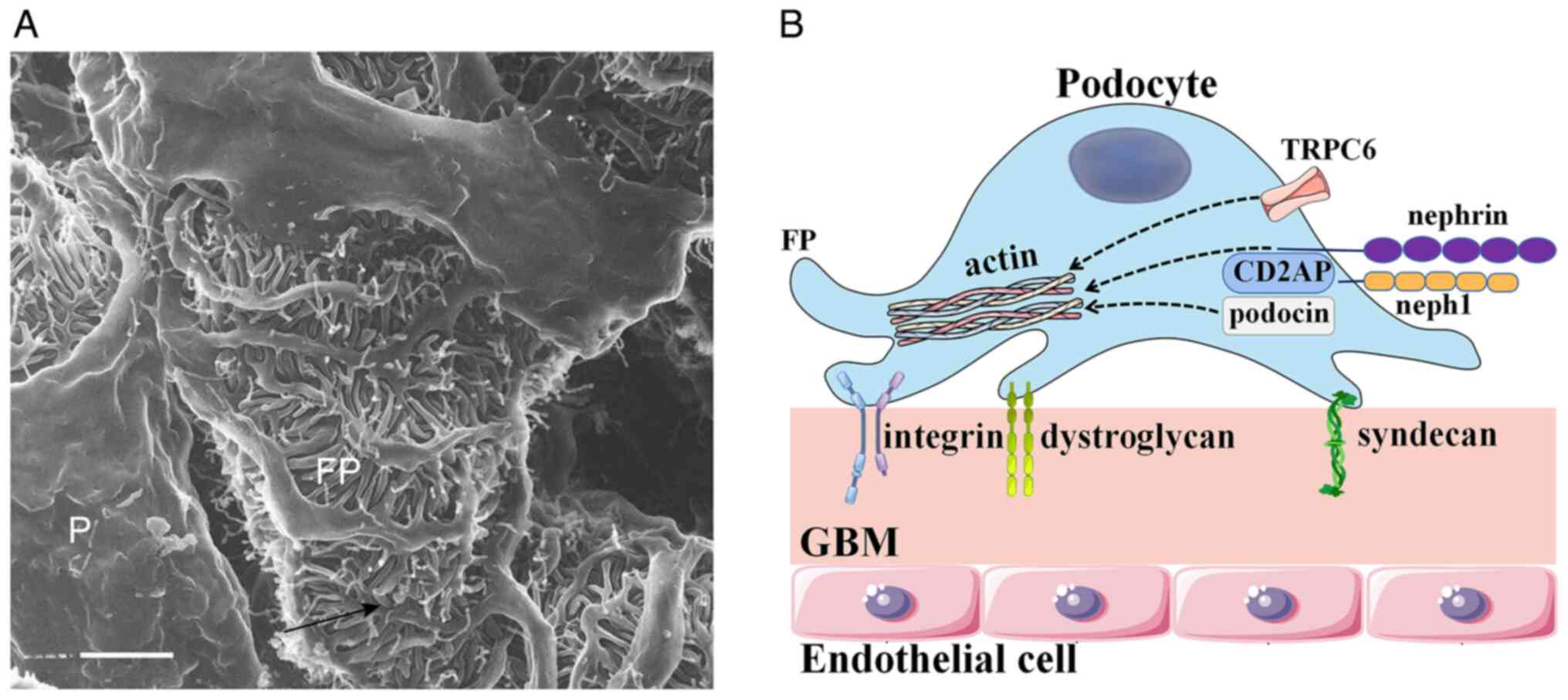
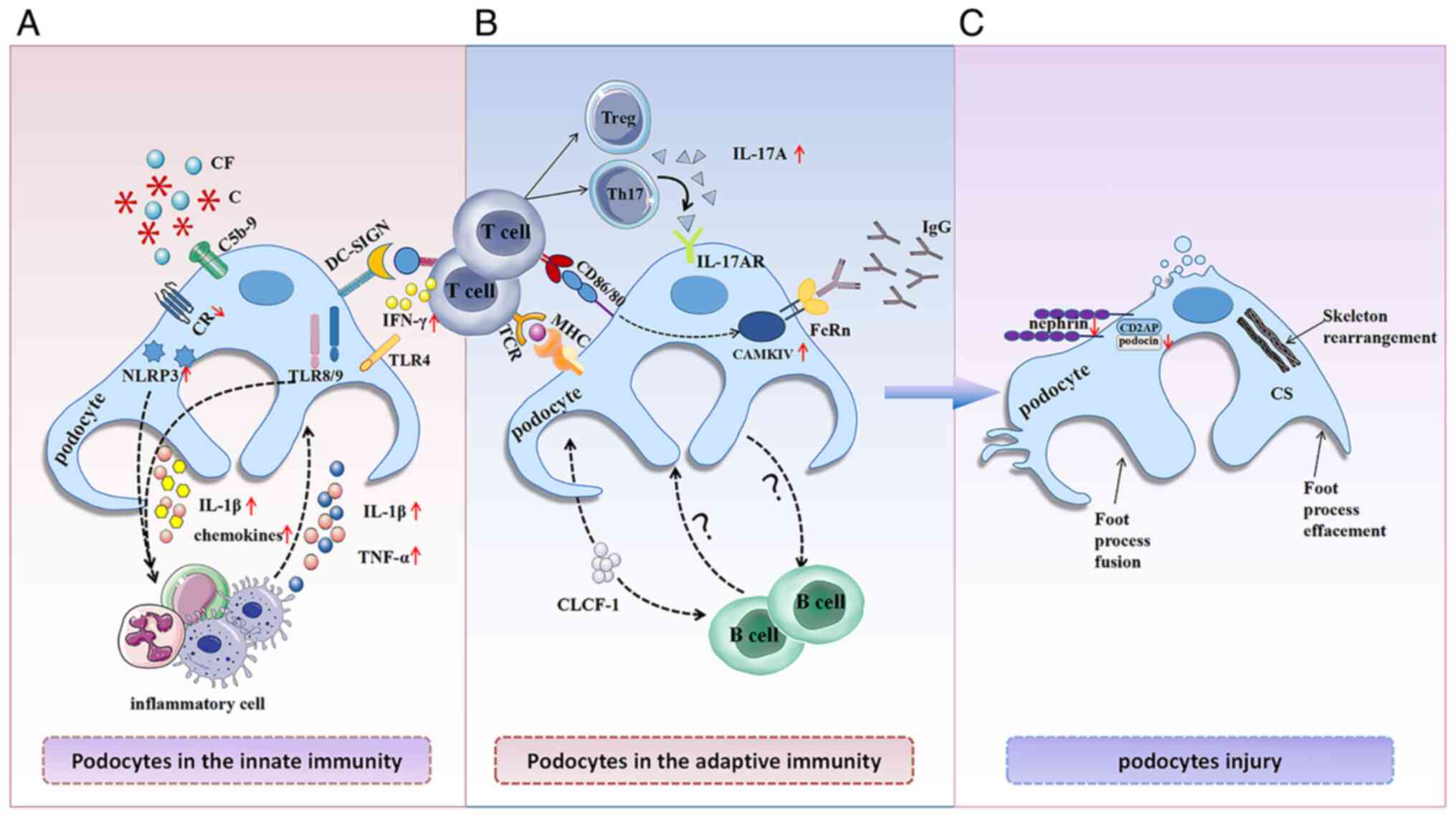
|
1
|
Tian J, Zhang D, Yao X, Huang Y and Lu Q:
Global epidemiology of systemic lupus erythematosus: A
comprehensive systematic analysis and modelling study. Ann Rheum
Dis. 82:351–356. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z,
Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, Ruiz-Irastorza G and Hughes G:
Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2:160392016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tektonidou MG, Dasgupta A and Ward MM:
Risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with lupus nephritis,
1971–2015: A systematic review and bayesian meta-analysis.
