Introduction
Maintaining of skeletal muscle functional
homeostasis is an important factor in the quality of life,
including posture, movement and breathing, in addition to
regulating glucose and protein metabolism and heat production
(1,2). In addition, skeletal muscle loss can
lead to adverse health outcomes including disability, weakness,
fatigue, insulin resistance and mortality (3–5).
Therefore, preventing muscle loss and strengthening the muscles
have important implications for athletes and individuals who want
to maintain a healthy body. Various factors, including acute or
chronic disease, biochemical changes due to aging, poor nutrition,
or lack of activity can lead to muscle loss, which is difficult to
control because it is multifactorial and genetically influenced
(3,6). However, decreased protein synthesis,
protein degradation, mitochondrial and satellite cell dysfunction,
and increased inflammation are associated with muscle loss
(7). Previously, research on the
development of various functional foods and medicines for the
strengthening muscle function and maintaining the balance between
protein synthesis and degradation in muscles is being actively
conducted. In addition, herbs and medicinal plants, whose various
beneficial functions have been proven in ethnopharmacological
studies, have been safely used for a long time. Therefore, they
have been the focus of development as natural medicines to prevent
and treat muscle loss (8–10).
Saururus chinensis (Lour.) Baill. (SC) is a
perennial herbaceous plant of the Saururaceae family, mainly
distributed in wet and humid regions of East Asia and rarely found
in lowland wetlands on Jeju Island, South Korea. In South Korea, SC
is an Endangered Species designated by the Korea Forest Service and
a Class 2 endangered wild animal or plant species by the Ministry
of Environment (11,12). It has been widely used as
traditional Chinese medicine for a wide range of disorders
including edema, pneumonia, hypertension, leprosy, jaundice,
gonorrhea, rheumatoid arthritis and inflammatory diseases (13–16).
SC contains essential oil such as quercetin, quercitrin,
isoquercitrin, rutin and tannin as main components, and contains
various lignans (17,18), which have several pharmacological
activities including anti-asthmatic (19), anti-oxidant (20), anti-inflammatory (21–23),
anti-atopic (24), anticancer
(25) and hepatoprotective
(26) properties. In addition,
according to a previous study, sauchinone isolated from the roots
of SC protects oxidative stress-induced C2C12 myoblast damage by
regulating heat shock protein-70 level (27). However, the effects of SC extract
(SCE) on muscle mass, function and metabolic mechanisms have not
yet been elucidated.
Therefore, to evaluate how SCE may be beneficial to
muscle function, the present study investigated the regulation of
muscle differentiation, mitochondrial biogenic factor, energy
metabolism and protein synthesis in C2C12 mouse skeletal muscle
cells via activation of the PGC-1α, AMP-activated protein kinase
(AMPK) and the AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway post-SCE
treatment.
Materials and methods
Chemical, reagents and antibodies
SCE (cat. no. KPM046-069) was purchased from the
Korea Plant Extract Bank of the Korea Research Institute of
Bioscience and Biotechnology (Cheongju, Korea). The maximum
concentration of DMSO in the cell culture medium was 0.1% (v/v).
TRIzol® reagent was purchased from Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc. Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (DMEM), fetal
bovine serum (FBS) and penicillin-streptomycin were obtained from
Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc. Specific antibodies against
myosin heavy chain (MyHC; 1:500; cat. no. sc-376157), myogenic
differentiation 1 (MyoD; 1:1,000; cat. no. sc-377460), myogenin and
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1 α
(PGC-1α; 1:1,000; cat. no. sc-518038) were obtained from Santa Cruz
Biotechnology, Inc. Antibodies against non-phospho (active)
β-catenin (1:1,000; cat. no. 8814), β-catenin (1:1,000; cat. no.
9582), phospho-AMPK (1:1,000; cat. no. 2535), AMPK (1:1,000; cat.
no. 2532), phospho-AKT (1:1,000; cat. no. 9271), AKT (1:1,000; cat.
no. 9272), phospho-mTOR (1:1,000; cat. no. 2971), mTOR (1:1,000;
cat. no. 2983), phospho-ribosomal protein S6 kinase B1(p70S6K1)
(1:1,000; cat. no. 9234), p70S6K1 (1:1,000; cat. no. 2708) and
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH; 1:1,000; cat. no.
2118) were purchased from Cell Signaling Technology, Inc. Specific
antibody against phospho-histone deacetylase 5 (HDAC5; 1:1,000;
cat. no. ab47283) was obtained from Abcam. Secondary antibodies,
including horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-mouse (1:3,000;
cat. no. ADI-SAB-100-J) and anti-rabbit IgG (1:3,000; cat. no.
ADI-SAB-300-J), were obtained from Enzo Life Sciences, Inc.
Cell culture
Murine C2C12 skeletal muscle cell line (cat. no.
CRL-1772) were purchased from American Type Culture Collection.
Cells were cultured in growth medium (GM; DMEM containing 10% FBS,
100 IU/ml penicillin, and 100 µg/ml streptomycin) in a humidified
incubator at 37°C with 5% CO2 until they reached 70%
confluence. To induce differentiation, nearly confluent C2C12 cells
were incubated in DMEM containing 2% heat-inactivated horse serum
(differentiation medium; DM) for varying lengths of time as
previously described (27).
Induction of myogenic differentiation
and observation of morphologic changes
C2C12 myoblasts were seeded in 6-well plates at a
density of 5×104 cells/well. For the myogenic
differentiation, GM was replaced with DM when the cells reached 80%
confluence. Then, the cells were treated with or without SCE at
final concentrations of 0,1,5, or 10 ng/ml for 5 days. Fresh SCE
was added to the DM every 2 days. The morphology of myotubes was
observed using a phase-contrast microscope (Nikon TS2; Nikon
Instruments Inc.). Images were captured at ×50 magnification.
Measurement of cell viability
To determine cytotoxicity, C2C12 myoblasts were
seeded in 96-well plates (1×103 cells/well) and
incubated in the culture medium until they reached 70–80%
confluence as previously described (28). The medium was then changed to a DM,
and the cells were treated with or without SCE (0,1,5, or 10
ng/ml). Following incubation for 5 days, after adding XTT solution
(50 µl) to each well and incubating for 4 h at 37°C, cell viability
was determined by absorbance at 450 nm using a multi-detection
microplate reader (Molecular Devices, LLC).
Immunofluorescence staining and
determination of the diameter
C2C12 myoblasts cultured in 48-well plates
(3×104 cells/well) were fixed using 3.7%
paraformaldehyde [in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS)],
permeabilized in 0.1% Triton X-100 for 15 min and blocked in 5%
bovine serum albumin (BSA; MiliporeSigma) for 3 h at room
temperature as previously described (27). After the cells were blocked in 5%
BSA, they were incubated with the primary antibody at 4°C for 24 h.
Mouse anti-MyHC antibody was used at a 1:200 dilution. MyHC was
detected by incubating the cells with anti-mouse secondary antibody
Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated (1:200; cat. no. A32723; Thermo Fisher
Scientific, Inc.) at 4°C for 24 h, and then
4′-6-diamidino-2-phenylindol (DAPI; 1 mg/ml) was used to label the
nuclei. Cells were observed using fluorescence Leica DM IRE2
microscope (Leica Microsystems GmbH) and Nikon Eclipse 50I
microscope (Nikon Instruments Inc.) and images of myotubes were
captured using IM50 software (Leica Microsystems GmbH) and
Nis-Elements D 4.00 software (Nikon Instruments Inc.),
respectively, for size comparison. For myotube diameter, the
average measurement on each slide was calculated from ~25 myotubes;
three fields were randomly selected, and all MyHC-positive
multinucleated cells containing at least three nuclei in each field
were quantified. The data were then converted to a percentage
increase compared with the control (DM).
Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR
(RT-qPCR)
Total RNA was extracted from C2C12 cells using
TRIzol® reagent (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.)
according to the manufacturer's instructions and cDNA was
synthesized, followed by qPCR using SYBR® Green Premix
(Bioneer Corp.) with specific primers as previously described
(29). qPCR primers were designed
using Primer3 software (Whitehead Institute for Biomedical
Research). The amplification conditions were 95°C for 5 min,
followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 1 min, 60°C for 30 sec, and 72°C
for 1 min. Using GAPDH as an internal control, the relative
gene expression was determined using the quantification cycle
(Cq) value (30). The
primer sequences were as follows: GAPDH forward,
5′-TCAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGCAG-3′ and reverse,
5′-AGTGGGAGTTGCTGTTGAAGT-3′; MyHC forward,
5′-GCCCAGTGGAGGACAAAATA-3′ and reverse, 5′-TCTACGTGCTCCTCAGCAT-3′;
MyoD forward, 5′-CGCTCCAACTGCTCTGATG-3′ and reverse,
5′-TAGTAGGCGGTGTCGTAGCC-3′; Myogenin forward,
5′-CTACAGGCCTTGCTCAGCTC-3′ and reverse, 5′-AGATTGTGGGCGTCTGTAGG-3′;
Myogenic Factor 5 (Myf5) forward, 5′-AGGAAAAGAAGCCCTGAAGC-3′ and
reverse, 5′-GCAAAAAGAACAGGCAGAGG-3′; PGC-1α forward,
5′-CACCAAACCCACAGAAAACAG-3′ and reverse,
5′-GGGTCAGAGGAAGAGATAAAGTTG-3′; and nuclear respiratory factor
(NRF)-1 forward, 5′-AGGGCGGTGAAATGACCATC-3′ and reverse,
5′CGGCAGCTTCACTGTTGAGG-3′.
Western blotting
C2C12 myoblasts were washed in a culture dish with
cold phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) and lysed in cold lysis buffer
containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100,
1 mM sodium fluoride, 1 mM sodium vanadate, 1% deoxycholate and
protease inhibitors as previously described (29). Samples were incubated in ice for 30
min with lysis buffer and cell debris were separated by
centrifugation at 10,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C. Protein
concentrations were determined using the Bio-Rad DC Protein Assay
Kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories Inc.). Total protein extracts (20–30 µg)
were then separated using 10% SDS-PAGE, transferred to PVDF
membranes (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc.), blocked with 5% non-fat
milk in TBST buffer (100 mM NaCl, 10 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5 and 0.1%
Tween-20) for 1 h at room temperature, and incubated with specific
primary antibody overnight at 4°C. The membranes were then washed
thrice and incubated with secondary antibodies for 1 h at room
temperature. The membranes were further washed three times and
visualized using Immobilon Western Chemiluminescent HRP Substrate
(MilliporeSigma). GAPDH was used as a loading control. The density
of western blotting bands was quantified using ImageJ software
(version 2; National Institutes of Health).
Statistical analysis
All experimental tests were performed at least three
times (n=3 per group) and all quantitative data are presented as
