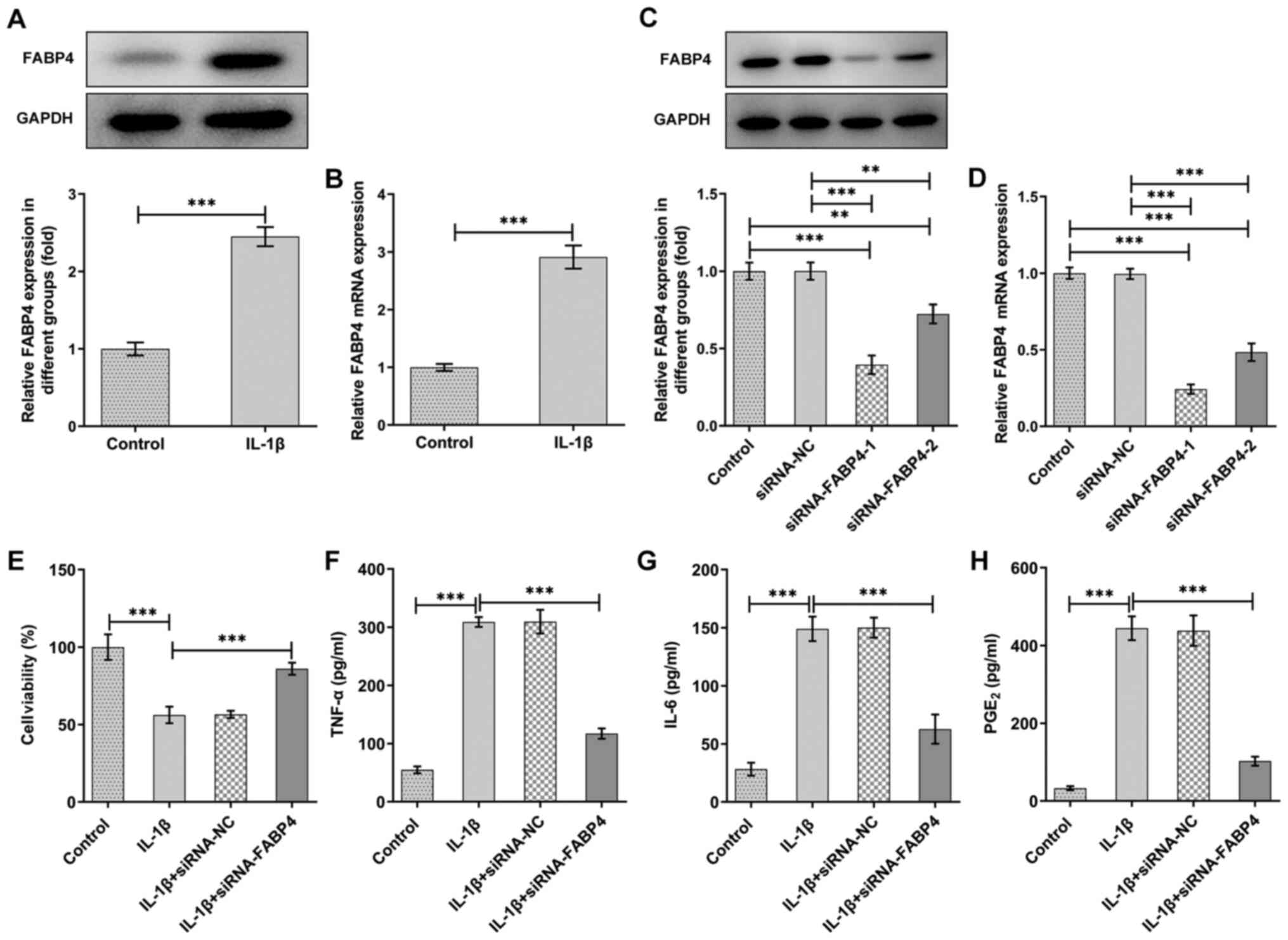
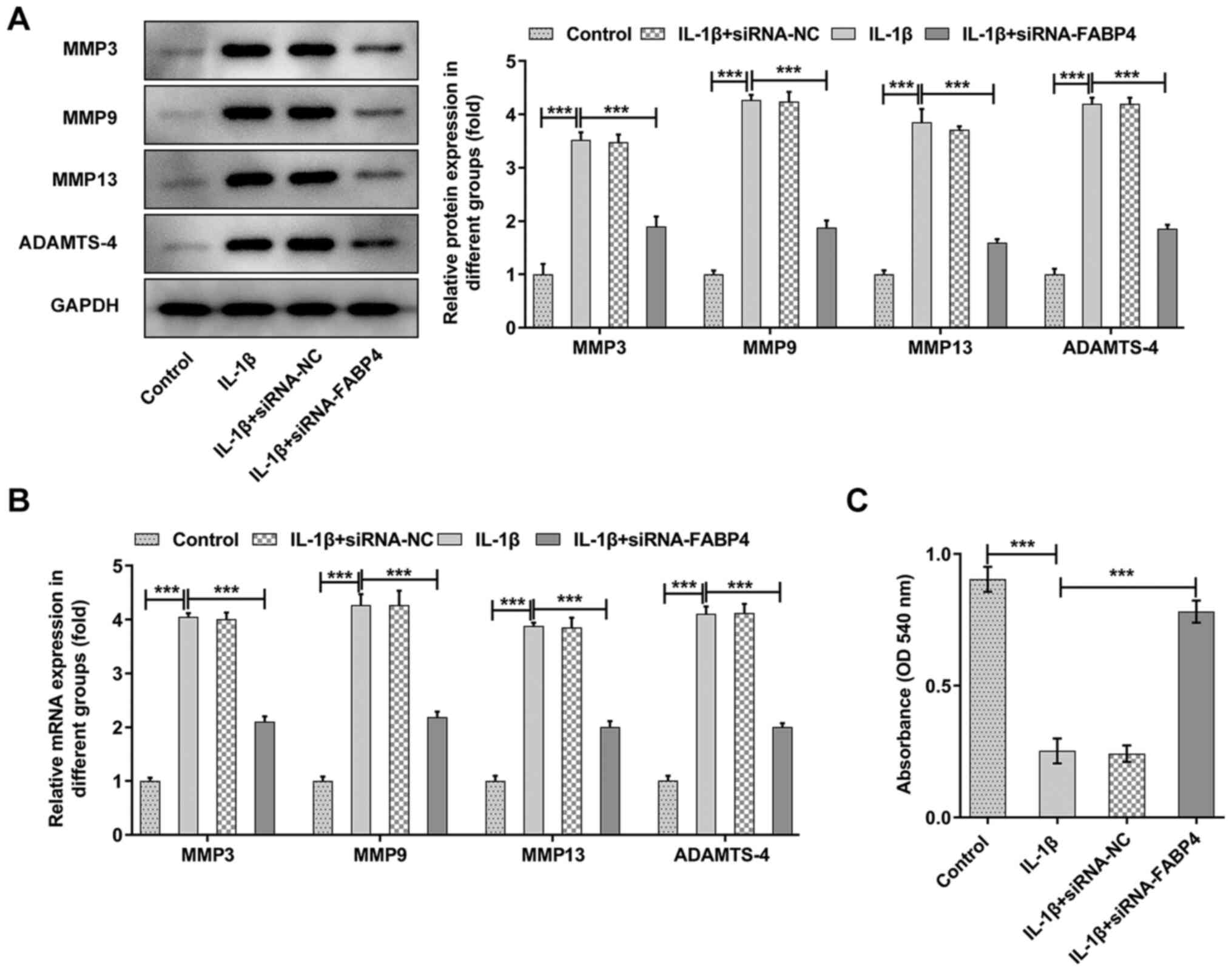
|
1
|
McAlindon TE and Bannuru RR: OARSI
recommendations for the management of hip and knee osteoarthritis:
The semantics of differences and changes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
18:473–475. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bian Q, Wang YJ, Liu SF and Li YP:
Osteoarthritis: Genetic factors, animal models, mechanisms, and
therapies. Front Biosci (Elite Ed). 4:74–100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Moon KH: New view on the initial
development site and radiographic classification system of
osteoarthritis of the knee based on radiographic analysis. Int J
Biomed Sci. 8:233–243. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Troeberg L and Nagase H: Proteases
involved in cartilage matrix degradation in osteoarthritis. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1824:133–145. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boehme KA and Rolauffs B: Onset and
Progression of Human Osteoarthritis-Can Growth Factors,
Inflammatory Cytokines, or Differential miRNA Expression
Concomitantly Induce Proliferation, ECM Degradation, and
Inflammation in Articular Cartilage? Int J Mol Sci. 19:22822018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Ding L, Yang J, Liu L and Dong L:
Intestinal fatty acid-binding protein, a biomarker of intestinal
barrier dysfunction, increases with the progression of type 2
diabetes. PeerJ. 9:e108002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sung CH, Hsu BG, Tasi JP, Wang CH and Kuo
CH: Positive Associations between Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding
Protein Level and Central Arterial Stiffness in Peritoneal Dialysis
Patients. Int J Hypertens. 2021:88491152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lei C, Li M, Zhang M, Wang S, Tian J, Wen
J and Li Y: Cloning, molecular characterization, and nutritional
