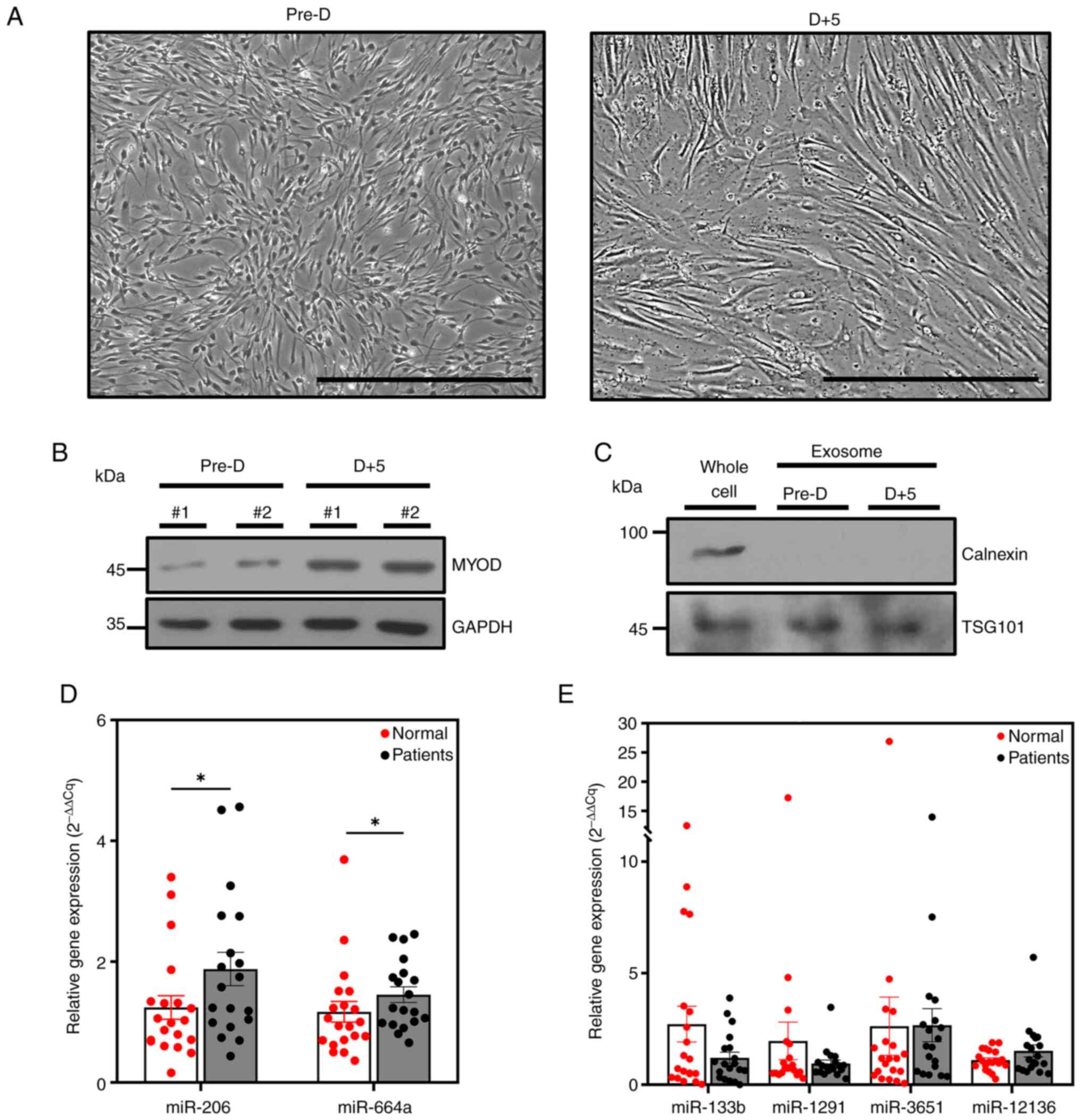
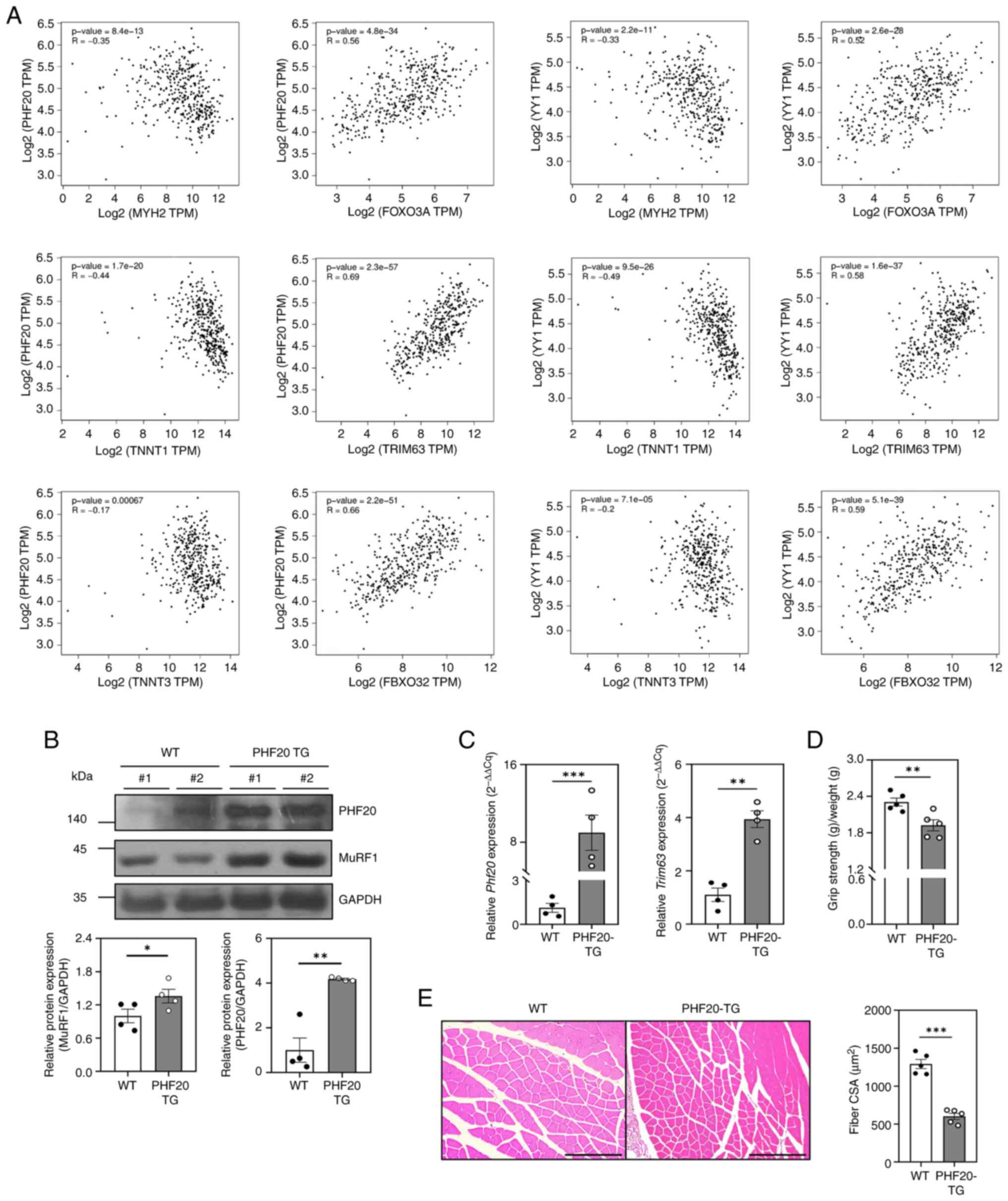
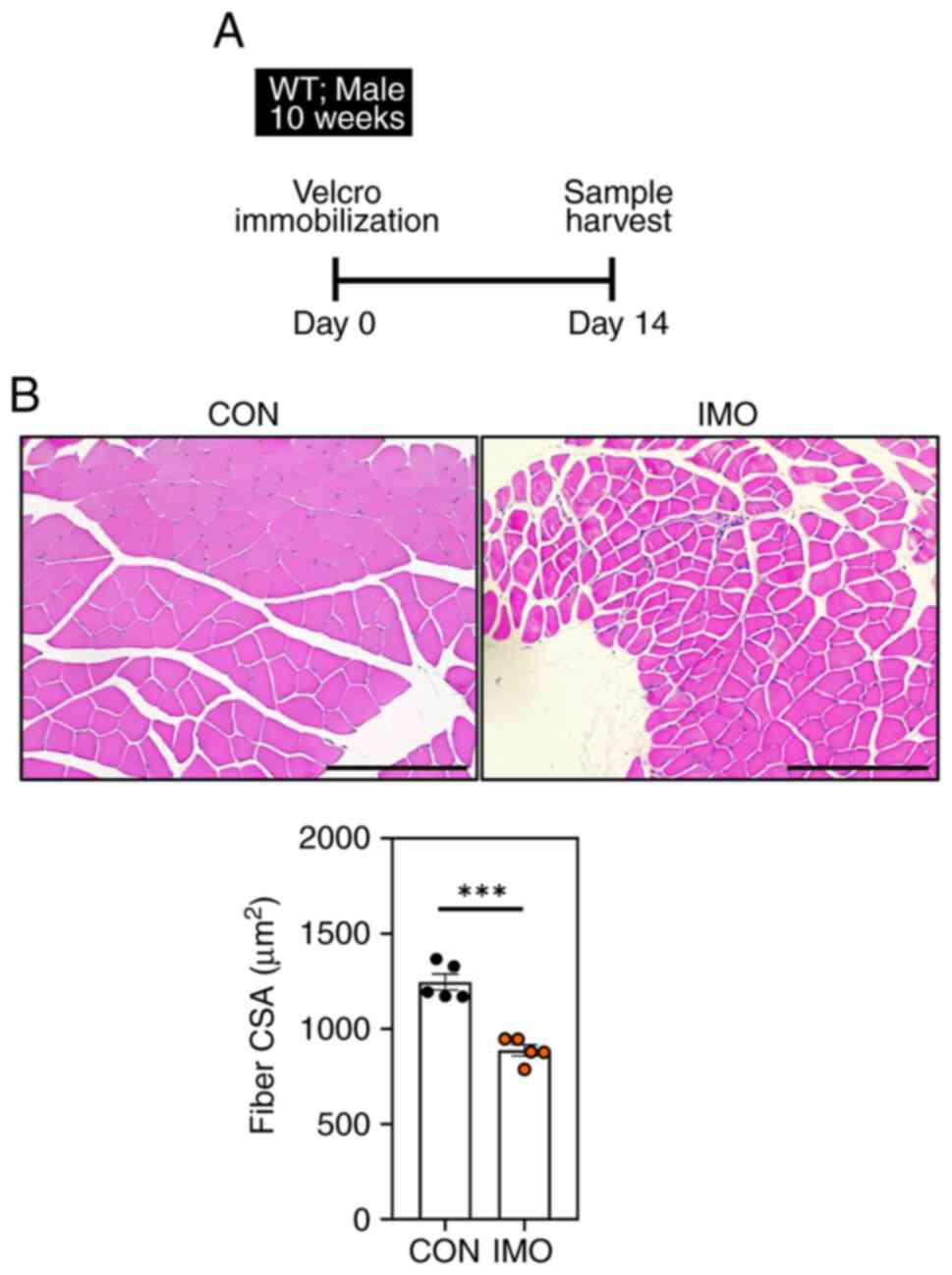