the mean ± standard deviation (SD). The data were analyzed using
one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test using
SPSS 14.0 (IBM Corp.). P<0.05 was considered to indicate a
statistically significant difference.
Results
SCE promotes myoblast
differentiation
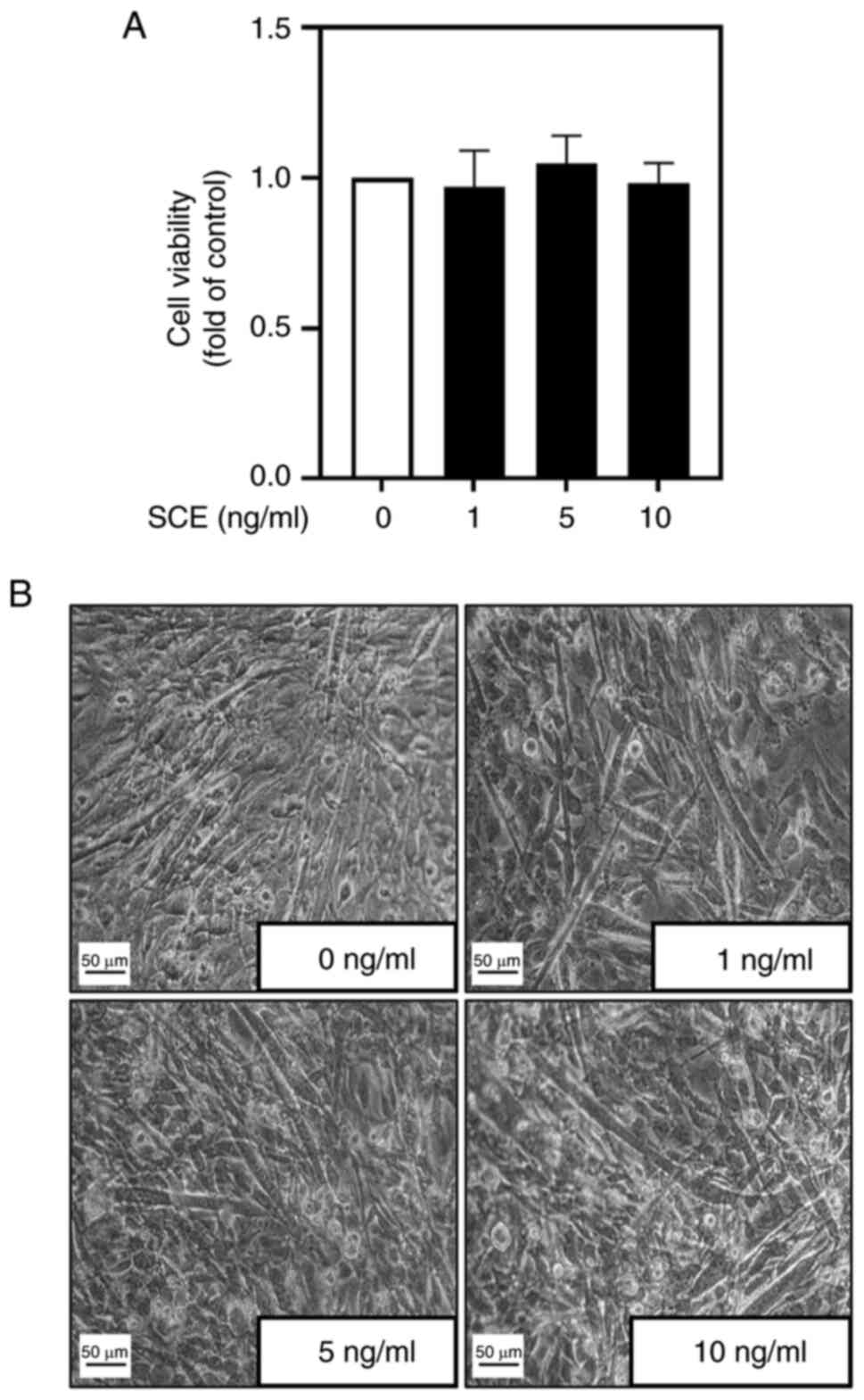
Before investigating the effects of SCE on myoblast
differentiation, its cytotoxicity during myoblast differentiation
was examined. No significant difference was observed in myoblast
viability with the addition of up to 10 ng/ml SCE (Fig. 1A). Subsequently, the morphological
changes in C2C12 cells according to SCE concentration during their
differentiation were examined. During differentiation for 5 days,
treatment with SCE led to the formation of larger and more
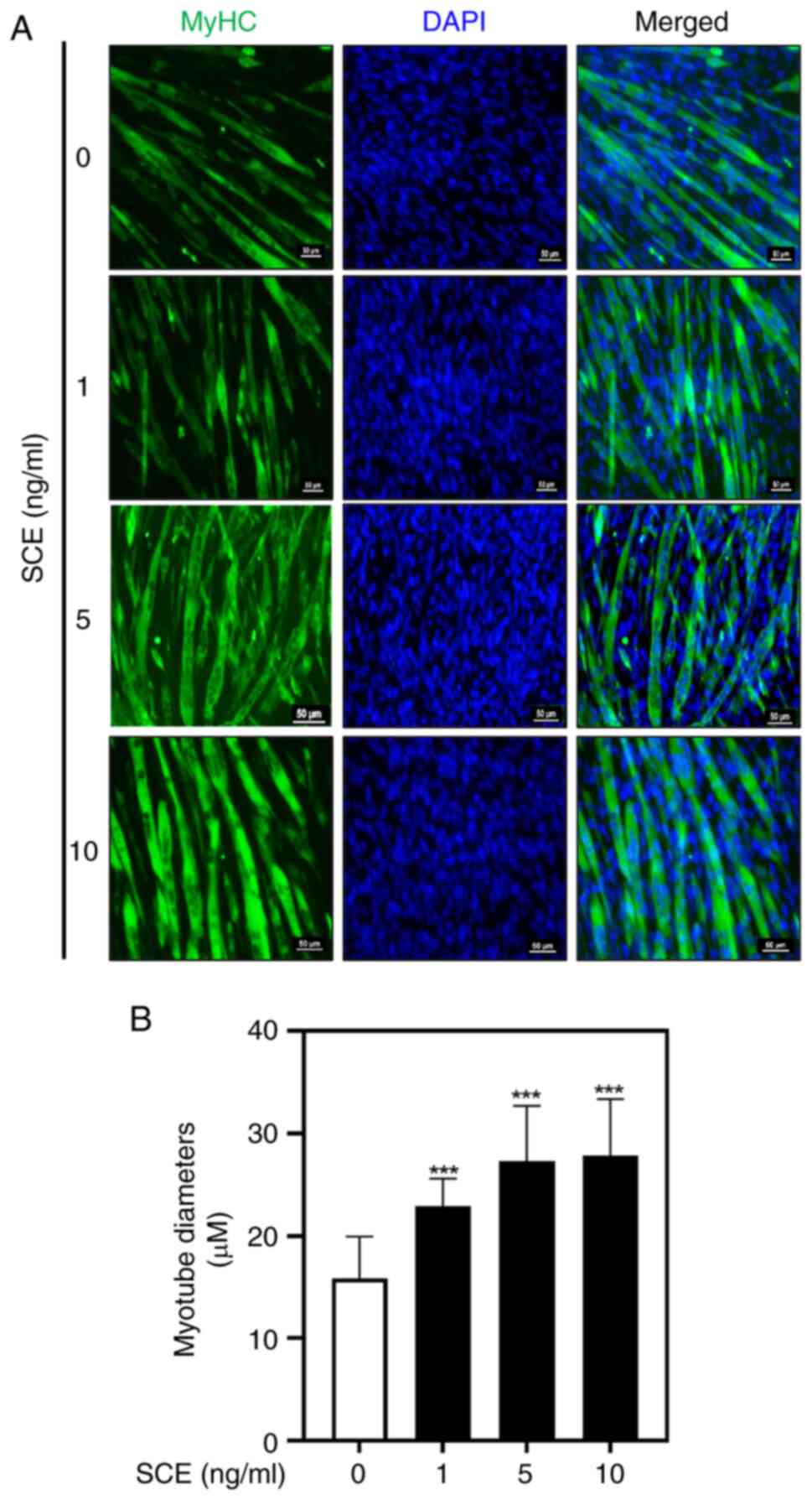
elongated myotubes compared with untreated cells (Fig. 1B). MyHC immunofluorescence staining
was performed to confirm the effect of SCE on myotube formation. As
demonstrated in Fig. 2A, SCE
treatment promoted C2C12 differentiation, as evaluated by the
visualization of MyHC-positive myotubes. DAPI staining was
performed to assess cell density and to determine myotube
formation, as observed in myotubes containing three or more nuclei
(Fig. 2A). On the 5th day of
differentiation, the myotube diameter was significantly increased
in the 1, 5 and 10 ng/ml SCE treatment groups compared with that in
the control group (Fig. 2B).
SCE increases the expression of
muscle-specific factors related to myogenesis
It was investigated whether SCE affects the
expression of muscle-specific genes involved in myogenic
differentiation. As revealed in Fig.
3A, RT-qPCR results revealed that SCE gradually increased the
mRNA expression of MyHC, MyoD, myogenin and Myf5 in a
dose-dependent manner. Protein expression of MyHC, MyoD and
myogenin was also significantly increased compared with that in the
control group, even after treatment with SCE 1 ng/ml for 5 days, as
expected (Fig. 3B). To confirm
changes in the expression of myogenesis factors during the myoblast
differentiation period, C2C12 myoblasts were treated with 10 ng/ml
SCE for 5 days. Myf5 mRNA level and the mRNA and protein levels of
MyHC and myogenin peaked on day 5 compared with those in the
control (Fig. 3C and D). Notably,
MyoD mRNA levels in SCE-treated cells were significantly higher
than those in control cells on days 1 and 3 (Fig. 3C). Furthermore, MyoD protein levels
were significantly upregulated in SCE-treated cells from day 3 to 5
compared with the control (Fig.
3D). Therefore, activation of MyoD is essential for the early
stages of myogenic determination. Next, the activity of β-catenin,
a major protein that regulates myoblast proliferation and myotube
formation, was confirmed according to dose and time via western
blotting (Fig. 3E and F). The
activity of β-catenin was significantly increased at 1, 5 and 10
ng/ml (Fig. 3E) and was activated
compared with the control group on days 1 and 3 after treatment
with 10 ng/ml SCE (Fig. 3F).
