Introduction
Ulcerative colitis (UC) is a chronic inflammatory
bowel disease, which causes numerous sporadic symptoms, including
abdominal pain, diarrhea, and bloody mucopurulent stool (1). The pathogenesis of UC, which is
generally considered to be influenced by multiple factors, is not
clearly understood.
The human microbiota comprises a wide array of
microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, protozoa, archaea, and fungi),
which are integral in multiple physiological processes of the host
(2). Microbial dysbiosis is
defined as a disturbance in the composition of the microbiome. A
state of imbalance in the human microbiota is often caused by
infection, inflammation, or immunity (3). Dysbiosis of the gut microbiome has
been reported in various inflammatory and immune-related diseases.
To date, several studies have focused on the role of the gut
microbiota in UC development (4–6).
Therefore, targeting the gut microbiota may be a potential
treatment for UC.
Recent developments in sequencing technologies and
bioinformatics have enabled researchers to explore the mechanisms
underlying the gut microbiota-mediated impact on the progress of
diseases, leading to developments in novel therapeutics, such as
prebiotics, probiotics, fecal transplantation, and drugs (7). Previous studies have focused on the
role of traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) in modulating gut
microbiota. Various studies have indicated that TCM can modulate
the composition and metabolism of the gut microbiota via direct and
indirect actions (8,9). Dracocephalum moldavica L.
(DML), a traditional ethnic medicine, possesses a wide range of
pharmacological properties such as antioxidative, cardioprotective,
anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities (10–12).
As DML contains a range of biologically active compounds that
belong to different chemical classes such as flavonoids, steroids,
glycosides, saponins, tannins, phenols, and essential oils
(13), it was speculated that it
may regulate the composition and metabolism of gut microbiota to
achieve its effects. Thus, the present study was designed to
explore the anti-colitis effect of DML in a dextran sulfate sodium
(DSS)-induced colitis model. Moreover, the mechanisms by which DML
exerted its beneficial effects on this disease were also
investigated by focusing on gut microbiota and inflammatory
pathways.
Materials and methods
Animals
A total of 24 male Sprague-Dawley rats (5–6 weeks
old, weighing 140–180 g) [Beijing Vital River Laboratory Animal
Technology Co., Ltd.; animal certificate no. SCXK (Jing) 2016-0006]
were housed individually in a ventilated cage, with free access to
food and water, at 23.0±2.0°C and a 12/12-h light/dark cycle.
Animals were acclimated to the laboratory environment for 1 week
before the experiments. The animal experiments were approved by the
Baotou Medical College Research and Ethics Review Committee
(approval no. 2021040).
Drug
The aerial parts of DML were obtained in the city of
Tongliao (Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China). A voucher
specimen (IMKLDRB-2022-01) was deposited in Inner Mongolia Key
Laboratory of Disease-Related Biomarkers, Baotou Medical College
(Baotou, Inner Mongolia, China). The samples were air-dried before
being ground into a fine powder. Next, DML extracts were prepared
as previously described (11).
Briefly, the plant powder was subjected to extraction twice with
65% ethanol for 120 min at 60°C. After removing the ethanol by
vacuum distillation, the obtained extracts were separated with
ethyl acetate using separating funnels.
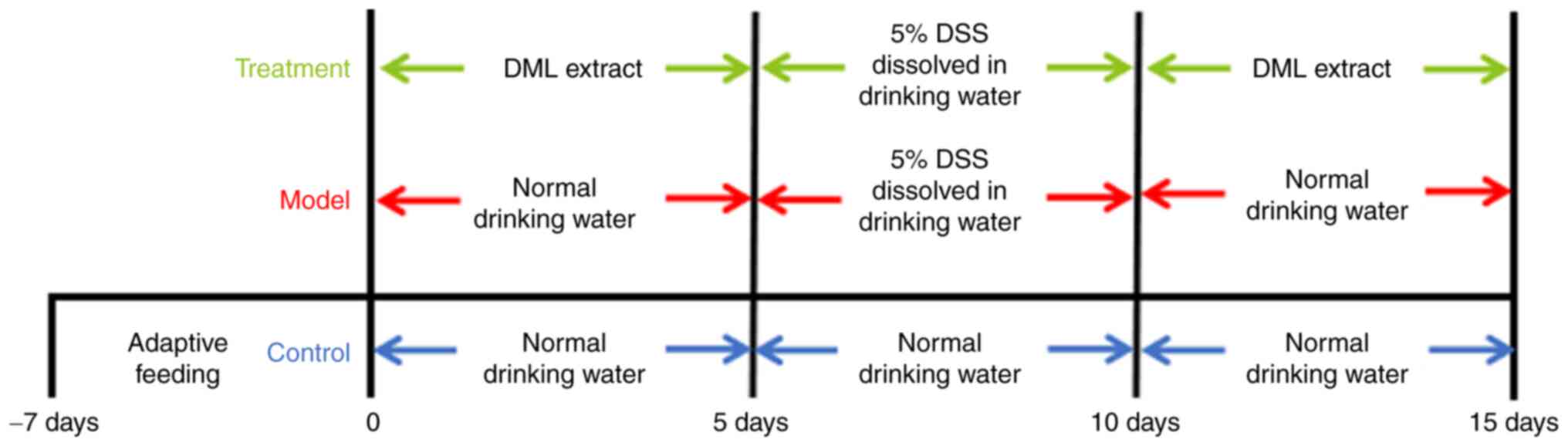
Experimental design
After a 1-week of acclimation, animals were randomly
allocated to one of three groups (n=8): Control, model, and
treatment. The control and model groups received normal drinking
water, while the treatment group received DML extract (400 mg/kg)
by oral gavage for 5 days. On day 6, 5% DSS dissolved in drinking
water was administered to the rats in the model and treatment
groups to induce UC. From days 11–15, the control and model groups
were administered normal drinking water only, while the treatment
group received DML extract at a dose of 400 mg/kg by oral gavage.
At the end of the experiment, the rats were euthanized with an
overdose of pentobarbital sodium (200 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal
injection. Fresh feces were collected and stored at −80°C for
future use. The length of the colon was determined, and then the
colon was removed and washed with ice-cold PBS. One part of colon
tissue was rapidly frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C
until required, and the remaining parts were fixed in 10% formalin
for 24 h at room temperature for histological examination.