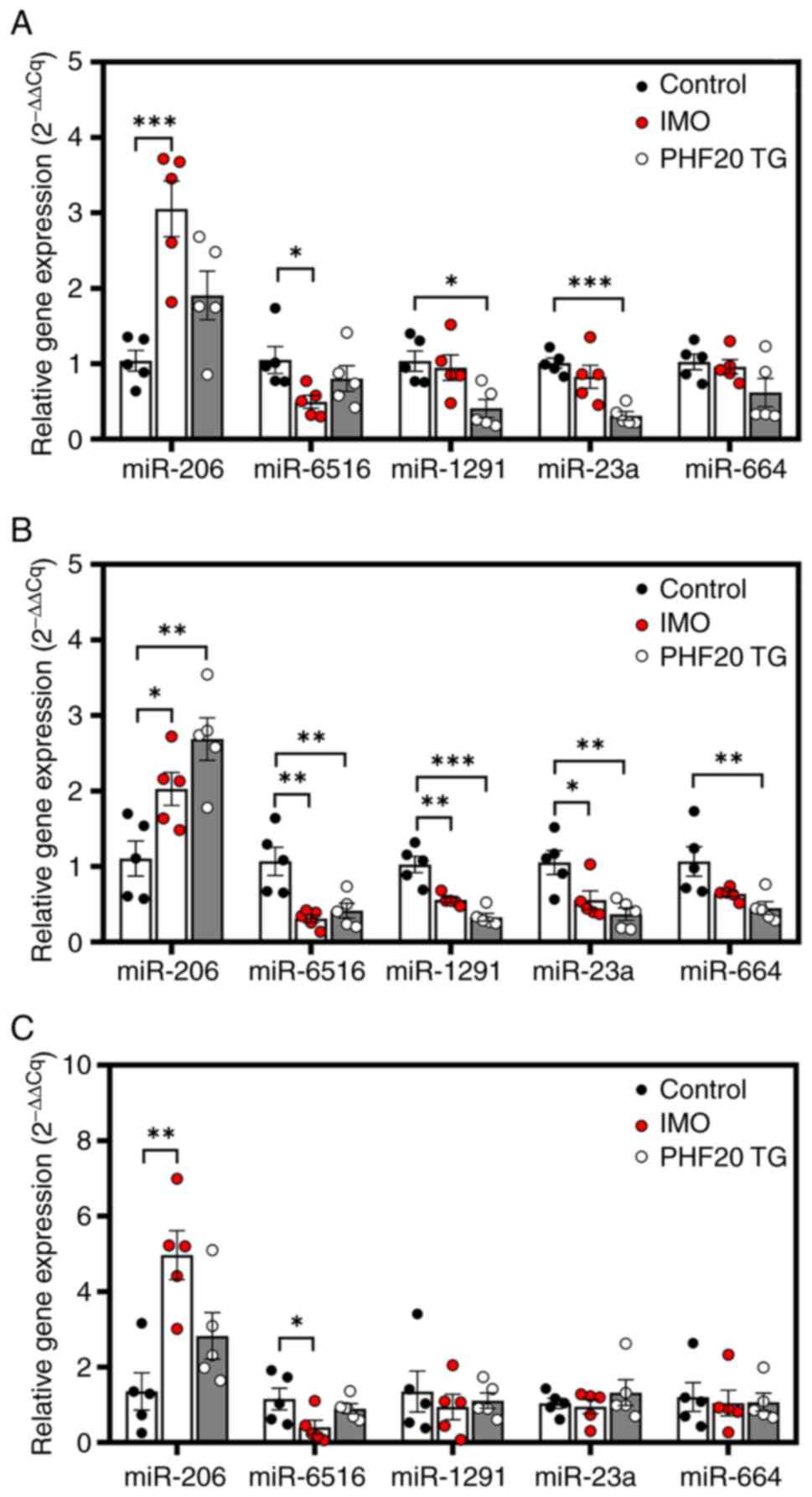
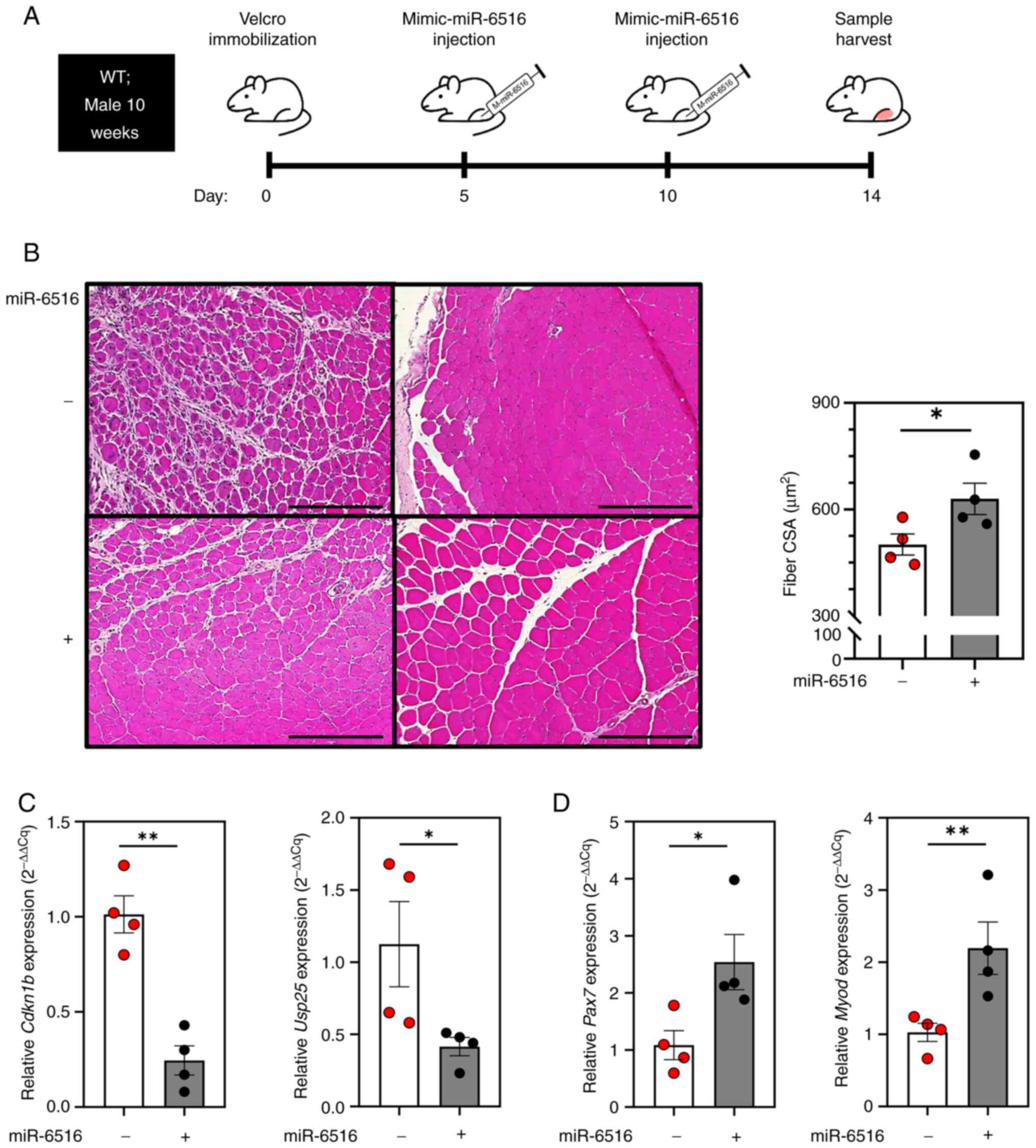
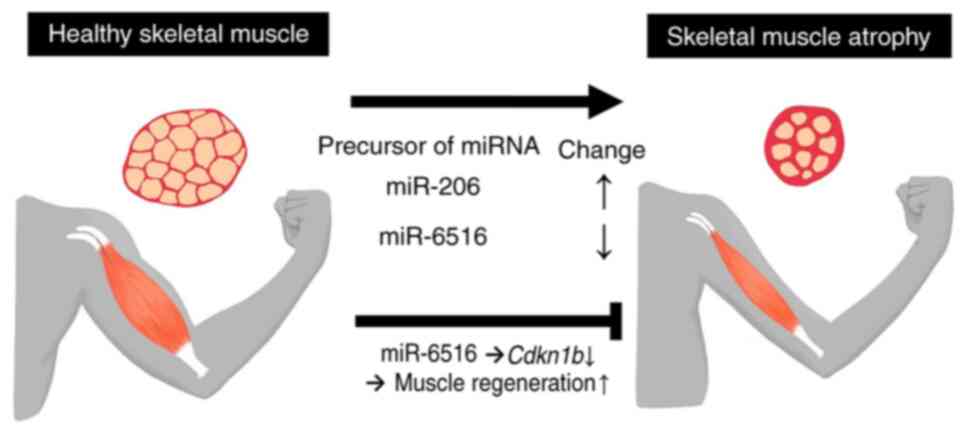
|
1
|
Larsson L, Degens H, Li M, Salviati L, Lee
YI, Thompson W, Kirkland JL and Sandri M: Sarcopenia: Aging-Related
loss of muscle mass and function. Physiol Rev. 99:427–511. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chianca V, Albano D, Messina C, Gitto S,
Ruffo G, Guarino S, Del Grande F and Sconfienza LM: Sarcopenia:
Imaging assessment and clinical application. Abdom Radiol (NY).
