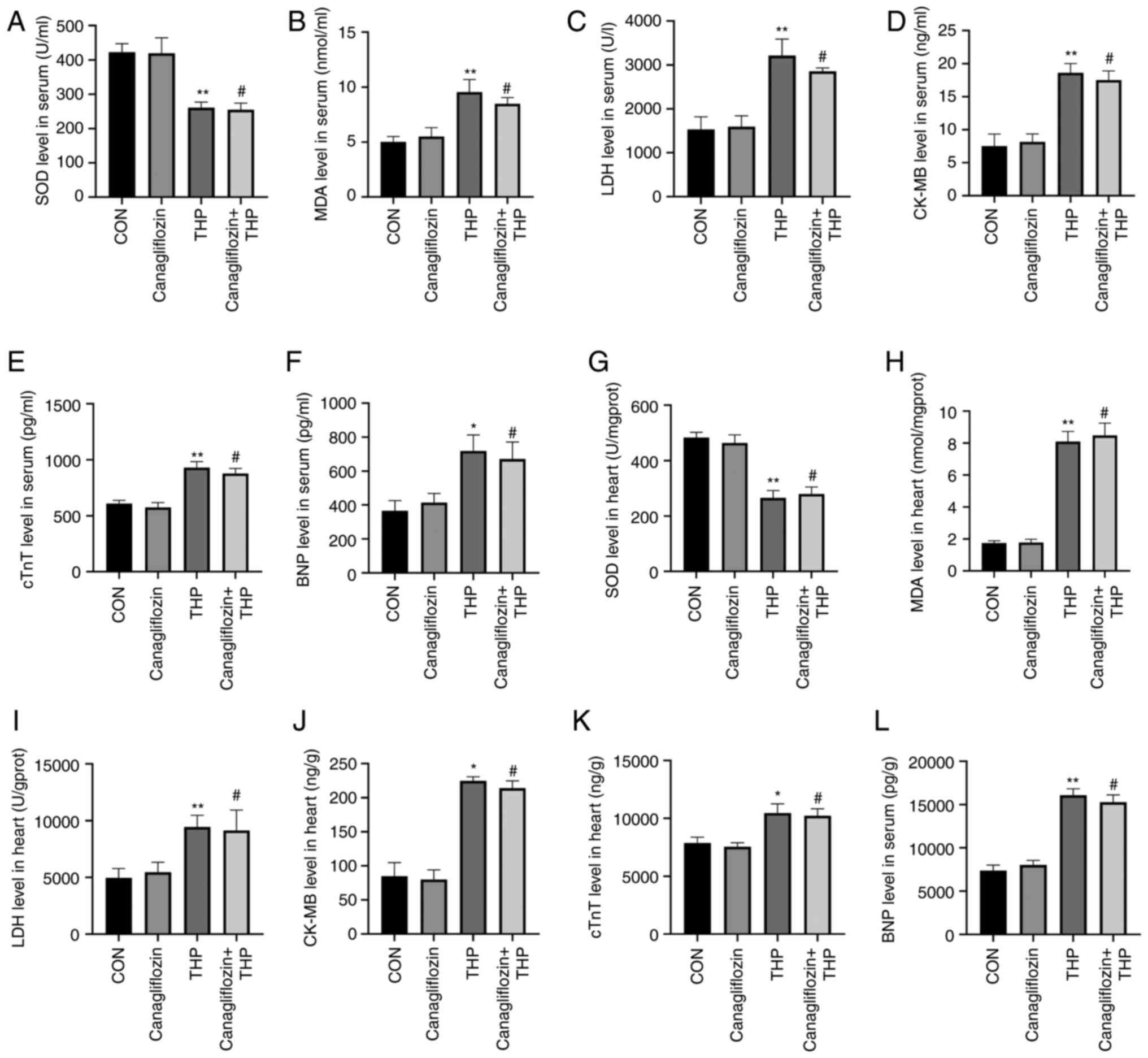
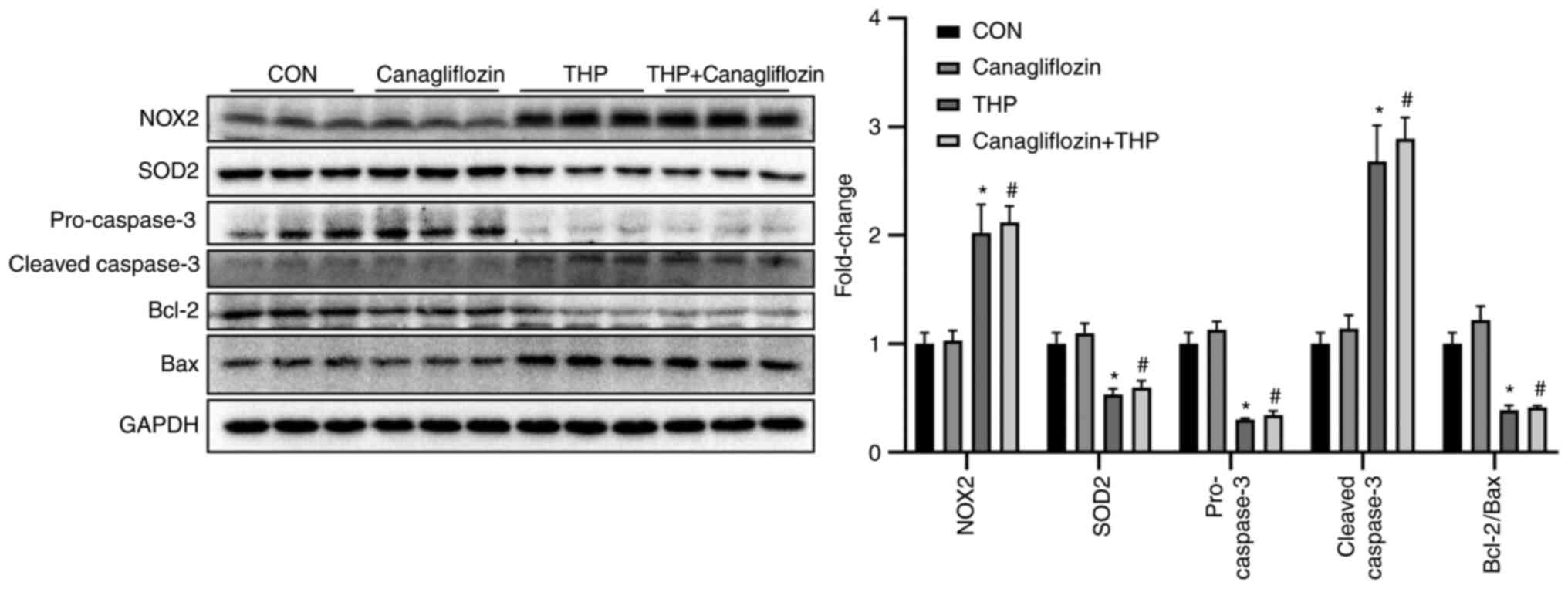
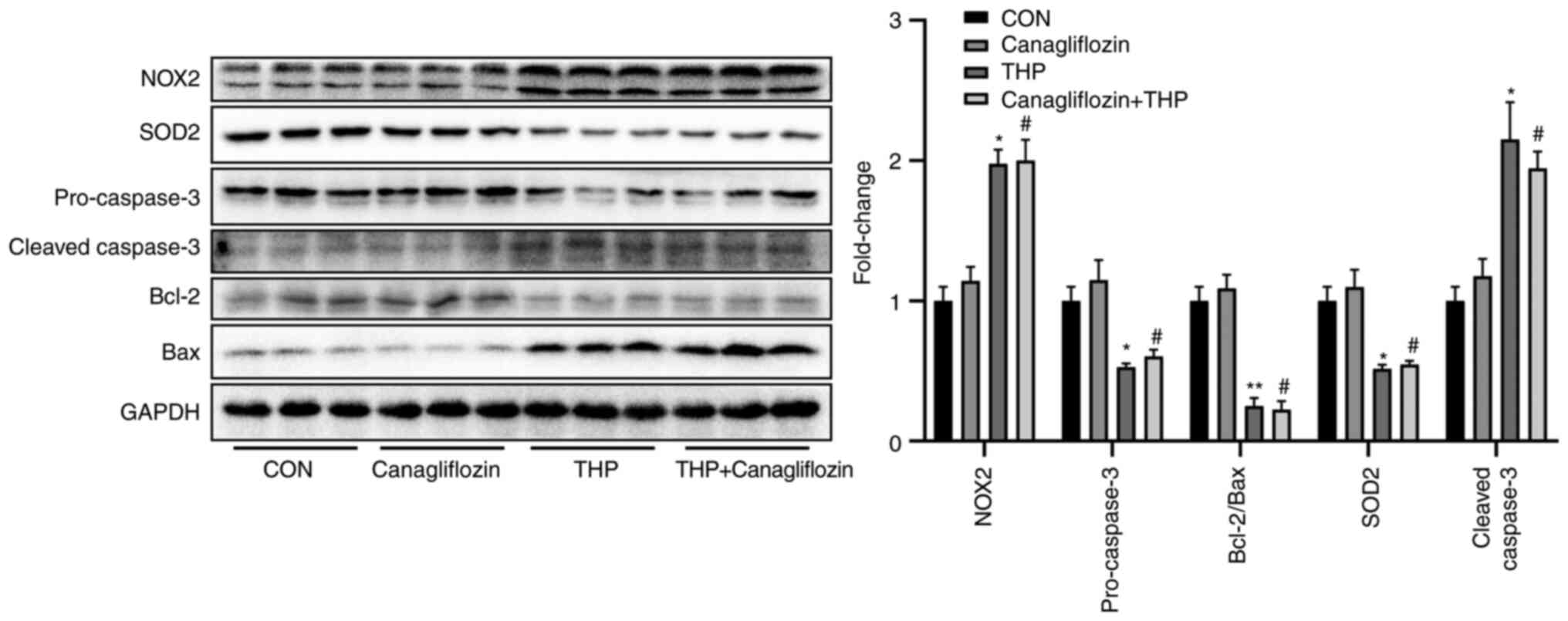
|
1
|
Zhou J, Zhang X, Li M, Wu W, Sun X, Zhang
L and Gong T: Novel lipid hybrid albumin nanoparticle greatly
lowered toxicity of pirarubicin. Mol Pharm. 10:3832–3841. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zheng SE, Xiong S, Lin F, Qiao GL, Feng T,
Shen Z, Min DL, Zhang CL and Yao Y: Pirarubicin inhibits
multidrug-resistant osteosarcoma cell proliferation through
induction of G2/M phase cell cycle arrest. Acta Pharmacologica
Sinica. 33:832–838. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Zhai L, Guo C, Cao Y, Xiao J, Fu X, Huang
J, Huang H, Guan Z and Lin T: Long-term results of pirarubicin
versus doxorubicin in combination chemotherapy for aggressive
