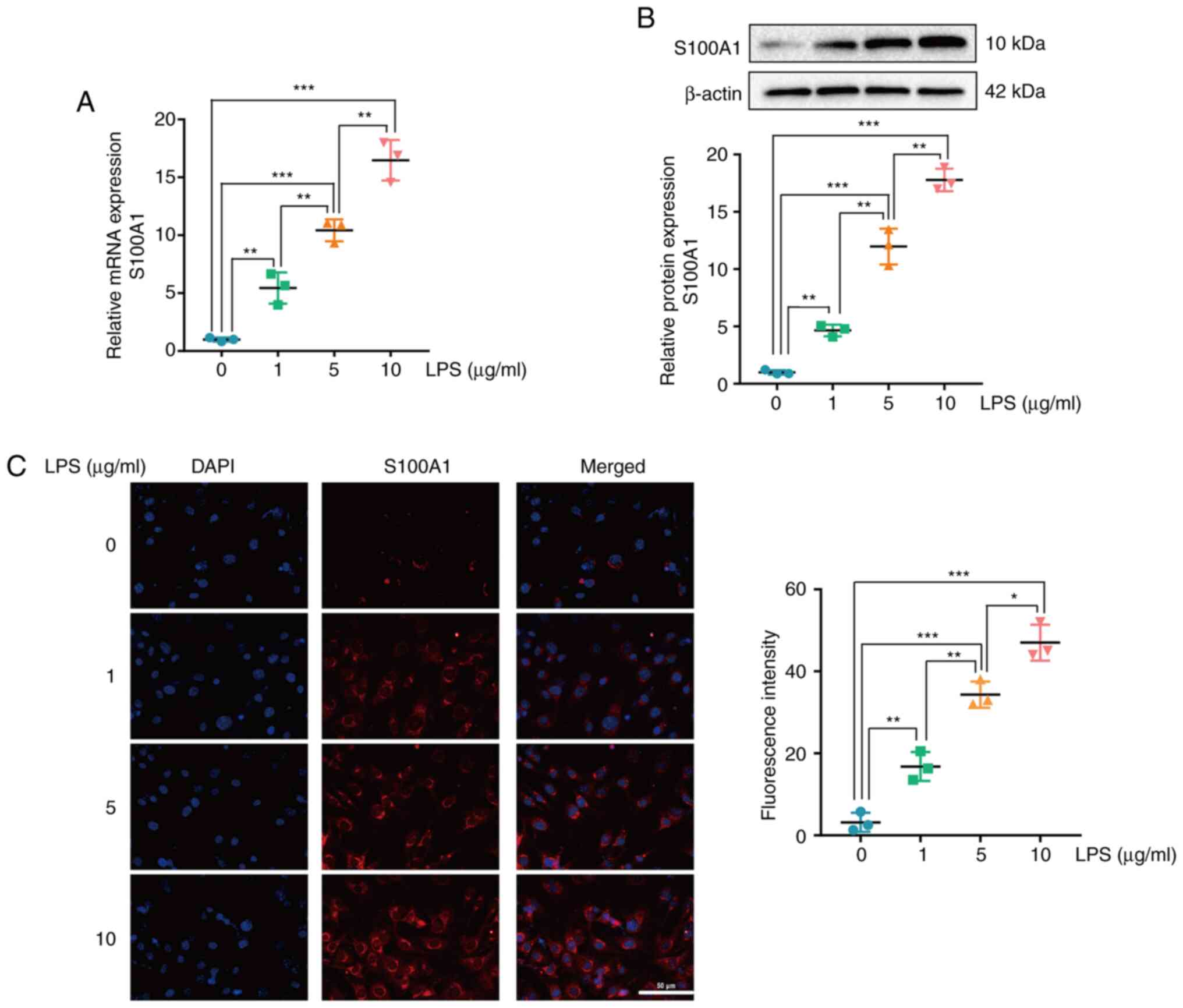
|
1
|
Ahuja CS, Wilson JR, Nori S, Kotter MRN,
Druschel C, Curt A and Fehlings MG: Traumatic spinal cord injury.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:170182017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alizadeh A, Dyck SM and Karimi-Abdolrezaee
S: Traumatic spinal cord injury: An overview of pathophysiology,
models and acute injury mechanisms. Front Neurol. 10:2822019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) 2016 facts and
figures at a glance. J Spinal Cord Med. 39:493–494. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ahuja CS, Nori S, Tetreault L, Wilson J,
Kwon B, Harrop J, Choi D and Fehlings MG: Traumatic spinal cord
injury-repair and regeneration. Neurosurgery. 80 (Suppl 1):S9–S22.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sabapathy V, Tharion G and Kumar S: Cell
therapy augments functional recovery subsequent to spinal cord
injury under experimental conditions. Stem Cells Int.
