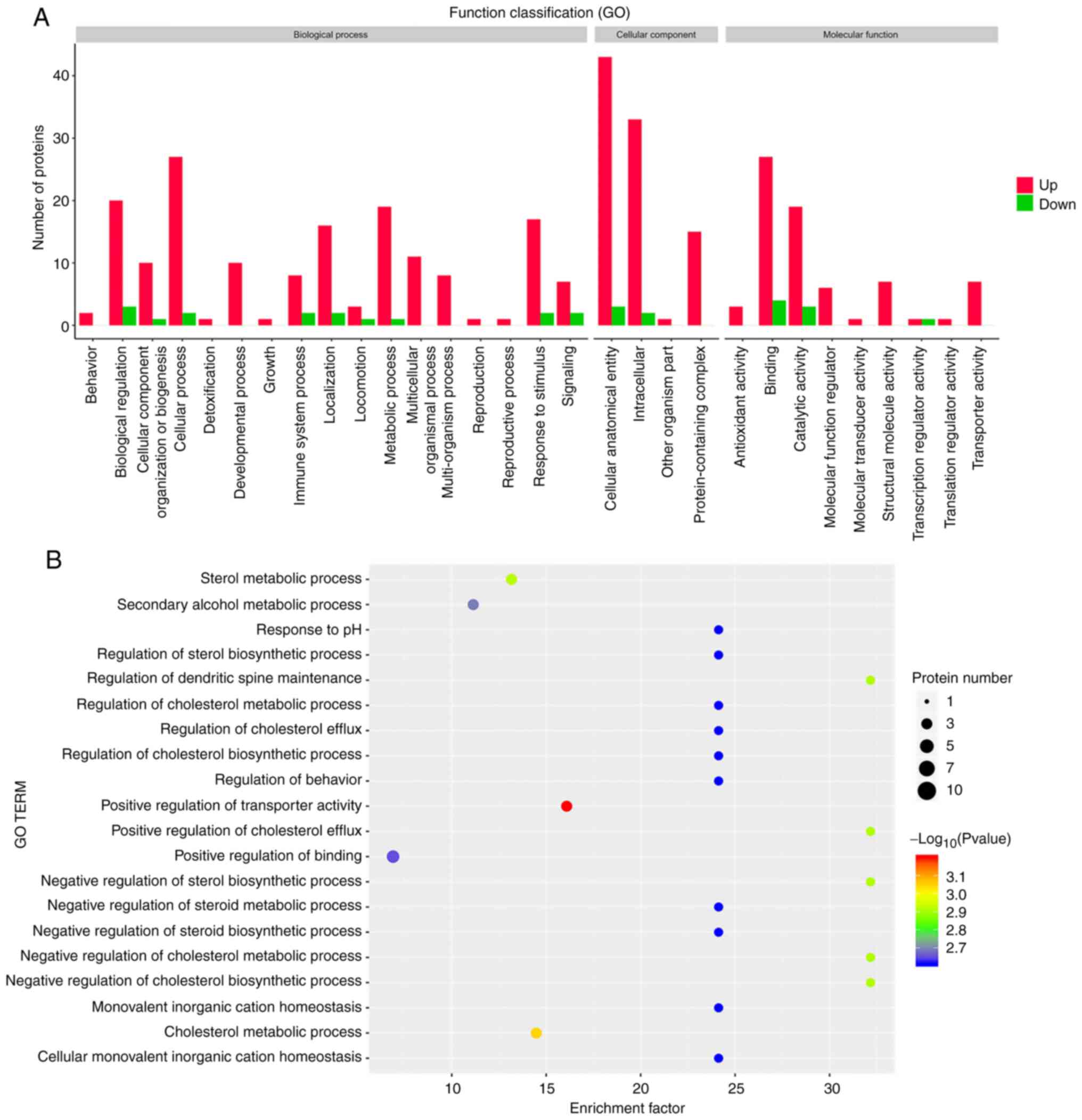
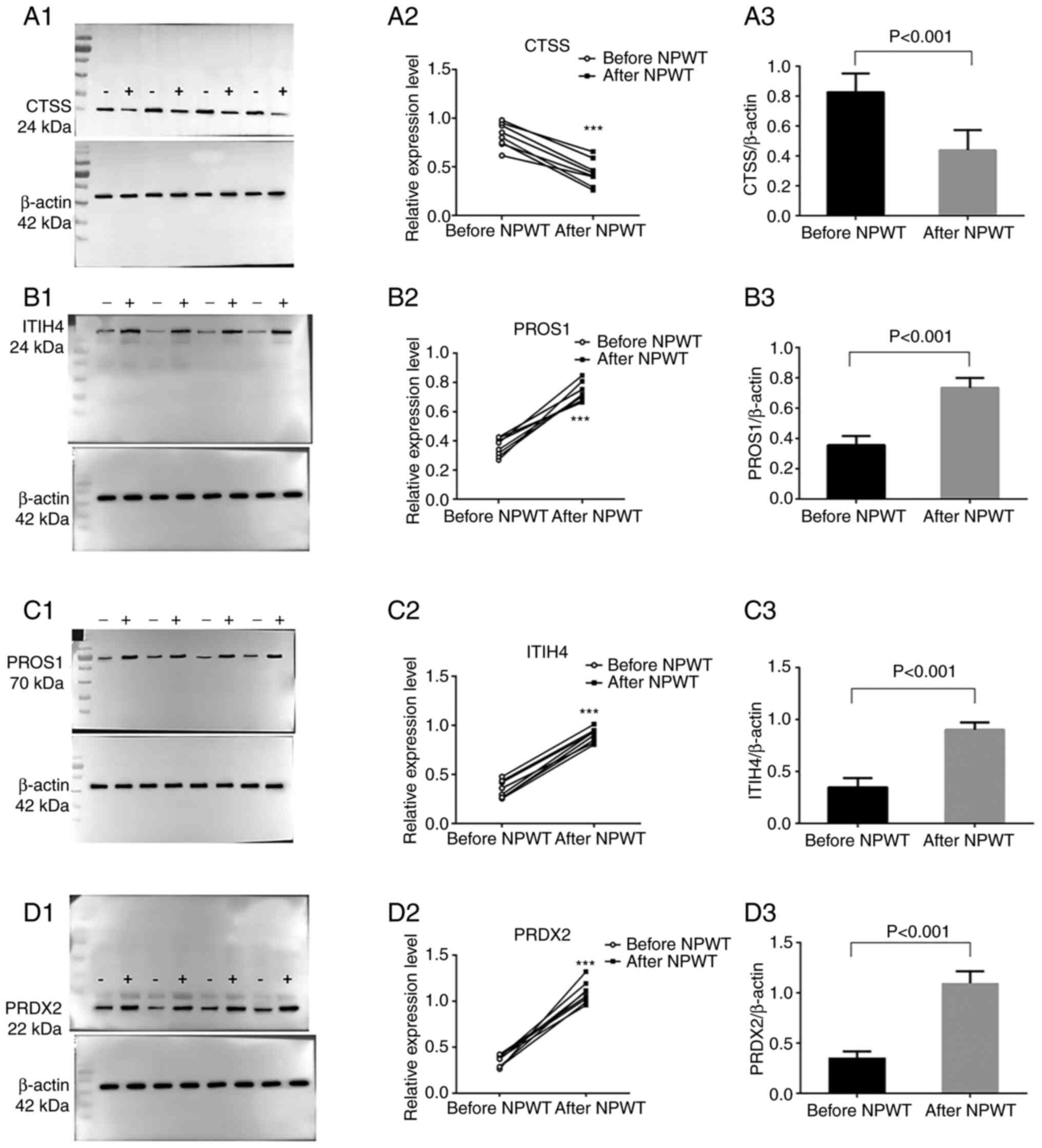
|
1
|
Zhang P, Lu J, Jing Y, Tang S, Zhu D and
Bi Y: Global epidemiology of diabetic foot ulceration: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Ann Med. 49:106–116. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhong A, Chang M, Yu T, Gau R, Riley DJ,
Chen Y and Chen PL: Aberrant DNA damage response and DNA repair
pathway in high glucose conditions. J Can Res Updates. 7:64–74.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Uccioli L, Izzo V, Meloni M, Vainieri E,
Ruotolo V and Giurato L: Non-healing foot ulcers in diabetic
patients: General and local interfering conditions and management
options with advanced wound dressings. J Wound Care. 24
(Suppl):S35–S42. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Noor S, Khan RU and Ahmad J: Understanding
diabetic foot infection and its management. Diabetes Metab Syndr.