non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: Single center, 15-year experience. Int J
Hematol. 91:78–86. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cong W, Liang Q, Li L, Shi J, Liu Q, Feng
Y, Wang Y and Luo G: Metabonomic study on the cumulative
cardiotoxicity of a pirarubicin liposome powder. Talanta. 89:91–98.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Getz KD, Sung L, Alonzo TA, Leger KJ,
Gerbing RB, Pollard JA, Cooper T, Kolb EA, Gamis AS, Ky B and
Aplenc R: Effect of dexrazoxane on left ventricular systolic
function and treatment outcomes in patients with acute myeloid
leukemia: A report from the children's oncology group. J Clin
Oncol. 38:2398–2406. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lamos EM, Younk LM and Davis SN:
Canagliflozin, an inhibitor of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2, for
the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Expert Opin Drug Metab
Toxicol. 9:763–775. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Neal B, Perkovic V and Matthews DR:
Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2
diabetes. N Engl J Med. 377:20992017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Budoff MJ and Wilding JPH: Effects of
canagliflozin on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type
2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Clin Pract. 71:e129482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Davies MJ, Merton K, Vijapurkar U, Yee J
and Qiu R: Efficacy and safety of canagliflozin in patients with
type 2 diabetes based on history of cardiovascular disease or
cardiovascular risk factors: A post hoc analysis of pooled data.
