872013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ghosh AK, Rai R, Flevaris P and Vaughan
DE: Epigenetics in reactive and reparative cardiac fibrogenesis:
The promise of epigenetic therapy. J Cell Physiol. 232:1941–1956.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sun YB, Qu X, Caruana G and Li J: The
origin of renal fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and the signals that
trigger fibrosis. Differentiation. 92:102–107. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jurkovicova D, Sedlakova B, Lacinova L,
Kopacek J, Sulova Z, Sedlak J and Krizanova O: Hypoxia differently
modulates gene expression of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors
in mouse kidney and HEK 293 cell line. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1148:421–427. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang G, Cheng QL, Li CL, Jia YL, Yue W,
Pei XT, Liu Y, Zhao JH, Du J and Ao QG: High glucose reduced the
repair function of kidney stem cells conditional medium to the
hypoxia-injured renal tubular epithelium cells. Beijing Da Xue Xue
Bao Yi Xue Ban. 49:125–130. 2017.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bienholz A, Reis J, Sanli P, de Groot H,
Petrat F, Guberina H, Wilde B, Witzke O, Saner FH, Kribben A, et
al: Citrate shows protective effects on cardiovascular and renal
function in ischemia-induced acute kidney injury. BMC Nephrol.
18:1302017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng Z, Liu L, Wang Z, Cai Y, Xu Q and
Chen P: Hypoxia activates src and promotes endocytosis which
decreases MMP-2 activity and aggravates renal interstitial
fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 19:5812018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Karakashev SV and Reginato MJ:
Hypoxia/HIF1α induces lapatinib resistance in ERBB2-positive breast
cancer cells via regulation of DUSP2. Oncotarget. 6:1967–1980.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xie J, Li DW, Chen XW, Wang F and Dong P:
Expression and significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and
MDR1/P-glycoprotein in laryngeal carcinoma tissue and hypoxic Hep-2
cells. Oncol Lett. 6:232–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qu K, Yan Z, Wu Y, Chen Y, Qu P, Xu X,
Yuan P, Huang X, Xing J, Zhang H, et al: Transarterial
chemoembolization aggravated peritumoral fibrosis via
hypoxia-inducible factor-1α dependent pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 30:925–932. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kimura K, Iwano M, Higgins DF, Yamaguchi
Y, Nakatani K, Harada K, Kubo A, Akai Y, Rankin EB, Neilson EG, et
al: Stable expression of HIF-1alpha in tubular epithelial cells
promotes interstitial fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
295:F1023–F1029. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cao D, Hu L, Lei D, Fang X, Zhang Z, Wang
T, Lin M, Huang J, Yang H, Zhou X and Zhong L: MicroRNA-196b
promotes cell proliferation and suppress cell differentiation in
vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan J, Xiao G, Peng G, Liu D, Wang Z,
Liao Y, Liu Q, Wu M and Yuan X: MiRNA-125a-5p inhibits glioblastoma
cell proliferation and promotes cell differentiation by targeting
TAZ. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 457:171–176. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhao N, Yu H, Yu H, Sun M, Zhang Y, Xu M
and Gao W: MiRNA-711-SP1-collagen-I pathway is involved in the
anti-fibrotic effect of pioglitazone in myocardial infarction. Sci
China Life Sci. 56:431–439. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Patil A, Sweeney WE, Pan CG and Avner ED:
Unique interstitial miRNA signature drives fibrosis in a murine
model of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. World J
Nephrol. 7:108–116. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Patel V, Williams D, Hajarnis S, Hunter R,
Pontoglio M, Somlo S and Igarashi P: miR-17~92 miRNA cluster
promotes kidney cyst growth in polycystic kidney disease. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 110:10765–10770. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lv LL, Cao YH, Ni HF, Xu M, Liu D, Liu H,
Chen PS and Liu BC: MicroRNA-29c in urinary exosome/microvesicle as
a biomarker of renal fibrosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
305:F1220–F1227. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Castoldi G, Gioia C, Giollo F, Carletti R,
Bombardi C, Antoniotti M, Roma F, Zerbini G and Stella A: Different
regulation of miR-29a-3p in glomeruli and tubules in an
experimental model of angiotensin II-dependent hypertension:
Potential role in renal fibrosis. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
43:335–342. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Makni K, Jarraya F, Khabir A, Hentati B,
Hmida MB, Makni H, Boudawara T, Jlidi R, Hachicha J and Ayadi H:
Renal alpha-smooth muscle actin: A new prognostic factor for lupus
nephritis. Nephrology (Carlton). 14:499–505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Racca MA, Novoa PA, Rodríguez I, Vedova
ABD, Pellizas CG, Demarchi M and Donadio AC: Renal dysfunction and
intragraft proMMP9 activity in renal transplant recipients with
interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy. Transpl Int. 28:71–78.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chow BSM, Kocan M, Bosnyak S, Sarwar M,
Wigg B, Jones ES, Widdop RE, Summers RJ, Bathgate RAD, Hewitson TD
and Samuel CS: Relaxin requires the angiotensin II type 2 receptor
to abrogate renal interstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int. 86:75–85.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kriegel AJ, Liu Y, Cohen B, Usa K, Liu Y
and Liang M: MiR-382 targeting of kallikrein 5 contributes to renal
inner medullary interstitial fibrosis. Physiol Genomics.