11:149–156. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Isaac AL and Armstrong DG: Negative
pressure wound therapy and other new therapies for diabetic foot
ulceration: The current state of play. Med Clin North Am.
97:899–909. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Borys S, Hohendorff J, Frankfurter C,
Kiec-Wilk B and Malecki MT: Negative pressure wound therapy use in
diabetic foot syndrome-from mechanisms of action to clinical
practice. Eur J Clin Invest. 49:e130672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Schintler MV: Negative pressure therapy:
Theory and practice. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 28 (Suppl 1):S72–S77.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Savage N: Proteomics: High-protein
research. Nature. 527:S6–S7. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang N, Zhu F, Chen L and Chen K:
Proteomics, metabolomics and metagenomics for type 2 diabetes and
its complications. Life Sci. 212:194–202. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oyibo SO, Jude EB, Tarawneh I, Nguyen HC,
Harkless LB and Boulton AJ: A comparison of two diabetic foot ulcer
classification systems: The wagner and the university of Texas
wound classification systems. Diabetes Care. 24:84–88. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Mu S, Hua Q, Jia Y, Chen MW, Tang Y, Deng
D, He Y, Zuo C, Dai F and Hu H: Effect of negative-pressure wound
therapy on the circulating number of peripheral endothelial
progenitor cells in diabetic patients with mild to moderate degrees
of ischaemic foot ulcer. Vascular. 27:381–389. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gene Ontology Consortium, . The gene
ontology resource: Enriching a GOld mine. Nucleic Acids Res.
49:D325–D334. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Z, Dumville JC, Hinchliffe RJ, Cullum
N, Game F, Stubbs N, Sweeting M and Peinemann F: Negative pressure
wound therapy for treating foot wounds in people with diabetes
mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 10:D103182018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Memmert S, Nokhbehsaim M, Damanaki A,
Nogueira AV, Papadopoulou AK, Piperi C, Basdra EK, Rath-Deschner B,
Götz W, Cirelli JA, et al: Role of cathepsin S in periodontal wound
healing-an in vitro study on human PDL cells. BMC Oral Health.
18:602018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Han YH, Jin MH, Jin YH, Yu NN, Liu J,
Zhang YQ, Cui YD, Wang AG, Lee DS, Kim SU, et al: Deletion of
peroxiredoxin II inhibits the growth of mouse primary mesenchymal
stem cells through induction of the G0/G1 cell-cycle arrest and
activation of AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin signaling. In Vivo. 34:133–141.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Che MM, Abdul MN, Ibrahim K, Mohd MN, Wan
NW, Harun R and Jamal R: Silencing of PROS1 induces apoptosis and
inhibits migration and invasion of glioblastoma multiforme cells.
Int J Oncol. 49:2359–2366. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hennies HC: All is balanced:
Inter-α-trypsin inhibitors as unseen extracellular matrix proteins
in epidermal morphology and differentiation. Exp Dermatol.
24:661–662. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Maione AG, Smith A, Kashpur O, Yanez V,
Knight E, Mooney DJ, Veves A, Tomic-Canic M and Garlick JA: Altered
ECM deposition by diabetic foot ulcer-derived fibroblasts
implicates fibronectin in chronic wound repair. Wound Repair Regen.
