Introduction
Neuroinflammation is initially useful for the
nervous system to successfully reduce infection and injury via the
production of proinflammatory cytokines and other molecules, such
as nitric oxide (NO), as it can restore homeostasis of the nervous
system (1–3). However, excessive or persistent
neuroinflammation is also harmful to the normal function of the
nervous system due to nerve cell dysfunction or disruption of the
blood-brain barrier (BBB) (4,5).
Therefore, neuroinflammation is increasingly recognized as a main
disease feature of neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson's
disease (PD) (6). Microglia are
the resident class of myeloid macrophages in the brain; their
activation is considered the first sign of neuroinflammation, and
overactivation of these cells contributes to the pathogenesis of PD
(7). Pattern recognition
receptors, such as the toll-like receptors (TLRs) are present on
microglia and can trigger the production of proinflammatory
cytokines following the sensing of pathogen-associated molecular
patterns or the damage associated molecular patterns in the brain
(8). The release of
proinflammatory cytokines can trigger the overactivation of protein
kinases on neuronal receptors, such as those found in hippocampal
and substantia nigra neurons, and subsequently lead to neuronal
death and acceleration of neurodegeneration, and there have been
numerous reported hypotheses that the inhibition of overactivated
microglia and neuro-inflammation is an effective strategy for the
treatment of neurodegenerative diseases (9–11).
A prerequisite for neurological drug development is
the identification of a therapeutic agent that can be effectively
delivered across the BBB (12).
Network pharmacology is widely used in the search of pharmaceutical
ingredients (13). Therefore, the
application of network pharmacology is feasible to identify the
candidate components that can cross the BBB and inhibit the
activation of microglia.
Neferine is a bis-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid
extracted from the seed embryos of Nelumbo nucifera, which
has multiple types of reported pharmacological activities, such as
anticancer, antidiabetic and antiatherosclerotic effects (14–16).
Previous studies have also reported the antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory properties of neferine on the prevention of liver
fibrosis and Graves' orbitopathy by suppressing MAPK-, NF-κB- and
autophagy-related inflammation (17,18).
In the nervous system, neferine was reported to prevent
neurodegeneration in the hippocampal tissue of Alzheimer's disease
models by potentially inhibiting the expression levels of
inflammatory factors such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) and
interleukin-6 (IL-6) (19).
However, limited information is available regarding the effects and
mechanisms of neferine on overactivated microglia-associated
inflammation and PD. Therefore, the present study explored the
function of neferine in the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced
microglia activation model and
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced PD
mouse model.
In the course of clinical treatment, prophylactic
use of neuroprotectants, such as coenzyme Q10 and inosine, is a
common option for individuals with a family history of PD and for
those with mild symptoms, such as mild tremor or slow movement in a
single limb, that have not yet been diagnosed. Furthermore,
pretreatment with neferine has been reported to exert a
neuroprotective effect in the Kainic Acid-induced seizure model in
rats (20), and pretreatment using
other neuroprotective drug like salidroside is also used in MPTP
models (21). Therefore,
pretreatment with neferine was used to assess its neuroprotective
effect in MPTP-induced PD mouse models in the present study.
Materials and methods
Cell culture and treatment
BV-2 cells (cat. no. CL-0493A; Procell Life Science
& Technology Co., Ltd.) were cultured in Eagle's Minimum
Essential Medium (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) containing
10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and
100 U/ml penicillin-streptomycin (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific,
Inc.) at 37°C in the presence of 5% CO2 and saturated
humidity. BV-2 cells were treated with LPS (InvivoGen) at a final
concentration of 100 ng/ml at 37°C in the presence of 5%
CO2. The duration of treatment is dependent on the
specific experiment as declared in figure legends.
Materials
Neferine (cat no. HY-N0441), nuciferine (cat. no.
HY-N0049), methoxsalen (cat. no. HY-30151), 3,4-dimethoxybenzoic
acid (cat. no. HY-N2007) and JSH23 (cat. no. HY-13982) were
purchased from MedChemExpress. BV-2 cells were pre-treated with
these compounds for 30 min before LPS treatment in order to assess
their anti-inflammatory activity at a concentration gradient from
0.1–10 µM at 37°C in the presence of 5% CO2.
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from BV-2 cells using
TRIzol® (Invitrogen; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) and
quantified using a nanodrop spectrophotometer (NanoDrop
Technologies; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). cDNA synthesis was
performed using PrimeScript RT Master Mix (Takara Bio, Inc.)
according to the manufacturer's instructions. Gene amplification
was performed using SYBR Green Master Mix (TransGen Biotech Co.,
Ltd.) on a Roche 480 light cycler instrument (Roche Diagnostics).
The thermocycling conditions were as follows: 95°C for 30 sec,
followed by 40 cycles at 95°C for 5 sec and 55°C for 30 sec, and
then 95°C for 15 sec and 60°C for 60 sec. The relative expression
of IL-6 or TNFα was quantified using the 2−ΔΔCq method
(22), and β-actin was used as an
internal control. All reactions were performed in triplicate.
Primer Premier 5 software was used for primer design, and the
sequences of the primers are as follows: IL-6 forward (F),
5′-GAGTTGTGCAATGGCAATTCTG-3′ and reverse (R)
5′-GCAAGTGCATCATCGTTGTTCAT-3′; TNF-α F,
5′-CCCTCACACTCAGATCATCTTCT-3′ and R, 5′-GCTACGACGTGGGCTACAG-3′; and
β-actin F, 5′-AGTGTGACGTTGACATCCGT-3′ and R
5′-GCAGCTCAGTAACAGTCCGC-3′.
Cell death assay
Cell death was investigated using the Dead Cell
Apoptosis Kits with Annexin V for Flow Cytometry (cat. no. V13242;
Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.). BV-2 cells were plated at a
density of 1×105 cells/well in 24-well plates and
treated with neferine (10 µM) at 37°C for either 24 or 48 h.
Trypsin was used to detach the cells from the plate (0.25%; 37°C
for 3 min). The cells were centrifuged at 200 × g for 5 min at 4°C.
Following removal of the supernatant, the cells were washed twice
with PBS buffer. The cells were re-suspended in 100 µl binding
buffer with 1 µl annexin V and incubated at room temperature (RT)
in the dark for 10 min. Subsequently, 5 µl PI solution was added
and incubated with the samples for 5 min in the dark at RT. The
cell death percentage was determined using a NovoCyte flow
cytometer equipped with the NovoExpress software (version 1.5.6;
ACEA Bioscience, Inc.; Agilent).
Cell Counting Kit (CCK)-8 assay
BV-2 cells were seeded in 96-well plates at a
density of 5×103 cells/well and incubated at 37°C with
5% CO2 on day 0 in the presence of neferine (10 µM). On
days 1 and day 2, 10 µl CCK-8 solution (Dojindo Laboratories, Inc.)
was added to every well and incubated at 37°C. After 2 h, the
96-well plates were removed, and a microplate reader (Bio-Rad
Laboratories, Inc.) was used to measure the absorbance at 450 nm.
