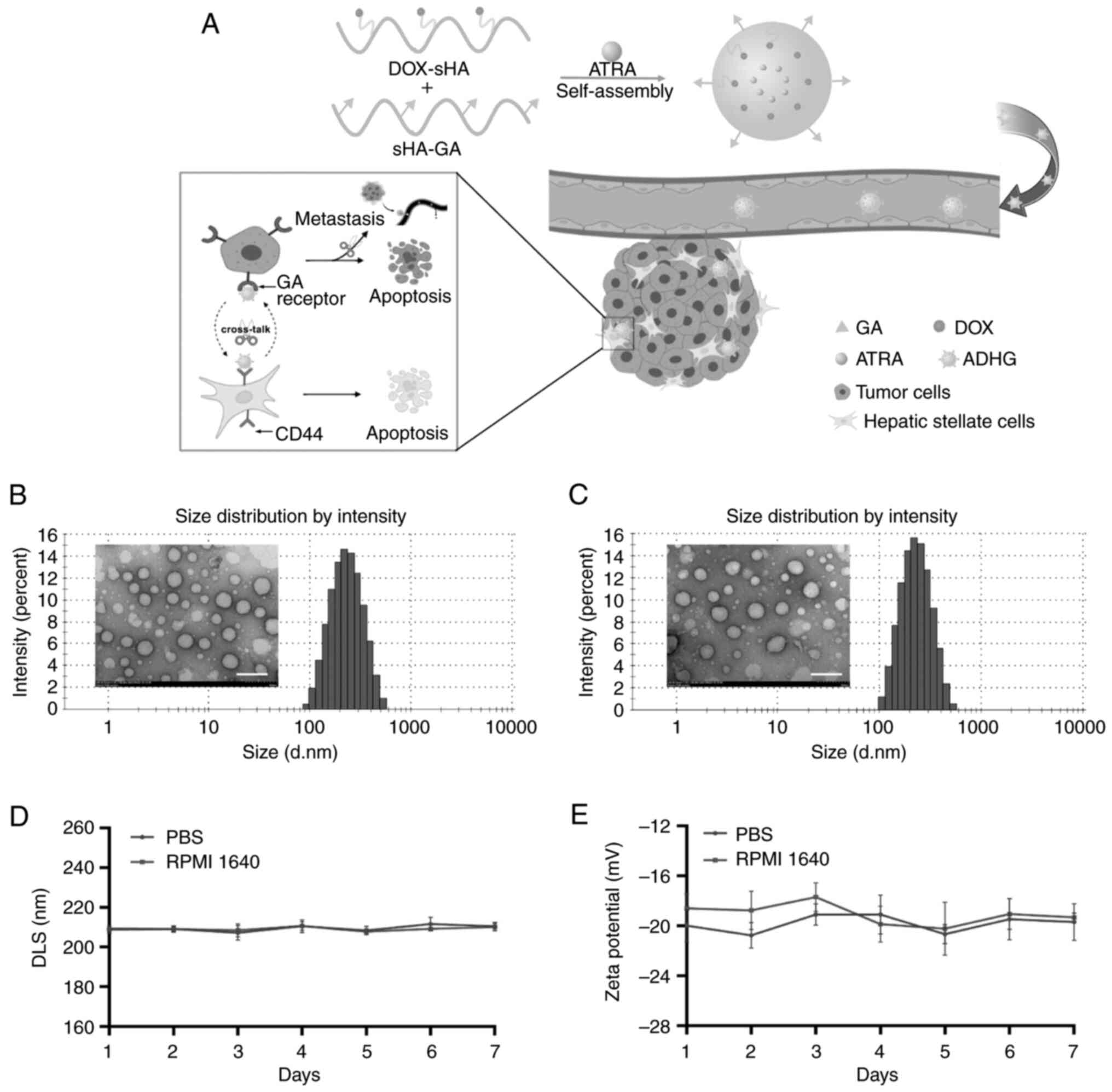
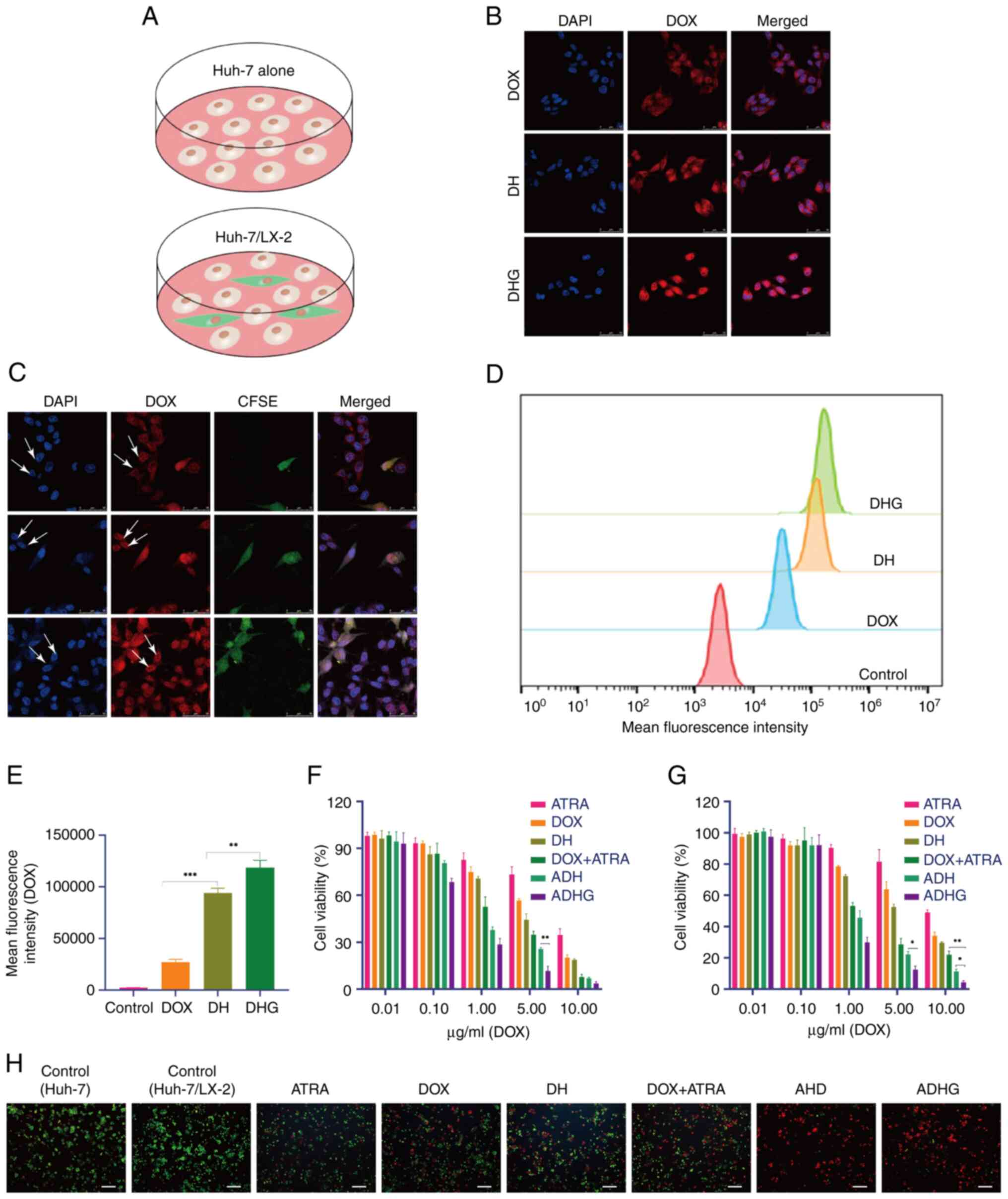
|
1
|
Lee YS and Jeong WI: Retinoic acids and
hepatic stellate cells in liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
27 (Suppl 2):S75–S79. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hisamori S, Tabata C, Kadokawa Y, Okoshi
K, Tabata R, Mori A, Nagayama S, Watanabe G, Kubo H and Sakai Y:
All-trans-retinoic acid ameliorates carbon tetrachloride-induced
liver fibrosis in mice through modulating cytokine production.
Liver Int. 28:1217–1225. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Mizobuchi Y, Shimizu I, Yasuda M, Hori H,
Shono M and Ito S: Retinyl palmitate reduces hepatic fibrosis in
rats induced by dimethylnitrosamine or pig serum. J Hepatol.
29:933–943. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Davis BH, Kramer RT and Davidson NO:
Retinoic acid modulates rat Ito cell proliferation, collagen, and
transforming growth factor beta production. J Clin Invest.
86:2062–2070. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tsuchida T and Friedman SL: Mechanisms of
hepatic stellate cell activation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
14:397–411. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Panebianco C, Oben JA, Vinciguerra M and
Pazienza V: Senescence in hepatic stellate cells as a mechanism of
liver fibrosis reversal: A putative synergy between retinoic acid
and PPAR-gamma signalings. Clin Exp Med. 17:269–280. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang L, Tankersley LR, Tang M, Potter JJ
and Mezey E: Regulation of the murine alpha(2)(I) collagen promoter
by retinoic acid and retinoid X receptors. Arch Biochem Biophys.