Arthritis Rheumatol. 68:1432–1441. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Seligman VA, Lum RF, Olson JL, Li H and
Criswell LA: Demographic differences in the development of lupus
nephritis: A retrospective analysis. Am J Med. 112:726–729. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aguirre A, Izadi Z, Trupin L, Barbour KE,
Greenlund KJ, Katz P, Lanata C, Criswell L, Dall'Era M and Yazdany
J: Race, ethnicity, and disparities in the risk of end-organ lupus
manifestations following a systemic lupus erythematosus diagnosis
in a multiethnic cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 75:34–43.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tsokos GC, Lo MS, Costa RP and Sullivan
KE: New insights into the immunopathogenesis of systemic lupus
erythematosus. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 12:716–730. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mohan C and Putterman C: Genetics and
pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis.
Nat Rev Nephrol. 11:329–341. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Costenbader KH, Desai A, Alarcón GS,
Hiraki LT, Shaykevich T, Brookhart MA, Massarotti E, Lu B, Solomon
DH and Winkelmayer WC: Trends in the incidence, demographics, and
outcomes of end-stage renal disease due to lupus nephritis in the
US from 1995 to 2006. Arthritis Rheum. 63:1681–1688. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Parikh SV and Rovin BH: Current and
emerging therapies for lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
27:2929–2939. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Davidson A: What is damaging the kidney in
lupus nephritis? Nat Rev Rheumatol. 12:143–153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kraft SW, Schwartz MM, Korbet SM and Lewis
EJ: Glomerular podocytopathy in patients with systemic lupus
erythematosus. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:175–179. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bomback AS and Markowitz GS: Lupus
podocytopathy: A distinct entity. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol.
11:547–548. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wright RD and Beresford MW: Podocytes
contribute, and respond, to the inflammatory environment in lupus
nephritis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 315:F1683–F1694. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Moustafa FE, Soliman NA, Bakr AM and El
Shwaf IM: Assessment of detached podocytes in the Bowman's space as
a marker of disease activity in lupus nephritis. Lupus. 23:146–150.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hu W, Chen Y, Wang S, Chen H and Liu Z,
Zeng C, Zhang H and Liu Z: Clinical-Morphological features and
outcomes of lupus podocytopathy. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 11:585–592.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jamaly S, Rakaee M, Abdi R, Tsokos GC and
Fenton KA: Interplay of immune and kidney resident cells in the
formation of tertiary lymphoid structures in lupus nephritis.
Autoimmun Rev. 20:1029802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kang S, Fedoriw Y, Brenneman EK, Truong
YK, Kikly K and Vilen BJ: BAFF induces tertiary lymphoid structures
and positions T cells within the glomeruli during lupus nephritis.
J Immunol. 198:2602–2611. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schwartz N, Goilav B and Putterman C: The
pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of lupus nephritis. Curr Opin
Rheumatol. 26:502–509. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dieker J, Tel J, Pieterse E, Thielen A,
Rother N, Bakker M, Fransen J, Dijkman HB, Berden JH, de Vries JM,
et al: Circulating apoptotic microparticles in systemic lupus
erythematosus patients drive the activation of dendritic cell
subsets and prime neutrophils for NETosis. Arthritis Rheumatol.
68:462–472. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Elkon KB: Review: Cell death, nucleic
acids, and immunity: Inflammation beyond the grave. Arthritis
Rheumatol. 70:805–816. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Salvi V, Gianello V, Busatto S, Bergese P,
Andreoli L, D'Oro U, Zingoni A, Tincani A, Sozzani S and Bosisio D:
Exosome-delivered microRNAs promote IFN-α secretion by human
plasmacytoid DCs via TLR7. JCI Insight. 3:e982042018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Leonard D, Eloranta ML, Hagberg N,
Berggren O, Tandre K, Alm G and Rönnblom L: Activated T cells
enhance interferon-α production by plasmacytoid dendritic cells
stimulated with RNA-containing immune complexes. Ann Rheum Dis.