regulation of fatty acid-binding protein family genes in gold
pompanos (Trachinotus ovatus). Comp Biochem Physiol B
Biochem Mol Biol. 246-247:1104632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hotamisligil GS and Bernlohr DA: Metabolic
functions of FABPs - mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat
Rev Endocrinol. 11:592–605. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yao F, Jiang DD, Guo WH, Guo LS, Gao MM,
Bai Y, Wang X and Zhang LS: FABP4 inhibitor attenuates inflammation
and endoplasmic reticulum stress of islet in leptin receptor
knockout rats. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:12808–12820.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ge XN, Bastan I, Dileepan M, Greenberg Y,
Ha SG, Steen KA, Bernlohr DA, Rao SP and Sriramarao P: FABP4
regulates eosinophil recruitment and activation in allergic airway
inflammation. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 315:L227–L240.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gong Y, Yu Z, Gao Y, Deng L, Wang M, Chen
Y, Li J and Cheng B: FABP4 inhibitors suppress inflammation and
oxidative stress in murine and cell models of acute lung injury.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 496:1115–1121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Furuhashi M: Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4
in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. J Atheroscler Thromb.
26:216–232. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang C, Li T, Chiu KY, Wen C, Xu A and
Yan CH: FABP4 as a biomarker for knee osteoarthritis. Biomarkers
Med. 12:107–118. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gu HY, Yang M, Guo J, Zhang C, Lin LL, Liu
Y and Wei RX: Identification of the Biomarkers and Pathological
Process of Osteoarthritis: Weighted Gene Co-expression Network