Cardiovasc Diabetol. 16:402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ismy J, Sugandi S, Rachmadi D,
Hardjowijoto S and Mustafa A: The effect of exogenous superoxide
dismutase (SOD) on caspase-3 activation and apoptosis induction in
Pc-3 prostate cancer cells. Res Rep Urol. 12:503–508.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yabaji SM, Dhamija E, Mishra AK and
Srivastava KK: ESAT-6 regulates autophagous response through SOD-2
and as a result induces intracellular survival of mycobacterium
bovis BCG. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 1868:1404702020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chocry M and Leloup L: The NADPH oxidase
family and its inhibitors. Antioxid Redox Signal. 33:332–353. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hegyi B, Borst JM, Bailey LRJ, Shen EY,
Lucena AJ, Navedo MF, Bossuyt J and Bers DM: Hyperglycemia
regulates cardiac K+ channels via O-GlcNAc-CaMKII and
NOX2-ROS-PKC pathways. Basic Res Cardiol. 115:712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Barthold SW, Bayne KA, Davis MA, Bayne K
and Davis M: Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Publication. 327:963–965. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Armenian S and Bhatia S: Predicting and
preventing anthracycline-related cardiotoxicity. Am Soc Clin Oncol
Educ Book. 38:3–12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lei X, Zhu SG, Das A, Chen Q, Durrant D,
Hobbs DC, Lesnefsky EJ and Kukreja RC: Dietary inorganic nitrate
alleviates doxorubicin cardiotoxicity: Mechanisms and implications.
Nitric Oxide. 26:274–284. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
O'Brien KM, Dirmeier R, Engle M and Poyton
RO: Mitochondrial protein oxidation in yeast mutants lacking
manganese-(MnSOD) or copper- and zinc-containing superoxide
dismutase (CuZnSOD): Evidence that MnSOD and CuZnSOD have both
unique and overlapping functions in protecting mitochondrial
proteins from oxidative damage. J Biol Chem. 279:51817–15827. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen M, Du ZY, Zheng X, Li DL, Zhou RP and
Zhang K: Use of curcumin in diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of
Alzheimer's disease. Neural Regen Res. 13:742–752. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fabrizio P, Liou LL, Moy VN, Diaspro A,
Valentine JS, Gralla EB and Longo VD: SOD2 functions downstream of
Sch9 to extend longevity in yeast. Genetics. 163:35–46. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Manuneedhi Cholan P, Cartland SP and
Kavurma MM: NADPH oxidases, angiogenesis, and peripheral artery
disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 6:562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vavrova A, Jansova H, Mackova E, Machacek
M, Haskova P, Tichotova L, Sterba M and Simunek T: Catalytic
inhibitors of topoisomerase II differently modulate the toxicity of
anthracyclines in cardiac and cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e766762013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Faulk A, Weissig V and Elbayoumi T:
Mitochondria-specific nano-emulsified therapy for myocardial
protection against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Methods Mol
Biol. 991:99–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cascales A, Sánchez-Vega B, Navarro N,
Pastor-Quirante F, Corral J, Vicente V and de la Peña FA: Clinical
and genetic determinants of anthracycline-induced cardiac iron
accumulation. Int J Cardiol. 154:282–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Paglia DE and Radcliffe RW: Anthracycline
cardiotoxicity in a black rhinoceros (Diceros bicornis): Evidence
for impaired antioxidant capacity compounded by iron overload. Vet
Pathol. 37:86–88. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Liu LS, Bai XQ, Gao Y, Wu Q, Ren Z, Li Q,
Pan LH, He NY, Peng J and Tang ZH: PCSK9 promotes oxLDL-induced