Evaluation of the disease activity
index
The body weight, gross rectal bleeding, and stool
consistency of rats were monitored daily. A disease activity index
(DAI) score, an indicator of disease activity, was calculated by
grading on a scale of 0–4 using the following parameters: weight
loss (0, normal; 1, 0–5%; 2, 5–10%; 3, 10–20%; 4, >20%), stool
consistency (0, normal; 2, loose stools; 4, watery diarrhea) and
the occurrence of gross blood in the stool (0, negative; 4,
positive). DAI was determined by averaging numerical scores of
weight loss, stool consistency and bleeding.
Histological analysis
The rat colon was fixed in 10% buffered formalin for
24 h at room temperature, embedded in paraffin, and stained with
hematoxylin and eosin (Beyotime Institute of Biotechnology)
according to the manufacturer's instructions. Each sample was
assessed under light microscopy at ×200 magnification (Nikon
Corporation).
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR) analysis
Total RNA was extracted from frozen tissue using an
RNAprep Pure Tissue Kit according to the manufacturer's protocol
(Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd.). RNA concentration and quality were
evaluated using a NanoDrop 2000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop
Technologies; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). First-strand cDNA
was performed on total RNA using a Prime Script RT MasterMix
according to the manufacturer's protocol (Takara Bio, Inc.). The
mRNA levels of IL-17 and TNF-α were measured by qPCR analysis using
TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (Takara Bio, Inc.). Each sample was
assayed in triplicate on an ABI PRISM 7500 System (Applied
Biosystems; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The thermal cycler
parameters were as follows: Denaturation at 95°C for 30 sec;
followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 5 sec and
combined annealing/extension at 60°C for 30 sec. The relative
quantification of genes was performed using the 2−ΔΔCq
method, with β-actin as an internal reference for normalization.
The sequences of primers are listed in Table SI (14).
ELISA
Colon tissues were homogenized in ice-cold PBS. The
homogenates were centrifuged at 3,000 × g for 10 min at 4°C and the
supernatants were then assayed to evaluate the levels of IL-17
(cat. no. M17F0) and TNF-α (cat. no. RTA00) using ELISA kits
according to the manufacturer's protocols (R&D Systems,
Inc.).
Fecal DNA extraction, metagenomic
sequencing, and analysis
MoBio Power Fecal DNA Isolation kit (MO BIO
Laboratories, Inc.) was used for DNA extraction according to the
manufacturer's instructions. The quality of the extracted DNA was
measured using 1% agarose gel electrophoresis (Beijing Solarbio
Science & Technology Co., Ltd.). DNA libraries were constructed
using TruSeq DNA LT Sample Prep Kit v2 according to the
manufacturer's protocol (Illumina, Inc.). Metagenomic sequencing
was performed on a HiSeq 3000 platform (Illumina, Inc.).
Bioinformatics analysis was performed as previously described
(15).
Network pharmacology analysis
Network pharmacology analysis was performed as
previously described (16).
Briefly, active ingredients of DML were collected from the PubChem
database (pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). The potential UC-related
targets were searched in the Human Gene Database (GeneCards,
http://www.genecards.org/) using the
search term ‘ulcerative colitis’. The potential protein targets of
active ingredients and UC-related targets were imported into a Venn
diagram web tool (https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/), and
common targets were identified as UC-related targets of the active
ingredients (Table SII) for
further investigation. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
(KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis (17) was performed using the Database for
Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery database
(https://david.ncifcrf.gov/) (18,19).
Western blotting
Colon tissue protein was extracted using
Pierce™ RIPA Buffer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.).
The protein concentration was measured using a Pierce™
BCA Protein Assay Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). Total
protein (60 µg) was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE. After transferring
the proteins onto PVDF membranes (MilliporeSigma), the membranes
were blocked with 5% non-fat milk and incubated overnight at 4°C
with antibodies against Toll-like receptor (TLR)4 (cat. no.
ab217274, 1:1,000, Abcam), MyD88 (cat. no. ab219413, 1:1,000,
Abcam), NF-κB p65 (cat. no. ab16502, 1:1,000, Abcam), phospho-NF-κB
p65 (cat. no. ab76302, 1:1,000, Abcam), and GAPDH (cat. no.
ab313650, 1:2,500, Abcam). After washing 5 times in TBS containing
Tween 20, each membrane was subsequently incubated with HPR-labeled
IgG (cat. no. ab6721, 1:10,000, Abcam) at room temperature for 2 h.
Signals were visualized using an enhanced chemiluminescence reagent
(Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.). The ratio of the gray value of TLR4
and MyD88 to GAPDH, or the ratio of the gray value of phospho-NF-κB
p65 to NF-κB p65, was analyzed using Image Lab software version
6.1.0 (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.).
Statistical analysis
All data were analyzed using SPSS 22.0 software (IBM
Corp.). After performing a normality test, statistical significance
was evaluated using an unpaired Student's t-test or one-way ANOVA
followed by a Student-Newman-Keul's test. Data are presented as the
mean ± SD. P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically
significant difference.