Experiments were performed in triplicate.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
(ELISA)
BV-2 cells were seeded in 24-well plates at a
density of 2×105 cells/ml and incubated at 37°C with 5%
CO2 on day 0. On day 1, BV-2 cells were pretreated with
either DMSO or neferine (10 µM) for 30 min and subsequently treated
with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 0 and 12 h. The levels of the
proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-6 were quantified using
Mouse IL-6 Quantikine ELISA Kit (cat. no. M6000B; R&D Systems,
Inc.) and Mouse TNF-α Quantikine ELISA Kit (cat. no. MTA00B;
R&D Systems, Inc.) according to the manufacturer's
instructions.
Western blotting
BV-2 cells were seeded in 6-well plates at a density
of 2×105 cells/ml and incubated at 37°C with 5%
CO2 on day 0. On day 1, BV-2 cells were pretreated with
either DMSO or neferine (10 µM) for 30 min and subsequently treated
with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 0, 2, 4, 8 or 12 h. The cell lysate was
prepared by scraping BV-2 cells or grinding the brain tissue of
mice in Pierce Immunoprecipitation Lysis Buffer (Invitrogen; Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.). The protein concentration was determined
using the bicinchoninic acid assay method. A total 20 µg protein
was separated by PAGE on a 10% SDS gel and transferred to
polyvinylidene membranes (MilliporeSigma). The membranes were
incubated with 5% BSA at RT for 60 min to block non-specific
binding. Subsequently, the membranes were incubated with the
corresponding primary antibodies (Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.)
against β-actin (1:1,000; cat. no. 12620), inducible NO synthase
(iNOS; 1:1,000; cat. no. 13120), phosphorylated (p)-NF-κB p65
(Ser536; 1:1,000; cat. no. 3033), p-SAPK/JNK (Thr183/Tyr185;
1:1,000; cat. no. 4668), p-p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2; Thr202/Tyr204);
1:1,000; cat. no. 4370), p-p38 MAPK (Thr180/Tyr182; 1:1,000; cat.
no. 4631), NF-κB p65 (1:1,000; cat. no. 6956), JNK2 (1:1,000; cat.
no. 9258), p44/42 MAPK (Erk1/2; 1:1,000; cat. no. 4695), p38 MAPK
(1:1,000; cat. no. 8690), Caveolin-1 (1:500; cat. no. 3267), Lamin
A (1:500; cat. no. 86846) and α-synuclein (α-syn; 1:1,000; cat. no.
ab212184; Abcam) diluted in 5% BSA at 4°C for 12 h. The membranes
were subsequently incubated with anti-rabbit IgG (1:2,000; cat.
no.7074; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.) and anti-mouse IgG
antibody (1:2,000; cat. no. 7076; Cell Signaling Technology, Inc.),
linked with HRP for 1 h at RT. The membranes were visualized using
SuperSignal™ West Femto Maximum Sensitivity Substrate (Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.). β-actin was used as a whole cell lysate
control and Lamin A was used as a nuclear lysate control.
Animal model and drug treatments
Male C57BL/6 mice (10 weeks old; n=32) at SPF level
weighing 20–25 g were obtained from the Department of Laboratory
Animal Science of China Medical University (Shenyang, China). All
mice were housed in standard cages at 22–24°C with relative
humidity range of 40–60%, a regular 12 h light/dark cycle and ad
libitum access to food and water in accordance with mousece
care protocols. The mice were divided into four groups (n=8/group)
as follows: i) Mice intraperitoneally injected with PBS for 14
days; ii) mice intraperitoneally injected with 15 mg/kg/day
neferine dissolved in PBS for 14 days; iii) mice intraperitoneally
injected with PBS for 3 days, 30 mg/kg/day MPTP (cat. no. M0896;
Sigma-Aldrich; Merck KGaA) for 5 days starting on day 4 and
subsequently continuously injected with PBS for 6 days; and iv)
mice intraperitoneally injected with 15 mg/kg/day neferine
dissolved in PBS for 3 days. On day 4, mice were intraperitoneally
injected with MPTP + neferine for 5 days, then neferine was
administered for 6 days. The health of mice was monitored daily,
and no animals died prior to sacrifice. During this time, none of
the animals exhibited symptoms that would require to be euthanized,
such as reduced appetite, breathing difficulties and convulsions.
Following the behavioral experiments on day 14, the mice were
euthanized by cervical dislocation following anesthesia with
isoflurane (5% for induction and 3% for maintenance). The death of
the mice was confirmed by respiratory and cardiac arrest, and pupil
dilation. The tissue samples of the substantia nigra were
collected, and the protein lysates were extracted for western
blotting to investigate the expression levels of the related
molecules. The mice were handled according to the Guide for the
Care and Use of Medical Laboratory Animals (Ministry of Health).
The experimental protocol was approved by the Laboratory Ethics
Committee of China Medical University (approval no. CMU:2020096;
Shenyang, China).
Behavioral tests
Behavioral tests were carried out as previously
described (23). The pole descent
test was performed as follows: A cork ball (diameter, 2.5 cm) was
fixed on the top of a wooden pole (50×1 cm), and the pole was
wrapped in gauze to prevent slipping. The test mice were placed on
the ball, and the time in sec required for the mice to descent back
into the cage was recorded. The recording of the time was initiated
when the mice started crawling headfirst and ended when their hind
legs reached the cage base. The average time was obtained from
three replicates for every mouse.
For the traction test, mice were suspended on a
horizontal wire (diameter, 5 mm), and their limbs were observed
when grasping the wire. Scoring of the test was performed as
follows: A total of 3 points were assigned if the two hind legs
grabbed the wire; 2 points if one hind leg grabbed the wire; 1
point if the front paw held the wire; and 0 points if the mice fell
off the wire. The average score was obtained from three replicates
for every mouse.
For the rotor-rod test, training experiments were
performed for 3 days to acclimate the mice to the device, and
minimize anxiety and exploratory behavior caused by unintentional
falls. Animals were placed back on the pole immediately after a
fall. Gradual acceleration of the device and rotation of the rod at
4–40 rpm was initiated. In the formal test, the mice were placed on
a rotating rod and spun at 15 rpm (rod length, 50 mm; rod diameter,
30 mm). In case the mouse had fallen from the device, the timing
end and rotating rod time periods were recorded. Every mouse
underwent three trials. The average of the three trials was used
for further analysis.
