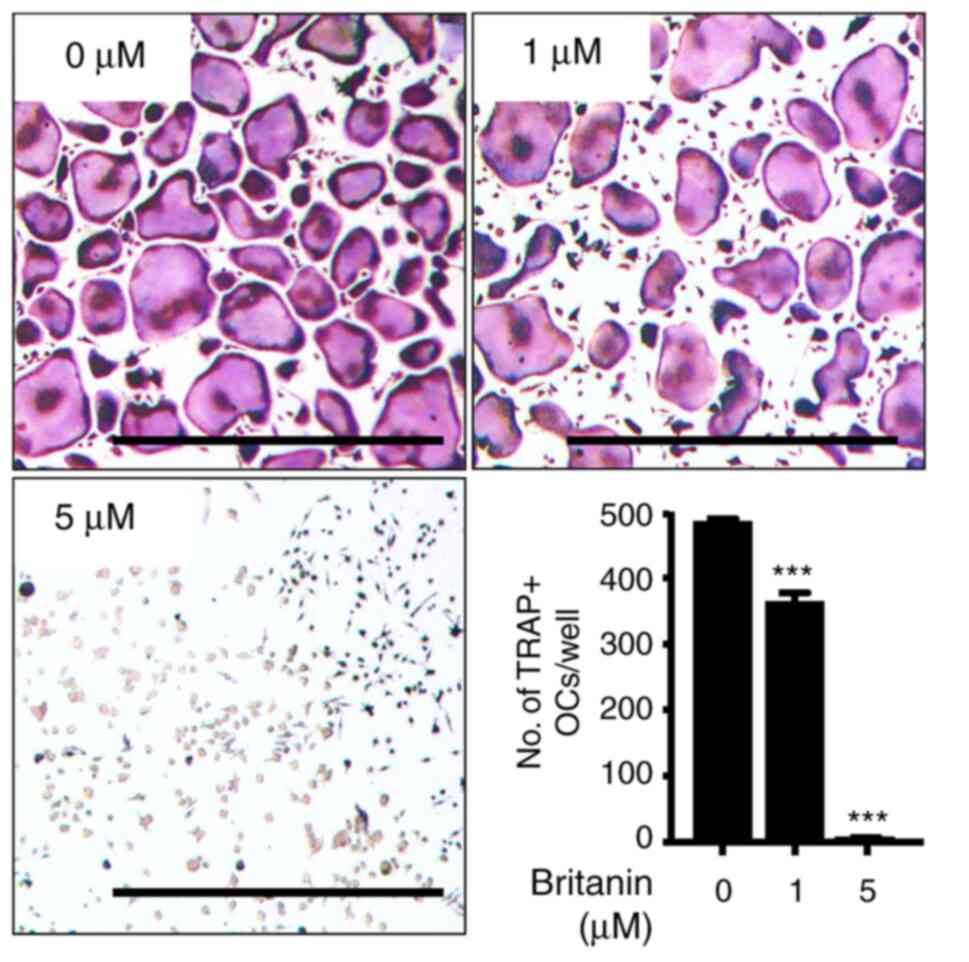
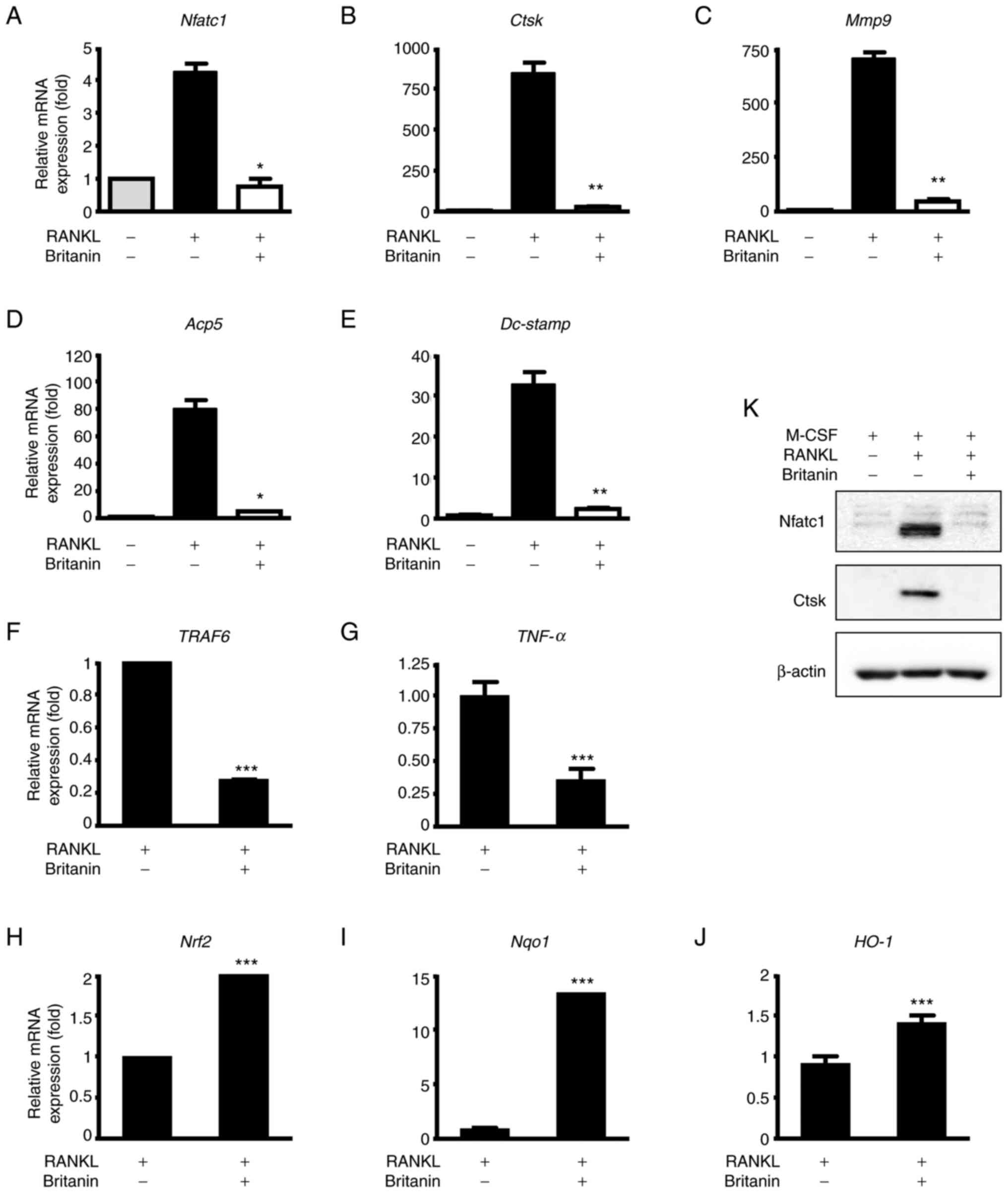
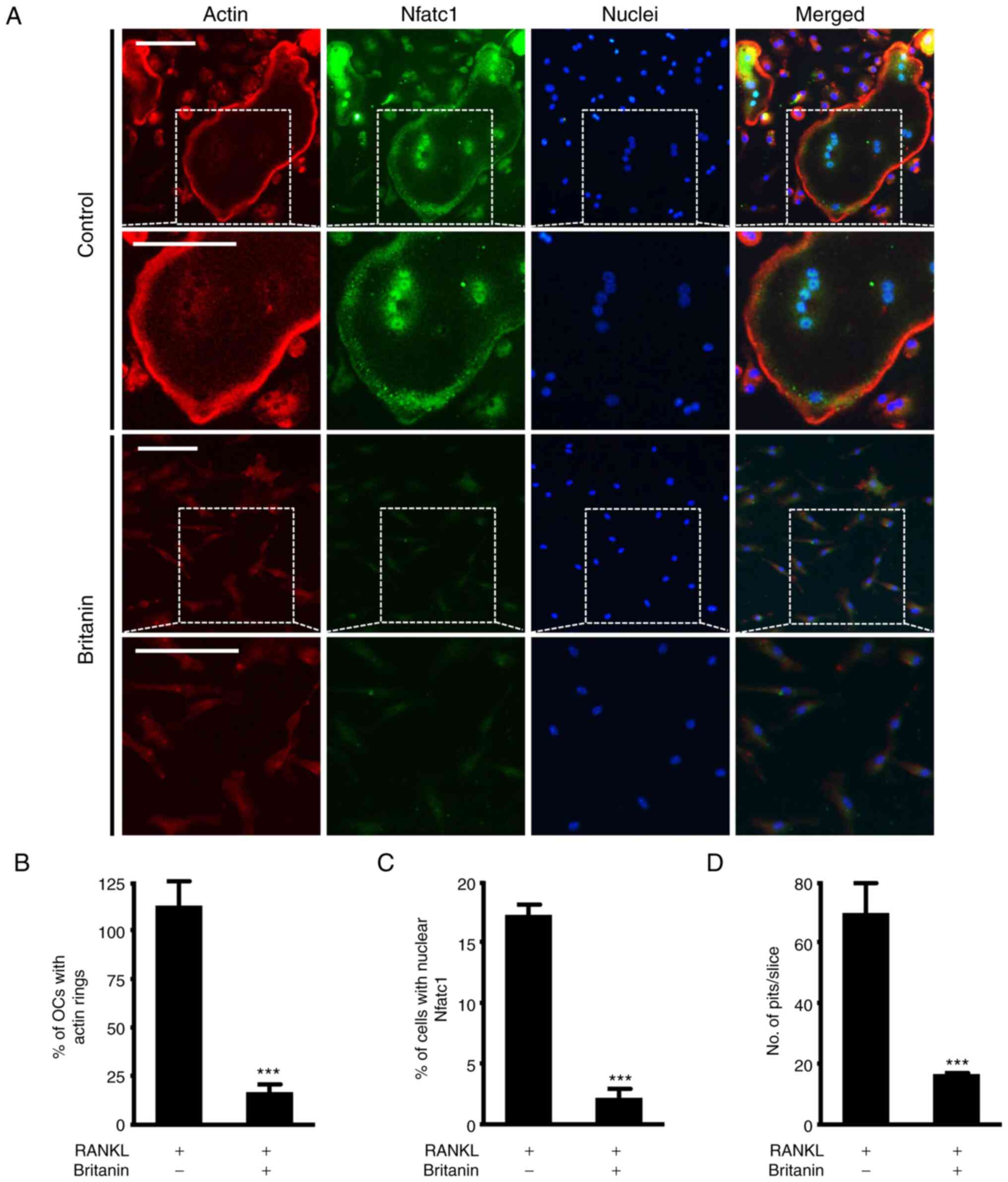
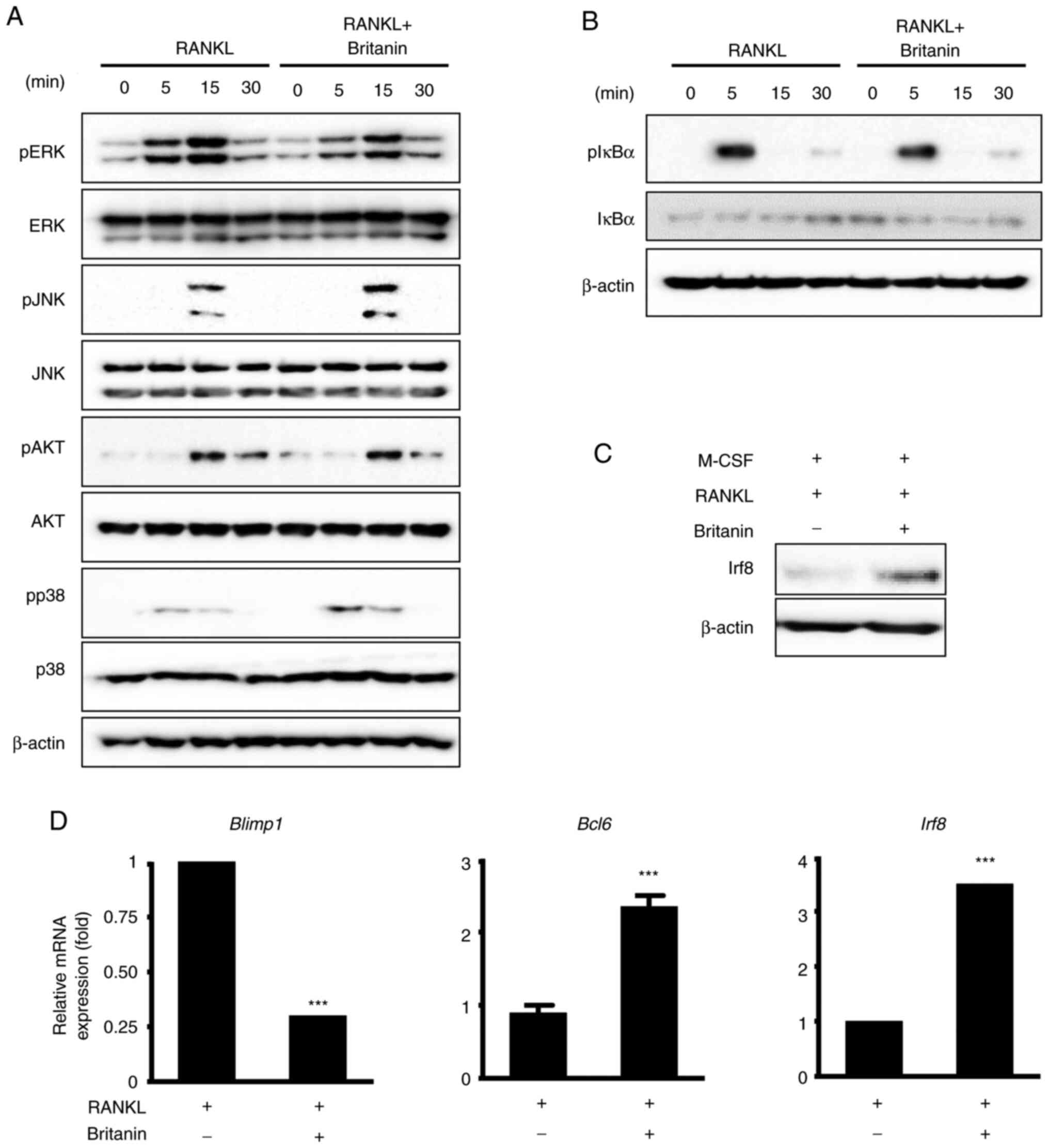
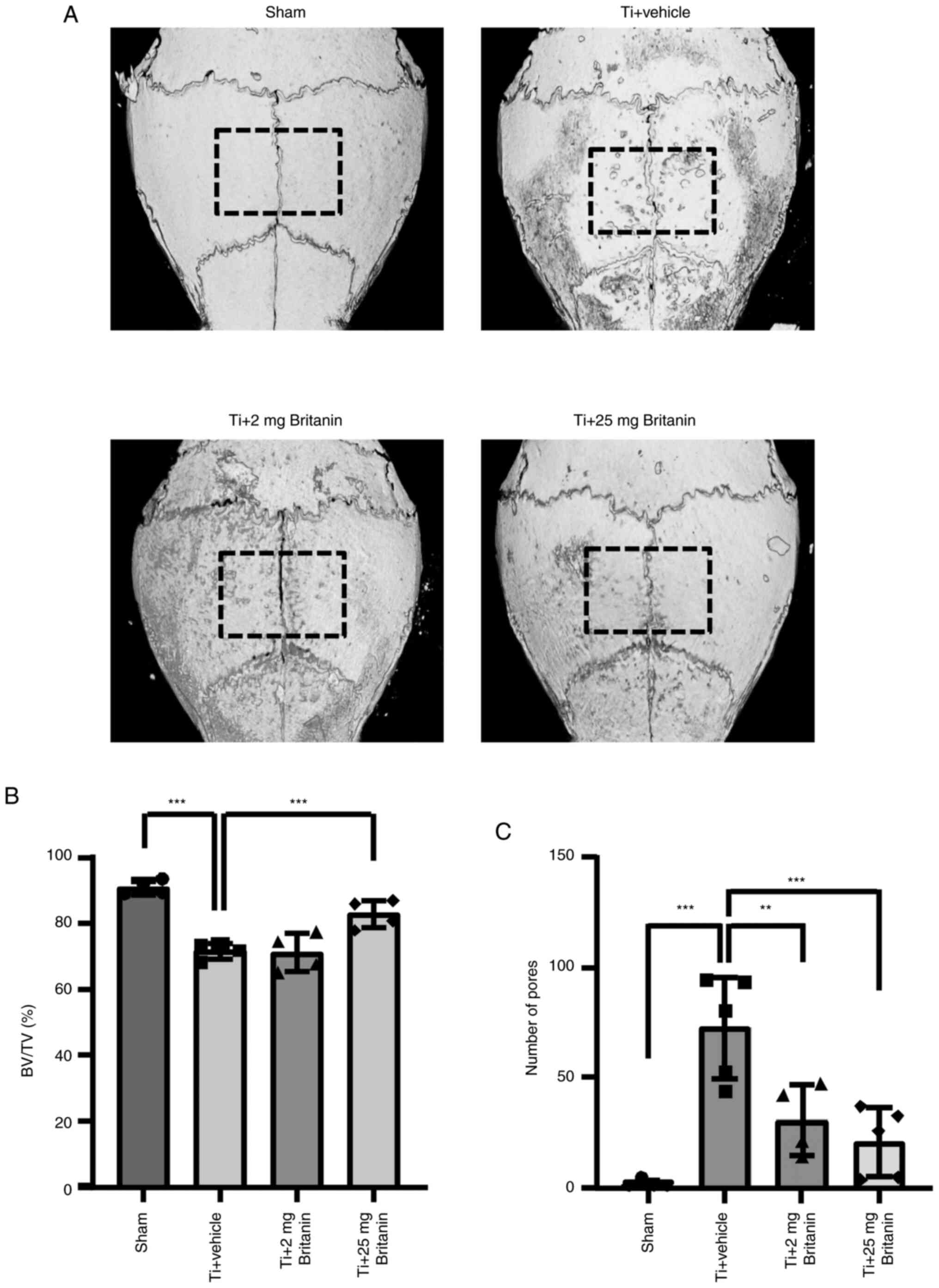
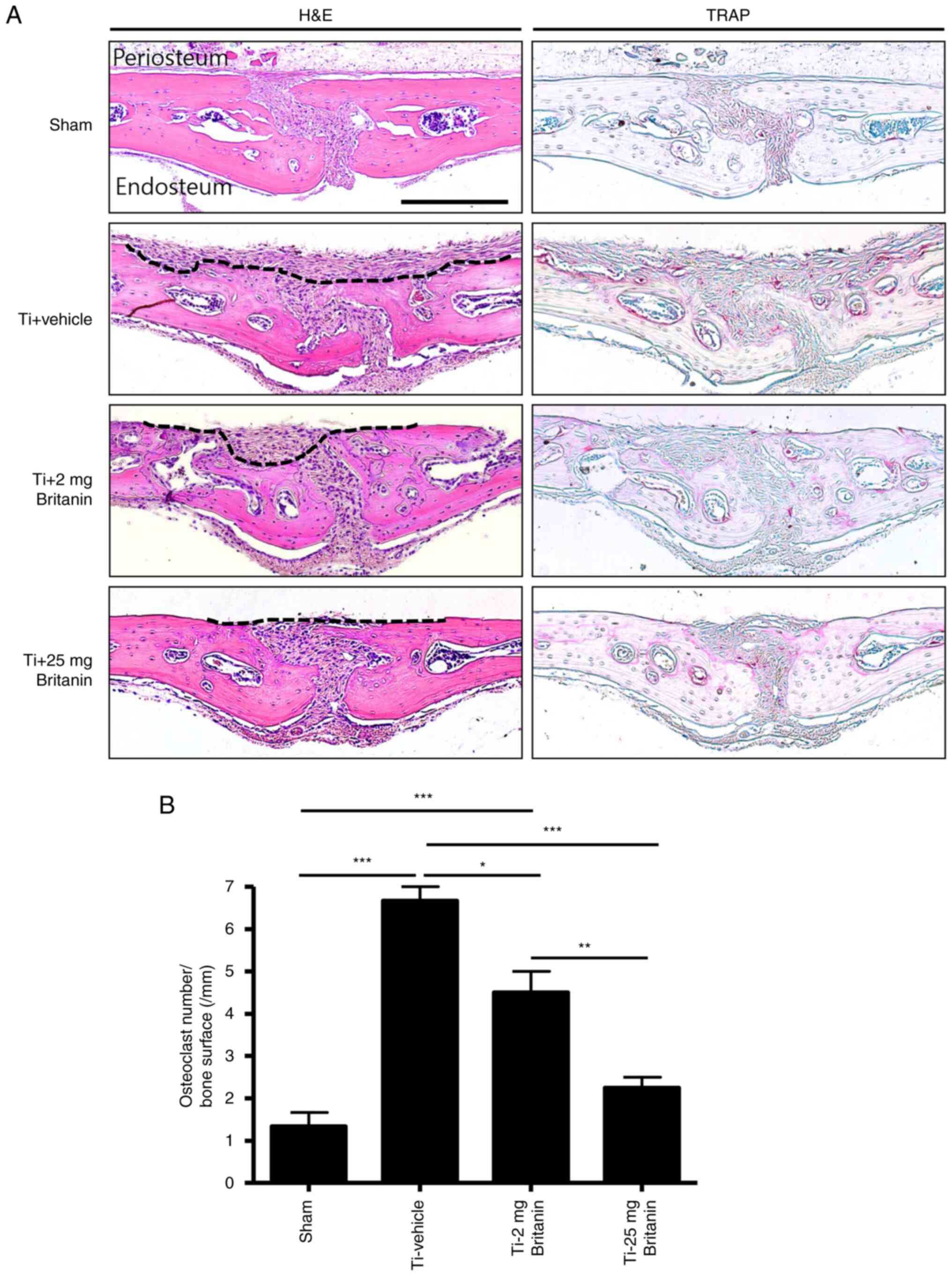
|
1
|
Eger M, Hiram-Bab S, Liron T, Sterer N,
Carmi Y, Kohavi D and Gabet Y: Mechanism and prevention of titanium
particle-induced inflammation and osteolysis. Front Immunol.
9:29632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Holding CA, Findlay DM, Stamenkov R, Neale
