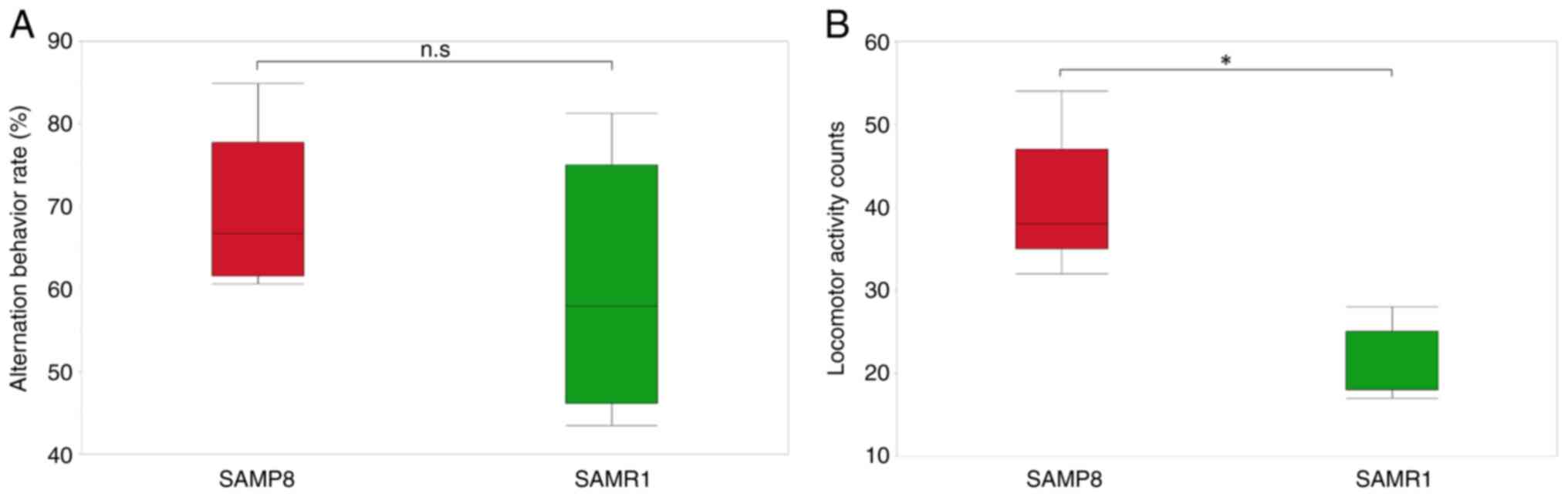
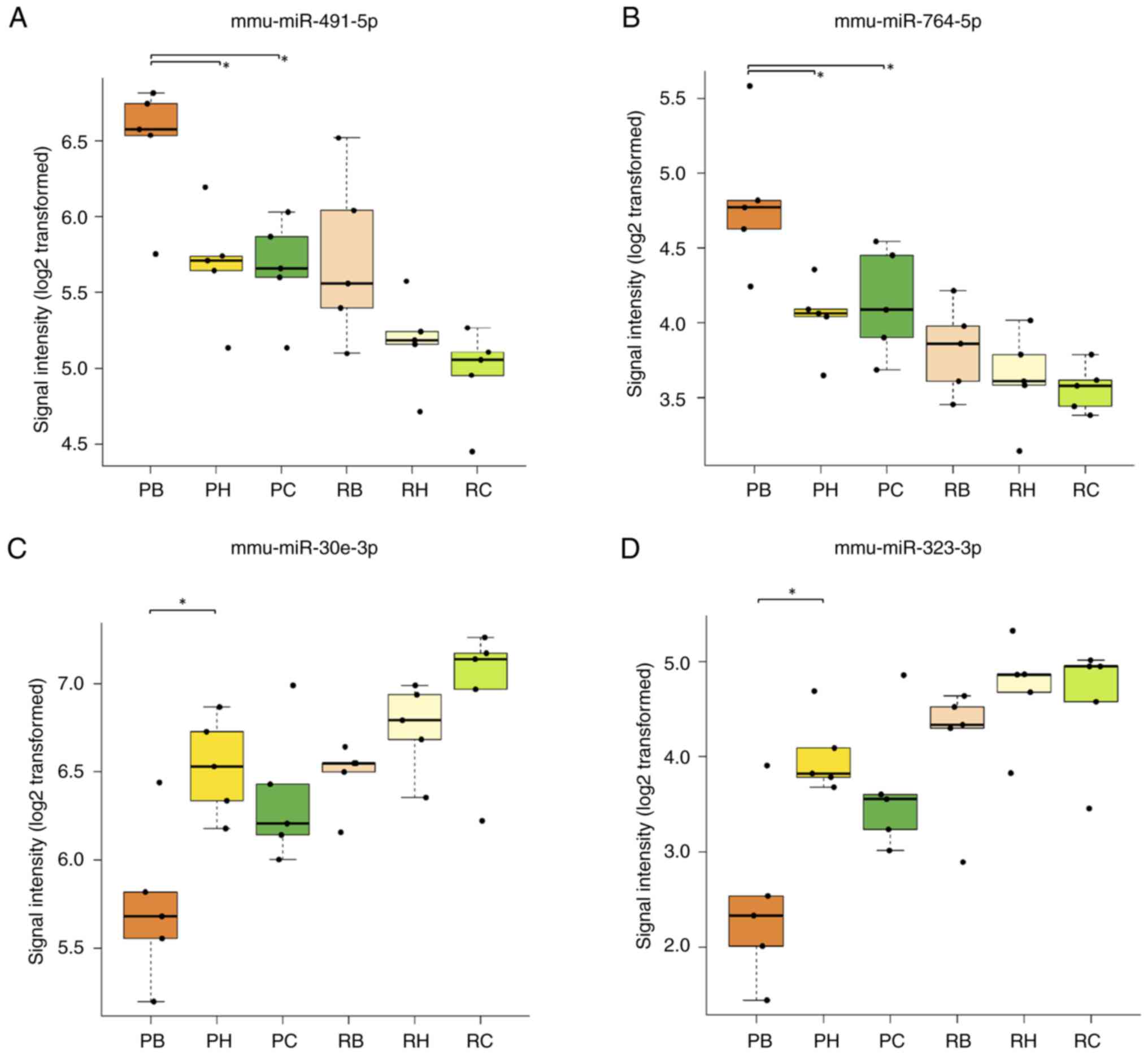
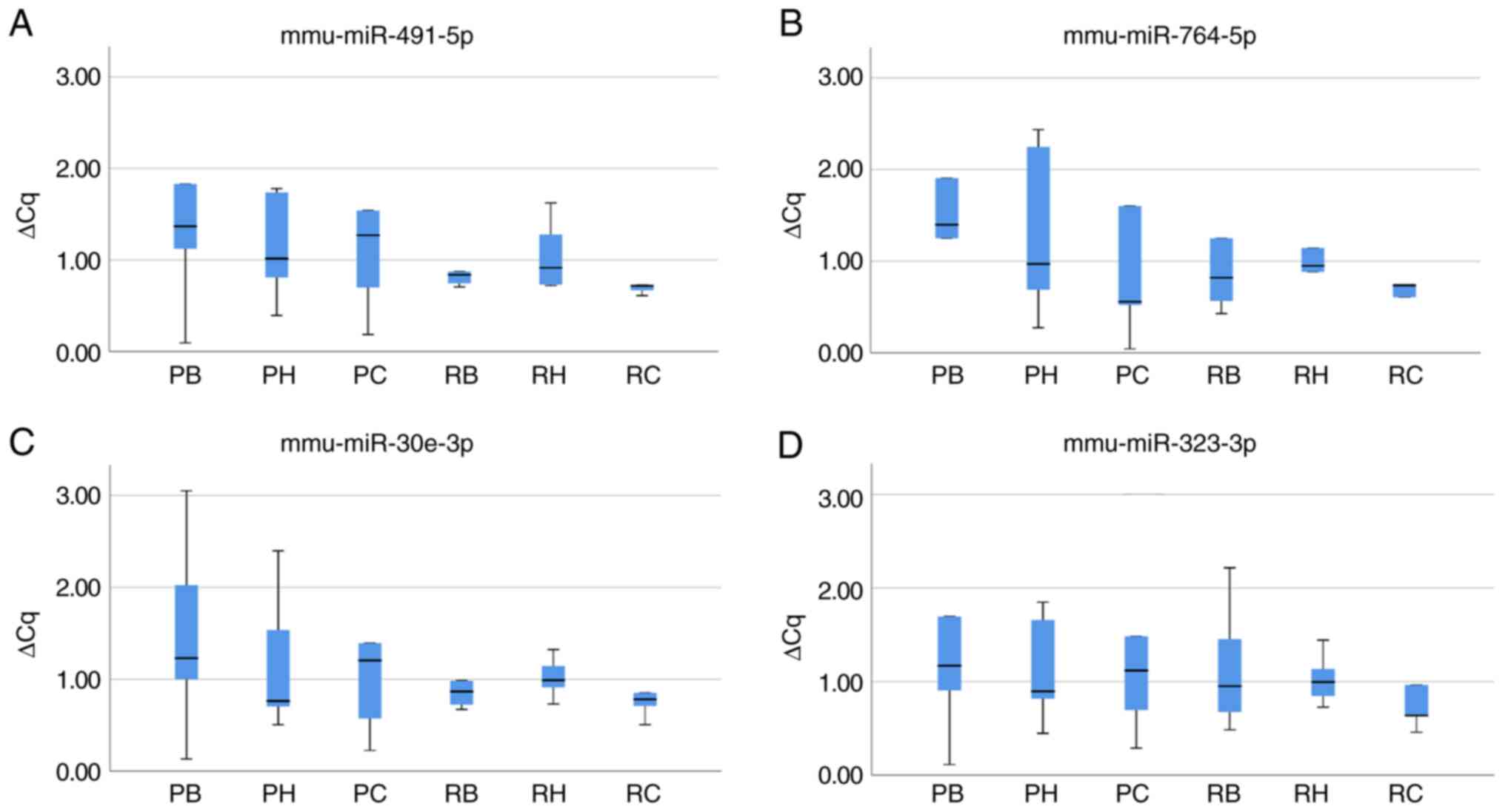
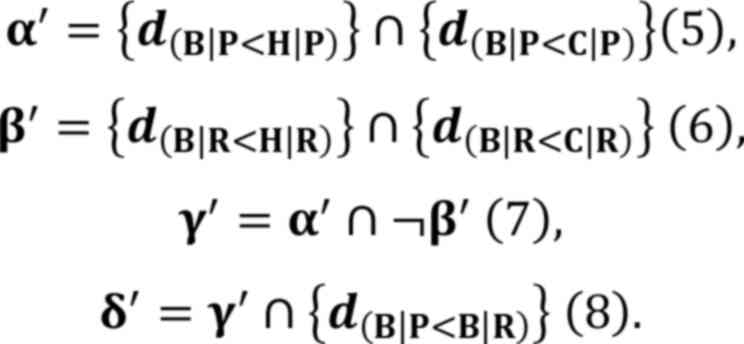|
1
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Reddy PH, Williams J, Smith F, Bhatti JS,
Kumar S, Vijayan M, Kandimalla R, Kuruva CS, Wang R, Manczak M, et
al: MicroRNAs, aging, cellular senescence, and Alzheimer's disease.
Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 146:127–171. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Salta E and De Strooper B: Non-coding RNAs
with essential roles in neurodegenerative disorders. Lancet Neurol.