Statistical analysis
The data are presented as mean ± standard deviation
from three independently repeated experiments. A total of three
samples were used for every in vitro experiment, and eight
samples were used for every in vivo experiment. SPSS
(version 16.0; SPSS, Inc.) was used to assess statistical
significance. The differences between different groups were
assessed by a Student's unpaired t-test. Multiple comparisons were
performed using one-way ANOVA followed by the Bonferroni multiple
comparisons test. Traction test data are shown as the median ±
interquartile range, and were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis
test followed by Dunn's post hoc test. P<0.05 was considered to
indicate a statistically significant difference.
Results
Neferine inhibits LPS-induced BV-2
activation
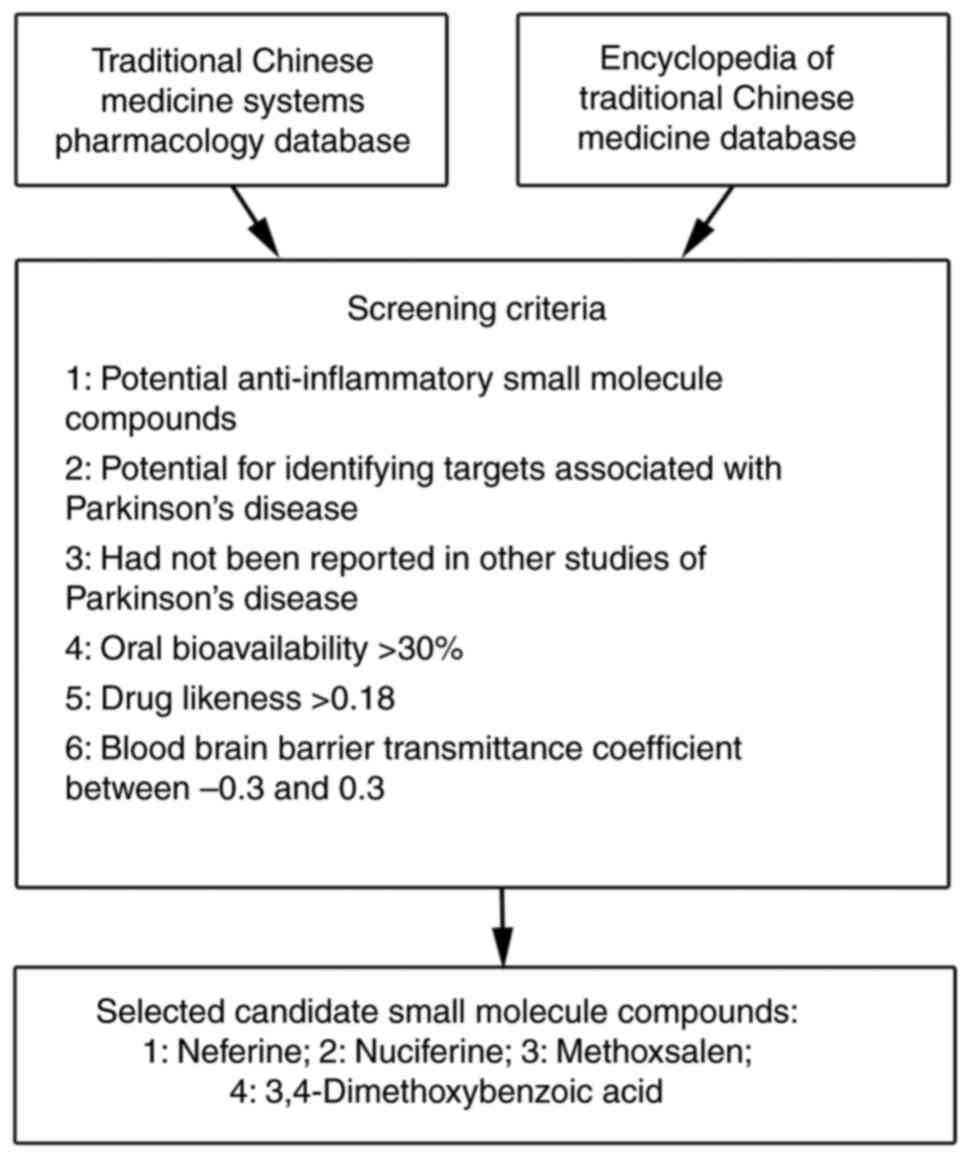
The Network pharmacology, the Traditional Chinese
Medicine Systems Pharmacology (https://tcmspw.com/), and The Encyclopedia of
Traditional Chinese Medicine (http://www.tcmip.cn/ETCM/index.php/Home/) databases
were used to select potential anti-PD small molecular weight
compounds. A total of four candidates were selected, neferine,
nuciferine, methoxsalen and 3,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid, which fit
the following six selection criteria: i) Potential
anti-inflammatory small molecule compounds; ii) potential for
identifying targets associated with Parkinson's disease; iii) not
reported in other studies of Parkinson's disease; iv) oral
bioavailability >30%; v) drug likeness >0.18; and vi) BBB
transmittance coefficient between −0.3 and 0.3 for subsequent
functional screening in LPS-induced activated microglia in BV-2
cells (Fig. 1).