44:259–267. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ben-Dov IZ, Muthukumar T, Morozov P,
Mueller FB, Tuschl T and Suthanthiran M: MicroRNA sequence profiles
of human kidney allografts with or without tubulointerstitial
fibrosis. Transplantation. 94:1086–1094. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu XJ, Hong Q, Wang Z, Yu YY, Zou X and
Xu LH: MicroRNA21 promotes interstitial fibrosis via targeting
DDAH1: A potential role in renal fibrosis. Mol Cell Biochem.
411:181–189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang B, Koh P, Winbanks C, Coughlan MT,
McClelland A, Watson A, Jandeleit-Dahm K, Burns WC, Thomas MC,
Cooper ME and Kantharidis P: miR-200a prevents renal fibrogenesis
through repression of TGF-β2 expression. Diabetes. 60:280–287.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Taylor NE, Lu L, Usa K, Cowley AW
Jr, Ferreri NR, Yeo NC and Liang M: Renal medullary microRNAs in
Dahl salt-sensitive rats: MiR-29b regulates several collagens and
related genes. Hypertension. 55:974–982. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhou H, Hasni SA, Perez P, Tandon M, Jang
SI, Zheng C, Kopp JB, Austin H III, Balow JE, Alevizos I and Illei
GG: miR-150 promotes renal fibrosis in lupus nephritis by
downregulating SOCS1. J Am Soc Nephrol. 24:1073–1087. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fang Y, Yu X, Liu Y, Kriegel AJ, Heng Y,
Xu X, Liang M and Ding X: miR-29c is downregulated in renal
interstitial fibrosis in humans and rats and restored by HIF-α
activation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 304:F1274–F1282. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Mezzano SA, Aros CA, Droguett A, Burgos
ME, Ardiles LG, Flores CA, Carpio D, Vío CP, Ruiz-Ortega M and
Egido J: Renal angiotensin II up-regulation and myofibroblast
activation in human membranous nephropathy. Kidney Int Suppl.