401:262–270. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim SJ, Park JH, Lee SA, Lee JG, Shin JM
and Lee HM: All-trans retinoic acid regulates TGF-β1-induced
extracellular matrix production via p38, JNK, and NF-κB-signaling
pathways in nasal polyp-derived fibroblasts. Int Forum Allergy
Rhinol. 10:636–645. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang Y, Guan DX, Shi J, Gao H, Li JJ,
Zhao JS, Qiu L, Liu J, Li N, Guo WX, et al: All-trans retinoic acid
potentiates the chemotherapeutic effect of cisplatin by inducing
differentiation of tumor initiating cells in liver cancer. J
Hepatol. 59:1255–1263. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abu Lila AS and Ishida T: Liposomal
delivery systems: Design optimization and current applications.
Biol Pharm Bull. 40:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li L and Wang H: Heterogeneity of liver
cancer and personalized therapy. Cancer Lett. 379:191–197. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu T and Dai Y: Tumor microenvironment and
therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 387:61–68. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han S, Wang W, Wang S, Yang T, Zhang G,
Wang D, Ju R, Lu Y, Wang H and Wang L: Tumor microenvironment
remodeling and tumor therapy based on M2-like tumor associated
macrophage-targeting nano-complexes. Theranostics. 11:2892–2916.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hui L and Chen Y: Tumor microenvironment:
Sanctuary of the devil. Cancer Lett. 368:7–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mohr R, Özdirik B, Lambrecht J, Demir M,
Eschrich J, Geisler L, Hellberg T, Loosen SH, Luedde T, Tacke F, et
al: From liver cirrhosis to cancer: The role of Micro-RNAs in
hepatocarcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci. 22:14922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brodt P: Role of the microenvironment in
liver metastasis: From pre- to prometastatic niches. Clin Cancer
Res. 22:5971–5982. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Muppala S: Significance of the tumor
microenvironment in liver cancer progression. Crit Rev Oncog.
25:1–9. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kahn AM, Blenman KRM, Sonis ST and
Lustberg MB: Strategies to mitigate the toxicity of cancer
therapeutics. Adv Cancer Res. 155:215–244. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhou F, Teng F, Deng P, Meng N, Song Z and
Feng R: Recent progress of nano-drug delivery system for liver
cancer treatment. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 17:1884–1897. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun D, Zhang J, Wang L, Yu Z, O'Driscoll
CM and Guo J: Nanodelivery of immunogenic cell death-inducers for
cancer immunotherapy. Drug Discov Today. 26:651–662. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sudha PN and Rose MH: Beneficial effects
of hyaluronic acid. Adv Food Nutr Res. 72:137–176. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vasvani S, Kulkarni P and Rawtani D:
Hyaluronic acid: A review on its biology, aspects of drug delivery,
route of administrations and a special emphasis on its approved
marketed products and recent clinical studies. Int J Biol Macromol.
151:1012–1029. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lokeshwar VB, Mirza S and Jordan A:
Targeting hyaluronic acid family for cancer chemoprevention and
therapy. Adv Cancer Res. 123:35–65. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Benitez A, Yates TJ, Lopez LE, Cerwinka
WH, Bakkar A and Lokeshwar VB: Targeting hyaluronidase for cancer
therapy: Antitumor activity of sulfated hyaluronic acid in prostate
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 71:4085–4095. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jordan AR, Lokeshwar SD, Lopez LE, Hennig
M, Chipollini J, Yates T, Hupe MC, Merseburger AS, Shiedlin A,
Cerwinka WH, et al: Antitumor activity of sulfated hyaluronic acid
fragments in pre-clinical models of bladder cancer. Oncotarget.
8:24262–24274. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhou X, He C, Liu M, Chen Q, Zhang L, Xu
X, Xu H, Qian Y, Yu F, Wu Y, et al: Self-assembly of hyaluronic
acid-mediated tumor-targeting theranostic nanoparticles. Biomater
Sci. 9:2221–2229. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Bai Y, Liu CP, Chen D, Liu CF, Zhuo LH, Li
H, Wang C, Bu HT and Tian W: β-Cyclodextrin-modified hyaluronic
acid-based supramolecular self-assemblies for pH- and
esterase-dual-responsive drug delivery. Carbohydr Polym.
246:1166542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cai J, Fu J, Li R, Zhang F, Ling G and
Zhang P: A potential carrier for anti-tumor targeted
delivery-hyaluronic acid nanoparticles. Carbohydr Polym.