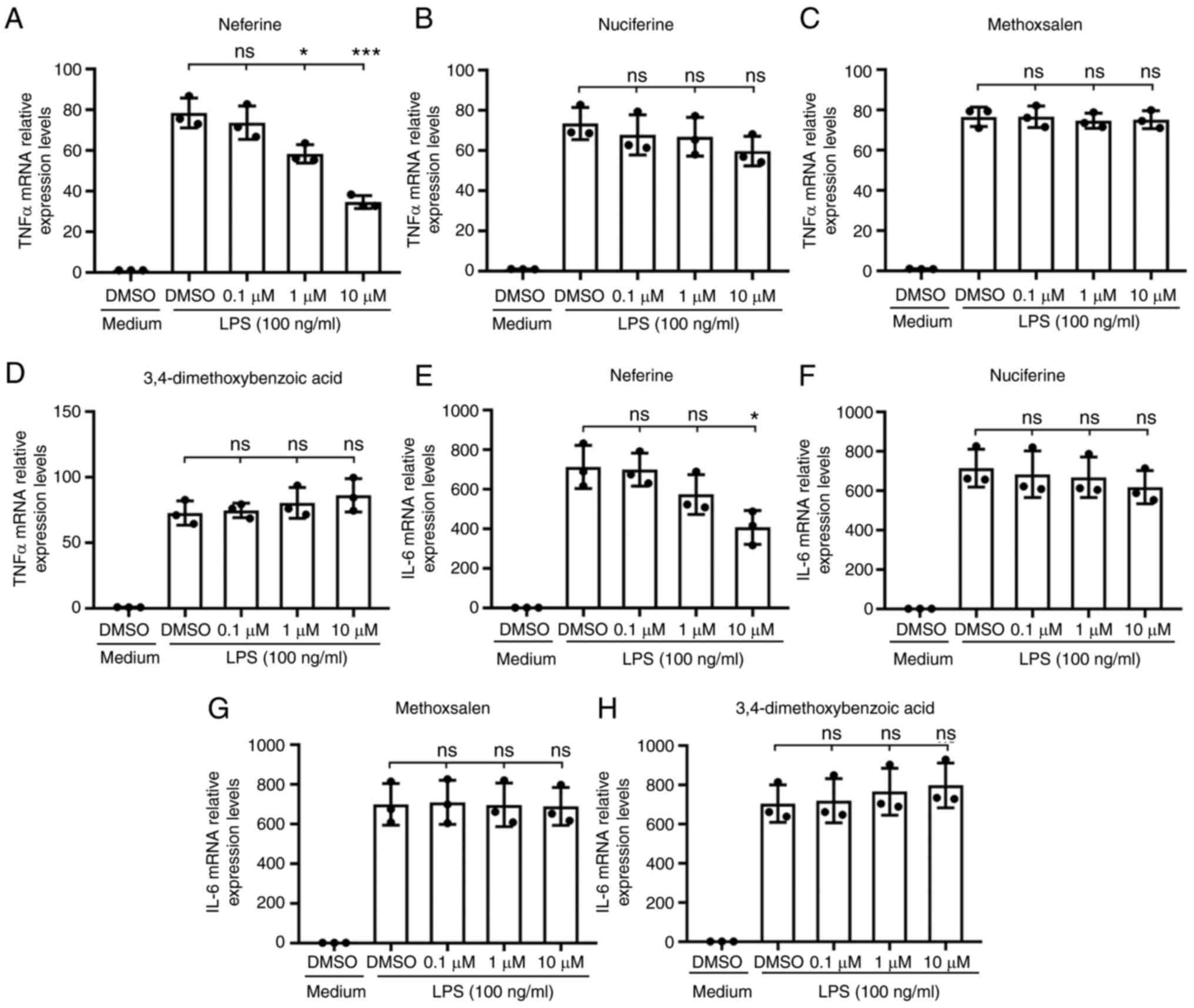
The transcription of TNF-α and IL-6 in BV-2 cells
treated with 100 ng/ml LPS was measured by RT-qPCR as an index of
microglia activation. Pretreatment with neferine (0.1, 1 and 10 µM)
and DMSO suppressed the activation of the BV-2 microglia cells in a
dose-dependent manner, particularly at the highest concentration
tested (Fig. 2A and E), while the
other three candidates, nuciferine, methoxsalen and
3,4-dimethoxybenzoic acid, did not exert this significant effect
(Fig. 2B-D, F-H). These results
suggested that neferine was a potential inhibitor of microglia
activation.
Neferine inhibits the production of
LPS-induced iNOS and proinflammatory cytokines in BV-2 cells
Neferine is a bis-benzylisoquinoline alkaloid
derived from lotus seed embryos, which has a wide range of
pharmacological activities (Fig.
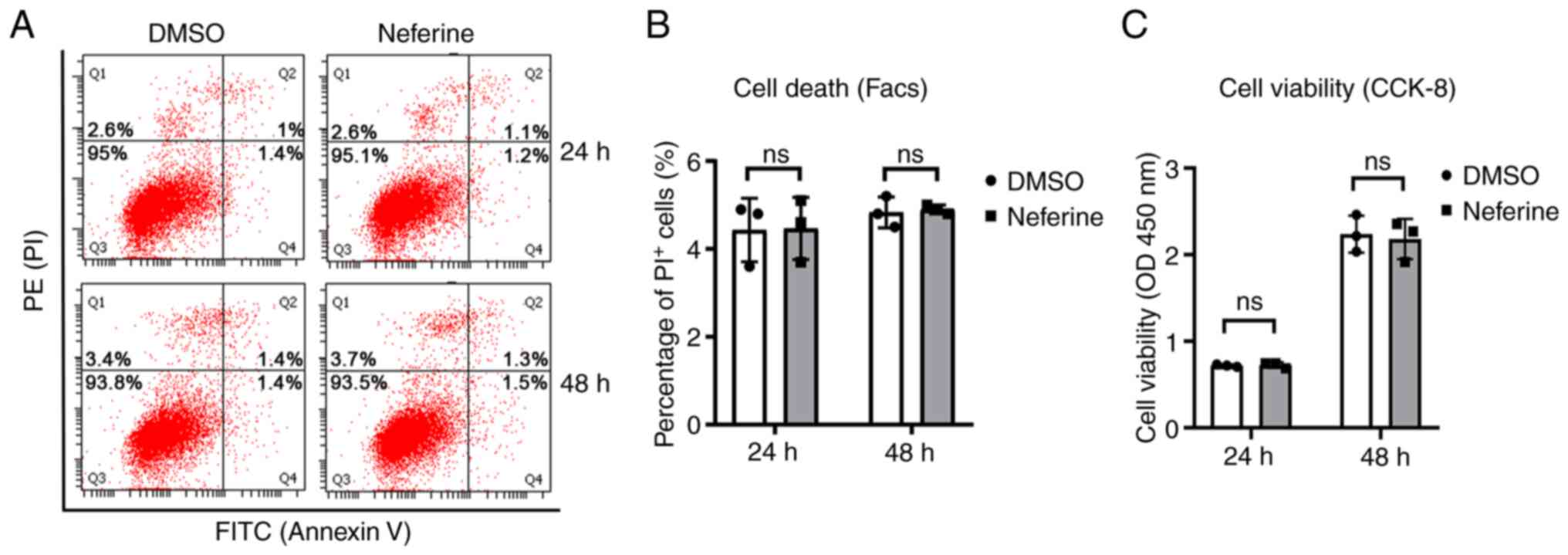
3). Initially, the cytotoxic effect of neferine was assessed in
BV-2 cells. Neferine (10 µM) did not induce cell death of BV-2
cells (Fig. 4A and B), and no
significant difference was observed in the viability between the
DMSO- and neferine-treated cells (Fig.
4C). This suggested that neferine exhibited no cytotoxic effect
at the concentrations tested.