24:630–643. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jozic I, Abujamra BA, Elliott MH,
Wikramanayake TC, Marjanovic J, Stone RC, Head CR, Pastar I,
Kirsner RS, Andreopoulos FM, et al: Glucocorticoid-mediated
induction of caveolin-1 disrupts cytoskeletal organization,
inhibits cell migration and re-epithelialization of non-healing
wounds. Commun Biol. 4:7572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yazdanpanah L, Shahbazian H, Nazari I,
Hesam S, Ahmadi F, Cheraghian B, Arti HR and Mohammadianinejad SE:
Risk factors associated with diabetic foot ulcer-free survival in
patients with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Syndr. 12:1039–1043. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gouin JP and Kiecolt-Glaser JK: The impact
of psychological stress on wound healing: Methods and mechanisms.
Immunol Allergy Clin North Am. 31:81–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ruiz-Llorente L, Contreras-Jurado C,
Martinez-Fernandez M, Paramio JM and Aranda A: Thyroid hormone
receptors regulate the expression of microRNAs with key roles in
skin homeostasis. Thyroid. 28:921–932. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Contreras-Jurado C, Lorz C, Garcia-Serrano
L, Paramio JM and Aranda A: Thyroid hormone signaling controls hair
follicle stem cell function. Mol Biol Cell. 26:1263–1272. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Zheng N, Shi YN, Yuan J and Li L:
Thyroid hormone induced angiogenesis through the integrin
αvβ3/protein kinase D/histone deacetylase 5 signaling pathway. J
Mol Endocrinol. 52:245–254. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
McGill NK, Vyas J, Shimauchi T, Tokura Y
and Piguet V: HTLV-1-associated infective dermatitis: Updates on
the pathogenesis. Exp Dermatol. 21:815–821. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shimauchi T and Piguet V: DC-T cell
virological synapses and the skin: Novel perspectives in
dermatology. Exp Dermatol. 24:1–4. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Capewell P, Cren-Travaille C, Marchesi F,
Johnston P, Clucas C, Benson RA, Gorman TA, Calvo-Alvarez E,
Crouzols A, Jouvion G, et al: The skin is a significant but
overlooked anatomical reservoir for vector-borne African
trypanosomes. Elife. 5:e177162016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alfituri OA, Ajibola O, Brewer JM, Garside
P, Benson RA, Peel T, Morrison LJ and Mabbott NA: Effects of
host-derived chemokines on the motility and viability of
Trypanosoma brucei. Parasite Immunol. 41:e126092019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Strauch ED, Bass BL, Rao JN, Vann JA and
Wang JY: NF-kappaB regulates intestinal epithelial cell and bile
salt-induced migration after injury. Ann Surg. 237:494–501. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Shen K, Xu L, Chen D, Tang W and Huang Y:
Human cytomegalovirus-encoded miR-UL112 contributes to
HCMV-mediated vascular diseases by inducing vascular endothelial
cell dysfunction. Virus Genes. 54:172–181. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Yu T, Gao M, Yang P, Liu D, Wang D, Song
F, Zhang X and Liu Y: Insulin promotes macrophage phenotype
transition through PI3K/Akt and PPAR-γ signaling during diabetic
wound healing. J Cell Physiol. 234:4217–4231. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhan R, Yang S, He W, Wang F, Tan J, Zhou
J, Yang S, Yao Z, Wu J and Luo G: Nitric oxide enhances
keratinocyte cell migration by regulating Rho GTPase via cGMP-PKG
signalling. PLoS One. 10:e1215512015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ikonen E and Jansen M: Cellular sterol
trafficking and metabolism: Spotlight on structure. Curr Opin Cell
Biol. 20:371–377. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Enrich C, Rentero C, Hierro A and Grewal
T: Role of cholesterol in SNARE-mediated trafficking on
intracellular membranes. J Cell Sci. 128:1071–1081. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Xie Y, Hou W, Song X, Yu Y, Huang J, Sun
X, Kang R and Tang D: Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death
Differ. 23:369–379. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Boulter E, Estrach S, Errante A, Pons C,
Cailleteau L, Tissot F, Meneguzzi G and Féral CC: CD98hc (SLC3A2)
regulation of skin homeostasis wanes with age. J Exp Med.