75:1728–1734. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wen L, Zhang B, Wu X, Liu R, Fan H, Han L,
Zhang Z, Ma X, Chu CQ and Shi X: Toll-like receptors 7 and 9
regulate the proliferation and differentiation of B cells in
systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 14:10932082023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schrezenmeier E, Jayne D and Dörner T:
Targeting B cells and plasma cells in glomerular diseases:
Translational perspectives. J Am Soc Nephrol. 29:741–758. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Flores-Mendoza G, Sansón SP,
Rodríguez-Castro S, Crispín JC and Rosetti F: Mechanisms of tissue
injury in lupus nephritis. Trends Mol Med. 24:364–378. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Parikh SV, Almaani S, Brodsky S and Rovin
BH: Update on lupus nephritis: Core curriculum 2020. Am J Kidney
Dis. 76:265–281. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sharma M, Vignesh P, Tiewsoh K and Rawat
A: Revisiting the complement system in systemic lupus
erythematosus. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 16:397–408. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pavenstädt H, Kriz W and Kretzler M: Cell
biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev. 83:253–307. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Garg P: A review of podocyte biology. Am J
Nephrol. 47 (Suppl 1):S3–S13. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Humphries JD, Wang P, Streuli C, Geiger B,
Humphries MJ and Ballestrem C: Vinculin controls focal adhesion
formation by direct interactions with talin and actin. J Cell Biol.
179:1043–1057. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sellin L, Huber TB, Gerke P, Quack I,
Pavenstädt H and Walz G: NEPH1 defines a novel family of podocin
interacting proteins. FASEB J. 17:115–117. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Garg P, Verma R, Nihalani D, Johnstone DB
and Holzman LB: Neph1 cooperates with nephrin to transduce a signal
that induces actin polymerization. Mol Cell Biol. 27:8698–8712.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huber TB, Simons M, Hartleben B, Sernetz
L, Schmidts M, Gundlach E, Saleem MA, Walz G and Benzing T:
Molecular basis of the functional podocin-nephrin complex:
Mutations in the NPHS2 gene disrupt nephrin targeting to lipid raft
microdomains. Hum Mol Genet. 12:3397–3405. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Dryer SE and Reiser J: TRPC6 channels and
their binding partners in podocytes: Role in glomerular filtration
and pathophysiology. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 299:F689–F701.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ha TS: Roles of adaptor proteins in
podocyte biology. World J Nephrol. 2:1–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Y, Yu F, Song D, Wang SX and Zhao MH:
Podocyte involvement in lupus nephritis based on the 2003 ISN/RPS
system: A large cohort study from a single centre. Rheumatology
(Oxford). 53:1235–1244. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Banas MC, Banas B, Hudkins KL, Wietecha
TA, Iyoda M, Bock E, Hauser P, Pippin JW, Shankland SJ, Smith KD,
et al: TLR4 links podocytes with the innate immune system to
mediate glomerular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 19:704–713. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Li X, Ding F, Zhang X, Li B and Ding J:
The expression profile of complement components in podocytes. Int J
Mol Sci. 17:4712016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gao S, Cui Z and Zhao MH: Complement C3a
and C3a receptor activation mediates podocyte injuries in the
mechanism of primary membranous nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol.
33:1742–1756. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang H, Lv D, Jiang S, Hou Q, Zhang L, Li
S, Zhu X, Xu X, Wen J, Zeng C, et al: Complement induces podocyte
pyroptosis in membranous nephropathy by mediating mitochondrial
dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 13:2812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pippin JW, Durvasula R, Petermann A,
Hiromura K, Couser WG and Shankland SJ: DNA damage is a novel
response to sublytic complement C5b-9-induced injury in podocytes.
J Clin Invest. 111:877–885. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Appay MD, Kazatchkine MD, Levi-Strauss M,
Hinglais N and Bariety J: Expression of CR1 (CD35) mRNA in
podocytes from adult and fetal human kidneys. Kidney Int.