2015:1321722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Raspa A, Pugliese R, Maleki M and Gelain
F: Recent therapeutic approaches for spinal cord injury. Biotechnol
Bioeng. 113:253–259. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fan B, Wei Z, Yao X, Shi G, Cheng X, Zhou
X, Zhou H, Ning G, Kong X and Feng S: Microenvironment imbalance of
spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant. 27:853–866. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hutson TH and Di Giovanni S: The
translational landscape in spinal cord injury: Focus on
neuroplasticity and regeneration. Nat Rev Neurol. 15:732–745. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bareyre FM and Schwab ME: Inflammation,
degeneration and regeneration in the injured spinal cord: Insights
from DNA microarrays. Trends Neurosci. 26:555–563. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Filippin LI, Vercelino R, Marroni NP and
Xavier RM: Redox signalling and the inflammatory response in
rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 152:415–422. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hazzaa SM, Abdou AG, Ibraheim EO, Salem
EA, Hassan MHA and Abdel-Razek HAD: Effect of L-carnitine and
atorvastatin on a rat model of ischemia-reperfusion injury of
spinal cord. J Immunoassay Immunochemistry. 42:596–619. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Donnelly DJ and Popovich PG: Inflammation
and its role in neuroprotection, axonal regeneration and functional
recovery after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 209:378–388. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yu J, Lu Y, Li Y, Xiao L, Xing Y, Li Y and
Wu L: Role of S100A1 in hypoxia-induced inflammatory response in
cardiomyocytes via TLR4/ROS/NF-κB pathway. J Pharm Pharmacol.
67:1240–1250. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bashir M, Frigiola A, Iskander I, Said HM,
Aboulgar H, Frulio R, Bruschettini P, Michetti F, Florio P,
Pinzauti S, et al: Urinary S100A1B and S100BB to predict hypoxic
ischemic encephalopathy at term. Front Biosci (Elite Ed).
1:560–567. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rohde D, Schön C, Boerries M, Didrihsone
I, Ritterhoff J, Kubatzky KF, Völkers M, Herzog N, Mähler M,
Tsoporis JN, et al: S100A1 is released from ischemic cardiomyocytes
and signals myocardial damage via Toll-like receptor 4. EMBO Mol
Med. 6:778–794. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Haw TJ, Starkey MR, Pavlidis S, Fricker M,
Arthurs AL, Nair PM, Liu G, Hanish I, Kim RY, Foster PS, et al:
Toll-like receptor 2 and 4 have opposing roles in the pathogenesis
of cigarette smoke-induced chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 314:L298–L317. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Afanador L, Roltsch EA, Holcomb L,
Campbell KS, Keeling DA, Zhang Y and Zimmer DB: The Ca2+
sensor S100A1 modulates neuroinflammation, histopathology and Akt
activity in the PSAPP Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Cell
Calcium. 56:68–80. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zimmer DB, Chaplin J, Baldwin A and Rast
M: S100-mediated signal transduction in the nervous system and
neurological diseases. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-Grand). 51:201–214.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Park JH, Seo YH, Jang JH, Jeong CH, Lee S
and Park B: Asiatic acid attenuates methamphetamine-induced
neuroinflammation and neurotoxicity through blocking of
NF-kB/STAT3/ERK and mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway. J
Neuroinflammation. 14:2402017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jing Y, Yu Y, Bai F, Wang L, Yang D, Zhang
C, Qin C, Yang M, Zhang D, Zhu Y, et al: Effect of fecal microbiota
transplantation on neurological restoration in a spinal cord injury
mouse model: Involvement of brain-gut axis. Microbiome. 9:592021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Howard B, Nevalainen T and Perretta G: The
COST manual of laboratory animal care and use:Refinement.