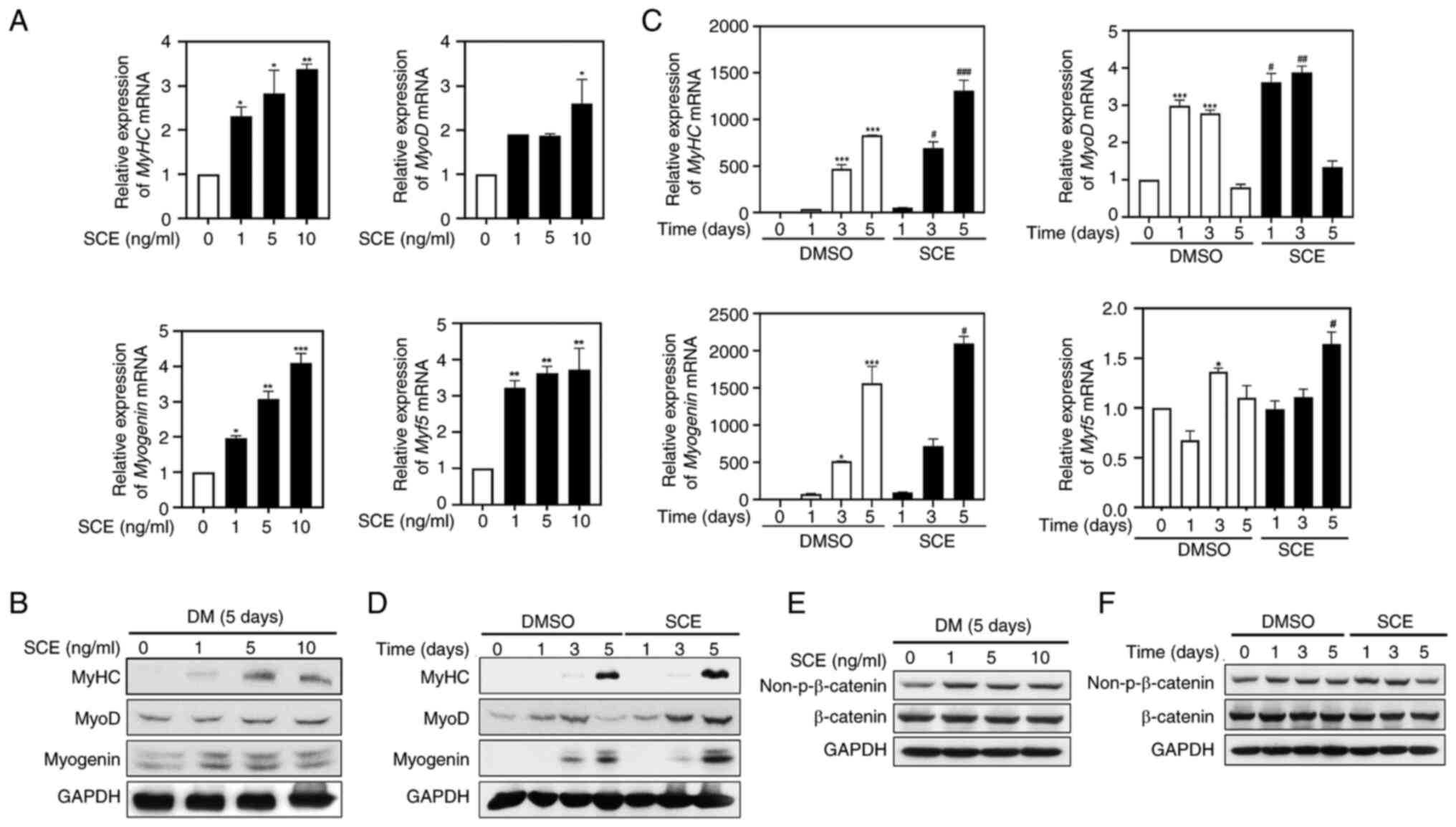 | Figure 3.SCE increases the expression of
muscle-specific factors related to myogenesis. C2C12 myoblasts were
induced to differentiate in DMEM containing 2% horse serum, treated
for 5 days with different concentrations of SCE (1, 5 and 10
ng/ml), and analyzed by (A) RT-qPCR (n=3 per group) and (B) western
blotting (n=3 per group). The expression of MyHC, MyoD, myogenin
and Myf5 over the time course of myogenesis was detected through
(C) RT-qPCR (n=3 per group) and (D) western blotting (n=3 per
group) in cells treated with SCE. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and
***P<0.001 vs. the control group; #P<0.05,
##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 vs. the
SCE-treated group at the corresponding indicated times.
Non-β-catenin and β-catenin were detected by western blotting
depending on (E) the concentration or (F) the time of SCE. SCE,
Saururus chinensis (Lour.) Baill. extract; RT-qPCR, reverse
transcription-quantitative PCR; MyHC, myosin heavy chain; MyoD,
myogenic differentiation 1; Myf5, Myogenic Factor 5. |
SCE upregulates the expression of
mitochondria biogenesis factors
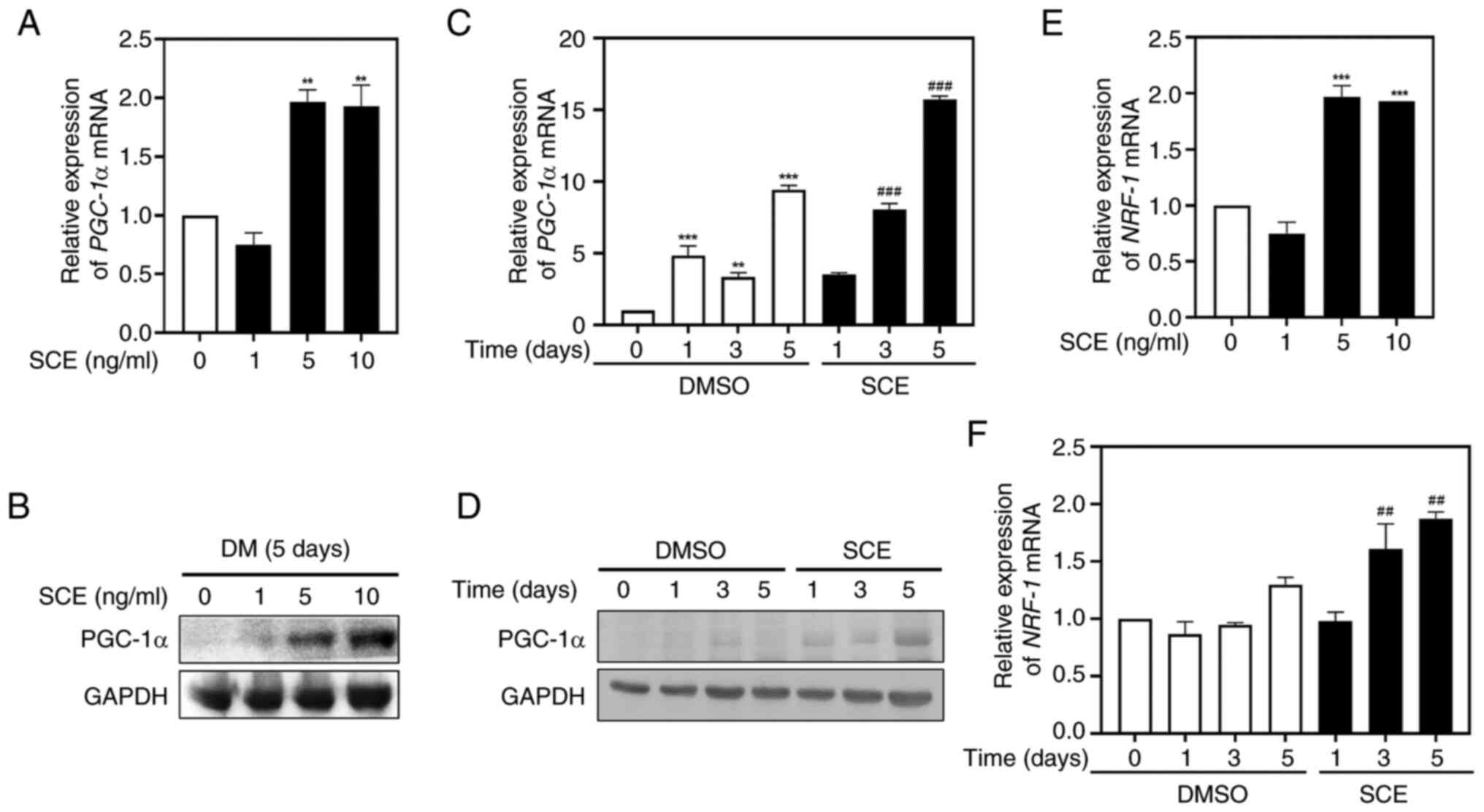
To demonstrate the effects of SCE on mitochondrial
biogenesis during myogenic differentiation, the expression of the
mitochondrial biogenesis transcription factors PGC-1α and NRF-1 at
the mRNA and protein levels were measured using quantitative
RT-qPCR and western blotting. Treatment of myotubes with 5 or 10
ng/ml SCE for 5 days increased the expression of PGC-1α mRNA
(Fig. 4A) and protein (Fig. 4B) compared with the control. In
addition, treatment with SCE 10 ng/ml significantly increased
PGC-1α in a time-dependent manner during myoblast differentiation
(Fig. 4C). As for the protein
levels, the expression of PGC-1α significantly increased in a
time-dependent manner (Fig. 4D),
suggesting the involvement of PGC-1α in myogenic differentiation.