38:289–293. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Teixeira JE, Costa RS, Lachmann PJ,
Würzner R and Barbosa JE: CR1 stump peptide and terminal complement
complexes are found in the glomeruli of lupus nephritis patients.
Clin Exp Immunol. 105:497–503. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Moll S, Miot S, Sadallah S, Gudat F,
Mihatsch MJ and Schifferli JA: No complement receptor 1 stumps on
podocytes in human glomerulopathies. Kidney Int. 59:160–168. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bao L, Haas M and Quigg RJ: Complement
factor H deficiency accelerates development of lupus nephritis. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 22:285–295. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Pickering MC, Ismajli M, Condon MB,
McKenna N, Hall AE, Lightstone L, Terence Cook H and Cairns TD:
Eculizumab as rescue therapy in severe resistant lupus nephritis.
Rheumatology (Oxford). 54:2286–2288. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Coppo R, Peruzzi L, Amore A, Martino S,
Vergano L, Lastauka I, Schieppati A, Noris M, Tovo PA and Remuzzi
G: Dramatic effects of eculizumab in a child with diffuse
proliferative lupus nephritis resistant to conventional therapy.
Pediatr Nephrol. 30:167–172. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Patole PS, Pawar RD, Lech M, Zecher D,
Schmidt H, Segerer S, Ellwart A, Henger A, Kretzler M and Anders
HJ: Expression and regulation of Toll-like receptors in lupus-like
immune complex glomerulonephritis of MRL-Fas(lpr) mice. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 21:3062–3073. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Devarapu SK and Anders HJ: Toll-like
receptors in lupus nephritis. J Biomed Sci. 25:352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kimura J, Ichii O, Miyazono K, Nakamura T,
Horino T, Otsuka-Kanazawa S and Kon Y: Overexpression of Toll-like
receptor 8 correlates with the progression of podocyte injury in
murine autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Sci Rep. 4:72902014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Marshak-Rothstein A and Rifkin IR:
Immunologically active autoantigens: The role of toll-like
receptors in the development of chronic inflammatory disease. Annu
Rev Immunol. 25:419–441. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Anders HJ, Lichtnekert J and Allam R:
Interferon-alpha and -beta in kidney inflammation. Kidney Int.
77:848–854. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Machida H, Ito S, Hirose T, Takeshita F,
Oshiro H, Nakamura T, Mori M, Inayama Y, Yan K, Kobayashi N and
Yokota S: Expression of Toll-like receptor 9 in renal podocytes in
childhood-onset active and inactive lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial
Transplant. 25:2530–2537. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Masum MA, Ichii O, Hosny Ali Elewa Y,
Nakamura T, Otani Y, Hosotani M and Kon Y: Overexpression of
toll-like receptor 9 correlates with podocyte injury in a murine
model of autoimmune membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis.
Autoimmunity. 51:386–398. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Takano Y, Yamauchi K, Hayakawa K,
Hiramatsu N, Kasai A, Okamura M, Yokouchi M, Shitamura A, Yao J and
Kitamura M: Transcriptional suppression of nephrin in podocytes by
macrophages: Roles of inflammatory cytokines and involvement of the
PI3K/Akt pathway. FEBS Lett. 581:421–426. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Zhang Z, Niu L, Tang X, Feng R, Yao G,
Chen W, Li W, Feng X, Chen H and Sun L: Mesenchymal stem cells
prevent podocyte injury in lupus-prone B6.MRL-Faslpr mice via
polarizing macrophage into an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Nephrol
Dial Transplant. 34:597–605. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Sung SJ and Fu SM: Interactions among
glomerulus infiltrating macrophages and intrinsic cells via
cytokines in chronic lupus glomerulonephritis. J Autoimmun.