SD, Lucas H, Dharmapatni AS, Callary SA, Shrestha KR, Atkins GJ,
Howie DW and Haynes DR: The correlation of RANK, RANKL and TNFalpha
expression with bone loss volume and polyethylene wear debris
around hip implants. Biomaterials. 27:5212–5219. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Landgraeber S, Jäger M, Jacobs JJ and
Hallab NJ: The pathology of orthopedic implant failure is mediated
by innate immune system cytokines. Mediators Inflamm.
2014:1851502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tao H, Ge G, Liang X, Zhang W, Sun H, Li M
and Geng D: ROS signaling cascades: Dual regulations for osteoclast
and osteoblast. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 52:1055–1062.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Samelko L, Caicedo MS, Lim SJ, Della-Valle
C, Jacobs J and Hallab NJ: Cobalt-Cobalt-alloy implant debris
induce HIF-1α hypoxia associated responses: A mechanism for
metal-specific orthopedic implant failure. PLoS One. 8:e671272013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun YX, Xu AH, Yang Y and Li J: Role of
Nrf2 in bone metabolism. J Biomed Sci. 22:1012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Udagawa N: The mechanism of osteoclast
differentiation from macrophages: Possible roles of T lymphocytes
in osteoclastogenesis. J Bone Miner Metab. 21:337–343. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Boyle WJ, Simonet WS and Lacey DL:
Osteoclast differentiation and activation. Nature. 423:337–342.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Negishi-Koga T and Takayanagi H:
Ca2+-NFATc1 signaling is an essential axis of osteoclast
differentiation. Immunol Rev. 231:241–256. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Nishikawa K, Nakashima T, Hayashi M,
Fukunaga T, Kato S, Kodama T, Takahashi S, Calame K and Takayanagi
H: Blimp1-mediated repression of negative regulators is required
for osteoclast differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:3117–3122. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Park SJ, Huh JE, Shin J, Park DR, Ko R,
Jin GR, Seo DH, Kim HS, Shin HI, Oh GT, et al: Sirt6 cooperates
with Blimp1 to positively regulate osteoclast differentiation. Sci
Rep. 6:261862016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu Y, Li X, Park YN, Kwon O, Piao D, Chang
YC, Kim CH, Lee E, Son JK and Chang HW: Britanin suppresses
IgE/Ag-induced mast cell activation by inhibiting the Syk pathway.