Similar to PGC-1α, the expression of NRF-1 mRNA was also
significantly increased when cells were treated with 5 or 10 ng/ml
SCE for 5 days (Fig. 4E), and
upregulated at 3 or 5 days when cells were treated with 10 ng/ml
SCE during myogenesis (Fig.
4F).
SCE enhances the AMPK-HDAC5 pathways
in myotubes
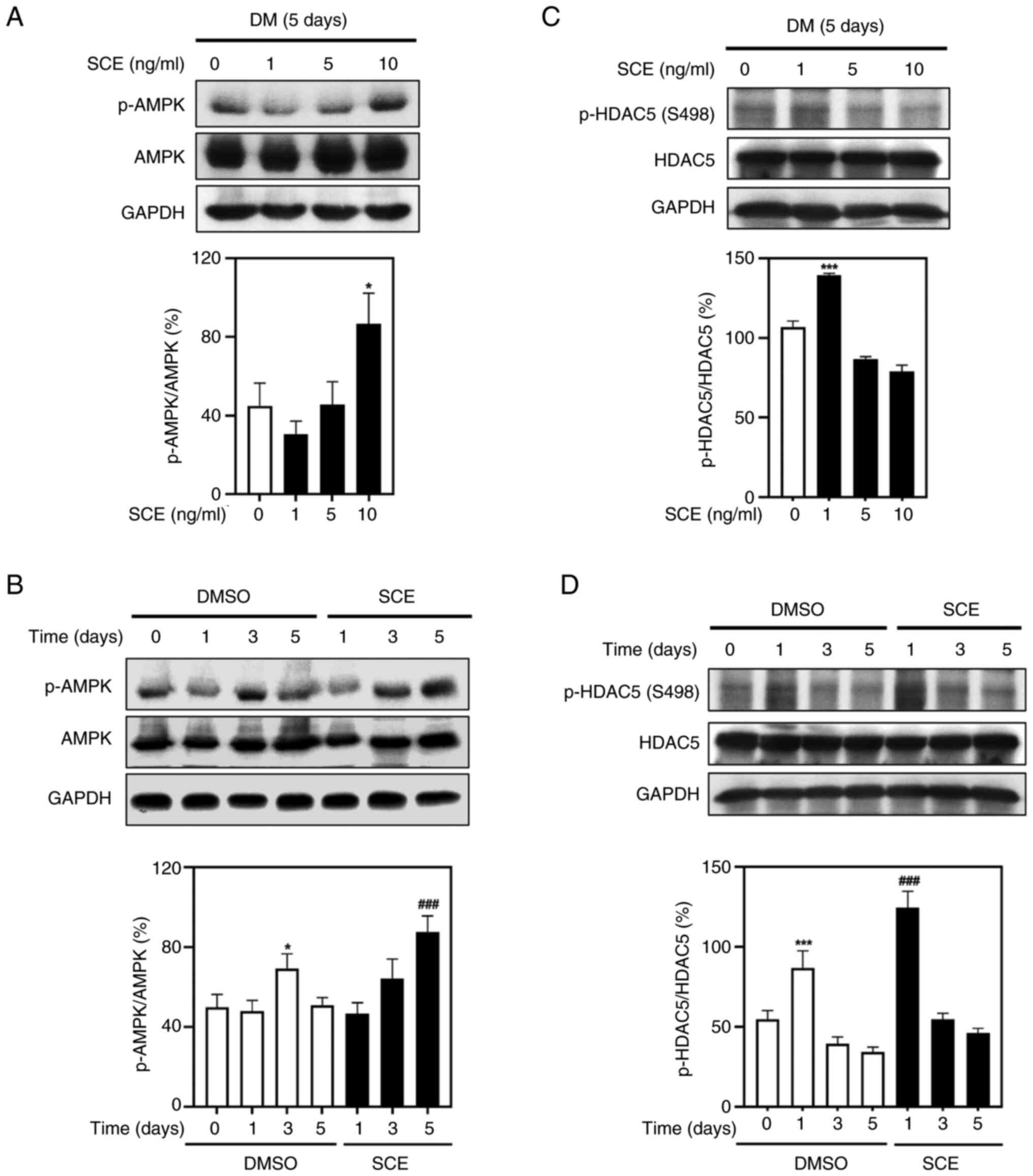
Next, the effects of SCE on the AMPK-HDAC5 signaling
pathway that activates energy metabolism in myotubes were tested.
Treatment with 1, 5 and 10 ng/ml SCE resulted in increased
phosphorylation of AMPK in the myotubes (Fig. 5A). Treatment with 10 ng/ml SCE
significantly increased the phosphorylation of AMPK compared with
that in the control (Fig. 5B).
Moreover, the phosphorylation of HDAC5 was increased at 1 ng/ml
(Fig. 5C) and was significantly
activated compared with the control group on day 1 (Fig. 5D). These results indicated that SCE
increases energy metabolism associated with mitochondrial
biogenesis in myotubes by activating the AMPK-HDAC5 signaling
pathway.