Reduction, and Research. Crc Press; 2010
|
|
22
|
Sun F, Zhang H, Huang T, Shi J, Wei T and
Wang Y: S100A9 blockade improves the functional recovery after
spinal cord injury via mediating neutrophil infiltration. Ex Ther
Med. 23:2912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li Y, Liu P and Wei F: Long non-coding RNA
MBI-52 inhibits the development of liver fibrosis by regulating the
microRNA-466g/SMAD4 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 25:332022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang R, Liu Y and Jing L: MiRNA-99a
alleviates inflammation and oxidative stress in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated PC-12 cells and rats post spinal cord
injury. Bioengineered. 13:4248–4259. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guo K, Chang Y, Jin Y, Yuan H and Che P:
circ-Ncam2 (mmu_circ_0006413) Participates in LPS-Induced Microglia
Activation and Neuronal Apoptosis via the TLR4/NF-κB Pathway. J Mol
Neurosci. 72:1738–1748. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
He X, Zhang J, Guo Y, Yang X, Huang Y and
Hao D: Exosomal miR-9-5p derived from BMSCs alleviates apoptosis,
inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in spinal cord injury
by regulating the HDAC5/FGF2 axis. Mol Immunol. 145:97–108. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wiatrak B, Kubis-Kubiak A, Piwowar A and
Barg E: PC12 cell line: Cell types, coating of culture vessels,
differentiation and other culture conditions. Cells. 9:9582020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li R, Ng TSC, Wang SJ, Prytyskach M,
Rodell CB, Mikula H, Kohler RH, Garlin MA, Lauffenburger DA,
Parangi S, et al: Therapeutically reprogrammed nutrient signalling
enhances nanoparticulate albumin bound drug uptake and efficacy in
KRAS-mutant cancer. Nat Nanotechnol. 16:830–839. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhou J, Li Z, Zhao Q, Wu T, Zhao Q and Cao
Y: Knockdown of SNHG1 alleviates autophagy and apoptosis by
regulating miR-362-3p/Jak2/stat3 pathway in LPS-injured PC12 cells.
Neurochemical Res. 46:945–956. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang Y, Li S, Chen H, Feng L, Yuan W and
Han T: Butorphanol reduces the neuronal inflammatory response and
apoptosis via inhibition of p38/JNK/ATF2/p53 signaling. Exp Ther
Med. 23:2292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ma Z, Lu Y, Yang F, Li S, He X, Gao Y,
Zhang G, Ren E, Wang Y and Kang X: Rosmarinic acid exerts a
neuroprotective effect on spinal cord injury by suppressing
oxidative stress and inflammation via modulating the Nrf2/HO-1 and
TLR4/NF-κB pathways. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 397:1150142020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Samatar AA and Poulikakos PI: Targeting
RAS-ERK signalling in cancer: Promises and challenges. Nat Rev Drug
Dis. 13:928–942. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhang X, Shen R, Shu Z, Zhang Q and Chen
Z: S100A12 promotes inflammation and apoptosis in
ischemia/reperfusion injury via ERK signaling in vitro study using
PC12 cells. Pathol International. 70:403–412. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yoo SR, Kim Y, Lee MY, Kim OS, Seo CS,
Shin HK and Jeong SJ: Gyeji-tang water extract exerts
anti-inflammatory activity through inhibition of ERK and NF-κB
pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 cells. BMC
Complement Altern Med. 16:3902016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Biswas SK: Does the interdependence
between oxidative stress and inflammation explain the antioxidant
paradox? Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016:56989312016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ganner A, Pfeiffer ZC, Wingendorf L, Kreis
S, Klein M, Walz G and Neumann-Haefelin E: The acetyltransferase
p300 regulates Nrf2 stability and localization. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 524:895–902. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Shi Z, Yuan S, Shi L, Li J, Ning G, Kong X
and Feng S: Programmed cell death in spinal cord injury
pathogenesis and therapy. Cell Prolif. 54:e129922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zipser CM, Cragg JJ, Guest JD, Fehlings
MG, Jutzeler CR, Anderson AJ and Curt A: Cell-based and
stem-cell-based treatments for spinal cord injury: Evidence from
clinical trials. Lancet Neurol. 21:659–670. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Cunningham CJ, Viskontas M, Janowicz K,
Sani Y, Håkansson ME, Heidari A, Huang W and Bo X: The potential of
gene therapies for spinal cord injury repair: A systematic review
and meta-analysis of pre-clinical studies. Neural Regen Res.