Biomol Ther (Seoul). 22:193–199. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Park HH, Kim SG, Park YN, Lee J, Lee YJ,
Park NY, Jeong KT and Lee E: Suppressive effects of britanin, a
sesquiterpene compound isolated from Inulae flos, on mast
cell-mediated inflammatory responses. Am J Chin Med. 42:935–947.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim SG and Lee E, Park NY, Park HH, Jeong
KT, Kim KJ, Lee YJ, Jin M and Lee E: Britanin attenuates
ovalbumin-induced airway inflammation in a murine asthma model.
Arch Pharm Res. 39:1006–1012. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Park HH, Kim MJ, Li Y, Park YN, Lee J, Lee
YJ, Kim SG, Park HJ, Son JK, Chang HW and Lee E: Britanin
suppresses LPS-induced nitric oxide, PGE2 and cytokine production
via NF-κB and MAPK inactivation in RAW 264.7 cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 15:296–302. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shi K, Liu X, Du G, Cai X and Zhan Y: In
vivo antitumour activity of britanin against gastric cancer through
nuclear factor-κB-mediated immune response. J Pharm Pharmacol.
72:607–618. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li K, Zhou Y, Chen Y, Zhou L and Liang J:
A novel natural product, britanin, inhibits tumor growth of
pancreatic cancer by suppressing nuclear factor-κB activation.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 85:699–709. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu G, Zhu L, Yuan X, Chen H, Xiong R,
Zhang S, Cheng H, Shen Y, An H, Li T, et al: Britanin ameliorates
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inducing the Nrf2
protective pathway. Antioxid Redox Signal. 27:754–768. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lu H, Xiao H, Dai M, Xue Y and Zhao R:
Britanin relieves ferroptosis-mediated myocardial
ischaemia/reperfusion damage by upregulating GPX4 through
activation of AMPK/GSK3β/Nrf2 signalling. Pharm Biol. 60:38–45.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Piao D, Kim T, Zhang HY, Choi HG, Lee CS,
Choi HJ, Chang HW, Woo MH and Son JK: DNA topoisomerase inhibitory
activity of constituents from the flowers of Inula japonica.
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 64:276–281. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee YE, Park KS, Park EK, Im SU, Choi YH
and Song KB: Polycan suppresses osteoclast differentiation and
titanium particle-induced osteolysis in mice. J Biomed Mater Res B
Appl Biomater. 104:1170–1175. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ihn HJ, Lee T, Kim JA, Lee D, Kim ND, Shin
HI, Bae YC and Park EK: OCLI-023, a novel pyrimidine compound,
suppresses osteoclastogenesis in vitro and alveolar bone resorption
in vivo. PLoS One. 12:e01701592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen W, Li Z, Guo Y, Zhou Y, Zhang Z,
Zhang Y, Luo G, Yang X, Liao W, Li C, et al: Wear particles promote
reactive oxygen species-mediated inflammation via the nicotinamide
adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase pathway in macrophages
surrounding loosened implants. Cell Physiol Biochem. 35:1857–1867.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ihn HJ, Kim K, Cho HS and Park EK:
Pentamidine inhibits titanium particle-induced osteolysis in vivo
and receptor activator of nuclear factor-κB ligand-mediated
osteoclast differentiation in vitro. Tissue Eng Regen Med.
16:265–273. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu X, Qu X, Wu C, Zhai Z, Tian B, Li H,
Ouyang Z, Xu X, Wang W, Fan Q, et al: The effect of enoxacin on
osteoclastogenesis and reduction of titanium particle-induced
osteolysis via suppression of JNK signaling pathway. Biomaterials.
35:5721–5730. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Deng W, Huang Y, Li H, Chen C, Lin Y, Wang
M, Huang H, Liu T, Qin Q, Shao Y, et al: Dehydromiltirone inhibits
osteoclast differentiation in RAW264.7 and bone marrow macrophages
by modulating MAPK and NF-κB activity. Front Pharmacol.
13:10156932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xu Q, Zhan P, Li X, Mo F, Xu H, Liu Y, Lai
Q, Zhang B, Dai M and Liu X: Bisphosphonate-enoxacin inhibit
osteoclast formation and function by abrogating RANKL-induced JNK
signalling pathways during osteoporosis treatment. J Cell Mol Med.
25:10126–10139. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hyeon S, Lee H, Yang Y and Jeong W: Nrf2
deficiency induces oxidative stress and promotes RANKL-induced
osteoclast differentiation. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:789–799. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Agidigbi TS and Kim C: Reactive oxygen
species in osteoclast differentiation and possible pharmaceutical
targets of ROS-mediated osteoclast diseases. Int J Mol Sci.