106:1023312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Zoja C, Wang JM, Bettoni S, Sironi M,
Renzi D, Chiaffarino F, Abboud HE, Van Damme J, Mantovani A,
Remuzzi G, et al: Interleukin-1 beta and tumor necrosis
factor-alpha induce gene expression and production of leukocyte
chemotactic factors, colony-stimulating factors, and interleukin-6
in human mesangial cells. Am J Pathol. 138:991–1003.
1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Latz E, Xiao TS and Stutz A: Activation
and regulation of the inflammasomes. Nat Rev Immunol. 13:397–411.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Fu R, Guo C, Wang S, Huang Y, Jin O, Hu H,
Chen J, Xu B, Zhou M, Zhao J, et al: Podocyte activation of NLRP3
inflammasomes contributes to the development of proteinuria in
lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 69:1636–1646. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Guo C, Fu R, Zhou M, Wang S, Huang Y, Hu
H, Zhao J, Gaskin F, Yang N and Fu SM: Pathogenesis of lupus
nephritis: RIP3 dependent necroptosis and NLRP3 inflammasome
activation. J Autoimmun. 103:1022862019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cai M, Zhou T, Wang X, Shang M, Zhang Y,
Luo M, Xu C and Yuan W: DC-SIGN expression on podocytes and its
role in inflammatory immune response of lupus nephritis. Clin Exp
Immunol. 183:317–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Haymann JP, Levraud JP, Bouet S, Kappes V,
Hagège J, Nguyen G, Xu Y, Rondeau E and Sraer JD: Characterization
and localization of the neonatal Fc receptor in adult human kidney.
J Am Soc Nephrol. 11:632–639. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Ichinose K, Ushigusa T, Nishino A,
Nakashima Y, Suzuki T, Horai Y, Koga T, Kawashiri SY, Iwamoto N,
Tamai M, et al: Lupus Nephritis IgG induction of
calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase IV expression in
podocytes and alteration of their function. Arthritis Rheumatol.
68:944–952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Bhargava R, Lehoux S, Maeda K, Tsokos MG,
Krishfield S, Ellezian L, Pollak M, Stillman IE, Cummings RD and
Tsokos GC: Aberrantly glycosylated IgG elicits pathogenic signaling
in podocytes and signifies lupus nephritis. JCI Insight.
6:e1477892021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Bruschi M, Moroni G, Sinico RA,
Franceschini F, Fredi M, Vaglio A, Cavagna L, Petretto A, Pratesi
F, Migliorini P, et al: Serum IgG2 antibody multi-composition in
systemic lupus erythematosus and in lupus nephritis (Part 2):
Prospective study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 60:3388–3397. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Mason LJ, Ravirajan CT, Rahman A,
Putterman C and Isenberg DA: Is alpha-actinin a target for
pathogenic anti-DNA antibodies in lupus nephritis? Arthritis Rheum.
50:866–870. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Renaudineau Y, Deocharan B, Jousse S,
Renaudineau E, Putterman C and Youinou P: Anti-alpha-actinin
antibodies: A new marker of lupus nephritis. Autoimmun Rev.
6:464–468. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Chen A, Lee K, D'Agati VD, Wei C, Fu J,
Guan TJ, He JC, Schlondorff D and Agudo J: Bowman's capsule
provides a protective niche for podocytes from cytotoxic CD8+ T
cells. J Clin Invest. 128:3413–3424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Reiser J, von Gersdorff G, Loos M, Oh J,
Asanuma K, Giardino L, Rastaldi MP, Calvaresi N, Watanabe H,
Schwarz K, et al: Induction of B7-1 in podocytes is associated with
nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 113:1390–1397. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Greka A, Weins A and Mundel P: Abatacept
in B7-1-positive proteinuric kidney disease. N Engl J Med.