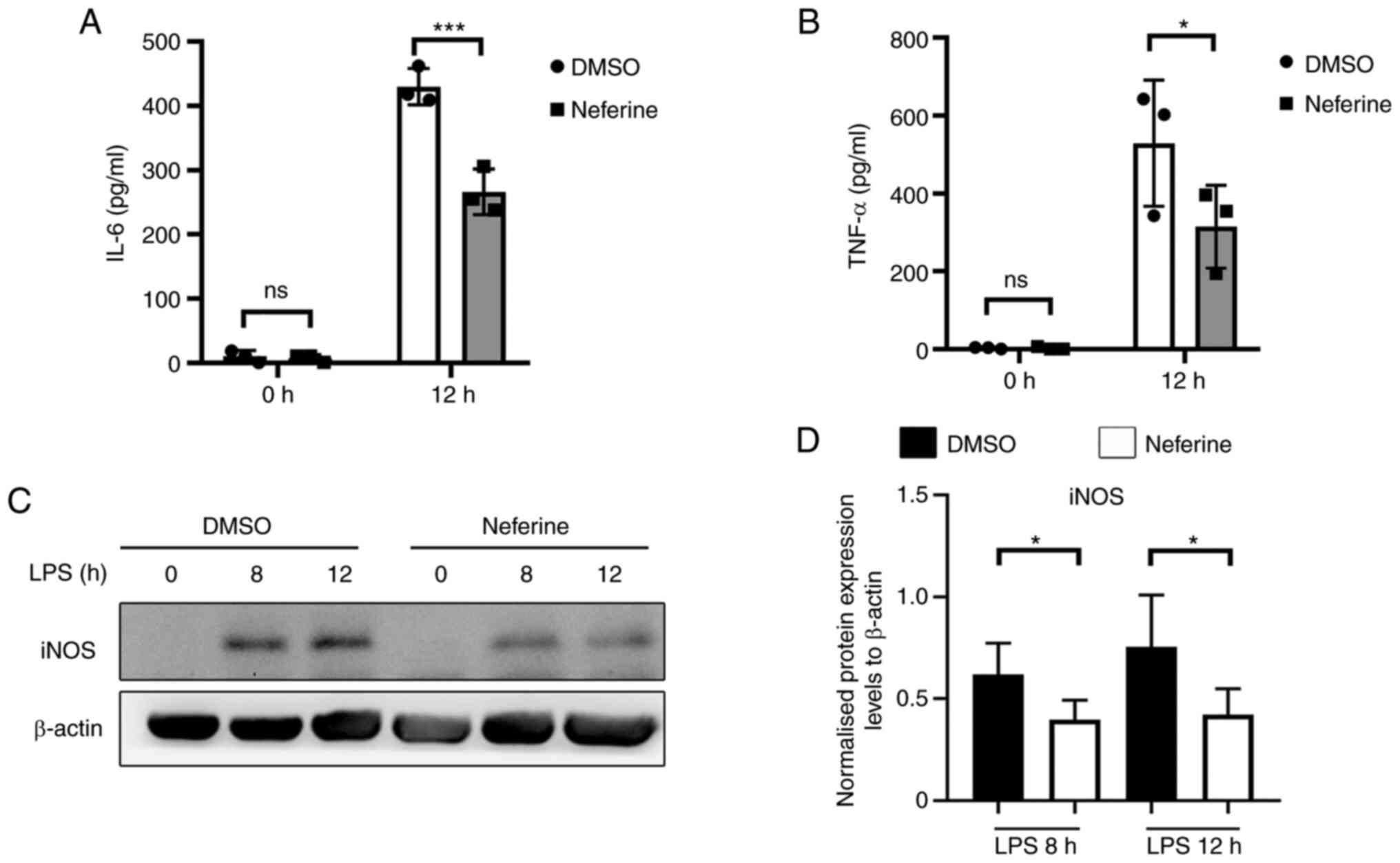
To further explore the role of neferine in
suppressing microglia activation, BV-2 cells were pretreated with
10 µM neferine, then inflammation was induced by 100 ng/ml LPS
treatment for 0, 8 and 12 h (Fig.
5A-C). The protein expression levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in the
cell supernatant were significantly decreased in the neferine
treatment groups after 12 h (Fig. 5A
and B). The production of iNOS was also significantly inhibited
by neferine compared with that in the DMSO-treated group (Fig. 5C and D). Therefore, neferine may
suppress the production of LPS-induced TNF-α, IL-6 and iNOS in BV-2
cells in the absence of cytotoxic effects.
Neferine inhibits LPS-induced
translocation and activation of NF-κB in BV-2 cells
The MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways have been
reported to mediate the activation of microglia cells (24). Therefore, the phosphorylation of
relevant signaling proteins was assessed to investigate the ability
of neferine to restrain BV-2 activation. Neferine exhibited no
significant effect on the phosphorylation of JNK1/2, ERK and p38
MAPK (Fig. 6A-E), whereas it
significantly inhibited the phosphorylation of p65 in BV-2 cells
treated with 100 ng/ml LPS. Cell treatment with neferine
significantly decreased the nuclear translocation of p65, which was
consistent with the aforementioned result (Fig. 6F and G). Caveolin-1, a cytoplasmic
protein, was used as a negative control for nucleoprotein
extraction. JSH23 was previously reported to inhibit NF-κB
transcriptional activity (25).
Therefore, JSH23 was selected as the positive control of neferine.
It was demonstrated that JSH23 and neferine exhibited similar
effects in the inhibition of the release of IL-6 in LPS-activated
BV-2 cells (Fig. 6H). These
results indicated that neferine inhibited LPS-induced BV-2 cell
activation via the inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
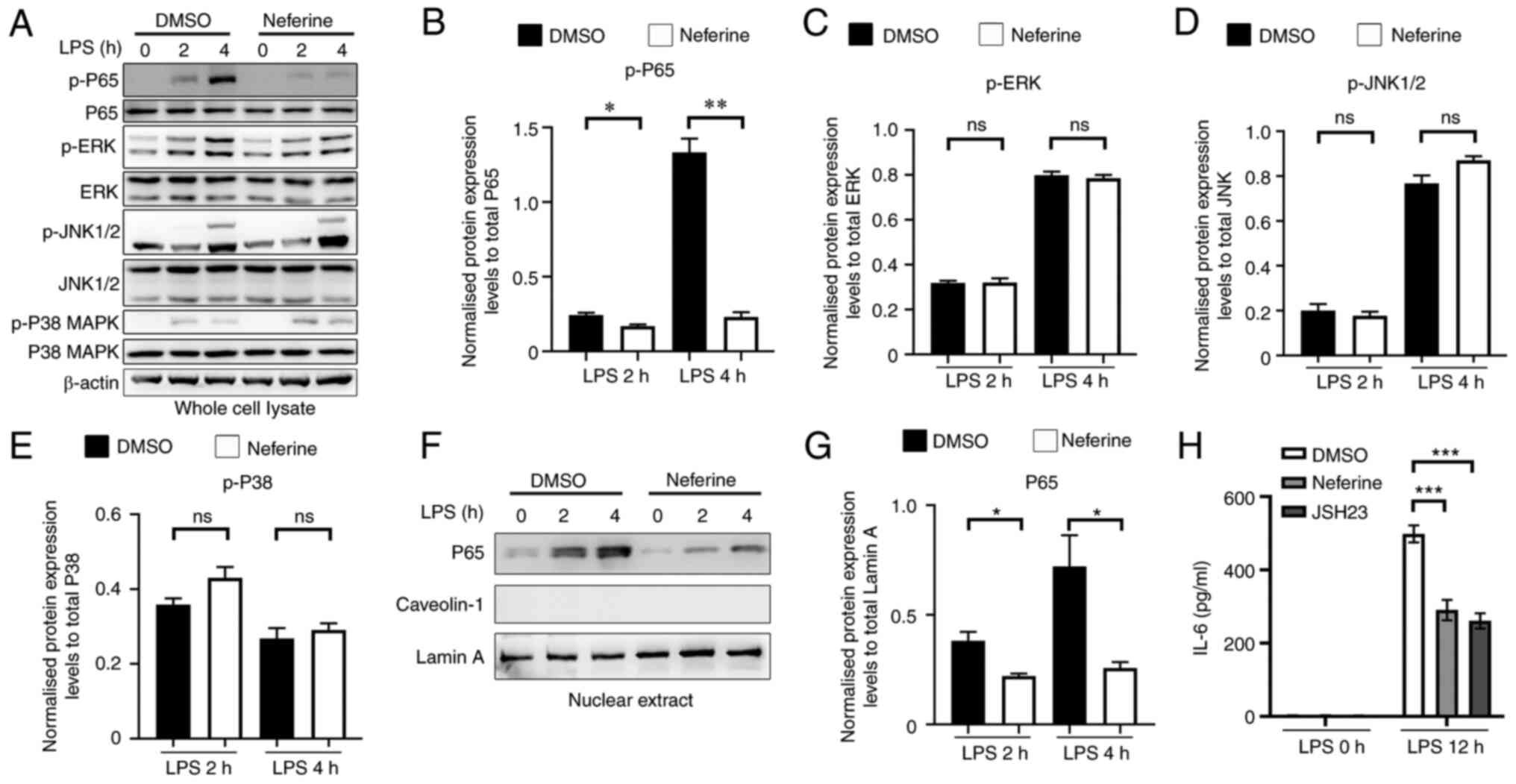 | Figure 6.Neferine inhibits NF-κB nuclear
translocation and activation induced by LPS in BV-2 cells. (A) BV-2
cells were pretreated with either DMSO or neferine (10 µM) for 1 h
and subsequently treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 2 and 4 h, and
(A) western blotting was used to measure the expression levels of
various proteins. Protein expression levels of (B) P65, (C) ERK,
(D) JNK and (E) P38 were semi-quantified. BV-2 cells were
pretreated with either DMSO or neferine (10 µM) for 1 h and