11:189–200. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kume K, Iwama H, Deguchi K, Ikeda K,
Takata T, Kokudo Y, Kamada M, Fujikawa K, Hirose K, Masugata H, et
al: Serum microRNA expression profiling in patients with multiple
system atrophy. Mol Med Rep. 17:852–860. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nonaka W, Takata T, Iwama H, Komatsubara
S, Kobara H, Kamada M, Deguchi K, Touge T, Miyamoto O, Nakamura T,
et al: A cerebrospinal fluid microRNA analysis: Progressive
supranuclear palsy. Mol Med Rep. 25:1–9. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lees AJ, Hardy J and Revesz T: Parkinson's
disease. Lancet. 373:2055–2066. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Braak H and Del Tredici K: The
pathological process underlying Alzheimer's disease in individuals
under thirty. Acta Neuropathol. 121:171–181. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Braak H and Del Tredici K: The preclinical
phase of the pathological process underlying sporadic Alzheimer's
disease. Brain. 138:2814–2833. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RAI,
Jansen Steur ENH and Braak E: Staging of brain pathology related to
sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 24:197–211. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng XR, Zhou WX and Zhang YX: The
behavioral, pathological and therapeutic features of the
senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 strain as an Alzheimer's
disease animal model. Ageing Res Rev. 13:13–37. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kawamata T, Akiguchi I, Yagi H, Irino M,
Sugiyama H, Akiyama H, Shimada A, Takemura M, Ueno M, Kitabayashi
T, et al: Neuropathological studies on strains of
senescence-accelerated mice (SAM) with age-related deficits in
learning and memory. Exp Gerontol. 32:161–169. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawamata T, Akiguchi I, Maeda K, Tanaka C,
Higuchi K, Hosokawa M and Takeda T: Age-related changes in the
brains of senescence-accelerated mice (SAM): Association with glial
and endothelial reactions. Microsc Res Tech. 43:59–67. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yagi H, Akiguchi I, Ohta A, Yagi N,
Hosokawa M and Takeda T: Spontaneous and artificial lesions of
magnocellular reticular formation of brainstem deteriorate
avoidance learning in senescence-accelerated mouse SAM. Brain Res.
791:90–98. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yagi H, Irino M, Matsushita T, Katoh S,
Umezawa M, Tsuboyama T, Hosokawa M, Akiguchi I, Tokunaga R and
Takeda T: Spontaneous spongy degeneration of the brain stem in
SAM-P/8 mice, a newly developed memory-deficient strain. J
Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 48:577–590. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Tan YX, Hong Y, Jiang S, Lu MN, Li S,
Chein B, Zhang L, Hu T, Mao R, Mei R and Xiyang YB: MicroRNA-449a
regulates the progression of brain aging by targeting SCN2B in
SAMP8 mice. Int J Mol Med. 45:1091–1102. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang SM, Mouri A, Kokubo H, Nakajima R,
Suemoto T, Higuchi M, Staufenbiel M, Noda Y, Yamaguchi H, Nabeshima
T, et al: Neprilysin-sensitive synapse-associated amyloid-β peptide
oligomers impair neuronal plasticity and cognitive function. J Biol
Chem. 281:17941–17951. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
del Valle J, Bayod S, Camins A,
Beas-Zárate C, Velázquez-Zamora DA, González-Burgos I and Pallàs M:
Dendritic spine abnormalities in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons
underlying memory deficits in the SAMP8 mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 32:233–240. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Miyamoto M: Characteristics of age-related
behavioral changes in senescence-accelerated mouse SAMP8 and
SAMP10. Exp Gerontol. 32:139–148. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Markowska AL, Spangler EL and Ingram DK:
Behavioral assessment of the senescence-accelerated mouse (SAM P8
and R1). Physiol Behav. 64:15–26. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Braak H and Braak E: Neuropathological
stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol.
82:239–259. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang LL, Min L, Guo QD, Zhang JX, Jiang
HL, Shao S, Xing JG, Yin LL, Liu JH, Liu R, et al: Profiling
microRNA from brain by microarray in a transgenic mouse model of
Alzheimer's disease. BioMed Res Int. 2017:80303692017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gong F, Ren P, Zhang Y, Jiang J and Zhang
H: MicroRNAs-491-5p suppresses cell proliferation and invasion by
inhibiting IGF2BP1 in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Transl Res.