47:3205–3216. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Geladari E, Alexopoulos T, Kontogianni MD,
Vasilieva L, Mani I and Alexopoulou A: Mechanisms of sarcopenia in
liver cirrhosis and the role of myokines. Ann Gastroenterol.
36:392–404. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu J, Wan CS, Ktoris K, Reijnierse EM and
Maier AB: Sarcopenia is associated with mortality in adults: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Gerontology. 68:361–376. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wahlen BM, Mekkodathil A, Al-Thani H and
El-Menyar A: Impact of sarcopenia in trauma and surgical patient
population: A literature review. Asian J Surg. 43:647–653. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mirzai S, Eck BL, Chen PH, Estep JD and
Tang WHW: Current approach to the diagnosis of sarcopenia in heart
failure: A narrative review on the role of clinical and imaging
assessments. Circ Heart Fail. 15:e0093222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fabian MR, Sonenberg N and Filipowicz W:
Regulation of mRNA translation and stability by microRNAs. Annu Rev
Biochem. 79:351–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chekulaeva M and Filipowicz W: Mechanisms
of miRNA-mediated post-transcriptional regulation in animal cells.
Curr Opin Cell Biol. 21:452–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
O'Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y and Peng C:
Overview of MicroRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and
circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 9:4022018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Brzeszczynska J, Brzeszczynski F, Hamilton
DF, McGregor R and Simpson AHRW: Role of microRNA in muscle
regeneration and diseases related to muscle dysfunction in atrophy,
cachexia, osteoporosis, and osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res.
9:798–807. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yanai K, Kaneko S, Ishii H, Aomatsu A, Ito
K, Hirai K, Ookawara S, Ishibashi K and Morishita Y: MicroRNAs in
Sarcopenia: A systematic review. Front Med (Lausanne). 7:1802020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee J and Kang H: Role of MicroRNAs and
Long Non-Coding RNAs in Sarcopenia. Cells. 11:1872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gan L and Denecke B: Profiling
Pre-MicroRNA and Mature MicroRNA expressions using a single
microarray and avoiding separate sample preparation. Microarrays
(Basel). 2:24–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pan B, Yu J and Liu X: Upregulation of
miR-886 indicates poor prognosis and promotes tumour progression of
prostate cancer. Andrologia. 54:e142962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee K, Kunkeaw N, Jeon SH, Lee I, Johnson
BH, Kang GY, Bang JY, Park HS, Leelayuwat C and Lee YS: Precursor
miR-886, a novel noncoding RNA repressed in cancer, associates with
PKR and modulates its activity. RNA. 17:1076–1089. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee H, Hong Y, Kong G, Lee DH, Kim M, Tran
Q, Cho H, Kim C, Park S, Kim SH, et al: Yin Yang 1 is required for
PHD finger protein 20-mediated myogenic differentiation in vitro
and in vivo. Cell Death Differ. 27:3321–3336. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vo TT, Tran Q, Hong Y, Lee H, Cho H, Kim
M, Park S, Kim C, Bayarmunkh C, Boldbaatar D, et al: AXL is
required for hypoxia-mediated hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha
function in glioblastoma. Toxicol Res. 39:669–679. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tang Z, Kang B, Li C, Chen T and Zhang Z:
GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling
and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:W556–W560. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
GTEx Consortium: Human genomics. The
Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) pilot analysis: Multitissue gene
regulation in humans. Science. 348:648–660. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee KP, Shin YJ, Panda AC, Abdelmohsen K,
Kim JY, Lee SM, Bahn YJ, Choi JY, Kwon ES, Baek SJ, et al: miR-431
promotes differentiation and regeneration of old skeletal muscle by
targeting Smad4. Genes Dev. 29:1605–1617. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salant GM, Tat KL, Goodrich JA and Kugel
JF: miR-206 knockout shows it is critical for myogenesis and
directly regulates newly identified target mRNAs. RNA Biol.