subsequently treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 2 and 4 h, and (F)
western blotting was used to measure the expression levels of
various proteins, while (G) the expression levels of P65 were
semi-quantified. BV-2 cells were pretreated with either DMSO,
neferine (10 µM) or JSH23 (10 µM) for 30 min and subsequently
treated with LPS (100 ng/ml) for 12 h, and (H) the expression
levels of IL-6 in the supernatant were measured by ELISA.
*P<0.05, **P<0.005, ***P<0.001 vs. DMSO treatment. Data
are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n=3). LPS,
lipopolysaccharide; ns, not significant; p-, phosphorylated. |
Neferine ameliorates dyskinesia in a
PD mouse model
The release of inflammatory cytokines and NO by
microglia leads to the deterioration of neurodegenerative diseases
(26). Therefore, the present
study assessed the anti-neuroinflammatory effect of neferine in
MPTP-induced PD in mice. Dyskinesia is a typical hallmark of PD,
therefore, a pole test was performed to assess bradykinesia, a
traction test to assess muscle strength and equilibrium, and a
rotor-rod test to assess motor coordination function of PD mice.
The mice in the MPTP + neferine group required lower time periods
to complete the pole test (Fig.
7A), exhibited a higher score in the traction test (single
treatment; Fig. 7B) and
demonstrated the ability to walk longer on the rotors (Fig. 7C) compared with the mice in the
MPTP + PBS group. Consistent with these behavioral experiments,
activation of NF-κB indicated by p-p65 and the levels of iNOS and
α-syn, which is closely associated with the pathogenesis of PD
(8), were significantly lower in
the substantia nigra tissues of MPTP + neferine-treated mice
compared with mice treated with MPTP alone (Fig. 7D-G). These results indicated that
neferine could exert a neuroprotective role in MPTP-induced PD in
mice by inhibiting the activation of NF-κB.
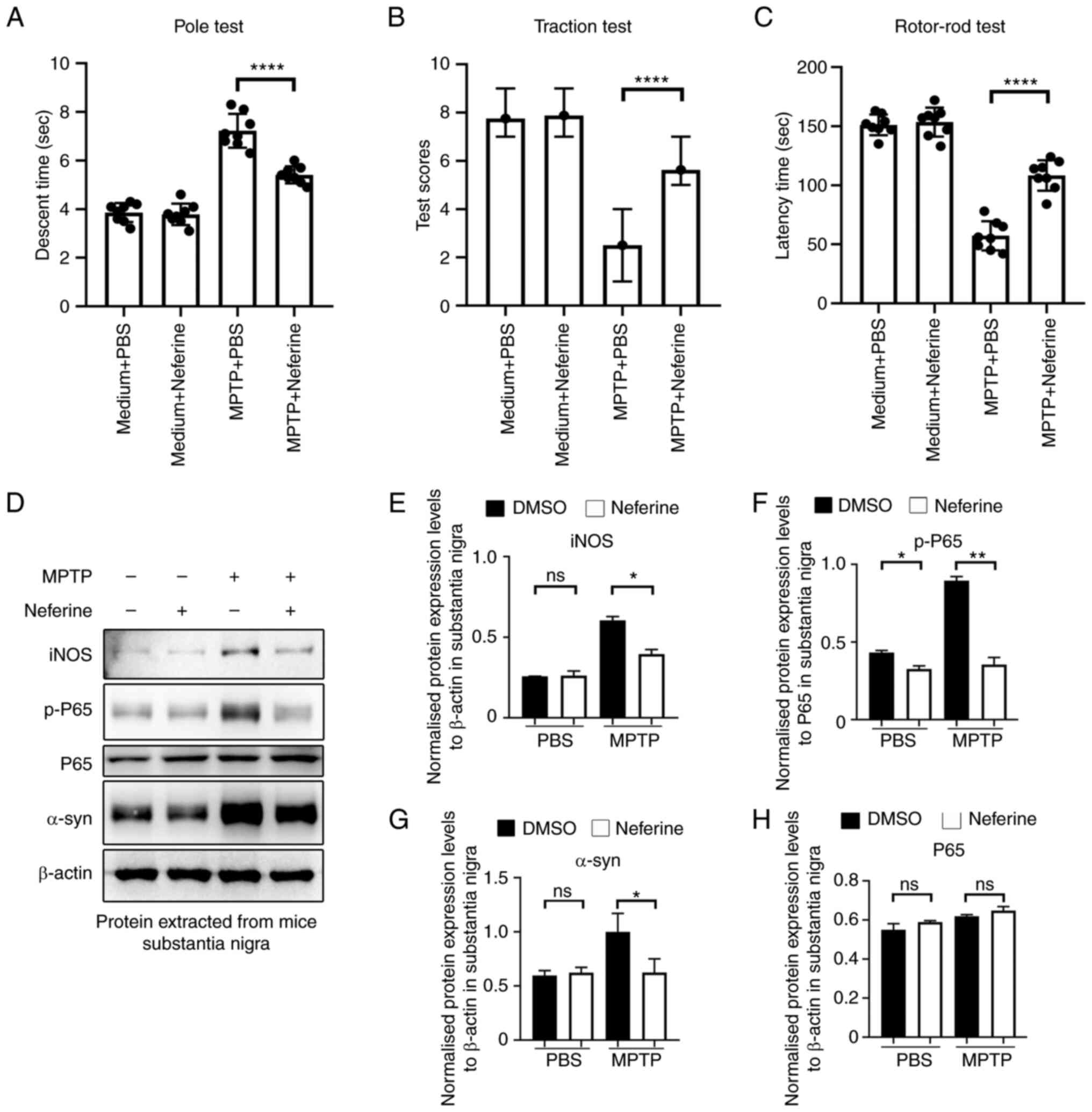 | Figure 7.Neferine ameliorates dyskinesia in
MPTP-treated mice. (A) Dyskinesia was assessed by a pole test by
recording the time required for the mice to descend the pole. Data
are presented as mean ± standard deviation (n=8). (B) Muscle
strength and equilibrium were assessed by a traction test by
recording the traction reflex score. Data are presented as median ±
interquartile range (n=8). (C) Motor coordination function was
assessed by the rotor-rod test by recording the time period
required for the mouse to stay on the pole. Data are presented as
mean ± standard deviation (n=8). ****P<0.0001 vs. PBS treatment.