210:173–190. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Baltzis D, Eleftheriadou I and Veves A:
Pathogenesis and treatment of impaired wound healing in diabetes
mellitus: New insights. Adv Ther. 31:817–836. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rekha PD, Rao SS, Sahana TG and Prabhu A:
Diabetic wound management. Br J Community Nurs. 23 (Suppl
9):S16–S22. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Catrina SB and Zheng X: Disturbed hypoxic
responses as a pathogenic mechanism of diabetic foot ulcers.
Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 32 (Suppl 1):S179–S185. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kimmel HM, Grant A and Ditata J: The
presence of oxygen in wound healing. Wounds. 28:264–270.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Widmer CC, Pereira CP, Gehrig P, Vallelian
F, Schoedon G, Buehler PW and Schaer DJ: Hemoglobin can attenuate
hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress by acting as an
antioxidative peroxidase. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:185–198. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Moreno-Acosta P, Carrillo S, Gamboa O,
Romero-Rojas A, Acosta J, Molano M, Balart-Serra J, Cotes M,
Rancoule C and Magné N: Novel predictive biomarkers for cervical
cancer prognosis. Mol Clin Oncol. 5:792–796. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li X, Wu Z, Wang Y, Mei Q, Fu X and Han W:
Characterization of adult α- and β-globin elevated by hydrogen
peroxide in cervical cancer cells that play a cytoprotective role
against oxidative insults. PLoS One. 8:e543422013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lu W, Fu Z, Wang H, Feng J, Wei J and Guo
J: Peroxiredoxin 2 is upregulated in colorectal cancer and
contributes to colorectal cancer cells' survival by protecting
cells from oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biochem. 387:261–270. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Low FM, Hampton MB, Peskin AV and
Winterbourn CC: Peroxiredoxin 2 functions as a noncatalytic
scavenger of low-level hydrogen peroxide in the erythrocyte. Blood.
109:2611–2617. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ryu J, Park SG, Park BC, Choe M, Lee KS
and Cho JW: Proteomic analysis of psoriatic skin tissue for
identification of differentially expressed proteins: Up-regulation
of GSTP1, SFN and PRDX2 in psoriatic skin. Int J Mol Med.
28:785–792. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ranieri D, Avitabile D, Shiota M, Yokomizo
A, Naito S, Bizzarri M and Torrisi MR: Nuclear redox imbalance
affects circadian oscillation in HaCaT keratinocytes. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 65:113–124. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Dunnill C, Patton T, Brennan J, Barrett J,
Dryden M, Cooke J, Leaper D and Georgopoulos NT: Reactive oxygen
species (ROS) and wound healing: The functional role of ROS and
emerging ROS-modulating technologies for augmentation of the
healing process. Int Wound J. 14:89–96. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yin X, Liu P, Liu YY, Liu MY, Fan WL, Liu
BY and Zhao JH: LRRFIP1 expression triggers platelet agglutination
by enhancing alphaIIbbeta3 expression. Exp Ther Med. 18:269–277.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Goodall AH, Burns P, Salles I, Macaulay
IC, Jones CI, Ardissino D, de Bono B, Bray SL, Deckmyn H, Dudbridge
F, et al: Transcription profiling in human platelets reveals
LRRFIP1 as a novel protein regulating platelet function. Blood.
116:4646–4656. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Sanchez-Pernaute O, Esparza-Gordillo J,
Largo R, Calvo E, Alvarez-Soria MA, Marcos ME, Herrero-Beaumont G
and de Córdoba SR: Expression of the peptide C4b-binding protein
beta in the arthritic joint. Ann Rheum Dis. 65:1279–1285. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Koedam JA, Meijers JC, Sixma JJ and Bouma
BN: Inactivation of human factor VIII by activated protein C.