17:956–965. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iannone F, Montesanto A, Cione E, Crocco
P, Caroleo MC, Dato S, Rose G and Passarino G: Expression Patterns
of Muscle-Specific miR-133b and miR-206 correlate with nutritional
status and Sarcopenia. Nutrients. 12:2972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Scott MS, Avolio F, Ono M, Lamond AI and
Barton GJ: Human miRNA precursors with box H/ACA snoRNA features.
PLoS Comput Biol. 5:e10005072009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Scott MS, Ono M, Yamada K, Endo A, Barton
GJ and Lamond AI: Human box C/D snoRNA processing conservation
across multiple cell types. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:3676–3688. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Scott MS and Ono M: From snoRNA to miRNA:
Dual function regulatory non-coding RNAs. Biochimie. 93:1987–1992.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Rother S and Meister G: Small RNAs derived
from longer non-coding RNAs. Biochimie. 93:1905–1915. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Coley AB, DeMeis JD, Chaudhary NY and
Borchert GM: Small nucleolar derived RNAs as regulators of human
cancer. Biomedicines. 10:18192022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Purnamasari D, Tetrasiwi EN, Kartiko GJ,
Astrella C, Husam K and Laksmi PW: Sarcopenia and chronic
complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Rev Diabet Stud.
18:157–165. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sabatino A, Cuppari L, Stenvinkel P,
Lindholm B and Avesani CM: Sarcopenia in chronic kidney disease:
What have we learned so far? J Nephrol. 34:1347–1372. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Owens J, Moreira K and Bain G:
Characterization of primary human skeletal muscle cells from
multiple commercial sources. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim.
49:695–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Harding CP and Vargis E: Muscle atrophy
marker expression differs between rotary cell culture system and
animal studies. Biomed Res Int. 2019:20428082019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kang SH, Lee HA, Kim M, Lee E, Sohn UD and
Kim I: Forkhead box O3 plays a role in skeletal muscle atrophy
through expression of E3 ubiquitin ligases MuRF-1 and atrogin-1 in
Cushing's syndrome. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 312:E495–E507.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chan J, Lu YC, Yao MM and Kosik RO:
Correlation between hand grip strength and regional muscle mass in
older Asian adults: An observational study. BMC Geriatr.
22:2062022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bodine SC: Disuse-induced muscle wasting.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 45:2200–2208. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nunes EA, Stokes T, McKendry J, Currier BS
and Phillips SM: Disuse-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in disease
and nondisease states in humans: Mechanisms, prevention, and
recovery strategies. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 322:C1068–C1084.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Urso ML, Scrimgeour AG, Chen YW, Thompson
PD and Clarkson PM: Analysis of human skeletal muscle after 48 h
immobilization reveals alterations in mRNA and protein for
extracellular matrix components. J Appl Physiol (1985).
