Introduction
Glioblastoma (GBM) is one of the most aggressive and
malignant types of primary cancer in the central nervous system,
accounting for ~3% of all cancers diagnosed worldwide (1) and 90,000 patient deaths per year
(2). Currently, the overall
survival of patients with GBM is <2 years (3,4). The
low survival rate is, at least in part, due to traditional
therapies, such as surgical resection, chemotherapy and
radiotherapy, being unsatisfactory for the treatment of GBM
(5). For example, the recurrence
rate of patients following surgery is high and the 2-year survival
rate after surgery was found to be <35% (6,7).
Therefore, there remains an urgent requirement to determine more
efficient GBM diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers, and to develop
novel strategies for the treatment of GBM.
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a class of non-coding
RNAs, which, similar to microRNAs (miRNAs/miRs), lack 5′ or 3′
ends, and form a circular structure with covalent bonds (8). Accumulating evidence has indicated
that the aberrant expression of circRNAs may exert important
biological functions in the progression of numerous types of
cancer, including hepatocellular carcinoma, gastric carcinoma,
colorectal cancer and glioma (9,10). In
fact, previous studies have demonstrated that dysregulated circRNAs
served as novel regulators of cancer progression, including in GBM
(11,12). The tumor invasion-associated
biomarkers, MMP-2 and MMP-9, belong to the MMP family, and are
known to promote extracellular matrix degradation and invasion of
cancer cells into adjacent healthy tissues during tumor development
(13).
circRNA filamin A (circFLNA), also known as
hsa_circ_0092012, is a newly discovered oncogene, that originates
from exon 9 to 15 of the FLNA gene and has a spliced mature
sequence length of 543 base pairs (14). Aberrant expression levels of
circFLNA have been reported in a variety of human cancer types,
including gastric cancer, oral squamous cell carcinoma and
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (14–17).
However, to the best of our knowledge, the role of circFLNA in GBM
remains to be determined.
miRNAs are small, non-coding RNAs that negatively
regulate gene expression levels by binding to the 3′-untranslated
region (UTR) of target mRNAs (18).
The aberrant expression of miRNAs was found to be associated with
the occurrence and progression of a number of human diseases,
including breast cancer, glioblastoma, thyroid papillary carcinoma,
hepatocellular carcinoma, lung cancer, colon cancer and endocrine
pancreatic tumors (18,19). In particular, the expression levels
of miR-199-3p have been reported to be downregulated in multiple
types of cancer, including GBM (20,21).
However, the role of miR-199-3p in GBM progression remains
elusive.
Thus, the present study aimed to detect the role and
underlying mechanism of circFLNA in glioblastoma and screened the
circRNAs-miRNA network that exist during the progression of
human.
Materials and methods
Cell lines
Human GBM cell lines (U251, LN229, T98G, A172 and
SHG44) were obtained from The Cell Bank of Type Culture Collection
of The Chinese Academy of Sciences. Normal human astrocytes (NHAs)
were purchased from American Type Culture Collection. Cells were
cultured in DMEM (cat. no. 670087; Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) supplemented with 10% FBS (cat. no. 16140071; Gibco; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) in a humidified atmosphere with 5%
CO2 at 37°C.
Patient studies
A total of 50 human GBM and paired adjacent healthy
brain tissues were collected from patients with GBM (25 male
patients and 25 female patients; median age, 40.5 years; age range,
18–69 years) at Harbin Medical University Cancer Hospital (Harbin,
China) between January 2015 and January 2019. Inclusion criteria:
i) Newly diagnosed GBM; ii) patients older than 18 years; iii) GBM
cases with confirmed pathology; and iv) patients with GBM were
treated by surgery. Exclusion criteria: i) GBM cases with
unconfirmed pathology; ii) GBM cases with spinal involvement; ii)
GBM cases with incomplete data records; and iv) patients receiving
chemotherapy and radiotherapy prior to the surgery. All GBM tissues
were histopathologically confirmed by two senior pathologists. The
patient were divided into the high or low circFLNA and high or low
miR-199-3p expression group according to the median expression
level of clinical patients with GBM or patients from The Cancer
Genome Atlas (TCGA)-GBM database. Informed written consent was
obtained from all patients prior to participation. The study was
approved by The Institutional Review Board of Harbin Medical
University (approval no. 2019HMUIRB0171).
Gene expression profiles of circFLNA
expression
The edgeR Bioconductor software package (RStudio,
Inc. version.4.1) was used to identify differentially expressed
circRNAs in two Gene Expression Omnibus (GEO; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo) datasets,
GSE92322 (22) and GSE86202
(23). Overall survival data based
on the expression levels of miRNAs were obtained from patients with
GBM from TCGA database (http://cancergenome.nih.gov). The DEseq2 package
(version 3.11; http://bioconductor.org/packages/release/bioc/html/DESeq2.html)
was used to detect the differentially expressed circRNAs using the
following criteria as significant cut-off values: Log2
fold-change (FC)>2 and false-discovery rate (FDR)<0.01.
Clinicopathological data were obtained from 50 patients with GBM
who underwent surgical resection. Gene Ontology (GO) functional
term enrichment analysis was performed using The Database for
Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery version 6.8
(https://david.ncifcrf.gov). Circos plots
were constructed using http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn, an online platform
for data analysis and visualization.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR)
RT-qPCR was used to analyze the expression levels of
circFLNA and miR-199-3p. Briefly, total RNA was extracted from
clinical tissues or cell lines using TRIzol® reagent
(Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Total RNA was reverse
transcribed into cDNA using a PrimeScript™ RT kit (cat. no. RR014A;
Takara Biotechnology Co., Ltd.) according to the manufacturer's
protocol. qPCR for mRNA detection was subsequently performed using
a SYBR-Green PCR Master Mix (cat. no. DRR820A; Takara Biotechnology
Co., Ltd.). RNase-R was applied to detect the presence of circFLNA
and eliminate the influence of linear RNAs. The expression levels
of miRNAs were analyzed using a miScript PCR system (cat. no.
339306; Qiagen GmbH). The following primers were used for the qPCR:
circFLNA forward, 5′-CCAGCTGAGGCTCTACCGTGCC-3′ and reverse,
5′-GAGGCGTCAGCATCCCCAACAG-3′; miR-199-3p forward,
5′-ACACTCCAGCTGGGTCCCTGAGACCCTTTA-3′ and reverse,
5′-CTCAACTGGTGTCGTGGAGTCGGCAATTCA-3′; miR-296-5p forward,
5′-ATGGCGGACGAGGAGAAGCTGC-3′ and reverse,
5′-TCACTCAGTGCGGAGGATGATG-3′; miR-515-3p forward,
5-CGGGTTCTCCAAAAGAAAGCA-3′ and reverse, 5-CAGCCACAAAAGAGCACAAT-3′
MMP-2 forward, 5′-CAGGACATTGTCTTTGATGGCATCGC-3′ and reverse,
5′-TGAAGAAGTAGCTATGACCACCGCC-3′; MMP-9 forward,
5′-ATCCCCCACCTTTACCA-3′ and reverse, 5′-TCAGAACCGACCCTACAA-3′; U6
forward, 5′-CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA-3′ and reverse,
5′-AACGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT-3′; U1 forward, 5′-GGACTCATCAAGACTCATCA-3′;
and reverse, 5′-GTGAGGACGAAACTGCCTTG-3′; and GAPDH forward,
5′-AGGCTGTTGGGAAAGTTCTTC-3′ and reverse,
5′-ACTGTTGGAACTCGGAATGC-3′. The following thermocycling conditions
were used for qPCR: Initial denaturation at 94°C for 10 min;
followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 94°C for 5 sec, annealing
at 60°C for 30 sec and extension at 72°C for 45 sec. GAPDH and U6
were used as the endogenous controls. The relative gene expression
levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCq method (24) and normalized to the expression
levels of the endogenous controls, GAPDH (for mRNA) and U6 (for
miRNA).