Proteins were extracted from the mouse substantia nigra tissue
(n=1/treatment group), and their expression was investigated by (D)
western blotting. One representative experiment out of a total of
four is shown. The total protein expression levels of (E) iNOS, (F)
p-P65, (G) α-syn and (H) P65. The house keeping protein β-actin and
total protein of P65 was used as a control. *P<0.05,
**P<0.005 ****P<0.0001 vs. DMSO treatment. MPTP,
1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine; ns, not significant;
iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; α-syn, α-synuclein; p-,
phosphorylated. |
Discussion
Excessive activation of microglia and the subsequent
production of inflammatory cytokines serve critical roles in the
pathogenesis and progression of PD (27). Therefore, the identification of
novel agents which can inhibit microglia-mediated inflammation is a
feasible therapeutic strategy against PD. Neferine has previously
been reported to exert its anti-inflammatory capacity in several
types of cells and mouse models, such as mast cells (RBL-2H3 cells)
(28), PC12 rat pheochromocytoma
cells (29), patient-derived
orbital fibroblasts (18) and in a
carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis mouse model
(17). The present study reported
for the first time that neferine could inhibit microglia activation
and subsequent release of TNF-α, IL-6 and production of iNOS. This
suggests that neferine exhibits a dual anti-inflammatory effect in
inhibiting neuronal and microglia inflammation.
A prerequisite for a drug to be used on the nervous
system is its ability to cross the BBB (12). In the present study, neferine was
selected by network pharmacology based on the following criterion,
appropriate BBB transmittance coefficient. Subsequent in
vivo experiments in mice suggested that neferine promoted the
remission of PD-related symptoms. In addition, it was shown that
neferine did not induce cell death of BV-2 cells. These results
suggested that neferine meets the basic requirements of a candidate
drug for the nervous system. Although preliminary results were
obtained indicating that neferine could alleviate the symptoms of
PD, further studies are required to investigate the feasibility of
the application of this compound as an effective treatment strategy
for PD.
LPS-induced activation of BV-2 cells is a widely
used cell model to study neurodegenerative diseases (19,30–32).
LPS triggers TLR4-mediated signaling, which initiates the
activation of NF-κB and MAPKs via different signalosomes, and
ultimately induces the transcription of inflammatory proteins and
cytokines (20). Neferine has
previously been reported to regulate several types of biological
effects. Wang et al (17)
reported that neferine acted as an antioxidant and
anti-inflammatory agent in CCl4-induced liver fibrosis by
inhibiting the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Pretreatment of
mast cells with neferine also inhibits the phosphorylation of the
MAPK/NF-κB pathway (28). However,
neferine can promote the activation of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK enzymes
in melanoma which leads to the induction of apoptosis in melanoma
cells (33). Neferine suppresses
the differentiation of osteoclasts by inhibiting the NF-κB
signaling pathway rather than the MAPKs, which in turn promotes
osteogenesis (34). Neferine was
also reported to inhibit the expression of the inflammatory
mediators iNOS and COX-2, and the matrix degrading enzymes MMP3 and
13 in IL-1β-treated rat chondrocytes by suppressing the MAPK and
NF-κB signaling pathways (35).
These findings suggest that neferine exhibits different regulatory
patterns in different cells. In the present study, the
phosphorylation of p65, which represents the activation of NF-κB,
JNK1/2, ERK and p38 MAPK, was examined to analyze the mechanism by
which neferine inhibited LPS-induced BV-2 cell activation. These
results indicated that neferine inhibited LPS-induced activation of
NF-κB as opposed to the MAPK-related signaling pathway. However,
the differential regulatory mode of neferine requires further
investigation.
In summary, the present study indicated that
neferine could inhibit microglia activation by suppressing the
NF-κB signaling pathway, which exerted a therapeutic effect in the
PD mouse model. The present study provides novel evidence that
neferine inhibits microglia overactivation, therefore, this
compound may be a potentially effective drug for relieving
neurodegenerative diseases such as PD.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by a grant from the National
Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81971125).
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current
study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable
request.
Authors' contributions
TL, YZ, TZ and BX contributed to the study
conception and design. Material preparation and data collection
were performed by TL and TZ. YZ and BX analyzed the data and
confirm the authenticity of all the raw data. The first draft of
the manuscript was prepared by TL and BX, and all authors commented
on the previous versions of the manuscript. All authors have read
and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
The mice used in the present study were handled
according to the Guide for the Care and Use of Medical Laboratory
Animals (Ministry of Health, Beijing, China). The experimental
protocol was approved by the Laboratory Ethics Committee of China
Medical University, Shenyang, China (approval no. CMU:2020096).
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
DiSabato DJ, Quan N and Godbout JP:
Neuroinflammation: The devil is in the details. J Neurochem. 139
(Suppl 2):S136–S153. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Konsman JP: Cytokines in the brain and
neuroinflammation: We didn't starve the fire! Pharmaceuticals
(Basel). 15:1402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yong HYF, Rawji KS, Ghorbani S, Xue M and
Yong VW: The benefits of neuroinflammation for the repair of the
injured central nervous system. Cell Mol Immunol. 16:540–546. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leng F and Edison P: Neuroinflammation and
microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: Where do we go from
here? Nat Rev Neurol. 17:157–172. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chakraborty B, Mukerjee N, Maitra S,
Zehravi M, Mukherjee D, Ghosh A, Massoud EES and Rahman MH:
Therapeutic potential of different natural products for the
treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022:68738742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC
and Fred H: Mechanisms underlying inflammation in
neurodegeneration. Cell. 140:918–934. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kwon HS and Koh SH: Neuroinflammation in
neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes.