18:299–305. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chaudhari LR, Kawale AA, Desai SS, Kashte
SB and Joshi MG: Pathophysiology of spinal cord injury and tissue
engineering approach for its neuronal regeneration: Current status
and future prospects. Adv Exp Med Bio. Aug 30–2022.(Epub ahead of
print) doi: 10.1007/5584_2022_731. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Karsy M and Hawryluk G: Modern medical
management of spinal cord injury. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep.
19:652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Anjum A, Yazid MD, Fauzi Daud M, Idris J,
Ng AMH, Selvi Naicker A, Ismail OHR, Athi Kumar RK and Lokanathan
Y: Spinal cord injury: Pathophysiology, multimolecular
interactions, and underlying recovery mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci.
21:75332020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li X, Zhan J, Hou Y, Hou Y, Chen S, Luo D,
Luan J, Wang L and Lin D: Coenzyme Q10 regulation of apoptosis and
oxidative stress in H2O2 induced BMSC death
by modulating the Nrf-2/NQO-1 signaling pathway and its application
in a model of spinal cord injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2019:64930812019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen S, Ye J, Chen X, Shi J, Wu W, Lin W,
Lin W, Li Y, Fu H and Li S: Valproic acid attenuates traumatic
spinal cord injury-induced inflammation via STAT1 and NF-κB pathway
dependent of HDAC3. J Neuroinflammation. 15:1502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shen K, Sun G, Chan L, He L, Li X, Yang S,
Wang B, Zhang H, Huang J, Chang M, et al: Anti-inflammatory
nanotherapeutics by targeting matrix metalloproteinases for
immunotherapy of spinal cord injury. Small. 17:e21021022021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rodríguez-Cal Y Mayor A,
Castañeda-Hernández G, Favari L, Martinez-Cruz A, Guízar-Sahagún G
and Cruz-Antonio L: Pharmacokinetics and anti-inflammatory effect
of naproxen in rats with acute and subacute spinal cord injury.
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 393:395–404. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Sun B and Kekenes-Huskey PM: Molecular
basis of S100A1 activation and target regulation within
physiological cytosolic Ca(2+) levels. Front Mol Biosci. 7:772020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Alanazi AM, Fadda L, Alhusaini A, Ahmad R,
Hasan IH and Mahmoud AM: Liposomal resveratrol and/or carvedilol
attenuate doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by modulating
inflammation, oxidative stress and S100A1 in Rats. Antioxidants
(Basel). 9:1592020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zeng Z, Huang N, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Su Y,
Zhang H and An Y: CTCF inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress and
apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by upregulating RYR2 via inhibiting
S100A1. Life Sci. 242:1171582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sahu R, Upadhayay S and Mehan S:
Inhibition of extracellular regulated kinase (ERK)-1/2 signaling
pathway in the prevention of ALS: Target inhibitors and influences
on neurological dysfunctions. Eur J Cell Biol. 100:1511792021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Ge X, Tang P, Rong Y, Jiang D, Lu X, Ji C,
Wang J, Huang C, Duan A, Liu Y, et al: Exosomal miR-155 from
M1-polarized macrophages promotes EndoMT and impairs mitochondrial
function via activating NF-κB signaling pathway in vascular
endothelial cells after traumatic spinal cord injury. Redox Biol.
41:1019322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cheng RD, Ren W, Sun P, Tian L, Zhang L,
Zhang J, Li JB and Ye XM: Spinal cord injury causes insulin
resistance associated with PI3K signaling pathway in hypothalamus.
Neurochem Int. 140:1048392020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Xiang Z, Zhang S, Yao X, Xu L, Hu J, Yin
C, Chen J and Xu H: Resveratrol promotes axonal regeneration after
spinal cord injury through activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway. Aging. 13:23603–23619. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ciesielska A, Matyjek M and Kwiatkowska K:
TLR4 and CD14 trafficking and its influence on LPS-induced
pro-inflammatory signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:1233–1261. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Chen J, Wang Z, Zheng Z, Chen Y, Khor S,
Shi K, He Z, Wang Q, Zhao Y, Zhang H, et al: Neuron and
microglia/macrophage-derived FGF10 activate neuronal FGFR2/PI3K/Akt
signaling and inhibit microglia/macrophages TLR4/NF-κB-dependent
neuroinflammation to improve functional recovery after spinal cord
injury. Cell Death Dis. 8:e30902017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|