Analysis. Front Physiol. 10:2752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schadler P, Lohberger B, Thauerer B,
Faschingbauer M, Kullich W, Stradner MH, Husic R, Leithner A and
Steinecker-Frohnwieser B: Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 (FABP4) Is
Associated with Cartilage Thickness in End-Stage Knee
Osteoarthritis. Cartilage. 194760352110115202021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang TL, Yang CH, Yanai G, Liao JY, Sumi
S and Yang KC: Synergistic effect of l-ascorbic acid and hyaluronic
acid on the expressions of matrix metalloproteinase-3 and −9 in
human chondrocytes. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.
106:1809–1817. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Brown KA, Davidson EJ, Johnson AL, Wulster
KB and Ortved K: Inflammatory cytokines in horses with cervical
articular process joint osteoarthritis on standing cone beam
computed tomography. Equine Vet J. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hwang HS, Park IY, Kim DW, Choi SY, Jung
YO and Kim HA: PEP-1-FK506BP12 inhibits matrix metalloproteinase
expression in human articular chondrocytes and in a mouse
carrageenan-induced arthritis model. BMB Rep. 48:407–412. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhi LQ, Yao SX, Liu HL, Li M, Duan N and
Ma JB: Hydroxytyrosol inhibits the inflammatory response of
osteoarthritis chondrocytes via SIRT6-mediated autophagy. Mol Med
Rep. 17:4035–4042. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang Y, Huang X and Yuan Y:
Anti-inflammatory capacity of Apremilast in human chondrocytes is
dependent on SOX-9. Inflamm Res. 69:1123–1132. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oliviero F, Ramonda R, Scanu A, Galozzi P,
Favero M and Punzi L: Levels of inflammatory cytokines and
metalloproteinases are increased in knee synovial fluid of patients
with concomitant erosive hand osteoarthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol.