Isolation of cytoplasmic and nuclear
RNA
Cellular cytoplasmic and nuclear RNA of glioblastoma
cells was extracted and purified using a PARIS kit (cat. no.
AM1921; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.), according to
the manufacturer's protocol.
Cell transfection
Small interfering RNA (siRNA/si)-circFLNA,
si-negative control (NC), miR-199-3p mimic, miR-199-3p inhibitor,
NC mimic, NC inhibitor, pcDNA3.1-circFLNA and pcDNA3.1 (empty
vector) were purchased from Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd. The
sequences of the constructs were as follows: si-circFLNA forward,
5′-AGCCCCTTCAGGGAGCTGGCA-3′ and reverse,
5′-CAACAGCCCCTTCAGGGAGCT-3′; pcDNA3.1-circFLNA forward,
5′-GUGCCAGCUCCCUGAAGGGTT-3′ and reverse,
5′-GCCAGCUCCCUGAAGGGGCTT-3′; si-NC forward,
5′-GGTAAGCAGTGGCTCCTCTAA-3′ and reverse,
5′-ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3′; miR-199-3p mimic forward,
5′-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3′ and reverse,
5′-AGGGCCCCCCCUCAAUCCUGU-3′; miR-199-3p inhibitor forward,
5′-ACAGGAUUGAGGGGGGGCCCU-3′; NC mimic forward,
5′-CAGUACUUUUGUGUAGUACAA-3′ and reverse,
5′-CAGUACUUUUGUGUAGUACAA-3′; and NC inhibitor forward,
5′-GGUAAGCAGUGGCUCCUCUAA-3′ and reverse,
5′-ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAAUU-3′. Cells were added in 6-well plates at
1×105 cells/well and were transfected with 20 µM
miR-199-3p mimic, miR-199-3p inhibitor, si-circFLNA,
pcDNA3.1-circFLNA or respective NCs using Lipofectamine®
2000 (cat. no. 11668030; Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Following
transfection at 37°C for 6 h, the culture medium was replaced and
cells were subsequently obtained at 24 h post-transfection for
further experiments.
Dual luciferase reporter assay
RNA22 (https://cm.jefferson.edu/rna22/Interactive) and
starBase (http://starbase.sysu.edu.cn) databases were used to
predict the potential target miRNAs of circFLNA. Among the
candidate miRNAs, the top three miRNAs, namely miR-199-3p,
miR-296-5p and miR-515-5p, were selected according to their
prediction score. Wild-type (WT) and mutant (MUT) putative
miR-199-3p binding sites of the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) in
circFLNA (Shanghai GenePharma Co., Ltd.), were cloned into
psiCHECK2 luciferase reporter vectors (Shanghai GenePharma Co.,
Ltd.). LN229 cells were seeded at the density of 3×105
cells/well into 6-well plates and co-transfected with 20 µl
psiCHECK2-circFLNA-WT or -MUT (108 TU/ml) and 20 µM
miR-199-3p mimic or NC mimic using Lipofectamine 2000. The medium
was removed with fresh medium at 4 h post-transfection. The
relative luciferase activity was detected at 48 h post-transfection
using a Dual Luciferase Reporter assay system (cat. no. E1910;
Promega Corporation) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Firefly luciferase activity was normalized to Renilla
luciferase activity.
Cell proliferation assay
Cell proliferation was measured using a Cell
Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) assay (cat. no. C0037; Beyotime Institute of
Biotechnology) according to the manufacturer's protocol. Briefly,
following transfection, GBM cells were seeded (1×104
cells/well) into 96-well plates and incubated for 24, 48 or 72 h.
The rescue experiment was performed at 72 h. Following the
incubation, 10 µl CCK-8 reagent was added to each well and
incubated for a further 4 h at 37°C. The absorbance was measured
using a microplate reader (Infinite F50; Tecan Group, Ltd.) at a
wavelength of 450 nm.
Transwell invasion assay
A total of 5×104 LN229 and A172 cells
were plated in serum-free DMEM into the upper chambers of Transwell
plates (Corning, Inc.), which were precoated with Matrigel (37°C
for 30 min), and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. The lower chambers
were filled with DMEM supplemented with 20% FBS before the
incubation. Following incubation, the invasive cells in the lower
chamber were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde for 15 min at room
temperature and stained with 1 mg/ml crystal violet for 20 min at
room temperature. The invasive cells were counted in five randomly
selected fields using a light microscope (Nikon Corporation;
magnification, ×100).
Western blotting
Total protein was extracted from LN229 and A172
cells using RIPA lysis buffer (cat. no. P0013B; Beyotime Institute
of Biotechnology) supplemented with complete Protease Inhibitor
Cocktail (cat. no. 04693124001; Roche Applied Science). Total
protein was quantified using a BCA protein assay kit (cat. no.
P0012; Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology). The absorbance was
measured using a microplate reader (Infinite F50; Tecan Group,
Ltd.) at a wavelength of 562 nm and 50 µg protein/lane was
separated via 10% SDS-PAGE. The separated proteins were
subsequently transferred onto PVDF membranes (cat. no. FFP24;
Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology) and blocked with 5% BSA (cat.
no. AR0004; Wuhan Boster Biological Technology, Ltd.) at 4°C for 1
h. The membranes were then incubated with the following primary
antibodies at 4°C overnight: Rabbit anti-MMP-2 (1:1,000; cat. no.
10373-2-AP; ProteinTech Group, Inc.), rabbit anti-MMP-9 (1:1,000;
cat. no. 10375-2-AP; ProteinTech Group, Inc.) and mouse anti-GAPDH
(1:1,000; cat. no. SC-47724; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Inc.).
Following primary antibody incubation, the membranes were incubated
with HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1 h (anti-mouse or
anti-rabbit; cat. nos. ab6721 and ab6728; 1:2,000; Abcam). Protein
bands were visualized using ECL reagent (cat. no. P0018S; Beyotime
Institute of Biotechnology) on a ChemiDoc™ MP Imaging system (cat.
no. 12003154; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). GAPDH was used as the
loading control.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 20.0
software (IBM Corp.) and data are presented as the mean ± SD.