208:356–364. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lei C, Liu XR, Chen QB, Li Y, Zhou JL,
Zhou LY and Zou T: Hyaluronic acid and albumin based nanoparticles
for drug delivery. J Control Release. 331:416–433. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Du W, Yang X, He S, Wang J, Guo Y, Kou B,
Jiang Y, Bian P, Li B and Yin L: Novel hyaluronic acid
oligosaccharide-loaded and CD44v6-targeting oxaliplatin
nanoparticles for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Drug Deliv.
28:920–929. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lai H, Ding X, Ye J, Deng J and Cui S:
pH-responsive hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles for targeted
curcumin delivery and enhanced cancer therapy. Colloids Surf B
Biointerfaces. 198:1114552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Nieto C, Vega MA and Martín Del Valle E:
Nature-inspired nanoparticles as paclitaxel targeted carrier for
the treatment of HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancers (Basel).
13:25262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Silva EL, Carneiro G, Caetano PA, Goulart
G, Ferreira Costa D, de Souza-Fagundes EM, Gomes DA and Ferreira
LA: Nanostructured lipid carriers loaded with tributyrin as an
alternative to improve anticancer activity of all-trans retinoic
acid. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 15:247–256. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xu ZC, Shen HX, Chen C, Ma L, Li WZ, Wang
L and Geng ZM: Neuropilin-1 promotes primary liver cancer
progression by potentiating the activity of hepatic stellate cells.
Oncol Lett. 15:2245–2251. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Justus CR, Leffler N, Ruiz-Echevarria M
and Yang LV: In vitro cell migration and invasion assays. J Vis
Exp. 88:510462014.
|
|
36
|
Bourebaba N and Marycz K: Hepatic stellate
cells role in the course of metabolic disorders development-A
molecular overview. Pharmacol Res. 170:1057392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gu L, Zhang F, Wu J and Zhuge Y:
Nanotechnology in drug delivery for liver fibrosis. Front Mol
Biosci. 8:8043962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hellerbrand C: Hepatic stellate cells-the
pericytes in the liver. Pflugers Arch. 465:775–778. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Iwahasi S, Rui F, Morine Y, Yamada S,
Saito YU, Ikemoto T, Imura S and Shimada M: Hepatic stellate cells
contribute to the tumor malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma
through the IL-6 pathway. Anticancer Res. 40:743–749. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Maeda H, Wu J, Sawa T, Matsumura Y and
Hori K: Tumor vascular permeability and the EPR effect in
macromolecular therapeutics: A review. J Control Release.
65:271–284. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Shi Y, van der Meel R, Chen X and Lammers
T: The EPR effect and beyond: Strategies to improve tumor targeting
and cancer nanomedicine treatment efficacy. Theranostics.
10:7921–7924. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li Z, Wang F, Li Y, Wang X, Lu Q, Wang D,
Qi C, Li C, Li Z, Lian B, et al: Combined anti-hepatocellular
carcinoma therapy inhibit drug-resistance and metastasis via
targeting ‘substance P-hepatic stellate cells-hepatocellular
carcinoma’ axis. Biomaterials. 276:1210032021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Meng Q, Luo X, Chen J, Wang D, Chen E,
Zhang W, Zhang G, Zhou W, Xu J and Song Z: Unmasking
carcinoma-associated fibroblasts: Key transformation player within
the tumor microenvironment. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1874:1884432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fiori ME, Di Franco S, Villanova L, Bianca
P, Stassi G and De Maria R: Cancer-associated fibroblasts as
abettors of tumor progression at the crossroads of EMT and therapy
resistance. Mol Cancer. 18:702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li T, Kang G, Wang T and Huang H: Tumor
angiogenesis and anti-angiogenic gene therapy for cancer. Oncol
Lett. 16:687–702. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bhat SM, Badiger VA, Vasishta S,
Chakraborty J, Prasad S, Ghosh S and Joshi MB: 3D tumor
angiogenesis models: Recent advances and challenges. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 147:3477–3494. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang Y, Xu Z, Guo S, Zhang L, Sharma A,
Robertson GP and Huang L: Intravenous delivery of siRNA targeting
CD47 effectively inhibits melanoma tumor growth and lung
metastasis. Mol Ther. 21:1919–1929. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Chen Q, Bai H, Wu W, Huang G, Li Y, Wu M,
Tang G and Ping Y: Bioengineering bacterial vesicle-coated
polymeric nanomedicine for enhanced cancer immunotherapy and
metastasis prevention. Nano Lett. 20:11–21. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|