Results
DML extract administration attenuates
DSS-induced rat colitis
The experimental design to assess the effects of DML
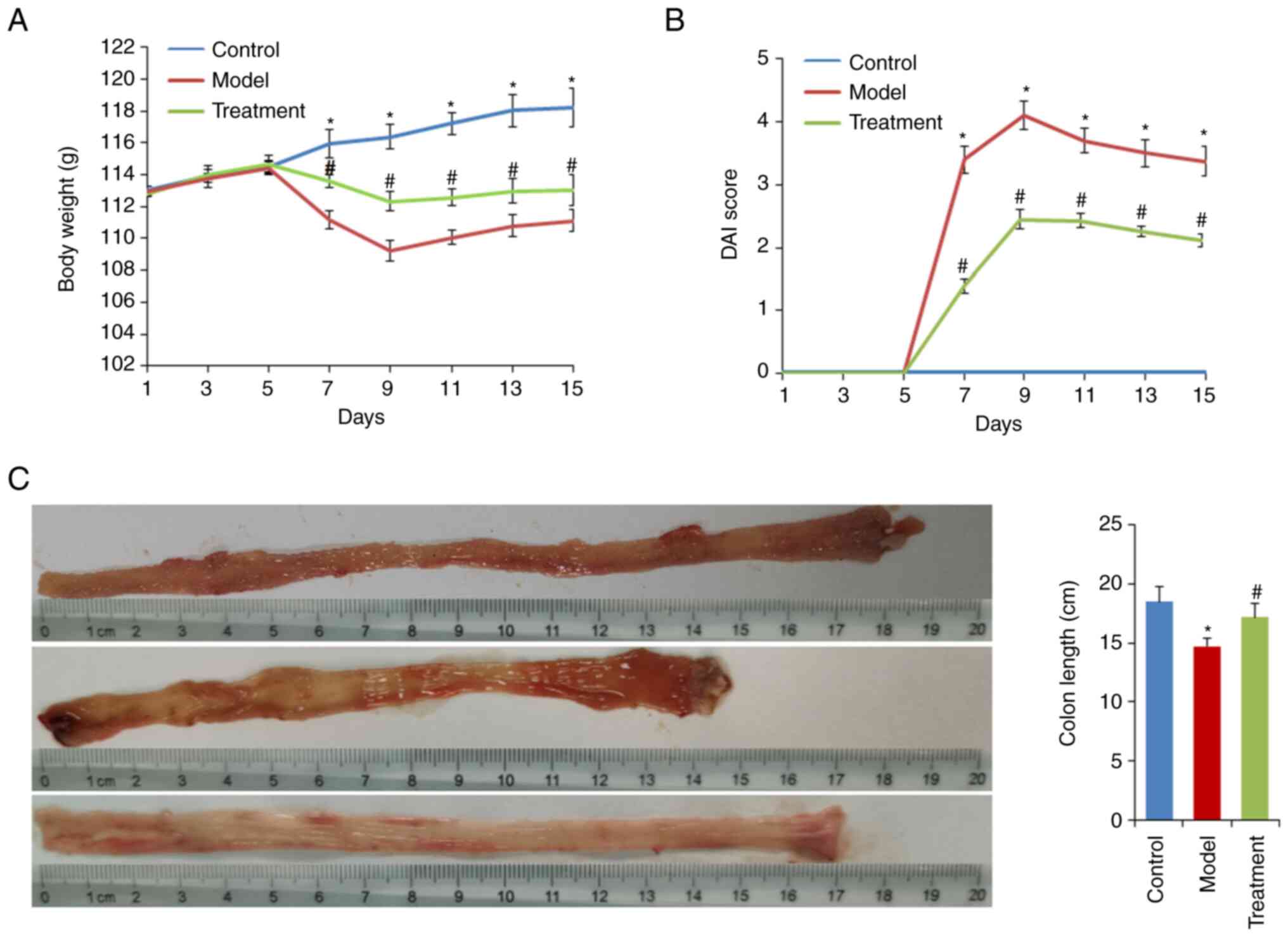
extract on DSS-induced rats is shown in Fig. 1. A steady increase in the body
weight of all three groups was observed on the first 5 days of the
experiment (Fig. 2A).
Subsequently, the rats were administered water containing 5% DSS.
The model group showed a significant reduction in body weight and
an increase in DAI score compared with the control group
(P<0.05). The maximum body weight loss was 12.7% at the end of 5
days after DSS administration.
DML extract administration alleviated body weight
loss and reduced the DAI score (both P<0.05; Fig. 2A and B). Additionally, DML extract
administration significantly attenuated DSS-induced colonic
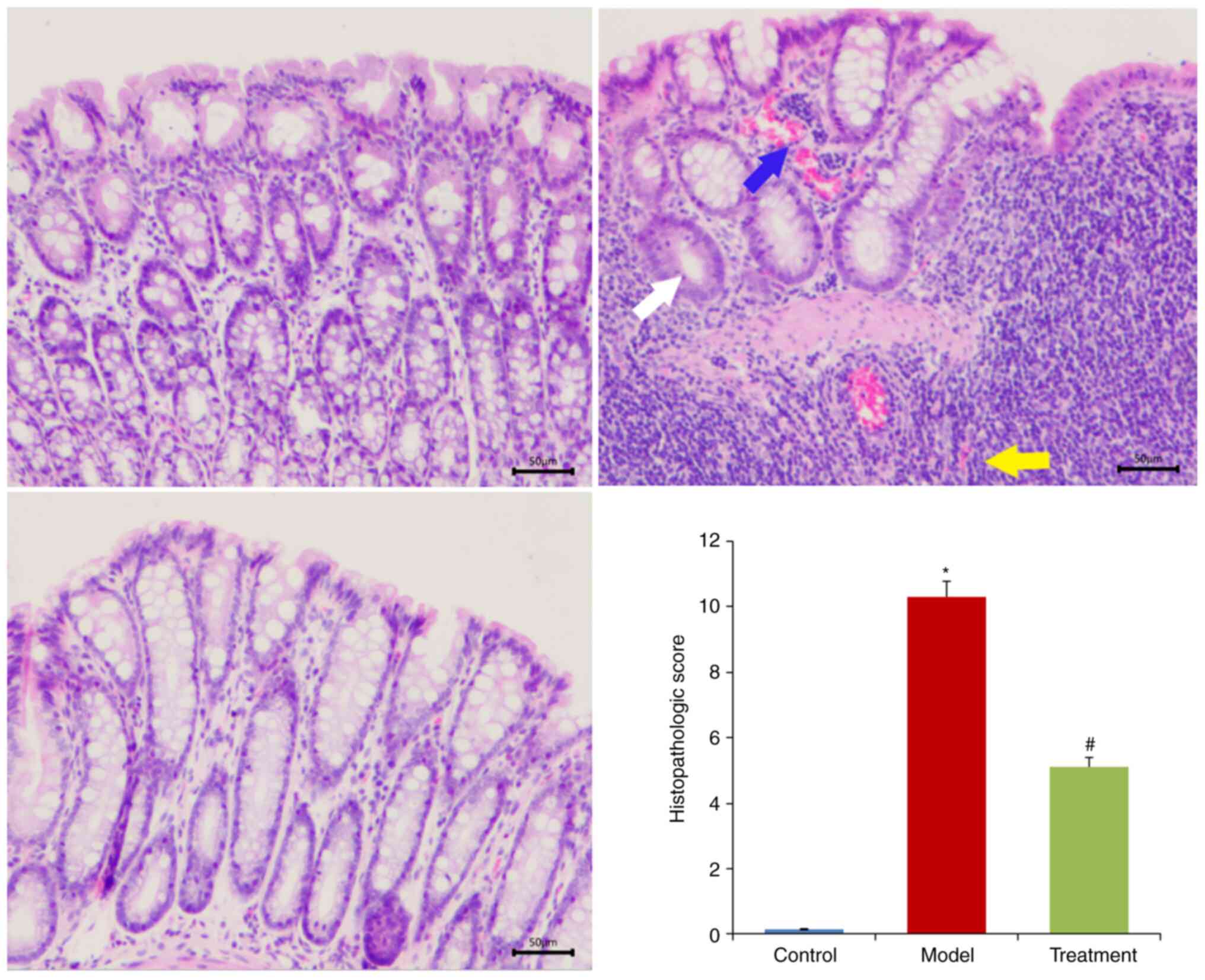
shortening (Fig. 2C). Histological
analysis showed that DSS treatment destroyed crypt structure and
goblet cells and induced inflammatory cell infiltration. However,
DML extract administration attenuated the DSS-induced tissue
morphological changes (Fig.