Statistical differences between groups were determined using
one-way or two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc test or an
unpaired Student's t-test. The expression levels of circFLNA and
miR-199-3p in clinical GBM tissues were analyzed using a Wilcoxon
signed-rank test. Kaplan-Meier curves were used to determine the
overall survival and a log-rank test was conducted to analyze the
significant differences in survival using GraphPad Prism 5.0
software (GraphPad Software, Inc.). The association between
circFLNA expression levels and the clinicopathological features of
patients with GBM was determined using a χ2 test. The
correlation between the expression of circFLNA and miR-199-3p was
analyzed using Pearson's correlation analysis. Experiments were
independently performed in triplicate. P<0.05 was considered to
indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
circRNA expression profile
analysis
The present study investigated the expression levels
of the top 20 differentially expressed circRNAs in the GSE86202
dataset obtained from the GEO database; the cut-off values were
determined based on the Benjamini-Hochberg method
(log2FC>2 and FDR<0.01) (25) and the circRNAs were identified
according to the log2FC level (Fig. 1A). Among the differentially
expressed circRNAs, circFLNA expression levels were the highest in
GBM tissues, demonstrating significantly upregulated expression
levels compared with adjacent healthy brain tissues (Fig. 1A and B). To further determine
whether circFLNA served a role in the progression of GBM, the
expression levels of circRNAs were evaluated using microarray data
downloaded from two GEO datasets and GSE86202. As shown in Fig. 1C, six intersecting circRNAs (three
upregulated, circ-FLNA, circ-ERBB2, circ-ATM; and three
downregulated, circ-0058971, circ-NBEA, circ-0024602) were
identified and investigated according to their log2FC
level. As the expression levels of circFLNA were upregulated in
both GEO databases, circFLNA was further analyzed in subsequent
experiments. circFLNA was discovered to originate from exon 9 to 15
of the FLNA gene, with a spliced mature sequence length of 543 base
pairs (Fig. 1D). The differentially
expressed circRNAs identified between GBM and healthy tissues from
the GEO database are displayed in Fig.
1E. circFLNA was subsequently subjected to GO functional term
enrichment analysis to predict its function in GBM progression. The
results revealed that circFLNA was associated with the biological
process of glioblastoma, and ‘Cell invasion’, ‘Cell migration’ and
‘Focal adhesion’ were identified as the most enriched malignant
biological processes (Fig. 1F).
These results suggested that circFLNA may participate in GBM
development.
circFLNA expression levels are
upregulated in GBM tissues
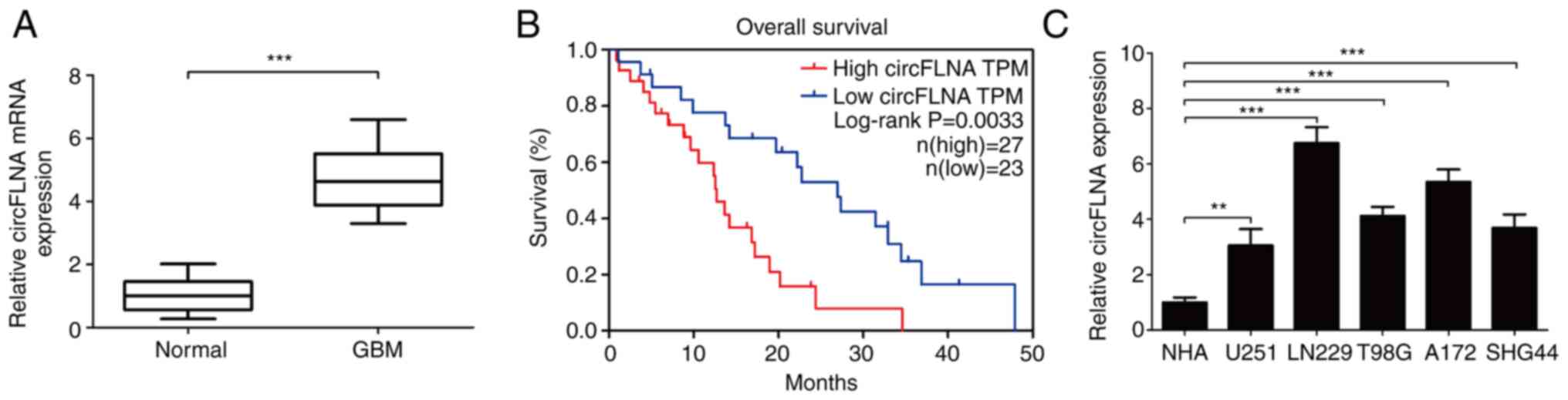
circFLNA expression levels were subsequently
analyzed in 50 clinical GBM cases using RT-qPCR. The results
demonstrated that circFLNA expression levels were significantly
upregulated in GBM tissues compared with healthy tissues (Fig. 2A). Furthermore, analysis of the
clinical data of the patients with GBM revealed that high
expression levels of circFLNA in GBM were associated with a worse
overall survival according to the median survival time of patients
with GBM (Fig. 2B). The expression
levels of circFLNA were also significantly associated with the
presence of necrosis in MRI scans (n=50; P=0.001; Table I). To determine the function of
circFLNA in GBM, the expression levels of circFLNA in GBM cell
lines (U251, T98G, LN229, SHG44 and A172) were compared with NHAs
(Fig. 2C). The expression levels of
circFLNA were upregulated in GBM cell lines compared with NHAs and
the expression level was highest in LN229 and A172 cells. Thus,
these cells were selected for use in subsequent experiment.
 | Table I.Association between circFLNA
expression levels and the clinical characteristics of patients with
glioblastoma (n=50). |
Table I.
Association between circFLNA
expression levels and the clinical characteristics of patients with
glioblastoma (n=50).
|
|
| circFLNA
expression |
|
|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|---|
| Variable | n | Low | High | P-value |
|---|
| Age, years |
|
|
| 0.845 |
|
<60 | 21 | 10 | 11 |
|
|
≥60 | 29 | 13 | 16 |
|
| Sex |
|
|
| 0.777 |
|
Male | 25 | 12 | 13 |
|
|
Female | 25 | 11 | 14 |
|
| Karnofsky
performance status scale |
|
|
| 0.260 |
|
<60 | 16 | 6 | 10 |
|
|
≥60 | 34 | 17 | 17 |
|
| Mean tumor
diameter, cm |
|
|
| 0.951 |
|
<5 | 15 | 7 | 8 |
|
| ≥5 | 35 | 16 | 19 |
|
| Presence of
necrosis on MRI |
|
|
| 0.001a |
|
Yes | 26 | 6 | 20 |
|
| No | 24 | 17 | 7 |
|
| Seizure |
|
|
| 0.586 |
|
Yes | 24 | 12 | 12 |
|
| No | 26 | 11 | 15 |
|
circFLNA knockdown inhibits GBM cell
proliferation and invasion
To investigate the effect of circFLNA on GBM
proliferation and invasion, circFLNA expression levels were knocked
down in LN229 and A172 cells. To identify the biological function
of circFLNA in the progression of glioblastoma, LN229 and A172
cells were transfected with si-circFLNA/si-NC or
pcDNA3.1-circFLNA/pcDNA3.1-NC, and the proliferative and invasive
abilities were determined. The transfection efficiencies were
confirmed via RT-qPCR, where circFLNA expression was significantly
decreased or increased compared with corresponding NC groups
(Fig. 3A). Furthermore, the results
of the CCK-8 assay discovered that circFLNA knockdown significantly
inhibited the proliferative ability of GBM cells following 48–72 h
of incubation compared with GBM cells transfected with si-NC
(Fig. 3B). In addition, the
findings of the Transwell invasion assay demonstrated that the
invasive ability of GBM cells was significantly inhibited by
si-circFLNA compared with si-NC (Fig.