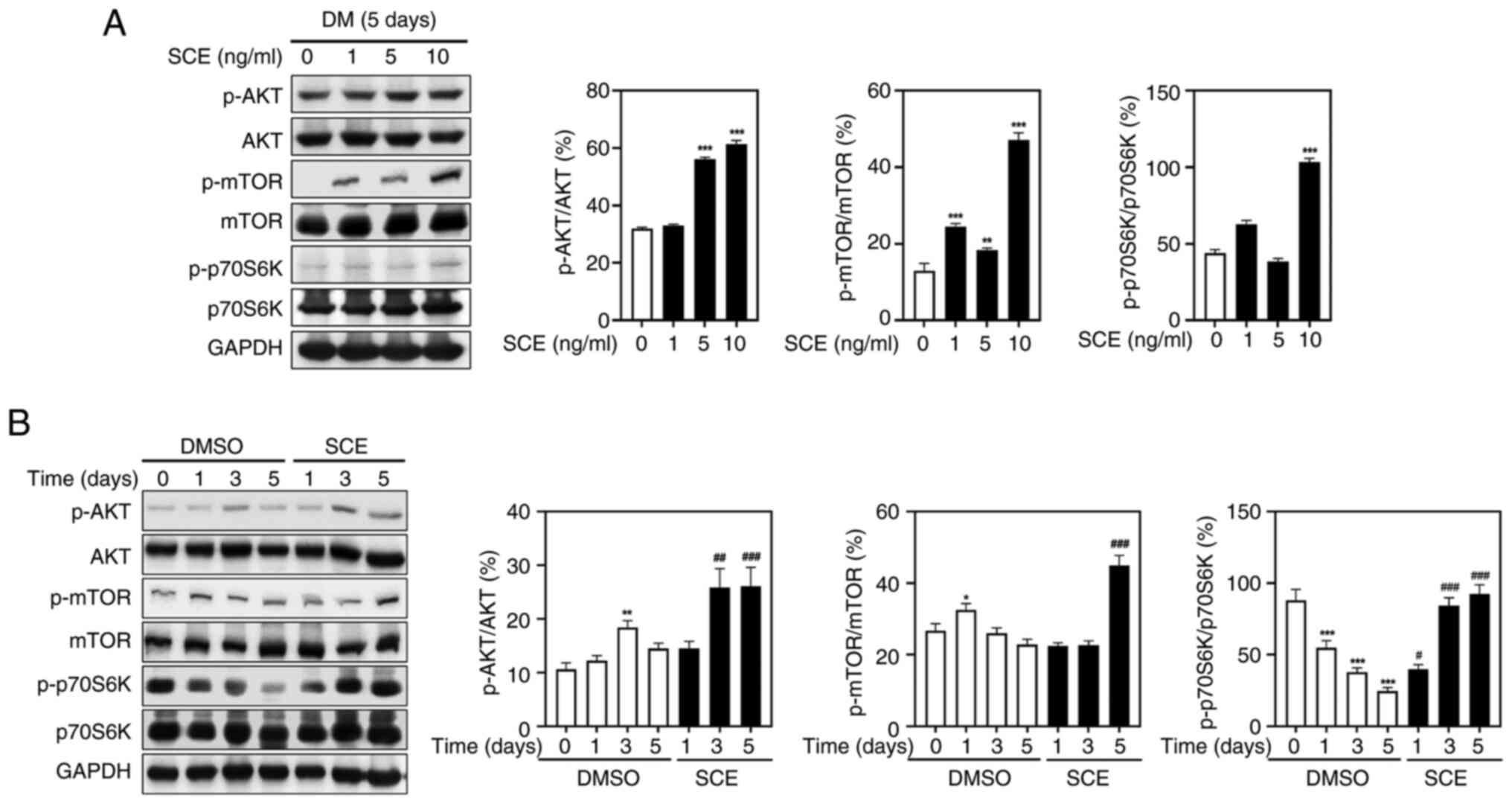
SCE activates muscle protein
synthesis-related biomarkers
To further prove the mechanism by which SCE promotes
formation of C2C12 myotubes, muscle protein turnover-related
biomarkers were evaluated. Western blotting was performed to
confirm whether SCE enhanced the AKT/mTOR pathway, an essential
regulator of protein synthesis and degradation. As demonstrated in
Fig. 6A, the phosphorylation of
AKT, mTOR and p70S6K was increased in a dose-dependent manner
following treatment with SCE. In addition, SCE significantly
increased AKT and mTOR phosphorylation during myogenesis.
Specifically, on day 5 of treatment, SCE increased the
phosphorylation of AKT and mTOR and subsequently activated p70S6K1,
a key downstream target of the AKT/mTOR signaling cascade (Fig. 6B). These data revealed that SCE
enhances differentiation of C2C12 cells by regulating the AKT/mTOR
signaling pathway, which is important for protein synthesis.
Discussion
Herbal medicines used as dietary supplements have
numerous useful effects and have long been known to improve health,
stamina and abnormalities in the elderly (31). SCE is widely used for medicinal
purposes owing to various physiological activities including
anti-oxidant, anticancer, anti-aging and anti-inflammatory
(13–26). In traditional medicine, SCE is used
for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases,
hypertension and angina because it clears the blood and the walls
of blood vessels, along with toxin discharge and diuretic action
(16,32). In addition, SCE protects against
oxidative stress-induced myoblast damage by downregulating ceramide
(27). However, the effects and
mechanisms of action of SCE on skeletal muscle cell differentiation
and function have not yet been investigated. In the present study,
for the first time SCE was investigated for its potential ability
to improve myotube muscle function. SCE promoted the
differentiation of myoblasts into myotubes by increasing MyHC,
MyoD, myogenin, Myf5 and β-catenin levels. These effects are due to
an increase in mitochondrial biogenesis by upregulating the
mitochondrial transcription factors PGC-1α and NRF-1 through
activation of the AMPK and AKT/mTOR signaling pathways and
promotion of protein synthesis.
In order to inhibit muscle wasting, it is necessary
to either stimulate muscle-building pathways or inhibit the
signaling pathways responsible for muscle wasting in the regulation
of muscle metabolism. Satellite cells, such as C2C12 myoblasts,
differentiate into multinucleated fibers and myotubes through
myoblast fusion (33). Muscle
tissue contains satellite cells, which are skeletal muscle-derived
stem cells, and myogenic differentiation begins when satellite
cells are activated (33). During
differentiation, satellite cells and myoblasts are orchestrated by
various myogenic regulatory factors (MRFs), including MyoD, Myf5
and myogenin, and structural muscle proteins, including MyHC
(33,34). Mature myotubes express structural
muscle proteins such as MyHC, which are motor proteins and specific
maturation marker proteins of thick muscle filaments (33,34).
Furthermore, β-catenin acts as a molecular switch that regulates
the transition from cell proliferation to myogenic differentiation
(35). In the present study, SCE
treatment significantly increased the mRNA and/or protein levels of
MyHC, MyoD, myogenin, Myf5 and β-catenin in C2C12 myotubes
(Fig. 3), suggesting that SCE
promotes myoblast differentiation. However, further experiments on
MRFs and the regulation of their signaling are needed to improve
elucidation of the impact of SCE on myogenesis and metabolism.
PGC-1α is a key transcriptional regulator of several
genes involved in various physiological responses related to energy
homeostasis, thermoregulation, lactate and fatty acid metabolism,
muscle growth and mitochondrial biogenesis (36). In skeletal muscle, PGC-1α increases
energy expenditure by increasing the rates of respiration and
mitochondrial biogenesis and interacts with NRF-1, a transcription
factor regulating the expression of several mitochondrial genes
(36,37). AMPK acts as an energy switch, which
is a key energy sensor controlling metabolic homeostasis at
cellular and systemic levels, regulating processes such as cell
growth, lipid-glucose metabolism and autophagy (38,39).
Specifically, in skeletal muscles, mitochondrial biogenesis
provides cells with ATP, which ultimately promotes AMPK activation
(38,39). AMPK inhibition downregulates
myogenin transcription and myogenesis, mainly through
phosphorylation of HDAC5 mediated by AMPKα1, meaning that AMPK is a
key molecular target to promote myogenesis and muscle regeneration
(40). In the present study, SCE
treatment of C2C12 myotubes increased the activation of PGC-1α,
NRF-1, AMPK and HDAC5 in a time- and concentration-dependent manner
(Figs. 4 and 5), indicating that the promotion of
myogenic differentiation by SCE is related to the enhancement of
mitochondrial biogenesis. However, changes in mitochondrial
biogenesis, caused by SCE treatment need to be further confirmed to
improve understanding of the role of the drug in muscle energy
metabolism.