3).
DML extract administration inhibits
the expression of TNF-α and IL-17
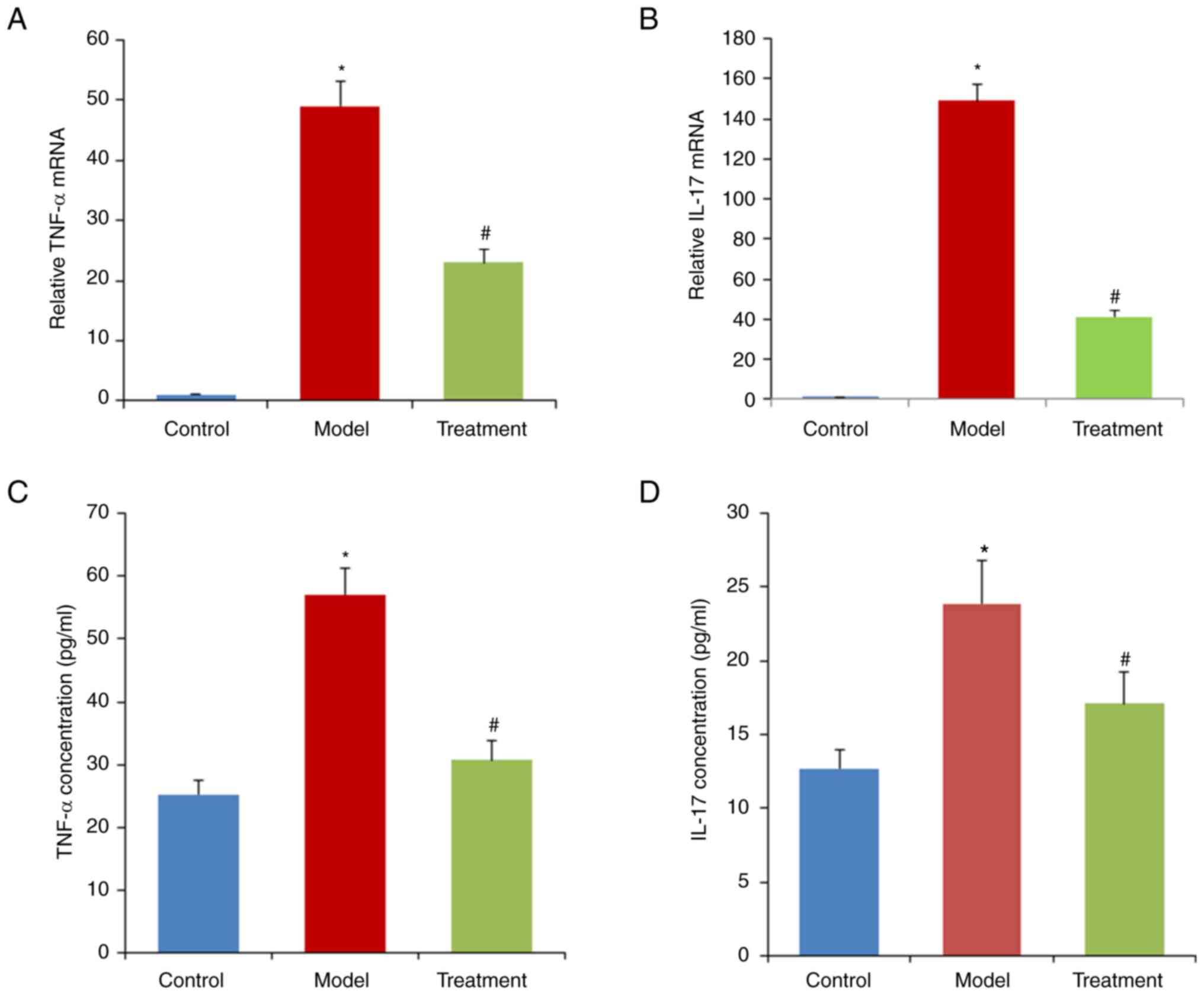
The relative expression levels of TNF-α and IL-17
were significantly increased in the model group compared with the
control group (P<0.05; Fig. 4).
By contrast, the increase in TNF-α and IL-17 induced by DSS was
alleviated in the treatment group (P<0.01; Fig. 4).
DML extract administration alters the
gut microbiota profile in rats with DSS-induced UC
The results from the species accumulation curve and
rank abundance curves indicated that the sequencing depth was
sufficient to provide coverage for the majority of microbial
species in each sample (Figs. S1
and S2). As shown in Fig. 5A, the dominant phyla were
Firmicutes and Actinobacteria. At the genus level
(Fig. 5B), the relative abundance
of 4 genera, namely Romboutsia, Lactobacillus, Clostridium sensu
stricto, and Allobaculum, was enriched in the three
groups. Compared with the control group, the model group had an
over-representation of Romboutsia and a lower abundance of
Lactobacillus (P<0.05). DML extract administration
prevented the decrease in Lactobacillus as well as the
increase in Romboutsia (Fig.
5B).