3C). These results suggested that the proliferative and
invasive abilities of GBM cells may be suppressed by circFLNA
knockdown in vitro.
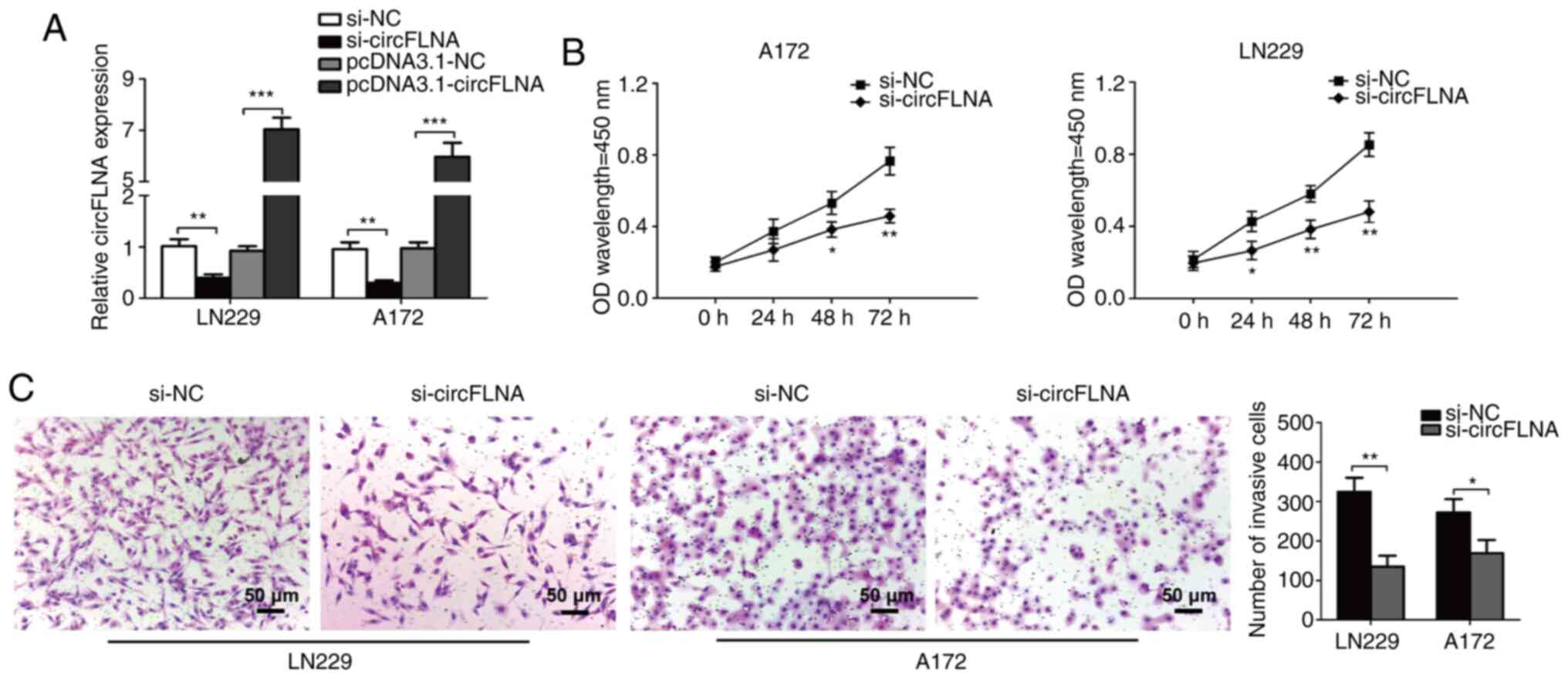 | Figure 3.circFLNA knockdown inhibits the
proliferative and invasive abilities of GBM cells in vitro.
(A) circFLNA expression levels were detected in LN229 and A172
cells following the transfection of si-circFLNA or
pcDNA3.1-circFLNA and respective NCs. (B) GBM cell proliferation
was analyzed using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay (si-circFLNA vs.
si-NC). *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs. si-NC. (C) Transwell invasion
assays were performed to determine the invasive ability of GBM
cells. Magnification, ×100; scale bar, 50-µm. *P<0.05,
**P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of
three independent experiments. circFLNA, circular RNA filamin A;
NC, negative control; GBM, glioblastoma; si, small interfering RNA;
OD, optical density. |
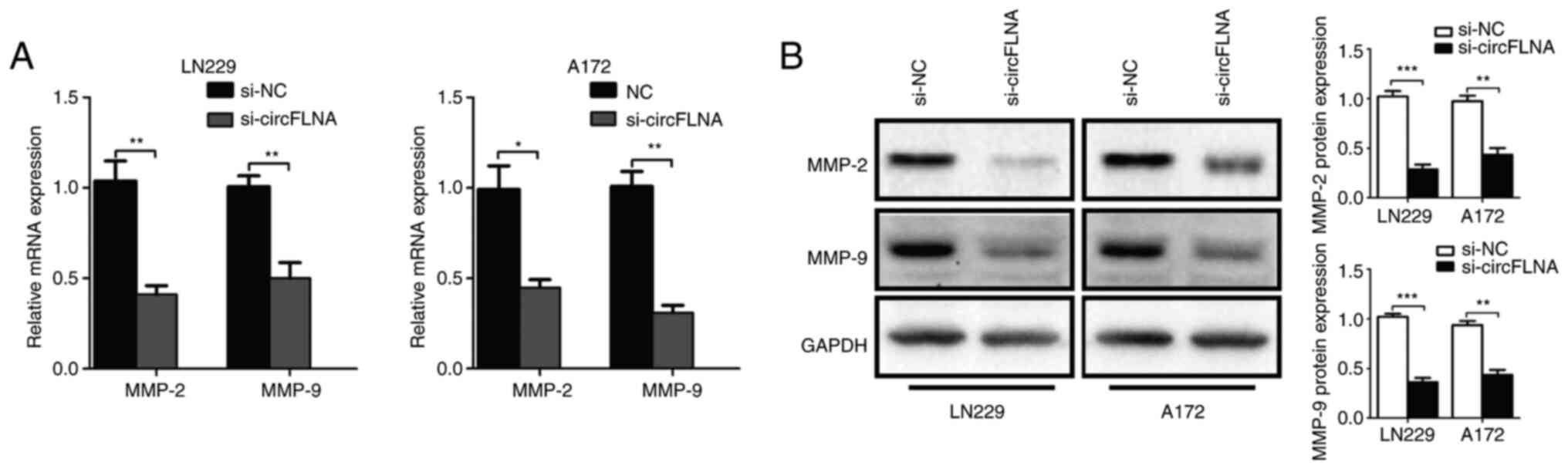
To further explore the effect of circFLNA on GBM
cell invasion, the mRNA and protein expression levels of tumor
invasion-related biomarkers, MMP-2 and MMP-9, in GBM cells were
analyzed using RT-qPCR and western blotting, respectively. The
results revealed that circFLNA knockdown significantly
downregulated the expression levels of MMP-2 and MMP-9 in GBM cells
compared with the si-NC group (Fig. 4A
and B). Based on these results, it was suggested that circFLNA
may regulate the invasive ability of GBM cells.
