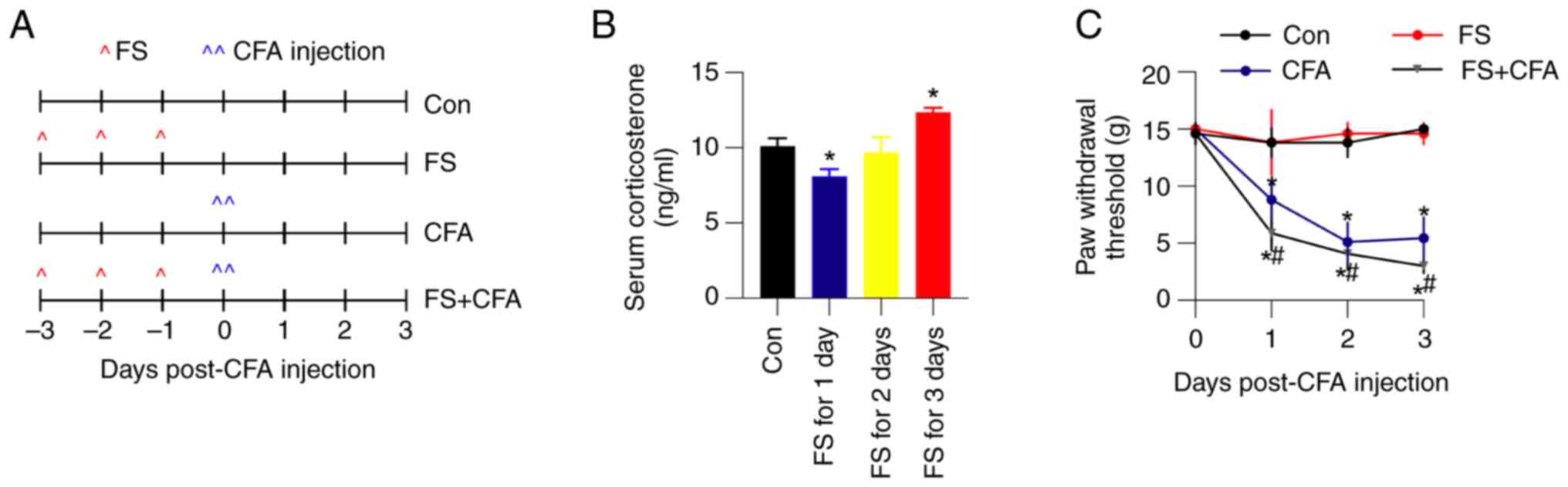
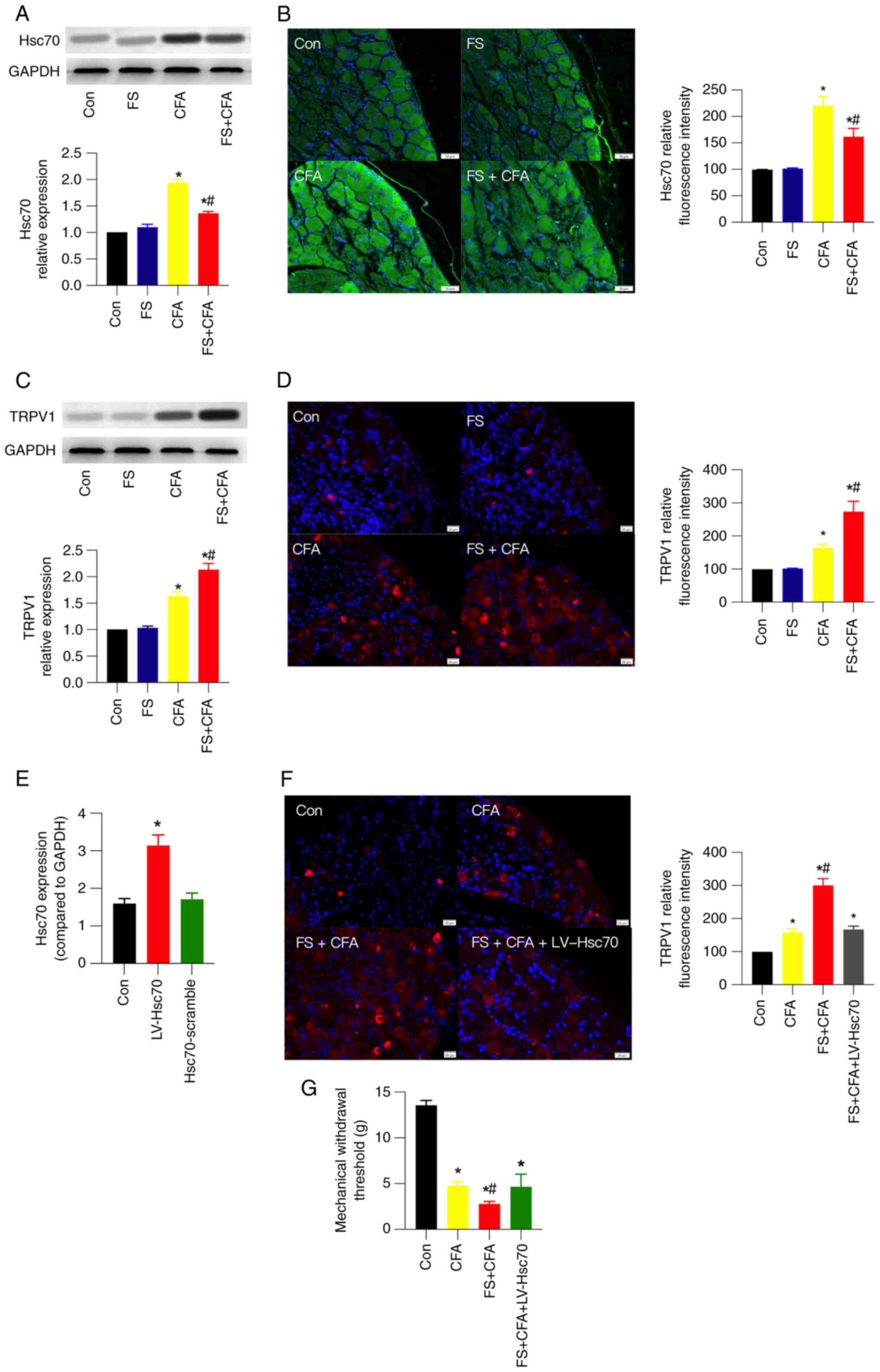
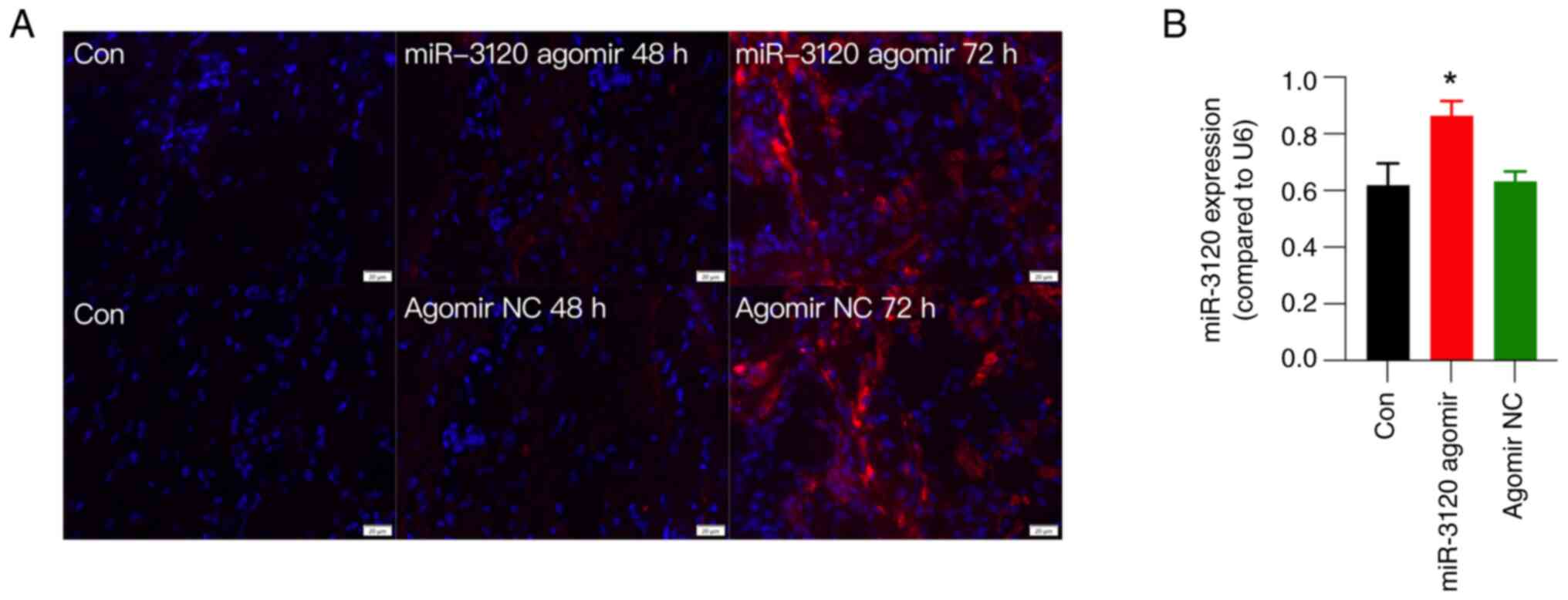
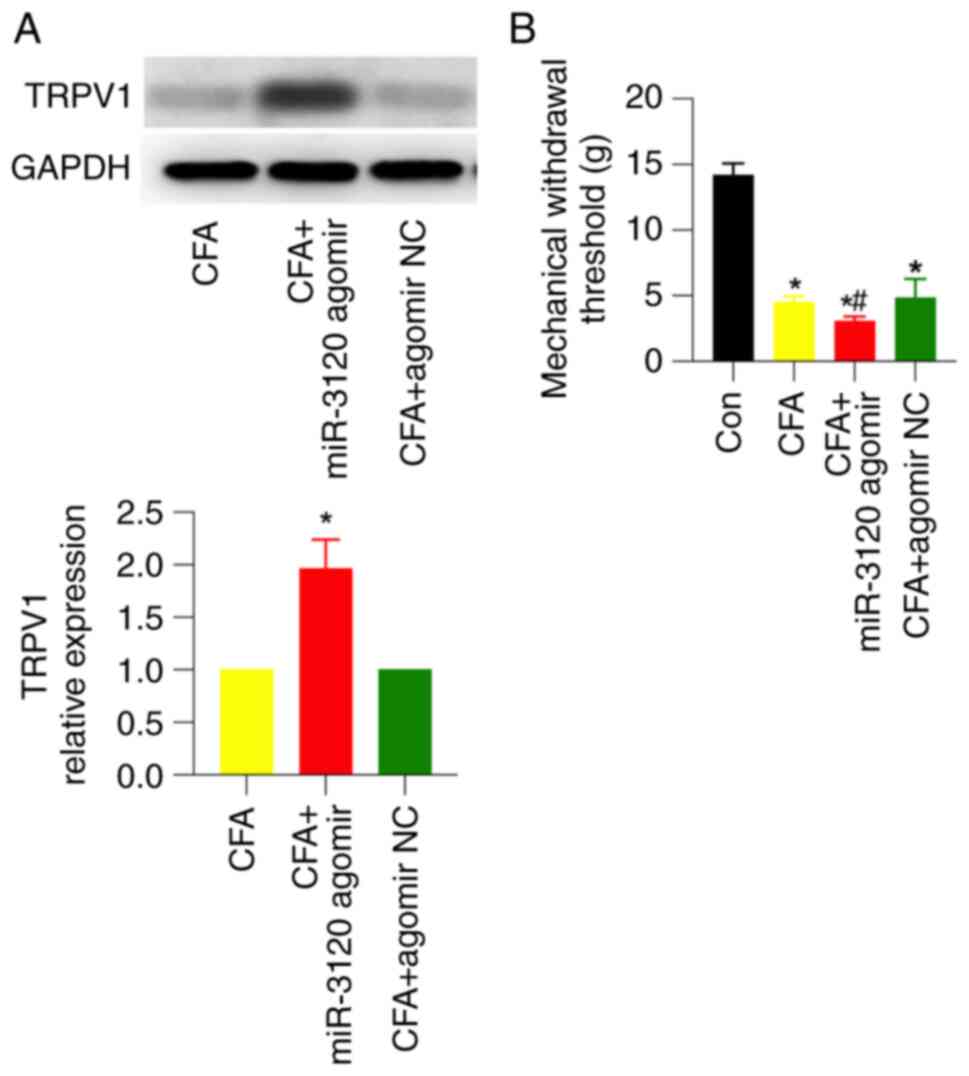
|
1
|
Jennings EM, Okine BN, Roche M and Finn
DP: Stress-induced hyperalgesia. Prog Neurobiol. 121:1–18. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Imbe H, Iwai-Liao Y and Senba E:
Stress-induced hyperalgesia: Animal models and putative mechanisms.
Front Biosci. 11:2179–2192. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lian YN, Lu Q, Chang JL and Zhang Y: The
role of glutamate and its receptors in central nervous system in
stress-induced hyperalgesia. Int J Neurosci. 128:283–290. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Itoga CA, Roltsch Hellard EA, Whitaker AM,
Lu YL, Schreiber AL, Baynes BB, Baiamonte BA, Richardson HN and
Gilpin NW: Traumatic stress promotes hyperalgesia via
corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptor (CRFR1) signaling in
central amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology. 41:2463–2472. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Qi J, Chen C, Meng QX, Wu Y, Wu H and Zhao
TB: Crosstalk between activated microglia and neurons in the spinal
dorsal horn contributes to stress-induced hyperalgesia. Sci Rep.