370:1263–1266. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Khullar B, Balyan R, Oswal N, Jain N,
Sharma A, Abdin MZ, Bagga A, Bhatnagar S, Wadhwa N, Natchu UCM, et
al: Interaction of CD80 with Neph1: A potential mechanism of
podocyte injury. Clin Exp Nephrol. 22:508–516. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Coers W, Brouwer E, Vos JT, Chand A,
Huitema S, Heeringa P, Kallenberg CG and Weening JJ: Podocyte
expression of MHC class I and II and intercellular adhesion
molecule-1 (ICAM-1) in experimental pauci-immune crescentic
glomerulonephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 98:279–286. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Goldwich A, Burkard M, Olke M, Daniel C,
Amann K, Hugo C, Kurts C, Steinkasserer A and Gessner A: Podocytes
are nonhematopoietic professional antigen-presenting cells. J Am
Soc Nephrol. 24:906–916. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Li S, Liu Y, He Y, Rong W, Zhang M, Li L,
Liu Z and Zen K: Podocytes present antigen to activate specific T
cell immune responses in inflammatory renal disease. J Pathol.
252:165–177. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Okamoto A, Fujio K, Tsuno NH, Takahashi K
and Yamamoto K: Kidney-infiltrating CD4+ T-cell clones promote
nephritis in lupus-prone mice. Kidney Int. 82:969–979. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
May CJ, Welsh GI, Chesor M, Lait PJ,
Schewitz-Bowers LP, Lee RWJ and Saleem MA: Human Th17 cells produce
a soluble mediator that increases podocyte motility via signaling
pathways that mimic PAR-1 activation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
317:F913–F921. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Cheng Y, Yang X, Zhang X and An Z:
Analysis of expression levels of IL-17 and IL-34 and influencing
factors for prognosis in patients with lupus nephritis. Exp Ther
Med. 17:2279–2283. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Wang N, Gao C, Cui S, Qin Y, Zhang C, Yi
P, Di X, Liu S, Li T, Gao G and Zheng Z: Induction therapy
downregulates the expression of Th17/Tfh cytokines in patients with
active lupus nephritis. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 7:67–75.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Yan J, Li Y, Yang H, Zhang L, Yang B, Wang
M and Li Q: Interleukin-17A participates in podocyte injury by
inducing IL-1β secretion through ROS-NLRP3 inflammasome-caspase-1
pathway. Scand J Immunol. 87:e126452018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yuan DH, Jia Y, Hassan OM, Xu LY and Wu
XC: LPS-Treated podocytes polarize naive CD4(+) T Cells into Th17
and treg cells. Biomed Res Int. 2020:85879232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Chang A, Henderson SG, Brandt D, Liu N,
Guttikonda R, Hsieh C, Kaverina N, Utset TO, Meehan SM, Quigg RJ,
et al: In situ B cell-mediated immune responses and
tubulointerstitial inflammation in human lupus nephritis. J
Immunol. 186:1849–1860. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Tsokos GC: Autoimmunity and organ damage
in systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Immunol. 21:605–614. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Kolovou K, Laskari K, Roumelioti M,
Tektonidou MG, Panayiotidis P, Boletis JN, Marinaki S and Sfikakis
PP: B-cell oligoclonal expansions in renal tissue of patients with
immune-mediated glomerular disease. Clin Immunol. 217:1084882020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Senaldi G, Stolina M, Guo J, Faggioni R,
McCabe S, Kaufman SA, Van G, Xu W, Fletcher FA, Boone T, et al:
Regulatory effects of novel neurotrophin-1/b cell-stimulating
factor-3 (cardiotrophin-like cytokine) on B cell function. J
Immunol. 168:5690–5698. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Schmidt-Ott KM, Yang J, Chen X, Wang H,
Paragas N, Mori K, Li JY, Lu B, Costantini F, Schiffer M, et al:
Novel regulators of kidney development from the tips of the
ureteric bud. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:1993–2002. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Savin VJ, Sharma M, Zhou J, Gennochi D,
Fields T, Sharma R, McCarthy ET, Srivastava T, Domen J, Tormo A and
Gauchat JF: Renal and Hematological Effects of CLCF-1, a
B-Cell-Stimulating Cytokine of the IL-6 Family. J Immunol Res.