Association between circFLNA and
miR-199-3p expression levels
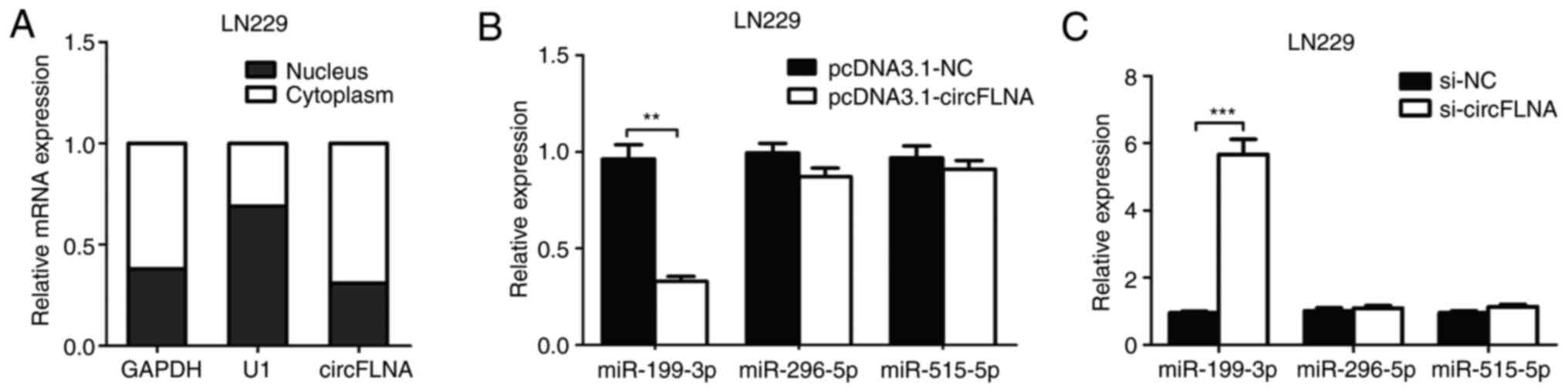
RT-qPCR analysis was used to determine the
subcellular localization of circFLNA in LN229 cells. As shown in
Fig. 5A, circFLNA was found to be
primarily localized in the cytoplasm of the GBM cells, indicating
that circFLNA may exert both transcriptional and
post-transcriptional regulatory effects in GBM. Using StarBase and
RNA22 database blast prediction, three potential miRNA targets of
circFLNA (miR-199-3p, miR-296-5p and miR-515-5p) were identified.
To investigate the regulatory relationship between circFLNA and the
miRNAs, RT-qPCR was performed to analyze miR-199-3p, miR-296-5p and
miR-515-5p expression levels in LN229 cells transfected with
pcDNA3.1-circFLNA plasmids, pcDNA3.1-NC plasmids, si-circFLNA or
si-NC. The data revealed that transfection with pcDNA3.1-circFLNA
significantly downregulated the expression levels of miR-199-3p
compared with the pcDNA3.1-NC plasmid, whereas circFLNA knockdown
significantly upregulated the expression levels of miR-199-3p
compared with si-NC-transfected cells; however, the expression
levels of miR-296-5p and miR-515-5p were unaffected by the
overexpression or knockdown of circFLNA (Fig. 5B and C).
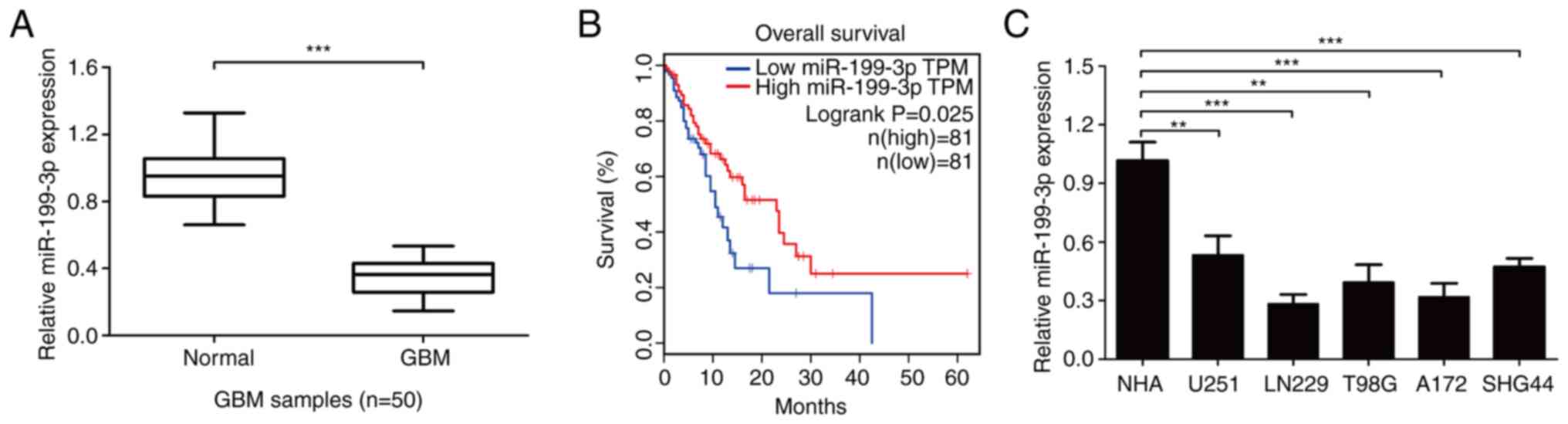
The expression levels of miR-199-3p in 50 GBM and
adjacent healthy brain tissues were subsequently determined. The
expression levels were significantly downregulated in GBM tissues
compared with adjacent healthy tissues (Fig. 6A). Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that
miR-199-3p expression was positively associated with the prognosis
of patients with GBM from TCGA-GBM database according to the median
overall survival time of patients with GBM (Fig. 6B). In addition, miR-199-3p
expression levels were significantly downregulated in GBM cell
lines compared with NHAs (Fig.
6C).
miR-199-3p targets the 3′-UTR of
circFLNA
miR-199-3p and circFLNA expression levels in tissues
from patients with GBM (n=50) were negatively correlated (n=50;
R=−0.6199; P=0.0006; Fig. 7A).
Using the RNA22 and StarBase databases, the complementary sequence
between circFLNA and miR-199-3p was identified (Fig. 7B). miR-199-3p mimic (miR-199-3p), NC
mimic or inhibitors were transfected into LN229 and A172 cells and
the transfection efficiencies were detected. The results
demonstrated that miR-199-3p was significantly increased or
decreased in transfected cells compared with NC groups (Fig. 7C). Subsequently, the circFLNA-WT or
circFLNA-MUT 3′-UTRs, which contained the predicted miR-199-3p
binding site, were cloned into psiCHECK2 luciferase reporter
vectors. The relative luciferase activity was significantly
decreased following the co-transfection of the circFLNA-WT vector
and miR-199-3p mimic compared with the circFLNA-WT and miR-NC,
whereas no significant differences were observed following the
co-transfection with the miR-199-3p mimic or miR-NC and
circFLNA-MUT vector in LN229 cells (Fig. 7D). These results indicated that
circFLNA may interact with miR-199-3p in GBM cells.