20:35762019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Miyamoto T: Regulators of osteoclast
differentiation and cell-cell fusion. Keio J Med. 60:101–105. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Matsubara T, Kinbara M, Maeda T, Yoshizawa
M, Kokabu S and Takano Yamamoto T: Regulation of osteoclast
differentiation and actin ring formation by the cytolinker protein
plectin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 489:472–476. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang D, Jing J, Lou F, Li R, Ping Y, Yu
F, Wu F, Yang X, Xu R, Li F, et al: Evidence for excessive
osteoclast activation in SIRT6 null mice. Sci Rep. 8:109922018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tarpada SP, Loloi J and Schwechter EM: A
case of titanium pseudotumor and systemic toxicity after total hip
arthroplasty polyethylene failure. Arthroplast Today. 6:710–715.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tribst JPM, Werner A and Blom EJ: Failed
dental implant: When titanium fractures. Diagnostics (Basel).
13:21232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kim KT, Eo MY, Nguyen TTH and Kim SM:
General review of titanium toxicity. Int J Implant Dent. 5:102019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Suda N, Morita I, Kuroda T and Murota S:
Participation of oxidative stress in the process of osteoclast
differentiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1157:318–323. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lee NK, Choi YG, Baik JY, Han SY, Jeong
DW, Bae YS, Kim N and Lee SY: A crucial role for reactive oxygen
species in RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation. Blood.
106:852–859. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee HI, Lee GR, Lee J, Kim N, Kwon M, Kim
HJ, Kim NY, Park JH and Jeong W: Dehydrocostus lactone inhibits
NFATc1 via regulation of IKK, JNK, and Nrf2, thereby attenuating
osteoclastogenesis. BMB Rep. 53:218–222. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wang W, Liang X, Liu X, Bai J, Zhang W, Li
W, Wang T, Li M, Wu Z, Chen L, et al: NOX4 blockade suppresses
titanium nanoparticle-induced bone destruction via activation of
the Nrf2 signaling pathway. J Nanobiotechnology. 20:2412022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tomomura M, Suzuki R, Shirataki Y,
Sakagami H, Tamura N and Tomomura A: Rhinacanthin C inhibits
osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption: Roles of
TRAF6/TAK1/MAPKs/NF-κB/NFATc1 signaling. PLoS One. 10:e01301742015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Teitelbaum SL: Bone resorption by
osteoclasts. Science. 289:1504–1508. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Takayanagi H, Kim S, Koga T, Nishina H,
Isshiki M, Yoshida H, Saiura A, Isobe M, Yokochi T, Inoue J, et al:
Induction and activation of the transcription factor NFATc1 (NFAT2)
integrate RANKL signaling in terminal differentiation of
osteoclasts. Dev Cell. 3:889–901. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shi JH and Sun SC: Tumor tumor necrosis
factor receptor-associated factor regulation of nuclear factor κB
and mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Front Immunol.
9:18492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zeng Q, Zeng Y, Nie X, Guo Y and Zhan Y:
Britanin exhibits potential inhibitory activity on human prostate
cancer cell lines through PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling pathways. Planta
Med. 86:1401–1410. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Miyauchi Y, Ninomiya K, Miyamoto H,
Sakamoto A, Iwasaki R, Hoshi H, Miyamoto K, Hao W, Yoshida S,
Morioka H, et al: The Blimp1-Bcl6 axis is critical to regulate
osteoclast differentiation and bone homeostasis. J Exp Med.
207:751–762. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhao J, Kong HJ, Li H, Huang B, Yang M,
Zhu C, Bogunovic M, Zheng F, Mayer L, Ozato K, et al:
IRF-8/interferon (IFN) consensus sequence-binding protein is
involved in Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling and contributes to
the cross-talk between TLR and IFN-gamma signaling pathways. J Biol
Chem. 281:10073–10080. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao B, Takami M, Yamada A, Wang X, Koga
T, Hu X, Tamura T, Ozato K, Choi Y, Ivashkiv LB, et al: Interferon
regulatory factor-8 regulates bone metabolism by suppressing
osteoclastogenesis. Nat Med. 15:1066–1071. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|