8:485–495. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang SN, Luo S, Liu C, Piao Z, Gou W, Wang
Y, Guan W, Li Q, Zou H, Yang ZZ, et al: miR-491 inhibits
osteosarcoma lung metastasis and chemoresistance by targeting
αB-crystallin. Mol Ther. 25:2140–2149. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Meng Y, Shang FR and Zhu YL: MiR-491
functions as a tumor suppressor through Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling
in the development of glioma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:10899–10907. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jing D, Yinzhu L, Jinjing P, Lishuang L
and Guozhuan Z: Targeting ninjurin 2 by miR-764 regulates hydrogen
peroxide (H2O2)-induced neuronal cell death. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 505:1180–1188. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Araki T and Milbrandt J: Ninjurin2, a
novel homophilic adhesion molecule, is expressed in mature sensory
and enteric neurons and promotes neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci.
20:187–195. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Henriques AD, Machado-Silva W, Leite REP,
Suemoto CK, Leite KRM, Srougi M, Pereira AC, Jacob-Filho W and
Nóbrega OT; Brazilian Aging Brain Study Group, : Genome-wide
profiling and predicted significance of post-mortem brain microRNA
in Alzheimer's disease. Mech Ageing Dev. 191:1113522020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chow LML and Baker SJ: PTEN function in
normal and neoplastic growth. Cancer Lett. 241:184–196. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shabanzadeh AP, D'Onofrio PM, Magharious
M, Choi KAB, Monnier PP and Koeberle PD: Modifying PTEN recruitment
promotes neuron survival, regeneration, and functional recovery
after CNS injury. Cell Death Dis. 10:5672019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Delay C, Calon F, Mathews P and Hébert SS:
Alzheimer-specific variants in the 3′UTR of Amyloid precursor
protein affect microRNA function. Mol Neurodegener. 6:702011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
De Strooper B: Proteases and proteolysis
in Alzheimer disease: A multifactorial view on the disease process.
Physiol Rev. 90:465–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shi CC, Pan LY, Zhao YQ, Li Q and Li JG:
MicroRNA-323-3p inhibits oxidative stress and apoptosis after
myocardial infarction by targeting TGF-β2/JNK pathway. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 24:6961–6970. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bartsch T and Wulff P: The hippocampus in
aging and disease: From plasticity to vulnerability. Neuroscience.
309:1–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang SZ, Wang QQ, Yang QQ, Gu HY, Yin YQ,
Li YD, Hou JC, Chen R, Sun QQ, Sun YF, et al: NG2 glia regulate
brain innate immunity via TGF-β2/TGFBR2 axis. BMC Med. 17:2042019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Nakano M, Tamura Y, Yamato M, Kume S,
Eguchi A, Takata K, Watanabe Y and Kataoka Y: NG2 glial cells
regulate neuroimmunological responses to maintain neuronal function
and survival. Sci Rep. 7:420412017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Knafo S, Sánchez-Puelles C, Palomer E,
Delgado I, Draffin JE, Mingo J, Wahle T, Kaleka K, Mou L,
Pereda-Perez I, et al: PTEN recruitment controls synaptic and
cognitive function in Alzheimer's models. Nat Neurosci. 19:443–453.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin KP, Chen SY, Lai LC, Huang YL, Chen
JH, Chen TF, Sun Y, Wen LL, Yip PK, Chu YM, et al: Genetic
polymorphisms of a novel vascular susceptibility gene, Ninjurin2
(NINJ2), are associated with a decreased risk of Alzheimer's
disease. PLoS One. 6:e205732011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Peress NS and Perillo E: Differential
expression of TGF-β 1, 2 and 3 isotypes in Alzheimer's disease: A
comparative immunohistochemical study with cerebral infarction,
aged human and mouse control brains. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
54:802–811. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|