Cofactor activity of protein S and protective effect of von
Willebrand factor. J Clin Invest. 82:1236–1243. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Broekmans AW, Bertina RM, Reinalda-Poot J,
Engesser L, Muller HP, Leeuw JA, Michiels JJ, Brommer EJ and Briët
E: Hereditary protein S deficiency and venous thrombo-embolism. A
study in three Dutch families. Thromb Haemost. 53:273–277. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Burstyn-Cohen T, Heeb MJ and Lemke G: Lack
of protein S in mice causes embryonic lethal coagulopathy and
vascular dysgenesis. J Clin Invest. 119:2942–2953. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhong F, Chen H, Xie Y, Azeloglu EU, Wei
C, Zhang W, Li Z, Chuang PY, Jim B, Li H, et al: Protein S protects
against podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
29:1397–1410. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Valacchi G, Zanardi I, Sticozzi C, Bocci V
and Travagli V: Emerging topics in cutaneous wound repair. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1259:136–144. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Reinke JM and Sorg H: Wound repair and
regeneration. Eur Surg Res. 49:35–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lopez-Lopez N, Gonzalez-Curiel I,
Trevino-Santa CM, Rivas-Santiago B, Trujillo-Paez V, Enciso-Moreno
JA and Serrano CJ: Expression and vitamin D-mediated regulation of
matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of
metalloproteinases (TIMPs) in healthy skin and in diabetic foot
ulcers. Arch Dermatol Res. 306:809–821. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Gary SR and Woo KY: The biology of chronic
foot ulcers in persons with diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 24
(Suppl 1):S25–S30. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Wilkinson RD, Young A, Burden RE, Williams
R and Scott CJ: A bioavailable cathepsin S nitrile inhibitor
abrogates tumor development. Mol Cancer. 15:292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Yao X, Cheng F, Yu W, Rao T, Li W, Zhao S,
Zhou X and Ning J: Cathepsin S regulates renal fibrosis in mouse
models of mild and severe hydronephrosis. Mol Med Rep. 20:141–150.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Klinngam W, Fu R, Janga SR, Edman MC and
Hamm-Alvarez SF: Cathepsin S alters the expression of
pro-inflammatory cytokines and MMP-9, partially through
protease-activated receptor-2, in human corneal epithelial cells.
Int J Mol Sci. 19:35302018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Taleb S, Cancello R, Clement K and Lacasa
D: Cathepsin S promotes human preadipocyte differentiation:
Possible involvement of fibronectin degradation. Endocrinology.
147:4950–4959. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Lenselink EA: Role of fibronectin in
normal wound healing. Int Wound J. 12:313–316. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhuo L and Kimata K: Structure and
function of inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor heavy chains. Connect
Tissue Res. 49:311–320. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhuo L, Hascall VC and Kimata K:
Inter-alpha-trypsin inhibitor, a covalent
protein-glycosaminoglycan-protein complex. J Biol Chem.
279:38079–38082. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Soury E, Olivier E, Daveau M, Hiron M,
Claeyssens S, Risler JL and Salier JP: The H4P heavy chain of
inter-alpha-inhibitor family largely differs in the structure and
synthesis of its prolin-rich region from rat to human. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 243:522–530. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pihl R, Jensen RK, Poulsen EC, Jensen L,
Hansen AG, Thøgersen IB, Dobó J, Gál P, Andersen GR, Enghild JJ, et
al: ITIH4 acts as a protease inhibitor by a novel inhibitory
mechanism. Sci Adv. 7:eaba73812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Taleb S, Cancello R, Poitou C, Rouault C,
Sellam P, Lev P, Bouillot JL, Coussieu C, Basdevant A, Guerre-Millo
M, et al: Weight loss reduces adipose tissue cathepsin S and its
circulating levels in morbidly obese women. J Clin Endocrinol
Metab. 91:1042–1047. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
El Eter E, Al Masri A, Habib S, Al Zamil
H, Al Hersi A, Al Hussein F and Al Omran M: Novel links among
peroxiredoxins, endothelial dysfunction, and severity of
atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetic patients with peripheral
atherosclerotic disease. Cell Stress Chaperones. 19:173–181. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wen W, Sun H, Yang Y, Jia Y, Fang F, Qin
Y, Zhang M and Wei Y: Usefulness of cathepsin S to predict risk for
obstructive sleep apnea among patients with type 2 diabetes. Dis
Markers. 2020:88191342020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Ma Y, Li R, Wang J, Jiang W, Yuan X, Cui J
and Wang C: ITIH4, as an inflammation biomarker, mainly increases
in bacterial bloodstream infection. Cytokine. 138:1553772021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|