PC12 cell apoptosis through the Bcl-2/Bax-caspase 9/3 signaling
pathway. J Alzheimers Dis. 57:723–734. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu R, Tang S, Wang M, Xu X, Yao C and Wang
S: MicroRNA-497 induces apoptosis and suppresses proliferation via
the Bcl-2/Bax-caspase9-caspase3 pathway and cyclin D2 protein in
HUVECs. PLoS One. 11:e01670522016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dong JW, Zhu HF, Zhu WZ, Ding HL, Ma TM
and Zhou ZN: Intermittent hypoxia attenuates ischemia/reperfusion
induced apoptosis in cardiac myocytes via regulating Bcl-2/Bax
expression. Cell Res. 13:385–391. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Finsterer J and Ohnsorge P: Influence of
mitochondrion-toxic agents on the cardiovascular system. Regul
Toxicol Pharmacol. 67:434–445. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pal MK, Jaiswar SP, Srivastav AK, Goyal S,
Dwivedi A, Verma A, Singh J, Pathak AK, Sankhwar PL and Ray RS:
Synergistic effect of piperine and paclitaxel on cell fate via
cyt-c, Bax/Bcl-2-caspase-3 pathway in ovarian adenocarcinomas
SKOV-3 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 791:751–762. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhao H, Xu M and Chu G: Association
between myocardial cell apoptosis and calpain-1/caspase-3
expression in rats with hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Mol Med Rep.
15:2727–2731. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mahaffey KW, Neal B, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw
D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, Fabbrini E, Sun T, Li Q, et al:
Canagliflozin for primary and secondary prevention of
cardiovascular events: Results from the CANVAS program
(canagliflozin cardiovascular assessment study). Circulation.
137:323–334. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ghezzi C, Neal B, Perkovic V, de Zeeuw D,
Fulcher G, Erondu N, Shaw W, Fabbrini E, Sun T and Li Q:
Dapagliflozin binds specifically to sodium-glucose cotransporter 2
in the proximal renal tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol. 28:802–810. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marx N and McGuire DK: Sodium-glucose
cotransporter-2 inhibition for the reduction of cardiovascular
events in high-risk patients with diabetes mellitus. Eur Heart J.
37:3192–3200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Verma S, McMurray JJV and Cherney DZI: The
metabolodiuretic promise of sodium-dependent glucose cotransporter
2 inhibition: The search for the sweet spot in heart failure. JAMA
Cardiol. 2:939–940. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Ma XY, Zhang T, Qin M, Sun B, Li
Q, Hu DW and Ren LQ: Protective effects of apocynum venetum against
pirarubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Am J Chin Med. 47:1075–1097.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gaal LV, Garvey T, Leiter L, Vijapurkar U,
List J, Cuddihy R, Ren J and Davies M: Effects of canagliflozin
versus glimepiride on inflammatory biomarkers and chemokines in
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Coll Cardiol. 69
(Suppl 11):S16722017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yaribeygi H, Atkin SL, Butler AE and
Sahebkar A: Sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitors and oxidative
stress: An update. J Cell Physiol. 234:3231–3237. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Clancy CE, Chen-Izu Y, Bers DM,
Belardinelli L, Boyden PA, Csernoch L, Despa S, Fermini B, Hool LC,
Izu L, et al: Deranged sodium to sudden death. J Physiol.
593:1331–1345. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kohlhaas M, Liu T, Knopp A, Zeller T, Ong
MF, Böhm M, O'Rourke B and Maack C: Elevated cytosolic
Na+ increases mitochondrial formation of reactive oxygen
species in failing cardiac myocytes. Circulation. 121:1606–1613.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|