101:1136–1148. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Aihara M, Hirose N, Katsuta W, Saito F and
Maruyama Hagiwara H: A new model of skeletal muscle atrophy induced
by immobilization using a hook-and-loop fastener in mice. J Phys
Ther Sci. 29:1779–1783. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shen Y, Zhang R, Xu L, Wan Q, Zhu J, Gu J,
Huang Z, Ma W, Shen M, Ding F and Sun H: Microarray analysis of
gene expression provides new insights into denervation-induced
skeletal muscle atrophy. Front Physiol. 10:12982019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Spangenburg EE, Chakravarthy MV and Booth
FW: p27Kip1: A key regulator of skeletal muscle satellite cell
proliferation. Clin Orthop Relat Res (403 Suppl). S221–S227. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Pruitt SC, Freeland A, Rusiniak ME, Kunnev
D and Cady GK: Cdkn1b overexpression in adult mice alters the
balance between genome and tissue ageing. Nat Commun. 4:26262013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Toklowicz M, Zbikowska A, Janusz P,
Kotwicki T, Andrusiewicz M and Kotwicka M: MicroRNA expression
profile analysis in human skeletal muscle tissue: Selection of
critical reference. Biomed Pharmacother. 162:1146822023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Mytidou C, Koutsoulidou A, Katsioloudi A,
Prokopi M, Kapnisis K, Michailidou K, Anayiotos A and Phylactou LA:
Muscle-derived exosomes encapsulate myomiRs and are involved in
local skeletal muscle tissue communication. FASEB J. 35:e212792021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ma G, Wang Y, Li Y, Cui L, Zhao Y, Zhao B
and Li K: MiR-206, a key modulator of skeletal muscle development
and disease. Int J Biol Sci. 11:345–352. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Giagnorio E, Malacarne C, Mantegazza R,
Bonanno S and Marcuzzo S: MyomiRs and their multifaceted regulatory
roles in muscle homeostasis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J
Cell Sci. 134:jcs2583492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhelankin AV, Iulmetova LN, Ahmetov II,
Generozov EV and Sharova EI: Diversity and Differential Expression
of MicroRNAs in the human skeletal muscle with distinct fiber type
composition. Life (Basel). 13:6592023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Powers SK, Lynch GS, Murphy KT, Reid MB
and Zijdewind I: Disease-Induced skeletal muscle atrophy and
fatigue. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 48:2307–2319. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Sartori R, Romanello V and Sandri M:
Mechanisms of muscle atrophy and hypertrophy: Implications in
health and disease. Nat Commun. 12:3302021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Marusic U, Narici M, Simunic B, Pisot R
and Ritzmann R: Nonuniform loss of muscle strength and atrophy
during bed rest: A systematic review. J Appl Physiol (1985).
131:194–206. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Gao Y, Arfat Y, Wang H and Goswami N:
Muscle atrophy induced by mechanical unloading: Mechanisms and
potential countermeasures. Front Physiol. 9:2352018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Hosoyama T, Van Dyke J and Suzuki M:
Applications of skeletal muscle progenitor cells for neuromuscular
diseases. Am J Stem Cells. 1:253–263. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Pang KT, Loo LSW, Chia S, Ong FYT, Yu H
and Walsh I: Insight into muscle stem cell regeneration and
mechanobiology. Stem Cell Res Ther. 14:1292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Ji LL and Yeo D: Mitochondrial
dysregulation and muscle disuse atrophy. F1000Res. 8:F1000 Faculty
Rev. 16212019. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Manas-Garcia L, Penedo-Vazquez A,
Lopez-Postigo A, Deschrevel J, Duran X and Barreiro E: Prolonged
immobilization exacerbates the loss of muscle mass and function
induced by cancer-associated cachexia through enhanced proteolysis
in mice. Int J Mol Sci. 21:81672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Thompson JM, West DWD, Doering TM, Budiono
BP, Lessard SJ, Koch LG, Britton SL, Byrne NM, Brown MA, Ashton KJ
and Coffey VG: Effect of short-term hindlimb immobilization on
skeletal muscle atrophy and the transcriptome in a low compared
with high responder to endurance training model. PLoS One.
17:e02617232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kim H, Bae YU, Lee H, Kim H, Jeon JS, Noh
H, Han DC, Byun DW, Kim SH, Park HK, et al: Effect of diabetes on
exosomal miRNA profile in patients with obesity. BMJ Open Diabetes
Res Care. 8:e0014032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Hata J, Nakashima D, Tsuji O, Fujiyoshi K,
Yasutake K, Sera Y, Komaki Y, Hikishima K, Nagura T, Matsumoto M,
et al: Noninvasive technique to evaluate the muscle fiber
characteristics using q-space imaging. PLoS One. 14:e02148052019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wang C, Yue F and Kuang S: Muscle
histology characterization using H&E staining and muscle fiber
type classification using immunofluorescence staining. Bio Protoc.
7:e22792017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|