AMPK is involved not only in mitochondrial
biogenesis but also in the synthesis and wasting metabolism of
skeletal muscle through the regulation of several downstream
targets, such as the PI3K/AKT pathway. AMPK plays an important role
in regulating skeletal muscle development and growth and regulating
muscle mass and regeneration by influencing anabolic and catabolic
cellular processes (41). AKT
plays an important role as a promyogenic kinase, and AKT signaling
is contributed to heterodimerization of MyoD/E-proteins and
alteration in chromatin remodeling at muscle-specific loci
(42,43). AKT/mTOR/p70S6K pathway is important
for the differentiation of myoblasts and hypertrophy of myotubes
(44). mTOR is a kinase downstream
of AKT, which phosphorylates 4E-BP1 and p70S6K thereby inducing
initiation of protein synthesis (45). In addition, AKT pathways prevent
muscle atrophy by inhibiting atrophy-related ubiquitin ligases and
FoxO transcriptional factors (45). In myostatin knockout mice, an
increase in AKT/mTOR/p70S6K signaling was observed (46). SCE induced the phosphorylation of
AKT, mTOR and p70 S6K in a concentration- and time-dependent manner
(Fig. 6). These results indicated
that SCE enhanced myogenic differentiation through the AKT/mTOR
protein synthesis signaling pathway.
In conclusion, the present study is the first, to
the best of the authors' knowledge, to reveal that SCE regulates
muscle differentiation, mitochondrial biogenesis and protein
synthesis. SCE significantly increased the expression of MyoD,
myogenin and MyHC in myotubes, as well as the expression of PGC-1α
and NRF-1, through the activation of AMPK and AKT/mTOR signaling
pathways. These results suggested that SCE improves muscle function
by enhancing myoblast differentiation and energy metabolism.
However, further in vitro/in vivo studies on the mechanism
of action of SCE in pathological conditions such as aging, energy
and nutritional imbalance and muscle loss are needed to clearly
understand the mechanisms by which SCE regulates muscle
differentiation, mitochondrial biogenesis and protein synthesis. A
limitation of the present study was that more specific experimental
evidence is needed to support the role of the AMPK-HDAC5 and
AKT/mTOR/p70S6K pathways, such as the use of inhibitors or
activators of these pathways. In addition, it will be necessary to
confirm the effectiveness of SCE in suppressing muscle loss and
enhancing muscle strength through additional in vivo
experiments.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
The present study was supported by the Wonkwang University in
2022 (grant no. 2022-10).
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
JYK and MSL designed the study and revised the
manuscript. SYE, CHC, YHC and GDP performed the experiments. SYE,
CHC and CHL analyzed the data. SYE and CHC drafted figures. JYK and
MSL wrote the manuscript. JYK and MSL confirm the authenticity of
all the raw data. All authors read and approved the final version
of the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
All methods were performed in accordance with
relevant international and national guidelines and regulations.
Because the present study was an in vitro experiment that
did not involve animals or humans, no animal or human ethics
approval was required. SC is stored at the ‘National Institute of
Biological Resources’ (Institution identification number: 50520),
and the specimen was collected from farms on Jeju Island, not from
its native habitat, grown for medicinal purposes. SC Methanolic
(99%) whole-plant extract (KPM046-069) was obtained from the Korea
Plant Extract Bank, Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and
Biotechnology (Cheongju) for research purposes. Experimental
studies were conducted according to the Natural Products Central
Bank (NPCB)'s ‘Standard operating procedure (2023 revised edition)’
(https://www.kobis.re.kr/npcb/uss/notice/library.do).
The NPCB does not collect or damage internationally endangered
species designated and announced by the Minister of Environment in
accordance with the Convention on International Trade in Endangered
Species of Wild Plants (CITES) (http://www.cites.org) and the international Union for
Conservation of Nature's (IUCN) standards (https://s3.amazonaws.com/iucnredlist-newcms/staging/public/attachments/3154/reg_guidelines_en.pdf),
and complies with permit procedures for protected species.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Hargreaves M and Spriet LL: Skeletal
muscle energy metabolism during exercise. Nat Metab. 2:817–828.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thyfault JP and Bergouignan A: Exercise
and metabolic health: Beyond skeletal muscle. Diabetologia.
63:1464–1474. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Newman AB, Kupelian V, Visser M, Simonsick
EM, Goodpaster BH, Kritchevsky SB, Tylavsky FA, Rubin SM and Harris
TB: Strength, but not muscle mass, is associated with mortality in
the health, aging and body composition study cohort. J Gerontol A
Biol Sci Med Sci. 61:72–77. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Landi F, Liperoti R, Russo A, Giovannini
S, Tosato M, Capoluongo E, Bernabei R and Onder G: Sarcopenia as a
risk factor for falls in elderly individuals: Results from the
ilSIRENTE study. Clin Nutr. 31:652–658. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Peng P, Hyder O, Firoozmand A, Kneuertz P,
Schulick RD, Huang D, Makary M, Hirose K, Edil B, Choti MA, et al:
Impact of sarcopenia on outcomes following resection of pancreatic
adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 16:1478–1486. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fielding RA, Vellas B, Evans WJ, Bhasin S,
Morley JE, Newman AB, Abellan van Kan G, Andrieu S, Bauer J,
Breuille D, et al: Sarcopenia: An undiagnosed condition in older
adults. Current consensus definition: Prevalence, etiology, and
consequences. International working group on sarcopenia. J Am Med
Dir Assoc. 12:249–256. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mankhong S, Kim S, Moon S, Kwak HB, Park
DH and Kang JH: Experimental models of sarcopenia: Bridging
molecular mechanism and therapeutic strategy. Cell. 9:13852020.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ma J, Meng X, Kang SY, Zhang J, Jung HW
and Park YK: Regulatory effects of the fruit extract of Lycium
chinense and its active compound, betaine, on muscle
differentiation and mitochondrial biogenesis in C2C12 cells. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1092972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shin EJ, Jo S, Choi S, Cho CW, Lim WC,
Hong HD, Lim TG, Jang YJ, Jang M, Byun S and Rhee Y: Red ginseng
improves exercise endurance by promoting mitochondrial biogenesis
and myoblast differentiation. Molecules. 25:8652020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim YH, Jung JI, Jeon YE, Kim SM, Oh TK,
Lee J, Moon JM, Kim TY and Kim EJ: Gynostemma pentaphyllum extract
and Gypenoside L enhance skeletal muscle differentiation and
mitochondrial metabolism by activating the PGC-1α pathway in C2C12
myotubes. Nutr Res Pract. 16:14–32. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
National Institute of Biological
Resources, . Korean Red List of Threatened Species. 2nd edition.