S39–S45. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tunçdemir M, Demirkesen O, Oztürk M,
Atukeren P, Gümüştaş MK and Turan T: Antiapoptotic effect of
angiotensin-II type-1 receptor blockade in renal tubular cells of
hyperoxaluric rats. Urol Res. 38:71–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhou L, Xue H, Yuan P, Ni J, Yu C, Huang Y
and Lu LM: Angiotensin AT1 receptor activation mediates high
glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal proximal
tubular cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:e152–e157. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zeisberg M and Kalluri R: Physiology of
the renal interstitium. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 10:1831–1840. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mimura I, Tanaka T and Nangaku M: Novel
therapeutic strategy with hypoxia-inducible factors via reversible
epigenetic regulation mechanisms in progressive tubulointerstitial
fibrosis. Semin Nephrol. 33:375–382. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Du R, Xia L, Ning X, Liu L, Sun W, Huang
C, Wang H and Sun S: Hypoxia-induced Bmi1 promotes renal tubular
epithelial cell-mesenchymal transition and renal fibrosis via
PI3K/Akt signal. Mol Biol Cell. 25:2650–2659. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang B, Liang X, Shi W, Ye Z, He C, Hu X
and Liu S: Role of impaired peritubular capillary and hypoxia in
progressive interstitial fibrosis after 56 subtotal nephrectomy of
rats. Nephrology (Carlton). 10:351–357. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Baek KJ, Cho JY, Rosenthal P, Alexander
LEC, Nizet V and Broide DH: Hypoxia potentiates allergen induction
of HIF-1α, chemokines, airway inflammation, TGF-β1, and airway
remodeling in a mouse model. Clin Immunol. 147:27–37. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Baumann B, Hayashida T, Liang X and
Schnaper HW: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α promotes
glomerulosclerosis and regulates COL1A2 expression through
interactions with Smad3. Kidney Int. 90:797–808. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Kushida N, Nomura S, Mimura I, Fujita T,
Yamamoto S, Nangaku M and Aburatani H: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
activates the transforming growth factor-β/SMAD3 pathway in kidney
tubular epithelial cells. Am J Nephrol. 44:276–285. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tang L, Yi R, Yang B, Li H, Chen H and Liu
Z: Valsartan inhibited HIF-1α pathway and attenuated renal
interstitial fibrosis in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetes Res
Clin Pract. 97:125–131. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ma C, Wei J, Zhan F, Wang R, Fu K, Wan X
and Li Z: Urinary hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha levels are
associated with histologic chronicity changes and renal function in
patients with lupus nephritis. Yonsei Med J. 53:587–592. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Matoba K, Kawanami D, Nagai Y, Takeda Y,
Akamine T, Ishizawa S, Kanazawa Y, Yokota T and Utsunomiya K:
Rho-Kinase blockade attenuates podocyte apoptosis by inhibiting the
notch signaling pathway in diabetic nephropathy. Int J Mol Sci.
18:17952017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhu Y, Tan J, Xie H, Wang J, Meng X and
Wang R: HIF-1α regulates EMT via the Snail and β-catenin pathways
in paraquat poisoning-induced early pulmonary fibrosis. J Cell Mol
Med. 20:688–697. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Higgins DF, Kimura K, Iwano M and Haase
VH: Hypoxia-inducible factor signaling in the development of tissue
fibrosis. Cell Cycle. 7:1128–1132. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Anorga S, Overstreet JM, Falke LL, Tang J,
Goldschmeding RG, Higgins PJ and Samarakoon R: Deregulation of
Hippo-TAZ pathway during renal injury confers a fibrotic
maladaptive phenotype. FASEB J. 32:2644–2657. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhu B, Ma AQ, Yang L and Dang XM:
Atorvastatin attenuates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via
suppressing iNOS expression and the CTGF (CCN2)/ERK signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 14:24476–24491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Montford JR and Furgeson SB: A new CTGF
target in renal fibrosis. Kidney Int. 92:784–786. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sun B, Xing CY, He WC, Wang NN, Yu XB,
Zhao XF, Qian J, Yang JW, Liu J and Wang XY: Expression of
connective tissue growth factor in renal interstitial fibrosis
after ureteral obstruction and effects of rapamycin thereupon:
Experiment with rats. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 87:562–566. 2007.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Montgomery TA, Xu L, Mason S, Chinnadurai
A, Lee CG, Elias JA and Cantley LG: Breast regression
protein-39/chitinase 3-like 1 promotes renal fibrosis after kidney
injury via activation of myofibroblasts. J Am Soc Nephrol.
28:3218–3226. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang Q, Peng Z, Xiao S, Geng S, Yuan J and
Li Z: RNAi-mediated inhibition of COL1A1 and COL3A1 in human skin
fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 16:611–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Schauer SN, Sontakke SD, Watson ED,
Esteves CL and Donadeu FX: Involvement of miRNAs in equine follicle
development. Reproduction. 146:273–282. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Lin JF, Zeng H and Zhao JQ: MiR-212-5p
regulates the proliferation and apoptosis of AML cells through
targeting FZD5. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:8415–8422.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|