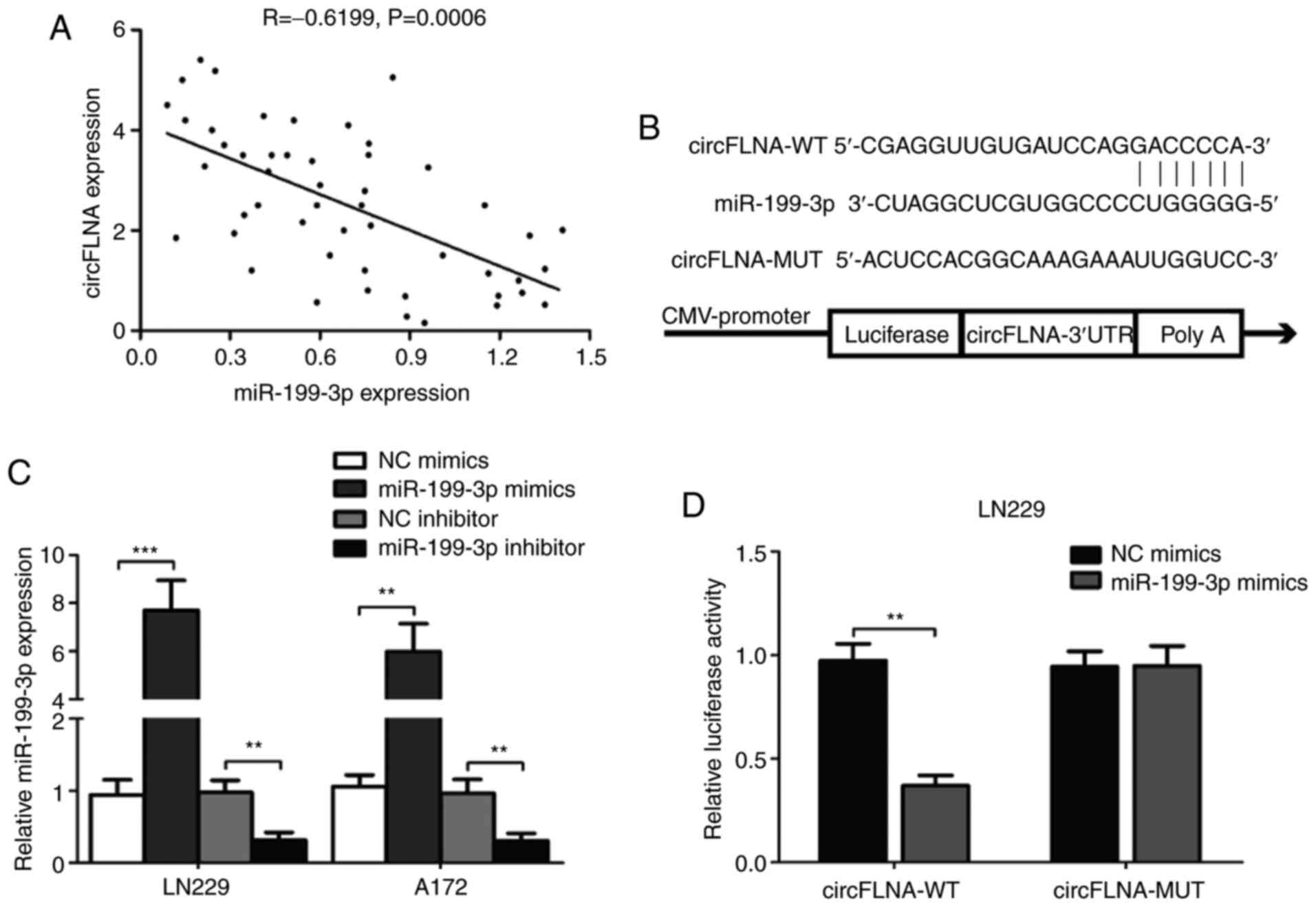 | Figure 7.miR-199-3p targets the 3′-UTR of
circFLNA. (A) Correlation between circFLNA and miR-199-3p
expression levels was determined. (B) Predicted binding site of
miR-199-3p on circFLNA is shown. (C) miR-199-3p expression levels
were analyzed in LN229 and A172 cells following transfection with
miR-199-3p mimic, NC mimic, miR-199-3p inhibitor or NC inhibitor
using reverse transcription-quantitative PCR. (D) Relative
luciferase activity was determined following co-transfection of
LN229 cells with miR-199-3p mimics or NC mimics and circFLNA-WT or
circFLNA-MUT. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three
independent experiments. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. circFLNA,
circular RNA filamin A; miR, microRNA; WT, wild-type; MUT, mutant;
NC, negative control; si, small interfering RNA; UTR, untranslated
region. |
miR-199-3p reverses the effect of
circFLNA in GBM cells
As aforementioned, miR-199-3p expression levels were
found to be negatively correlated with circFLNA expression levels
in GBM cells. LN229 cells were subsequently used to perform rescue
experiments. The expression levels of miR-199-3p were significantly
upregulated following transfection with si-circFLNA compared with
si-NC in GBM cells (Fig. 8A). The
co-transfection of miR-199-3p inhibitor+si-circFLNA significantly
downregulated the expression levels of miR-199-3p vs. the NC
inhibitor + si-circFLNA group (Fig.
8B). Conversely, the expression levels of miR-199-3p were
significantly upregulated following the co-transfection of cells
with si-circFLNA vs. the si-NC + miR-199-3p inhibitor group.
Transfection with miR-199-3p inhibitor also partially attenuated
the suppressive effect of circFLNA knockdown on the viability and
invasion of LN229 cells (Fig. 8C and
D). These data indicated that miR-199-3p may be a crucial
mediator of circFLNA-regulated tumor proliferation and invasion
processes.