2015:7149642015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Dos Santos M, Poletti PT, Milhoransa P,
Monticielo OA and Veronese FV: Unraveling the podocyte injury in
lupus nephritis: Clinical and experimental approaches. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 46:632–641. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Andrews BS, Eisenberg RA, Theofilopoulos
AN, Izui S, Wilson CB, McConahey PJ, Murphy ED, Roths JB and Dixon
FJ: Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and
immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med.
148:1198–1215. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
McGaha TL and Madaio MP: Lupus Nephritis:
Animal modeling of a complex disease syndrome pathology. Drug
Discov Today Dis Models. 11:13–18. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Pawar RD, Castrezana-Lopez L, Allam R,
Kulkarni OP, Segerer S, Radomska E, Meyer TN, Schwesinger CM, Akis
N, Gröne HJ and Anders HJ: Bacterial lipopeptide triggers massive
albuminuria in murine lupus nephritis by activating Toll-like
receptor 2 at the glomerular filtration barrier. Immunology. 128 (1
Suppl):e206–e221. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Maibaum MA, Haywood ME, Walport MJ and
Morley BJ: Lupus susceptibility loci map within regions of BXSB
derived from the SB/Le parental strain. Immunogenetics. 51:370–372.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Pisitkun P, Deane JA, Difilippantonio MJ,
Tarasenko T, Satterthwaite AB and Bolland S: Autoreactive B cell
responses to RNA-related antigens due to TLR7 gene duplication.
Science. 312:1669–1672. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Jayne D, Rovin B, Mysler EF, Furie RA,
Houssiau FA, Trasieva T, Knagenhjelm J, Schwetje E, Chia YL,
Tummala R and Lindholm C: Phase II randomised trial of type I
interferon inhibitor anifrolumab in patients with active lupus
nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 81:496–506. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Parodis I and Houssiau FA: From sequential
to combination and personalised therapy in lupus nephritis: Moving
towards a paradigm shift? Ann Rheum Dis. 81:15–19. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Steiger S, Ehreiser L, Anders J and Anders
HJ: Biological drugs for systemic lupus erythematosus or active
lupus nephritis and rates of infectious complications. Evidence
from large clinical trials. Front Immunol. 13:9997042022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Markowitz GS, Nasr SH, Stokes MB and
D'Agati VD: Treatment with IFN-{alpha}, -{beta}, or -{gamma} is
associated with collapsing focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Clin
J Am Soc Nephrol. 5:607–615. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Liao R, Liu Q, Zheng Z, Fan J, Peng W,
Kong Q, He H, Yang S, Chen W, Tang X and Yu X: Tacrolimus protects
podocytes from injury in lupus nephritis partly by stabilizing the
cytoskeleton and inhibiting podocyte apoptosis. PLoS One.
10:e1327242015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Yasuda H, Fukusumi Y, Ivanov V, Zhang Y
and Kawachi H: Tacrolimus ameliorates podocyte injury by restoring
FK506 binding protein 12 (FKBP12) at actin cytoskeleton. FASEB J.
35:e219832021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Lee J, Park Y, Jang SG, Hong SM, Song YS,
Kim MJ, Baek S, Park SH and Kwok SK: Baricitinib attenuates
autoimmune phenotype and podocyte injury in a murine model of
systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. 12:7045262021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Rice WL, Van Hoek AN, Păunescu TG, Huynh
C, Goetze B, Singh B, Scipioni L, Stern LA and Brown D: High
resolution helium ion scanning microscopy of the rat kidney. PLoS
One. 8:e570512013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Howie JB and Helyer BJ: The immunology and
pathology of NZB mice. Adv Immunol. 9:215–266. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Hall AM, Ward FJ, Shen CR, Rowe C, Bowie
L, Devine A, Urbaniak SJ, Elson CJ and Barker RN: Deletion of the
dominant autoantigen in NZB mice with autoimmune hemolytic anemia:
Effects on autoantibody and T-helper responses. Blood.
110:4511–4517. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|