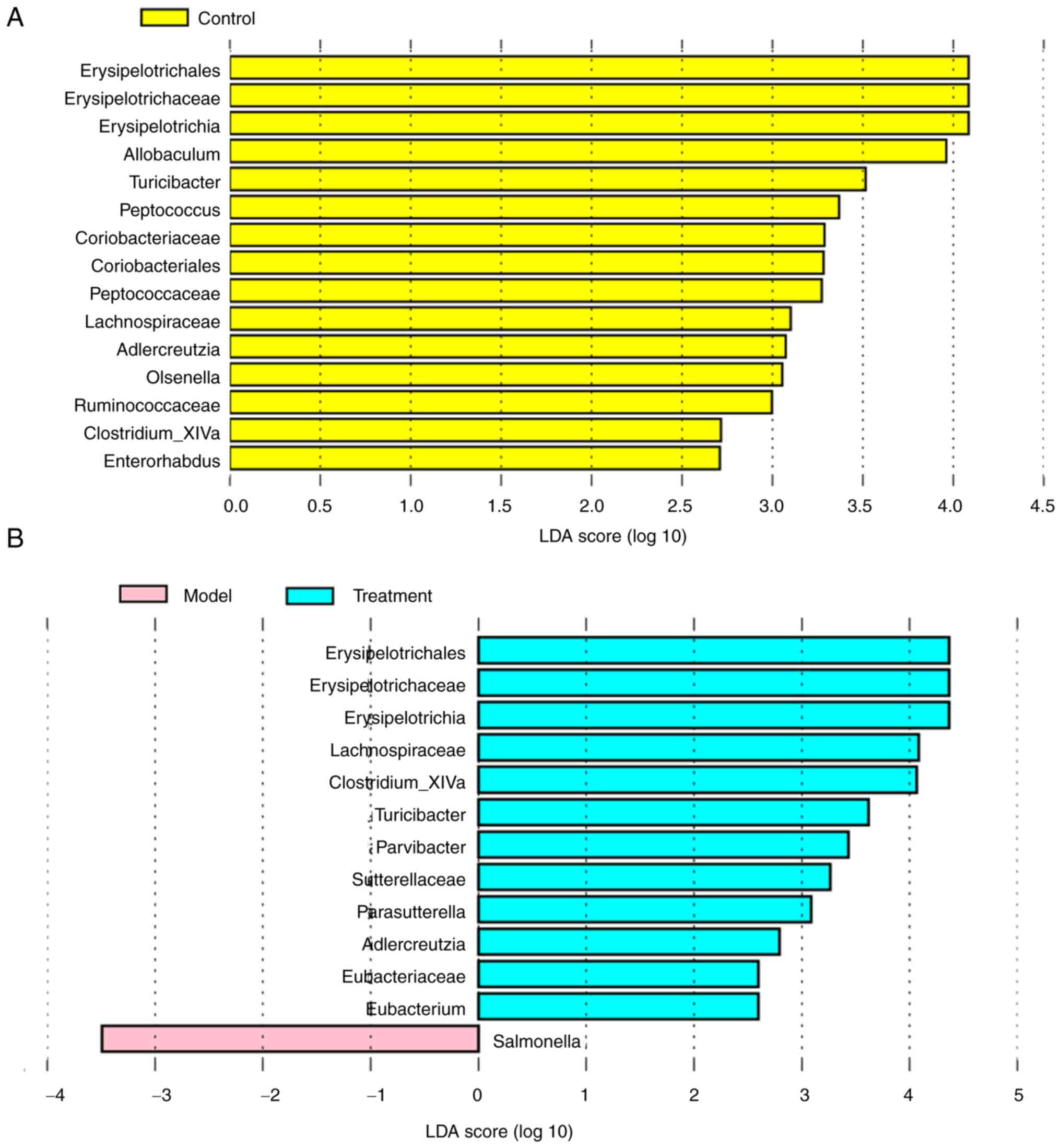
The linear discriminant analysis (LDA) effect size
(LEfSe) analysis showed that 15 taxa were enriched in the model and
control groups (Fig. 6A). The
control rats primarily showed higher enrichment of
Coriobacteriaceae, Olsenella, Erysipelotrichia, Allobaculum,
Ruminococcaceae, Clostridium_XlVa, Turicibacter,
Erysipelotrichaceae, Peptococcaceae, Lachnospiraceae,
Enterorhabdus, Erysipelotrichales, Adlercreutzia,
Coriobacteriales, and Peptococcus. Based on the results
of LEfSe analysis, taxa with significantly different abundances
between the model group and the treatment group were also observed
(Fig. 6B). The model group had
higher scores for Salmonella. However, the proportion of
Erysipelotrichia, Clostridium_XlVa, Turicibacter,
Erysipelotrichaceae, Lachnospiraceae, Erysipelotrichales, and
Adlercreutzia in the treatment group was similar to that of
the control rats, indicating that the DML extract administration
improves the imbalance of intestine microbiota composition in
DSS-induced UC rat to a normal-like level.
DML extract administration regulates
the inflammatory pathway in rats with DSS-induced UC
Upon analyzing PubChem database, 31 active
ingredients of DML were identified. Among them, 16 active
ingredients were selected for identifying potential targets
(Table SII). Candidate targets of
active ingredients in DML and UC disease were searched. A total of
194 targets related to active components in DML, 7,855 targets
related to UC, and 170 targets overlapping between active
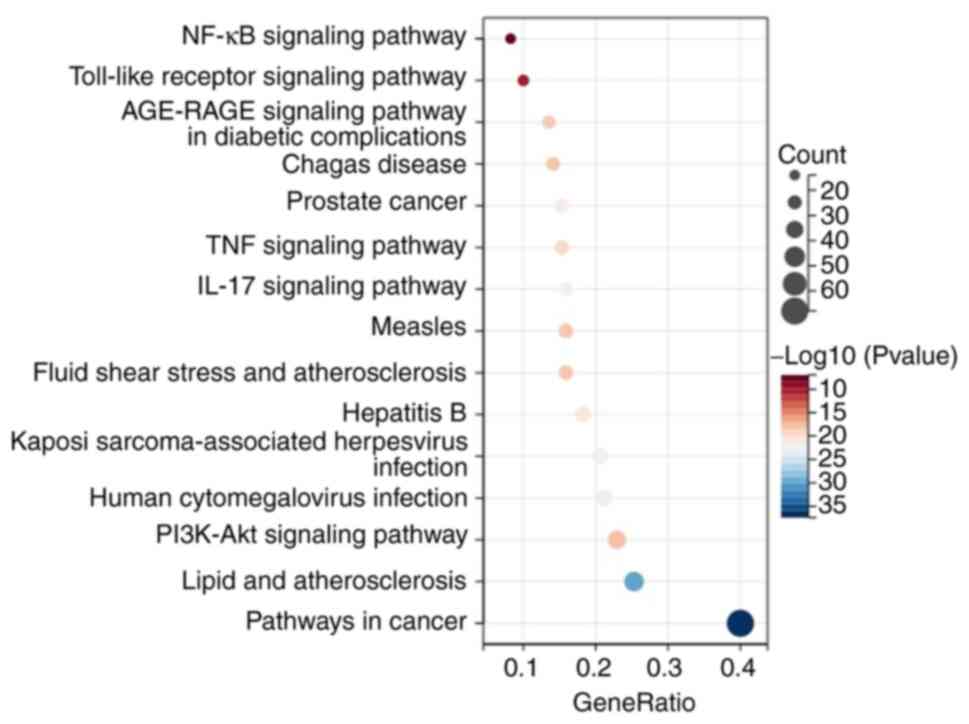
components in DML and UC were found (Figs. S3 and 4). KEGG annotation showed that the
common targets of active components in DML and UC were primarily
involved in the inflammatory response and immune regulation, such
as the NF-κB, IL-17, TNF, and TLR signaling pathways (Fig. 7). These results suggested that DML
extract alleviated UC by controlling pro-inflammatory pathways in
response to gut microbiota imbalances.