6:394422016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen S and Brown IR: Translocation of
constitutively expressed heat shock protein Hsc70 to
synapse-enriched areas of the cerebral cortex after hyperthermic
stress. J Neurosci Res. 85:402–409. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iftinca M, Flynn R, Basso L, Melo H,
Aboushousha R, Taylor L and Altier C: The stress protein heat shock
cognate 70 (Hsc70) inhibits the transient receptor potential
vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channel. Mol Pain.
12:17448069166639452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Huang YK, Lu YG, Zhao X, Zhang JB, Zhang
FM, Chen Y, Bi LB, Gu JH, Jiang ZJ, Wu XM, et al: Cytokine activin
C ameliorates chronic neuropathic pain in peripheral nerve injury
rodents by modulating the TRPV1 channel. Br J Pharmacol.
177:5642–5657. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bourinet E, Altier C, Hildebrand ME, Trang
T, Salter MW and Zamponi GW: Calcium-permeable ion channels in pain
signaling. Physiol Rev. 94:81–140. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scott H, Howarth J, Lee YB, Wong LF,
Bantounas I, Phylactou L, Verkade P and Uney JB: MiR-3120 is a
mirror microRNA that targets heat shock cognate protein 70 and
auxilin messenger RNAs and regulates clathrin vesicle uncoating. J
Biol Chem. 287:14726–14733. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hammond SM: An overview of microRNAs. Adv
Drug Delivery Rev. 87:3–14. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sakai A and Suzuki H: Emerging roles of
microRNAs in chronic pain. Neurochem Int. 77:58–67. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Imbe H and Kimura A: Attenuation of pCREB
and Egr1 expression in the insular and anterior cingulate cortices
associated with enhancement of CFA-evoked mechanical
hypersensitivity after repeated forced swim stress. Brain Res Bull.
134:253–261. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Piriyaprasath K, Kakihara Y, Kurahashi A,
Taiyoji M, Kodaira K, Aihara K, Hasegawa M, Yamamura K and Okamoto
K: kojipreventive roles of rice-extracts and ergothioneine on
anxiety- and pain-like responses under psychophysical stress
conditions in male mice. Nutrients. 15:39892023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang FM, Wang B, Hu H, Zhang YY, Chen HH,
Jiang ZJ, Zeng MX and Liu XJ: Transcriptional profiles of TGF-β
superfamily members in the lumbar DRGs and the effects of activins
A and C on inflammatory pain in rats. J Physiol Biochem.
79:313–325. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang J, Zhou F, Zhang S, Mao M, Feng S and
Wang X: Participation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1
in the analgesic effect of duloxetine for paclitaxel induced
peripheral neuropathic pain. Neurosci Lett. 773:1365122022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KL and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sun Q, Zhang S, Zhang BY, Zhang Y, Yao L,
Hu J and Zhang HH: microRNA-181a contributes to gastric
hypersensitivity in rats with diabetes by regulating TLR4
expression. Mol Pain. 19:174480692311593562023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang FM, Wang B, Hu H, Li QY, Chen HH,
Luo LT, Jiang ZJ, Zeng MX and Liu XJ: Transcriptional profiling of
TGF-β superfamily members in lumbar DRGs of rats following sciatic
nerve axotomy and activin C inhibits neuropathic pain. Endocr Metab
Immune Disord Drug Targets. 23:375–388. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang V and Wu W: MicroRNA-based
therapeutics for cancer. BioDrugs. 23:15–23. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Stricher F, Macri C, Ruff M and Muller S:
HSPA8/HSC70 chaperone protein: Structure, function, and chemical
targeting. Autophagy. 9:1937–1954. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Houenou LJ, Li L, Lei M, Kent CR and
Tytell M: Exogenous heat shock cognate protein Hsc 70 prevents
axotomy-induced death of spinal sensory neurons. Cell Stress
Chaperones. 1:161–166. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Urban MJ, Li C, Yu C, Lu Y, Krise JM,
Mcintosh MP, Rajewski RA, Blagg BS and Dobrowsky RT: Inhibiting
heat-shock protein 90 reverses sensory hypoalgesia in diabetic
mice. ASN Neuro. 2:e000402010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Ma S, Ke X, Yi Y, Yu H, Yu D, Li
Q, Shang Y, Lu Y and Pei L: The mechanism of Annexin A1 to modulate
TRPV1 and nociception in dorsal root ganglion neurons. Cell Biosci.