38:8002020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Deng Z, Zhang R, Li M, Wang S, Fu G, Jin
J, Wang Z, Ma Y and Zheng Q: STAT3/IL-6 dependent induction of
inflammatory response in osteoblast and osteoclast formation in
nanoscale wear particle-induced aseptic prosthesis loosening.
Biomater Sci. 9:1291–1300. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang TTCC, Chen CL, Lin WC, Lin YS, Tseng
PC, Hsieh CY, Chen YH, Huang WC, Tsai CC, Wang CY, et al: Glycogen
synthase kinase-3β inactivation is an intracellular marker and
regulator for endotoxemic neutrophilia. J Mol Med (Berl).
91:207–217. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Solovykh EA, Karaoglanova TB, Kushlinskii
NE and Yanushevich OO: Matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory
cytokines in the oral fluid of patients with chronic generalized
periodontitis various structural materials restoration of teeth and
dentition. Klin Lab Diagn. 55-58:18–21. 2013.(In English, Russian).
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hwang HS and Kim HA: Chondrocyte Apoptosis
in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
16:26035–26054. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ding W, Du D and Chen S: LIPUS promotes
synthesis and secretion of extracellular matrix and reduces cell
apoptosis in human osteoarthritis through upregulation of SOX9
expression. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 13:810–817. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gepstein A, Arbel G, Blumenfeld I, Peled M
and Livne E: Association of metalloproteinases, tissue inhibitors
of matrix metalloproteinases, and proteoglycans with development,
aging, and osteoarthritis processes in mouse temporomandibular
joint. Histochem Cell Biol. 120:23–32. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wen Y, Qin J, Deng Y, Wang H, Magdalou J
and Chen L: The critical role of UDP-galactose-4-epimerase in
osteoarthritis: Modulating proteoglycans synthesis of the articular
chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 452:906–911. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Slovacek H, Khanna R, Poredos P, Jezovnik
M, Hoppensteadt D, Fareed J and Hopkinson W: Interrelationship of
Osteopontin, MMP-9 and ADAMTS4 in Patients With Osteoarthritis
Undergoing Total Joint Arthroplasty. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost.
26:10760296209648642020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ojanen SP, Finnilä MAJ, Reunamo AE,
Ronkainen AP, Mikkonen S, Herzog W, Saarakkala S and Korhonen RK:
Site-specific glycosaminoglycan content is better maintained in the
pericellular matrix than the extracellular matrix in early
post-traumatic osteoarthritis. PLoS One. 13:e01962032018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mehana EE, Khafaga AF and El-Blehi SS: The
role of matrix metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis pathogenesis:
An updated review. Life Sci. 234:1167862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Garin-Shkolnik T, Rudich A, Hotamisligil
GS and Rubinstein M: FABP4 attenuates PPARγ and adipogenesis and is
inversely correlated with PPARγ in adipose tissues. Diabetes.
63:900–911. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang JS, Xiao WW, Zhong YS, Li XD, Du SX,
Xie P, Zheng GZ and Han JM: Galectin-3 deficiency protects
lipopolysaccharide-induced chondrocytes injury via regulation of
TLR4 and PPAR-γ-mediated NF-κB signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem.
120:10195–10204. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kobayashi T, Notoya K, Naito T, Unno S,
Nakamura A, Martel-Pelletier J and Pelletier JP: Pioglitazone, a
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma agonist, reduces
the progression of experimental osteoarthritis in guinea pigs.
Arthritis Rheum. 52:479–487. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rigoglou S and Papavassiliou AG: The NF-κB
signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
45:2580–2584. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jia T, Cai M, Ma X, Li M, Qiao J and Chen
T: Oridonin inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammation in human
osteoarthritis chondrocytes by activating PPAR-γ. Int
Immunopharmacol. 69:382–388. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qu Y, Zhou L and Wang C: Mangiferin
Inhibits IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Response by Activating PPAR-γ
in Human Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Inflammation. 40:52–57. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|