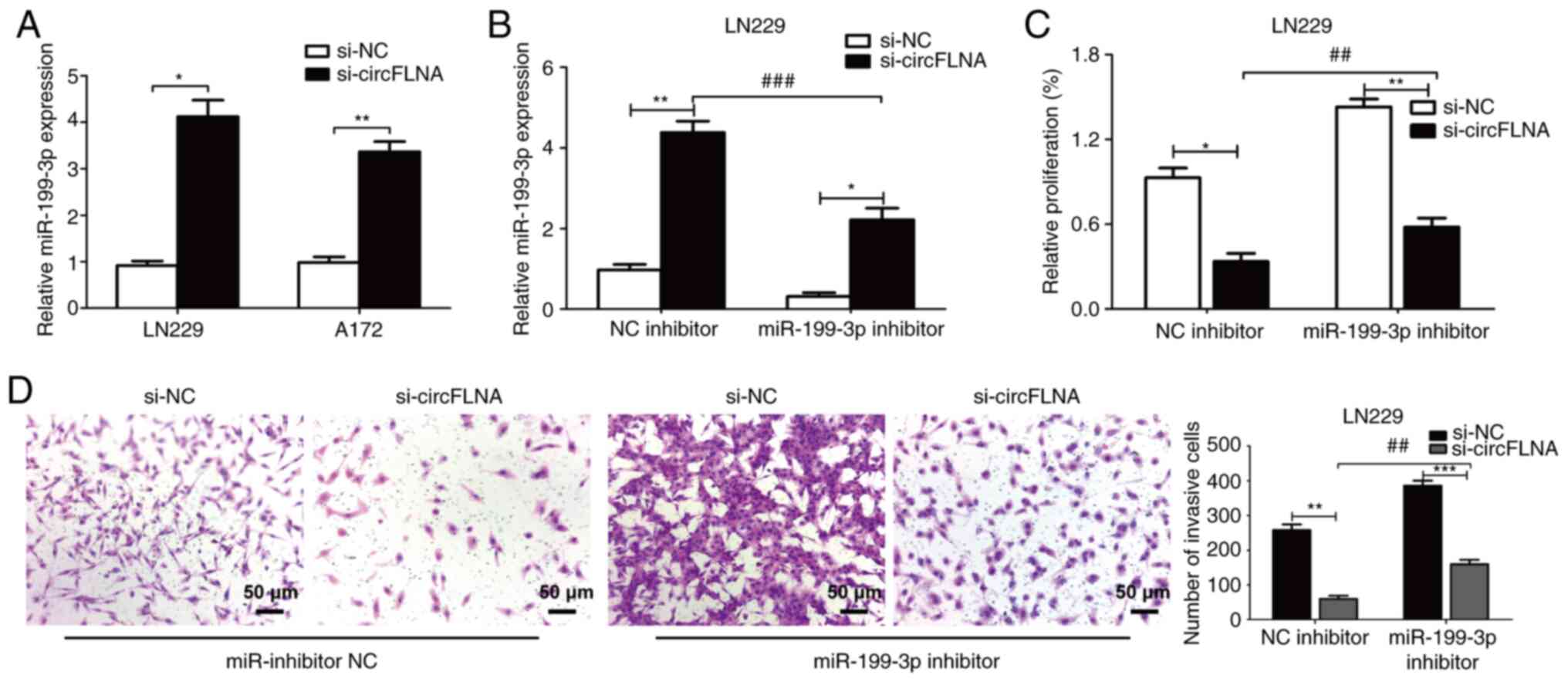 | Figure 8.miR-199-3p reverses the effect of
circFLNA on glioblastoma cells. (A) miR-199-3p expression levels
were upregulated following circFLNA knockdown in LN229 and A172
cells. (B) Expression levels of miR-199-3p in LN229 cells
co-transfected with combinations of si-circFLNA, si-NC, miR-199-3p
inhibitor and NC inhibitor. (C) Cell viability was detected using a
Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. (D) Invasive ability was analyzed using
a Transwell assay. Magnification, ×100; scale bar, 50 µm. Data are
presented as the mean ± SD of 3 independent experiments.
*P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001; ##P<0.01,
###P<0.001. miR, microRNA; circFLNA, circular RNA
filamin A; NC, negative control; si, small interfering RNA. |
Discussion
GBM is an aggressive and malignant type of primary
brain cancer with a >90% 5-year mortality (1,2).
Although significant progress has been achieved in research into
treatments for GBM, the therapeutic strategies available (resection
techniques, chemotherapy strategies and radiation therapy) for GBM
remain unsatisfactory (5).
Accumulating evidence has reported that circRNAs were associated
with the occurrence of numerous types of cancer and the aberrant
expression of circRNAs was found to be associated with promoting
the tumorigenesis of cancer (26–29).
however, its underlying mechanism of action requires further
investigation.
The mechanism via which circFLNA acts as an oncogene
in GBM remains unknown. In the present study, circFLNA expression
was significantly increased in GBM tissues compared with adjacent
normal tissues. In addition, miR-199-3p expression was decreased in
GBM tissues, and miR-199-3p expression was negatively correlated
with circFLNA expression. Using bioinformatics analysis, miR-199-3p
was predicted as the potential target of circFLNA. Notably,
circFLNA knockdown suppressed the proliferative and invasive
abilities of GBM cells, whereas co-transfection with miR-199-3p
inhibitor partially reversed these trends. Therefore, circFLNA
knockdown may suppress the proliferation and invasion of GBM,
indicating a potential therapeutic strategy for GBM.
The competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) theory is
considered to be an important mechanism for circRNAs, in which
circRNAs have been demonstrated to act as sponges to regulate the
expression and function of miRNAs (11,30). A
previous study reported that circRNA_001783 expression levels were
downregulated in breast cancer, which regulated cancer cell
proliferation via miR-200c-3p (31). circRNA activin A receptor type 2A
was also demonstrated to function as a ceRNA for miR-626, which
suppressed cell proliferation and invasion in bladder cancer
(32). In gastric cancer, circRNA
Ran GTPase activating protein 1 regulated invasion and metastasis
by upregulating VEGFA expression levels via interacting with
miR-877-3p (33). It was
hypothesized that circFLNA may act as a ceRNA towards miR-199-3p.
Accumulating evidence has revealed that the aberrant expression of
miRNAs serves important roles in the occurrence and development of
numerous types of cancer (34–38).
For example, Zhang et al (39) reported that miR-199-3p directly
regulated the expression levels of snail family transcriptional
repressor 1 in hepatoma cells. Koshizuka et al (40) demonstrated that miR-199-3p
expression levels were downregulated in head and neck cancer, which
suppressed malignant biological behaviors. The present study
detected that circFLNA knockdown may suppress the proliferation and
invasion of GBM, these results highlighted the potential role of
the circFLNA/miR-199-3p axis in GBM development.
In conclusion, the findings of the present study
suggested that circFLNA may serve as an oncogenic circRNA by acting
as a ceRNA and sponging miR-199-3p in GBM. In a future study, the
patient-derived xenograft model will be used to follow the effects
of circRNA on tumorigenesis, which is a more clinically predictive
model of human glioblastoma. The results identified a novel role of
circFLNA in GBM and elucidated the underlying mechanisms of
circFLNA in the progression of GBM. Therefore, circFLNA may be
regarded as a novel approach for the treatment of GBM.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Scientific
Research Project of Health Commission of Heilongjiang Province
(grant no. 2019-368).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
YS, GM and HX designed the study, performed the
experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. XW, HX and
HW performed the in vitro experiments. FQ, YS and CL
analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. CL, YZ and GM
designed and supervised the study, and edited the manuscript. YS,
YZ and CL confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors
read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Written informed consent was obtained from all
patients and the study protocol was approved by the Ethics
Committee of Harbin Medical University (Harbin, China; approval no.
2019HMUIRB0171). All procedures were performed in accordance with
national (D.L.n.26, March 4th, 2014) and international laws and
policies (directive 2010/63/EU) (41).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bernstock JD, Mooney JH, Ilyas A, Chagoya
G, Estevez-Ordonez D, Ibrahim A and Nakano I: Molecular and
cellular intratumoral heterogeneity in primary glioblastoma:
Clinical and translational implications. J Neurosurg. 23:1–9.