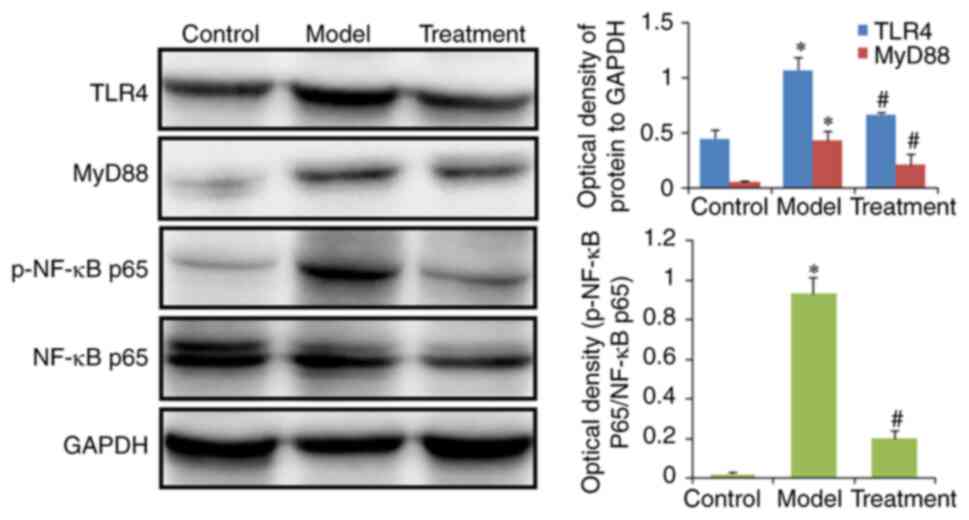
Furthermore, western blotting was performed to
verify the effect of DML extract on the TLR and NF-κB signaling
pathways. The results demonstrated that the protein expression
levels of TLR4, MyD88, and phosphorylated NF-κB p65 in colon
tissues were higher in the model group than in the control group.
However, these changes were reversed in the treated group (Fig. 8).
Discussion
The pathogenesis of UC is complex and involves
imbalances in the gut microbiota and disorders of immune
regulation. DSS-induced animal models of experimental colitis have
been widely used for investigating the pathological mechanisms of
UC (20–22). Thus, the current study investigated
the effect of DML extract on colitis in a rat model. Microbial
imbalances were evaluated in the absence and presence of DML
extract treatment. Next, network pharmacology analysis was
performed to determine the mechanism by which DML extract was
involved in UC regulation.
To study the alleviating effect of DML extract on
colitis, an experimental colitis model was established in rats by
feeding them with 5% DSS. Oral DML extract intervention alleviated
DSS-induced colitis, as evidenced by the marked increase in the
area of goblet cells, relieved infiltration of inflammatory cells,
and decreased the presence of colonic mucosal ulcers. These
experimental results indicate that DML extract has a therapeutic
effect against DSS-induced UC in rats.
DSS can induce a severe immune response in the
intestinal mucosa and can induce the release of a large number of
inflammatory mediators such as IL-17 and TNF-α (23). It has been reported that the
induction of inflammatory mediators promotes the occurrence and
development of UC (24).
Therefore, the present study investigated the effects of DML
extract on inflammatory factors in the colon of rats with UC
induced by DSS. Decreased expression of IL-17 and TNF-α after DML
extract treatment was observed. These data indicate that DML
extract suppresses inflammatory responses and thereby exerts a
protective effect against DSS-induced UC in rats.
The interplay between the gut microbiota and the
host immune system plays a crucial role in modulating intestinal
function. Multiple studies have shown that natural active products
lead to alterations in the intestinal microbiota and improve
DSS-induced colitis symptoms (25,26).
The current study aimed to determine whether DML extract could
affect the gut microbiota in UC rats. Analysis of the gut
microbiota indicated that administration of DML extract
significantly increased the number of Lactobacillus. This is
in agreement with another study, which reported that
Lactobacillus could alleviate DSS-induced UC (27). The current study also showed that
the relative abundance of Romboutsia was markedly increased
after chronic DSS induction. Romboutsia has been identified
as a potential pathobiont in UC (28). However, DML extract treatment led
to higher counts of Lactobacillus and lower counts for
Romboutsia, indicating that DML extract administration
restored the imbalance in the gut microbiota in rats with UC.
The LEfSe algorithm has been widely used to analyze
bacteria in different groups. The present study showed that
Salmonella played an important role in DSS-treated rats. It
has been reported that Salmonella infection promotes the
recurrence of UC (29). It is well
established that a variety of Lactobacilli can effectively
alleviate UC, which is possibly related to the upregulation of
short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) and balancing of profiles of
intestinal microbiota (30,31).
A previous study showed that Lactobacillus reduced the
release of inflammatory factors (TNF-α and IL-17) in mice with
DSS-induced colitis (32).
Lactobacilli suppressed the production of inflammatory
factors through the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in the colon
tissues of mice with UC (33). The
current findings showed that DML extract could decrease the levels
of TNF-α and IL-17 in rats with colitis. Thus, the involvement of
the TLR4/NF-κB pathway in the anti-colitis effects of DML extract
was next investigated.