National Institute of Biological Resources 2014; 2nd edition. Suh
MH, Lee BY, Kim ST, Park CH, Oh HK, Kim HY, Lee JH and Lee SY:
National Institute of Biological Resources; Incheon: 2014
|
|
12
|
Chang CS, Lee JS, Park TY and Kim H:
Reconsideration of rare and endangered plant species in Korea based
on the IUCN red list categories. Korean J Pl Taxon. 31:107–142.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ryu SY, Oh KS, Kim YS and Lee BH:
Antihypertensive, vasorelaxant and inotropic effects of an
ethanolic extract of the roots of Saururus chinensis. J
Ethnopharmacol. 118:284–289. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yoo HJ, Kang HJ, Jung HJ, Kim K, Lim CJ
and Park EH: Anti-inflammatory, anti-angiogenic and
anti-nociceptive activities of Saururus chinensis extract. J
Ethnopharmacol. 120:282–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nho JH, Lee HJ, Jung HK, Jang JH, Lee KH,
Kim AH, Sung TK and Cho HW: Effect of Saururus chinensis
leaves extract on type II collagen-induced arthritis mouse model.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 19:22019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cheng Y, Yin Z, Jiang F, Xu J, Chen H and
Gu Q: Two new lignans from the aerial parts of Saururus
chinensis with cytotoxicity toward nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Fitoterapia. 141:1043442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sung SH, Lee EJ, Cho JH, Kim HS and Kim
YC: Sauchinone, a lignan from Saururus chinensis, attenuates
CCl4-induced toxicity in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. Biol
Pharm Bull. 23:666–668. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hwang BY, Lee JH, Nam JB, Hong YS and Lee
JJ: Lignans from Saururus chinensis inhibiting the
transcription factor NF-kappaB. Phytochemistry. 64:765–771. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Quan Z, Lee YJ, Yang JH, Lu Y, Li Y, Lee
YK, Jin M, Kim JY, Choi JH, Son JK and Chang HW: Ethanol extracts
of Saururus chinensis suppress ovalbumin-sensitization
airway inflammation. J Ethnopharmacol. 132:143–149. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Alaklabi A, Arif IA, Ahamed A, Surendra
Kumar R and Idhayadhulla A: Evaluation of antioxidant and
anticancer activities of chemical constituents of the Saururus
chinensis root extracts. Saudi J Biol Sci. 25:1387–1392. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Rho Y, Kim MY and Cho JY: TAK1 in
the AP-1 pathway is a critical target of Saururus chinensis
(Lour.) Baill in its anti-inflammatory action. J Ethnopharmacol.
279:1144002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yoo SR, Ha H, Shin HK and Seo CS:
Anti-inflamatory activity of neolignan compound isolated from the
roots of Saururus chinensis. Plants (Basel). 9:9322020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jung YW, Lee BM, Ha MT, Tran MH, Kim JA,
Lee S, Lee JH, Woo MH and Min BS: Lignans from Saururus
chinensis exhibit anti-inflammatory activity by influencing the
Nrf2/HO-1 activation pathway. Arch Pharm Res. 42:332–343. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Choi MS, Kim EC, Lee HS, Kim SK, Choi HM,
Park JH, Han JB, An HJ, Um JY, Kim HM, et al: Inhibitory effects of
Saururus chinensis (LOUR.) BAILL on the development of
atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in NC/Nga mice. Biol Pharm
Bull. 31:51–56. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jeong HJ, Koo BS, Kang TH, Shin HM, Jung S
and Jeon S: Inhibitory effects of Saururus chinensis and its
components on stomach cancer cells. Phytomedicine. 22:256–261.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang L, Cheng D, Wang H, Di L, Zhou X, Xu
T, Yang X and Liu Y: The hepatoprotective and antifibrotic effects
of Saururus chinensis against carbon tetrachloride induced
hepatic fibrosis in rats. J Ethnopharmacol. 126:487–491. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jung MH, Song MC, Bae K, Kim HS, Kim SH,
Sung SH, Ye SK, Lee KH, Yun YP and Kim TJ: Sauchinone attenuates
oxidative stress-induced skeletal muscle myoblast damage through
the down-regulation of ceramide. Biol Pharm Bull. 34:575–579. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liu H, Lee SM and Joung H: 2-D08 treatment
regulates C2C12 myoblast proliferation and differentiation via the
Erk1/2 and proteasome signaling pathways. J Muscle Res Cell Motil.
42:193–202. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim JY, Cheon YH, Ahn SJ, Kwak SC, Chung
CH, Lee CH and Lee MS: Harpagoside attenuates local bone Erosion
and systemic osteoporosis in collagen-induced arthritis in mice.
BMC Complement Med Ther. 22:2142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sayer AA, Robinson SM, Patel HP,
Shavlakadze T, Cooper C and Grounds MD: New horizons in the
pathogenesis, diagnosis and management of sarcopenia. Age Ageing.
42:145–150. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Oh KS, Choi YH, Ryu SY, Oh BK, Seo HW, Yon
GH, Kim YS and Lee BH: Cardiovascular effects of lignans isolated
from Saururus chinensis. Planta Med. 74:233–238. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Dumont NA, Bentzinger CF, Sincennes MC and
Rudnicki MA: Satellite cells and skeletal muscle regeneration.
Compr Physiol. 5:1027–1059. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Langley B, Thomas M, Bishop A, Sharma M,
Gilmour S and Kambadur R: Myostatin inhibits myoblast
differentiation by down-regulating MyoD expression. J Biol Chem.
277:49831–49840. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tanaka S, Terada K and Nohno T: Canonical
Wnt signaling is involved in switching from cell proliferation to
myogenic differentiation of mouse myoblast cells. J Mol Signal.
6:122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kang C and Li Ji L: Role of PGC-1α
signaling in skeletal muscle health and disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1271:110–117. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Taherzadeh-FardE SC, Akkad DA, Wieczorek
S, Haghikia A, Chan A, Epplen JT and Arning L: PGC-1alpha
downstream transcription factors NRF-1 and TFAM are genetic
modifiers of Huntington disease. Mol Neurodegener. 6:322011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hardie DG, Ross FA and Hawley SA: AMPK: A
nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 13:251–262. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gasparrini M, Giampieri F, Alvarez Suarez
J, Mazzoni L, Y Forbes Hernandez T, Quiles JL, Bullon P and Battino
M: AMPK as a new attractive therapeutic target for disease
prevention: The role of dietary compounds AMPK and disease
prevention. Curr Drug Targets. 17:865–889. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fu X, Zhao JX, Liang J, Zhu MJ, Foretz M,
Viollet B and Du M: AMP-activated protein kinase mediates myogenin
expression and myogenesis via histone deacetylase 5. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 305:C887–C895. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tao R, Gong J, Luo X, Zang M, Guo W, Wen R
and Luo Z: AMPK exerts dual regulatory effects on the PI3K pathway.
J Mol Signal. 5:12010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Simone C, Forcales SV, Hill DA, Imbalzano
AN, Latella L and Puri PL: p38 pathway targets SWI-SNF
chromatin-remodeling complex to muscle-specific loci. Nat Genet.
36:738–743. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Bae GU, Lee JR, Kim BG, Han JW, Leem YE,
Lee HJ, Ho SM, Hahn MJ and Kang JS: Cdo interacts with APPL1 and
activates Akt in myoblast differentiation. Mol Biol Cell.
21:2399–2411. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Glass DJ: Signalling pathways that mediate
skeletal muscle hypertrophy and atrophy. Nat Cell Biol. 5:87–90.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bodine SC, Stitt TN, Gonalez M, Kline WO,
Stover GL, Bauerlein R, Zlotchenko E, Scrimgeour A, Lawrence JC,
Glass DJ and Yancopoulos GD: Akt/mTOR pathway is a crucial
regulator of skeletal muscle hypertrophy and can prevent muscle
atrophy in vivo. Nat Cell Biol. 3:1014–1019. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lipina C, Kendall H, McPherron AC, Taylor
PM and Hundal HS: Mechanisms involved in the enhancement of
mammalian target of rapamycin signalling and hypertrophy in
skeletal muscle of myostatin-deficient mice. FEBS Lett.
584:2403–2408. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|