2019.
|
|
4
|
Aldape K, Zadeh G, Mansouri S,
Reifenberger G and von Deimling A: Glioblastoma: Pathology,
molecular mechanisms and markers. Acta Neuropathol. 129:829–848.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hara A, Kanayama T, Noguchi K, Niwa A,
Miyai M, Kawaguchi M, Ishida K, Hatano Y, Niwa M and Tomita H:
Treatment strategies based on histological targets against invasive
and resistant glioblastoma. J Oncol. 2019:29647832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Garton ALA, Kinslow CJ, Rae AI, Mehta A,
Pannullo SC, Magge RS, Ramakrishna R, McKhann GM, Sisti MB, Bruce
JN, et al: Extent of resection, molecular signature, and survival
in 1p19q-codeleted gliomas. J Neurosurg. 134:1357–1367. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang X, Zhang W, Mao XG, Cao WD, Zhen HN
and Hu SJ: Malignant intracranial high grade glioma and current
treatment strategy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 19:101–108. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qu S, Yang X, Li X, Wang J, Gao Y, Shang
R, Sun W, Dou K and Li H: Circular RNA: A new star of noncoding
RNAs. Cancer Lett. 365:141–148. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhong Y, Du Y, Yang X, Mo Y, Fan C, Xiong
F, Ren D, Ye X, Li C, Wang Y, et al: Circular RNAs function as
ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol
Cancer. 17:792018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin Y, Long J, He Q, Li Y, Liao Y, He P
and Zhu W: Emerging roles of circRNA in formation and progression
of cancer. J Cancer. 10:5015–5021. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hao Z, Hu S, Liu Z, Song W, Zhao Y and Li
M: Circular RNAs: Functions and prospects in glioma. J Mol
Neurosci. 67:72–81. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cheng J, Meng J, Zhu L and Peng Y:
Exosomal noncoding RNAs in Glioma: Biological functions and
potential clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 19:662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hingorani DV, Lippert CN, Crisp JL,
Savariar EN, Hasselmann JPC, Kuo C, Nguyen QT, Tsien RY, Whitney MA
and Ellies LG: Impact of MMP-2 and MMP-9 enzyme activity on wound
healing, tumor growth and RACPP cleavage. PLoS One.
13:e01984642018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Qu J, Yang J, Chen M, Wei R and Tian J:
CircFLNA Acts as a sponge of miR-646 to facilitate the
proliferation, metastasis, glycolysis, and apoptosis inhibition of
gastric cancer by targeting PFKFB2. Cancer Manag Res. 12:8093–8103.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang N, Gao L, Ren W, Li S, Zhang D, Song
X, Zhao C and Zhi K: Fucoidan affects oral squamous cell carcinoma
cell functions in vitro by regulating FLNA derived circular RNA.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1462:65–78. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu C, Shi X, Wang AY, Tao Y, Wang Z, Huang
C, Qiao Y, Hu H and Liu L: RNA-Seq profiling of circular RNAs in
human laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Mol Cancer. 17:862018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang JX, Liu Y, Jia XJ, Liu SX, Dong JH,
Ren XM, Xu O, Zhang HZ, Duan HJ and Shan CG: Upregulation of
circFLNA contributes to laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma migration
by circFLNA-miR-486-3p-FLNA axis. Cancer Cell Int. 19:1962019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen Z, Li J, Tian L, Zhou C, Gao Y, Zhou
F, Shi S, Feng X, Sun N, Yao R, et al: MiRNA expression profile
reveals a prognostic signature for esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 350:34–42. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Ye B, Wang P, Yao F, Zhang C and
Yu G: Overview of microRNA-199a regulation in cancer. Cancer Manag
Res. 11:10327–10335. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chi GN, Yang FW, Xu DH and Liu WM:
Silencing hsa_circ_PVT1 (circPVT1) suppresses the growth and
metastasis of glioblastoma multiforme cells by up-regulation of
miR-199a-5p. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 48:188–196. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhu J, Ye J, Zhang L, Xia L, Hu H, Jiang
H, Wan Z, Sheng F, Ma Y, Li W, et al: Differential expression of
circular RNAs in glioblastoma multiforme and its correlation with
prognosis. Transl Oncol. 10:271–279. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yuan Y, Jiaoming L, Xiang W, Yanhui L, Shu
J, Maling G and Qing M: Analyzing the interactions of mRNAs,
miRNAs, lncRNAs and circRNAs to predict competing endogenous RNA
networks in glioblastoma. J Neurooncol. 137:493–502. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate-A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc. 1:289–300. 1995.
|
|
26
|
Zhang HD, Jiang LH, Sun DW, Hou JC and Ji
ZL: CircRNA: A novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer.
25:1–7. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kristensen LS, Hansen TB, Venø MT and
Kjems J: Circular RNAs in cancer: Opportunities and challenges in
the field. Oncogene. 37:555–565. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Vo JN, Cieslik M, Zhang Y, Shukla S, Xiao
L, Zhang Y, Wu YM, Dhanasekaran SM, Engelke CG, Cao X, et al: The
landscape of circular RNA in cancer. Cell. 176:869–881. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhao W, Dong M, Pan J, Wang Y, Zhou J, Ma
J and Liu S: Circular RNAs: A novel target among non-coding RNAs
with potential roles in malignant tumors (Review). Mol Med Rep.
20:3463–3474. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ng WL, Mohd Mohidin TB and Shukla K:
Functional role of circular RNAs in cancer development and
progression. RNA Biol. 15:995–1005. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Z, Zhou Y, Liang G, Ling Y, Tan W, Tan
L, Andrews R, Zhong W, Zhang X, Song E and Gong C: Circular RNA
hsa_circ_001783 regulates breast cancer progression via sponging
miR-200c-3p. Cell Death Dis. 10:552019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dong W, Bi J, Liu H, Yan D, He Q, Zhou Q,
Wang Q, Xie R, Su Y, Yang M, et al: Circular RNA ACVR2A suppresses
bladder cancer cells proliferation and metastasis through
miR-626/EYA4 axis. Mol Cancer. 18:952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lu J, Wang YH, Yoon C, Huang XY, Xu Y, Xie
JW, Wang JB, Lin JX, Chen QY, Cao LL, et al: Circular RNA
circ-RanGAP1 regulates VEGFA expression by targeting miR-877-3p to
facilitate gastric cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Lett.
471:38–48. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Oliveto S, Mancino M, Manfrini N and Biffo
S: Role of microRNAs in translation regulation and cancer. World J
Biol Chem. 8:45–56. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wu M, Wang G, Tian W, Deng Y and Xu Y:
miRNA-based therapeutics for lung cancer. Curr Pharm Des.
23:5989–5996. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shin VY and Chu KM: miRNA as potential
biomarkers and therapeutic targets for gastric cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 20:10432–10439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fridrichova I and Zmetakova I: MicroRNAs
contribute to breast cancer invasiveness. Cells. 8:13612019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Deng JH, Deng Q, Kuo CH, Delaney SW and
Ying SY: miRNA targets of prostate cancer. Methods Mol Biol.
936:357–369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhang HY, Li CH, Wang XC, Luo YQ, Cao XD
and Chen JJ: miR-199 inhibits EMT and invasion of hepatoma cells
through inhibition of Snail expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:7884–7891. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Koshizuka K, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Arai
T, Okato A, Kurozumi A, Kato M, Katada K, Okamoto Y and Seki N:
Regulation of ITGA3 by the anti-tumor miR-199 family inhibits
cancer cell migration and invasion in head and neck cancer. Cancer
Sci. 108:1681–1692. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A,
Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl
U, et al: The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for
reporting animal research. PLOS Biol. 18:e30004102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|