In the present study, network pharmacology
approaches were used to explore the potential mechanism by which
DML extract relieves colitis in rats. Ingredients-targets network
analysis revealed that luteolin, rosmarinic acid, oleanolic acid,
ursolic acid, apigenin, acacetin, kaempferol, isorhamnetin, and
other active components could regulate multiple targets. Previous
studies have found that these components have potential therapeutic
effects on UC (34–40). The findings suggested that these
active ingredients may be related to the anti-colitis effects of
DML in UC. To explore the mechanism by which DML extract relieves
colitis in rats, KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was carried out
for the 170 targets of DML with activity in UC. The results
revealed pathways associated with UC included the NF-κB, IL-17,
TNF, and TLR signaling pathways. TLR4 is a specific receptor for
lipopolysaccharides (LPS) derived from Gram-negative bacteria and
is a key regulatory factor in colon immune inflammation regulation
(41). It has been reported that
microbiota and their metabolites can inhibit the TLR4 signaling
pathway. Downregulating TLR4 decreased the expression of NF-κB, and
reduced the expression and release of inflammatory factors, which
led to the alleviation of UC (42). To further verify whether DML
extract can affect the expression of TLR4/NF-κB, the expression of
TLR4, MyD88, and NF-κB in the colon was examined. The results
confirmed that TLR4/NF-κB signaling was downregulated by DML
extract. These results agree with a previous report, which
demonstrated that DML extract could exert anti-inflammatory effects
via downregulation of the NF-κB signaling pathway (43).
Taken together, intestinal microbiota dysbiosis in
rats with colitis may result in increased LPS production, causing
intestinal inflammation by activating TLR4 and consequently
upregulating cytokine secretion. DML extract reshaped the profile
of the gut microbiota and its metabolites (such as SCFAs), thereby
suppressing LPS-induced TLR4/NF-κB signaling, as well as the
production of the cytokines, TNF-α and IL-17, to alleviate
DSS-induced UC damage. In the present study, there was no direct
evidence of gut microbiota regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling.
However, the present study showed that gut microbiota can regulate
TLR4/NF-κB signaling and the release of inflammatory mediators
(44).
In summary, the current results suggest that DML
extract may mediate inflammatory regulation through the intestinal
flora and TLR4-related signaling pathways to exert its anti-colitis
effects. However, the exact mechanism of this effect requires
further investigation. The present findings offer alternative
treatment strategies for UC by using natural medicines.
Supplementary Material
Supporting Data
Supporting Data
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the National Natural Science
Foundation of China (grant nos. 82060084, 82260092, and 82170296),
and the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region Science and Technology
Innovation Guidance Project (grant no. CXYD2021BT02).
Authors' contributions
SG, WB and HY designed the experiments. SG and WB
performed the experiments. WB and ZW participated in data curation.
HY, ZW, and GA participated in data interpretation and discussion,
and writing of the manuscript. All authors reviewed the manuscript.
WB and ZW confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. All authors
read and approved the final manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of the present
study have been deposited into CNGB Sequence Archive of China
National GeneBank database with accession no. CNP0003841
(http://db.cngb.org/cnsa/project/CNP0003841_c66117f4/reviewlink/).
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Ethical approval was obtained from Baotou Medical
College Research and Ethical Review Committee (approval no.
2021040).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Yuan X, Chen B, Duan Z, Xia Z, Ding Y,
Chen T, Liu H, Wang B, Yang B, Wang X, et al: Depression and
anxiety in patients with active ulcerative colitis: Crosstalk of
gut microbiota, metabolomics and proteomics. Gut Microbes.
13:19877792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gomaa EZ: Human gut microbiota/microbiome
in health and diseases: A review. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek.
113:2019–2040. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Weiss GA and Hennet T: Mechanisms and
consequences of intestinal dysbiosis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
74:2959–2977. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Popov J, Caputi V, Nandeesha N, Rodriguez
DA and Pai N: Microbiota-immune interactions in ulcerative colitis
and colitis associated cancer and emerging microbiota-based
therapies. Int J Mol Sci. 22:113652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Richard ML, Liguori G, Lamas B, Brandi G,
da Costa G, Hoffmann TW, Pierluigi Di Simone M, Calabrese C,
Poggioli G, Langella P, et al: Mucosa-associated microbiota
dysbiosis in colitis associated cancer. Gut Microbes. 9:131–142.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ramos GP and Papadakis KA: Mechanisms of
disease: Inflammatory bowel diseases. Mayo Clin Proc. 94:155–165.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adak A and Khan MR: An insight into gut
microbiota and its functionalities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:473–493.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gong X, Li X, Bo A, Shi RY, Li QY, Lei LJ,
Zhang L and Li MH: The interactions between gut microbiota and
bioactive ingredients of traditional Chinese medicines: A review.
Pharmacol Res. 157:1048242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen YZ, Yuan MY, Chen YL, Zhang X, Xu XT,
Liu SL, Zou X, Tao JL, Qiang YH, Wu J and Sun QM: The gut
microbiota and traditional Chinese medicine: A new clinical
frontier on cancer. Curr Drug Targets. 22:1222–1231. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jin M, Yu H, Jin X, Yan L, Wang J and Wang
Z: Dracocephalum moldavica L. extracts protect H9c2
cardiomyocytes against H2O2-induced apoptosis
and oxidative stress. Biomed Res Int. 2020:83793582020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yu H, Liu M, Liu Y, Qin L, Jin M and Wang
Z: Antimicrobial activity and mechanism of action of
Dracocephalum moldavica L. extracts against clinical
isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Front Microbiol. 10:12492019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nie L, Li R, Huang J, Wang L, Ma M, Huang
C, Wu T, Yan R and Hu X: Abietane diterpenoids from
Dracocephalum moldavica L. and their anti-inflammatory
activities in vitro. Phytochemistry. 184:1126802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Fattahi A, Shakeri A, Tayarani-Najaran Z,
Kharbach M, Segers K, Heyden YV, Taghizadeh SF, Rahmani H and Asili
J: UPLC-PDA-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS and GC-MS analysis of Iranian
Dracocephalum moldavica L. Food Sci Nutr. 9:4278–4286. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang J, Dou W, Zhang E, Sun A, Ding L,
Wei X, Chou G, Mani S and Wang Z: Paeoniflorin abrogates
DSS-induced colitis via a TLR4-dependent pathway. Am J Physiol
Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 306:G27–G36. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu H, Yu H, Si L, Meng H, Chen W, Wang Z
and Gula A: Influence of warm acupuncture on gut microbiota and
metabolites in rats with insomnia induced by PCPA. PLoS One.