Transl Neurodegener. 9:422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fiebich BL, Batista CRA, Saliba SW, Yousif
NM and de Oliveira ACP: Role of microglia TLRs in
neurodegeneration. Front Cell Neurosci. 12:3292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu L, He D and Bai Y: Microglia-mediated
inflammation and neurodegenerative disease. Mol Neurobiol.
53:6709–6715. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deng M, Yan W, Gu Z, Li Y, Chen L and He
B: Anti-neuroinflammatory potential of natural products in the
treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Molecules. 28:14862023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Guzman-Martinez L, Maccioni RB, Andrade V,
Navarrete LP, Pastor MG and Ramos-Escobar N: Neuroinflammation as a
common feature of neurodegenerative disorders. Front Pharmacol.
10:10082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Terstappen GC, Meyer AH, Bell RD and Zhang
W: Strategies for delivering therapeutics across the blood-brain
barrier. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:362–383. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu F, Wang D, Li RL, He LY, Ai L and Wu
CJ: Current strategies and technologies for finding drug targets of
active components from traditional Chinese medicine. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 26:572–589. 2021. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pan T, Cai B, Wang K, Wang S, Zhou S, Yu
X, Xu B and Chen L: Neferine enhances insulin sensitivity in
insulin resistant rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 124:98–102. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xu L, Zhang X, Li Y, Lu S, Lu S, Li J,
Wang Y, Tian X, Wei JJ, Shao C and Liu Z: Neferine induces
autophagy of human ovarian cancer cells via p38 MAPK/JNK
activation. Tumor Biol. 37:8721–8729. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jun MY, Karki R, Paudel KR, Sharma BR,
Adhikari D and Kim DW: Alkaloid rich fraction from Nelumbo
nucifera targets VSMC proliferation and migration to suppress
restenosis in balloon-injured rat carotid artery. Atherosclerosis.
248:179–189. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang Y, Wang S, Wang R, Li S and Yuan Y:
Neferine exerts antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects on carbon
tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis by inhibiting the MAPK and
NF-κB/IκBα pathways. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2021:41360192021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li H, Gao L, Min J, Yang Y and Zhang R:
Neferine suppresses autophagy-induced inflammation, oxidative
stress and adipocyte differentiation in Graves' orbitopathy. J Cell
Mol Med. 25:1949–1957. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yin S, Ran Q, Yang J, Zhao Y and Li C:
Nootropic effect of neferine on aluminium chloride-induced
Alzheimer's disease in experimental models. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
34:e224292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lin TY, Hung CY, Chiu KM, Lee MY, Lu CW
and Wang SJ: Neferine, an alkaloid from lotus seed embryos, exerts
antiseizure and neuroprotective effects in a kainic acid-induced
seizure model in rats. Int J Mol Sci. 23:41302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang SH, He H, Chen L, Zhang W, Zhang XJ
and Chen JZ: Protective effects of salidroside in the
MPTP/MPP(+)-induced model of Parkinson's disease through
ROS-NO-related mitochondrion pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 51:718–728.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhong Z, Chen W, Gao H, Che N, Xu M, Yang
L, Zhang Y and Ye M: Fecal microbiota transplantation exerts a
protective role in MPTP-induced parkinson's disease via the
TLR4/PI3K/AKT/NF-κB pathway stimulated by α-synuclein. Neurochem
Res. 46:3050–3058. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hiramatsu G, Uta D, Mihara K, Andoh T and
Kume T: Inhibitory effect of panaxytriol on BV-2 microglial cell
activation. J Pharmacol Sci. 145:273–278. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shin HM, Kim MH, Kim BH, Jung SH, Kim YS,
Park HJ, Hong JT, Min KR and Kim Y: Inhibitory action of novel
aromatic diamine compound on lipopolysaccharide-induced nuclear
translocation of NF-kappaB without affecting IkappaB degradation.
FEBS Lett. 571:50–54. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Verri M, Pastoris O, Dossena M, Aquilani
R, Guerriero F, Cuzzoni G, Venturini L, Ricevuti G and Bongiorno
AI: Mitochondrial alterations, oxidative stress and
neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Int J Immunopathol
Pharmacol. 25:345–353. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lull ME and Block ML: Microglial
activation and chronic neurodegeneration. Neurotherapeutics.
7:354–365. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chiu KM, Hung YL, Wang SJ, Tsai YJ, Wu NL,
Liang CW, Chang DC and Hung CF: Anti-allergic and anti-inflammatory
effects of neferine on RBL-2H3 cells. Int J Mol Sci. 22:109942021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu JJ, Yu BY, Huang XK, He MZ, Chen BW,
Chen TT, Fang HY, Chen SQ, Fu XQ, Li PJ, et al: Neferine protects
against hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats by
suppressing NLRP3-mediated inflammasome activation. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2021:66549542021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu XF, Li C, Yang G, Wang YZ, Peng Y, Zhu
DD, Sui AR, Wu Q, Li QF, Wang B, et al: Scorpion venom
heat-resistant peptide attenuates microglia activation and
neuroinflammation. Front Pharmacol. 12:7047152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu J, Zhu H, Taheri S, Mondy W, Bonilha L,
Magwood GS, Lackland D, Adams RJ and Kindy MS: Serum amyloid
A-mediated inflammasome activation of microglial cells in cerebral
ischemia. J Neurosci. 39:9465–9476. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li D, Xu J, Qin Y, Cai N, Cheng Y and Wang
H: Roflupram, a novel phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitor, inhibits
lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammatory responses through
activation of the AMPK/Sirt1 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol.
90:1071762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xie J, Chen MH, Ying CP and Chen MY:
Neferine induces p38 MAPK/JNK1/2 activation to modulate melanoma
proliferation, apoptosis, and oxidative stress. Ann Transl Med.
8:16432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen S, Chu B, Chen Y, Cheng X, Guo D,
Chen L, Wang J, Li Z, Hong Z and Hong D: Neferine suppresses
osteoclast differentiation through suppressing NF-κB signal pathway
but not MAPKs and promote osteogenesis. J Cell Physiol.
234:22960–22971. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ni B, Huang X, Xi Y, Mao Z, Chu X, Zhang
R, Ma X and You H: Neferine inhibits expression of inflammatory
mediators and matrix degrading enzymes in IL-1β-treated rat
chondrocytes via suppressing MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways.
Inflammation. 43:1209–1221. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|