11:1672021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ruan Y, Ling J, Ye F, Cheng N, Wu F, Tang
Z, Cheng X and Liu H: Paeoniflorin alleviates CFA-induced
inflammatory pain by inhibiting TRPV1 and
succinate/SUCNR1-HIF-1α/NLPR3 pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 101((Pt
B)): 1083642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sato M, Ueda E, Konno A, Hirai H, Kurauchi
Y, Hisatsune A, Katsuki H and Seki T: Glucocorticoids negatively
regulates chaperone mediated autophagy and microautophagy. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 528:199–205. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scheich B, Vincze P, Szőke É, Borbély É,
Hunyady Á, Szolcsányi J, Dénes Á, Környei Z, Gaszner B and Helyes
Z: Chronic stress-induced mechanical hyperalgesia is controlled by
capsaicin-sensitive neurones in the mouse. Eur J Pain.
21:1417–1431. 2017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hong S, Zheng G, Wu X, Snider NT, Owyang C
and Wiley JW: Corticosterone mediates reciprocal changes in CB 1
and TRPV1 receptors in primary sensory neurons in the chronically
stressed rat. Gastroenterology. 140:627–637.e4. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhang C, Zhao Y, Wang Y, Wu H, Fang X and
Chen H: Deep RNA sequencing reveals that microRNAs play a key role
in lactation in rats. J Nutr. 144:1142–1149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu M, Wu R, Zhang L, Zhu HY, Xu GY, Qian W
and Zhang PA: Decreased miR-485-5p contributes to inflammatory pain
through post-transcriptional upregulation of ASIC1 in rat dorsal
root ganglion. J Pain Res. 13:3013–3022. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ni J, Gao Y, Gong S, Guo S, Hisamitsu T
and Jiang X: Regulation of µ-opioid type 1 receptors by microRNA134
in dorsal root ganglion neurons following peripheral inflammation.
Eur J Pain. 17:313–323. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kusuda R, Cadetti F, Ravanelli MI, Sousa
TA, Zanon S, De Lucca FL and Lucas G: Differential expression of
microRNAs in mouse pain models. Mol Pain. 7:172011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun W, Yang F, Wang Y, Fu H, Yang Y, Li
CL, Wang XL, Lin Q and Chen J: Contribution of large-sized primary
sensory neuronal sensitization to mechanical allodynia by
upregulation of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide gated
channels via cyclooxygenase 1 cascade. Neuropharmacology. 113((Pt
A)): 217–230. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xiao WH and Bennett GJ: Persistent
low-frequency spontaneous discharge in A-fiber and C-fiber primary
afferent neurons during an inflammatory pain condition.
Anesthesiology. 107:813–821. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu T, Daniels CK and Cao S: Comprehensive
review on the HSC70 functions, interactions with related molecules
and involvement in clinical diseases and therapeutic potential.
Pharmacol Ther. 136:354–374. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang YT and Lu JH: Chaperone-mediated
autophagy in neurodegenerative diseases: Molecular mechanisms and
pharmacological opportunities. Cells. 11:22502022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Rubio E, Valenciano AI, Segundo C, Sánchez
N, De Pablo F and De La Rosa EJ: Programmed cell death in the
neurulating embryo is prevented by the chaperone heat shock cognate
70. Eur J Neurosci. 15:1646–1654. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Robinson MB, Taylor AR, Gifondorwa DJ,
Tytell M and Milligan CE: Exogenous Hsc70, but not thermal
preconditioning, confers protection to motoneurons subjected to
oxidative stress. Dev Neurobiol. 68:1–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ekimova IV, Nitsinskaya LE, Romanova IV,
Pastukhov YF, Margulis BA and Guzhova IV: Exogenous protein
Hsp70/Hsc70 can penetrate into brain structures and attenuate the
severity of chemically-induced seizures. J Neurochem.
115:1035–1044. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xu X, Zhan G, Chen R, Wang D, Guan S and
Xu H: Gut microbiota and its role in stress-induced hyperalgesia:
Gender-specific responses linked to different changes in serum
metabolites. Pharmacol Res. 177:1061292022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Quintero L, Cardenas R and Suarez-Roca H:
Stress-induced hyperalgesia is associated with a reduced and
delayed GABA inhibitory control that enhances post-synaptic NMDA
receptor activation in the spinal cord. Pain. 152:1909–1922. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|