17:e02678432022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhang L, Han L, Wang X, Wei Y, Zheng J,
Zhao L and Tong X: Exploring the mechanisms underlying the
therapeutic effect of Salvia miltiorrhiza in diabetic nephropathy
using network pharmacology and molecular docking. Biosci Rep.
41:BSR202035202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID
bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. 4:44–57. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Huang da W, Sherman BT and Lempicki RA:
Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive
functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
37:1–13. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chassaing B, Aitken JD, Malleshappa M and
Vijay-Kumar M: Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS)-induced colitis in
mice. Curr Protoc Immunol. 104:15.25.1–15.25.14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, Gerlach K,
Weigmann B, Fichtner-Feigl S and Neurath MF: Chemically induced
mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat
Protoc. 12:1295–1309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fujino Y, Kanmura S, Morinaga Y, Kojima I,
Maeda N, Tanaka A, Maeda H, Kumagai K, Sasaki F, Tanoue S and Ido
A: Hepatocyte growth factor ameliorates dextran sodium
sulfate-induced colitis in a mouse model by altering the phenotype
of intestinal macrophages. Mol Med Rep. 27:702023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Alex P, Zachos NC, Nguyen T, Gonzales L,
Chen TE, Conklin LS, Centola M and Li X: Distinct cytokine patterns
identified from multiplex profiles of murine DSS and TNBS-induced
colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 15:341–352. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu D, Zhao Y, Wang H, Kong D, Jin W, Hu Y,
Qin Y, Zhang B, Li X, Hao J, et al: IL-1β pre-stimulation enhances
the therapeutic effects of endometrial regenerative cells on
experimental colitis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 12:3242021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang C, Du Y, Ren D, Yang X and Zhao Y:
Gut microbiota-dependent catabolites of tryptophan play a
predominant role in the protective effects of turmeric
polysaccharides against DSS-induced ulcerative colitis. Food Funct.
12:9793–9807. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fan Q, Guan X, Hou Y, Liu Y, Wei W, Cai X,
Zhang Y, Wang G, Zheng X and Hao H: Paeoniflorin modulates gut
microbial production of indole-3-lactate and epithelial autophagy
to alleviate colitis in mice. Phytomedicine. 79:1533452020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hasannejad-Bibalan M, Mojtahedi A, Eshaghi
M, Rohani M, Pourshafie MR and Talebi M: The effect of selected
Lactobacillus strains on dextran sulfate sodium-induced
mouse colitis model. Acta Microbiol Immunol Hung. 67:138–142. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang HG, Zhang MN, Wen X, He L, Zhang MH,
Zhang JL and Yang XZ: Cepharanthine ameliorates dextran sulphate
sodium-induced colitis through modulating gut microbiota. Microb
Biotechnol. 15:2208–2222. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Adams SM, Close ED and Shreenath AP:
Ulcerative colitis: Rapid evidence review. Am Fam Physician.
105:406–411. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yılmaz İ, Dolar ME and Özpınar H: Effect
of administering kefir on the changes in fecal microbiota and
symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease: A randomized controlled
trial. Turk J Gastroenterol. 30:242–253. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pang B, Jin H, Liao N, Li J, Jiang C, Shao
D and Shi J: Lactobacillus rhamnosus from human breast milk
ameliorates ulcerative colitis in mice via gut microbiota
modulation. Food Funct. 12:5171–5186. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yang B, Li M, Wang S, Ross RP, Stanton C,
Zhao J, Zhang H and Chen W: Lactobacillus ruminis alleviates
DSS-induced colitis by inflammatory cytokines and gut microbiota
modulation. Foods. 10:13492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang T, Zheng J, Dong S, Ismael M, Shan Y,
Wang X and Lü X: Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus LS8 ameliorates
azoxymethane/dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis-associated
tumorigenesis in mice via regulating gut microbiota and inhibiting
inflammation. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 14:947–959. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Duan L, Cheng S, Li L, Liu Y, Wang D and
Liu G: Natural anti-inflammatory compounds as drug candidates for
inflammatory bowel disease. Front Pharmacol. 12:6844862021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sen A: Prophylactic and therapeutic roles
of oleanolic acid and its derivatives in several diseases. World J
Clin Cases. 8:1767–1792. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Sheng Q, Li F, Chen G, Li J, Li J, Wang Y,
Lu Y, Li Q, Li M and Chai K: Ursolic acid regulates intestinal
microbiota and inflammatory cell infiltration to prevent ulcerative
colitis. J Immunol Res. 2021:66793162021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lv F, Zhang Y, Peng Q, Zhao X, Hu D, Wen
J, Liu K, Li R, Wang K and Sun J: Apigenin-Mn(II) loaded hyaluronic
acid nanoparticles for ulcerative colitis therapy in mice. Front
Chem. 10:9699622022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Ren J, Yue B, Wang H, Zhang B, Luo X, Yu
Z, Zhang J, Ren Y, Mani S, Wang Z and Dou W: Acacetin ameliorates
experimental colitis in mkice via inhibiting macrophage
inflammatory response and regulating the composition of gut
microbiota. Front Physiol. 11:5772372021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Dou W, Zhang J, Li H, Kortagere S, Sun K,
Ding L, Ren G, Wang Z and Mani S: Plant flavonol isorhamnetin
attenuates chemically induced inflammatory bowel disease via a
PXR-dependent pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 25:923–933. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ren J, Lu Y, Qian Y, Chen B, Wu T and Ji
G: Recent progress regarding kaempferol for the treatment of
various diseases. Exp Ther Med. 18:2759–2776. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pastille E, Faßnacht T, Adamczyk A, Ngo
Thi Phuong N, Buer J and Westendorf AM: Inhibition of TLR4
signaling impedes tumor growth in colitis-associated colon cancer.
Front Immunol. 12:6697472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang QY, Ma LL, Zhang C, Lin JZ, Han L, He
YN and Xie CG: Exploring the mechanism of indigo naturalis in the
treatment of ulcerative colitis based on TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling
pathway and gut microbiota. Front Pharmacol. 12:6744162021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shen W, Anwaier G, Cao Y, Lian G, Chen C,
Liu S, Tuerdi N and Qi R: Atheroprotective mechanisms of tilianin
by inhibiting inflammation through down-regulating NF-κB pathway
and foam cells formation. Front Physiol. 10:8252019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhou Y, Zhang M, Zhao X and Feng J:
Ammonia exposure induced intestinal inflammation injury mediated by
intestinal microbiota in broiler chickens via TLR4/TNF-α signaling
pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 226:1128322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|